Abstract
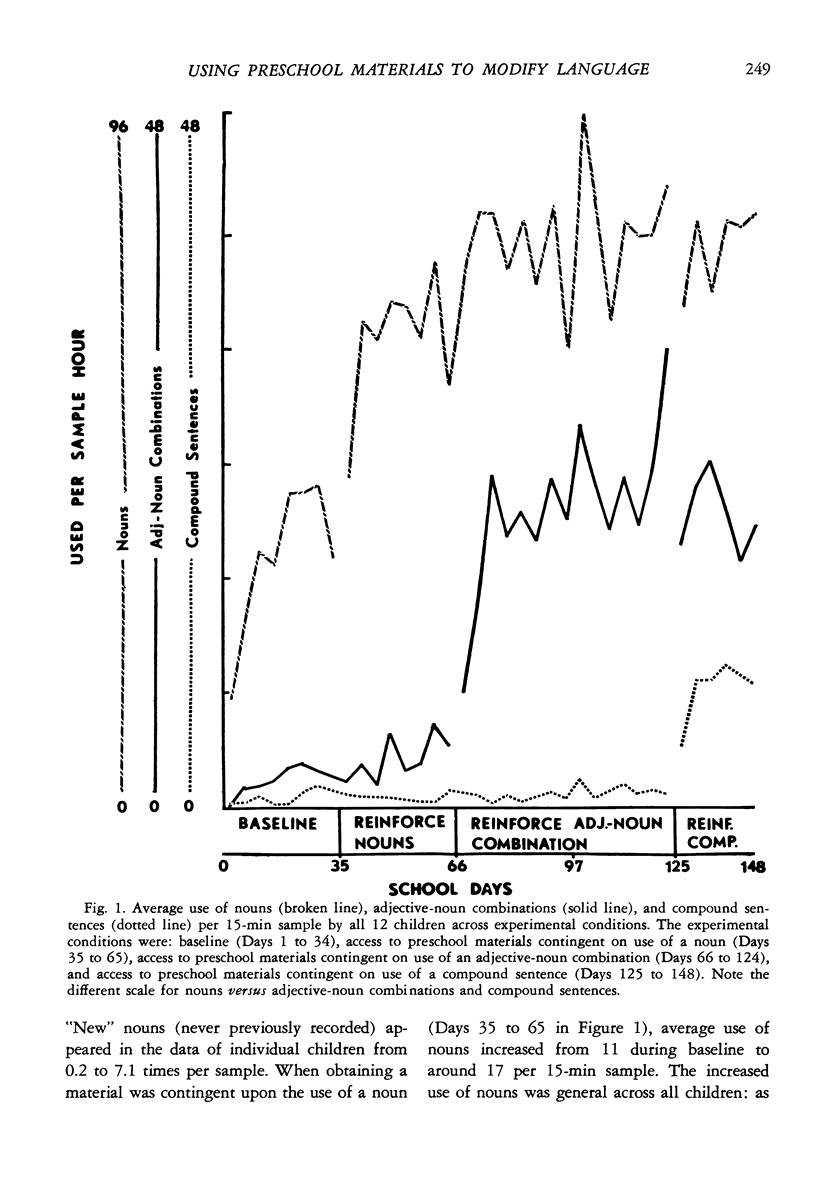
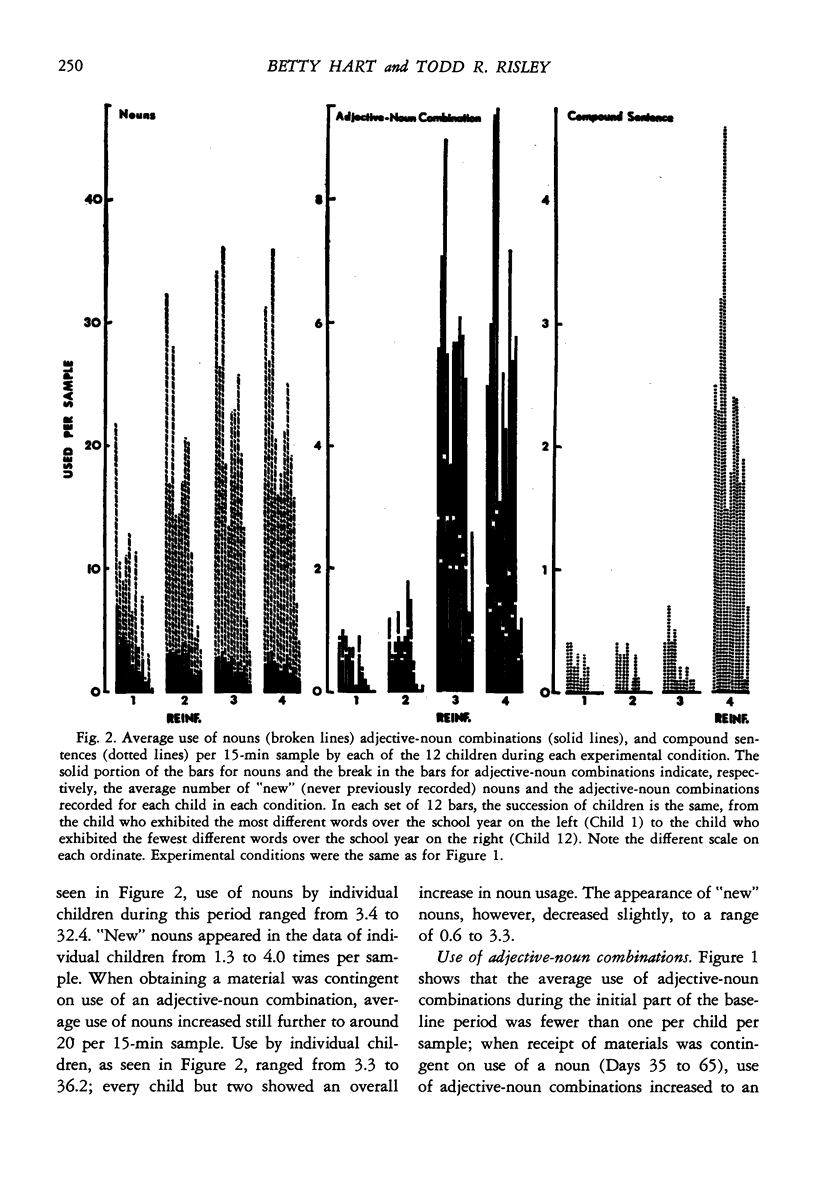
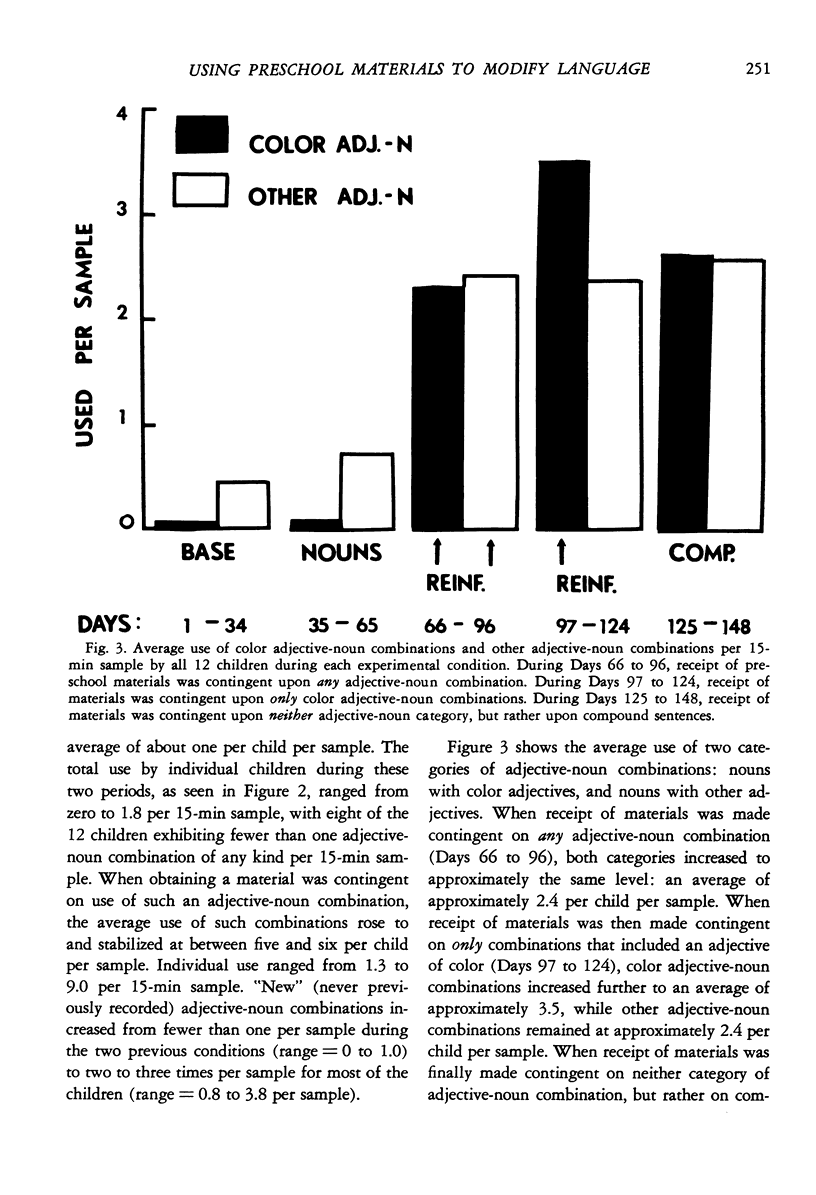
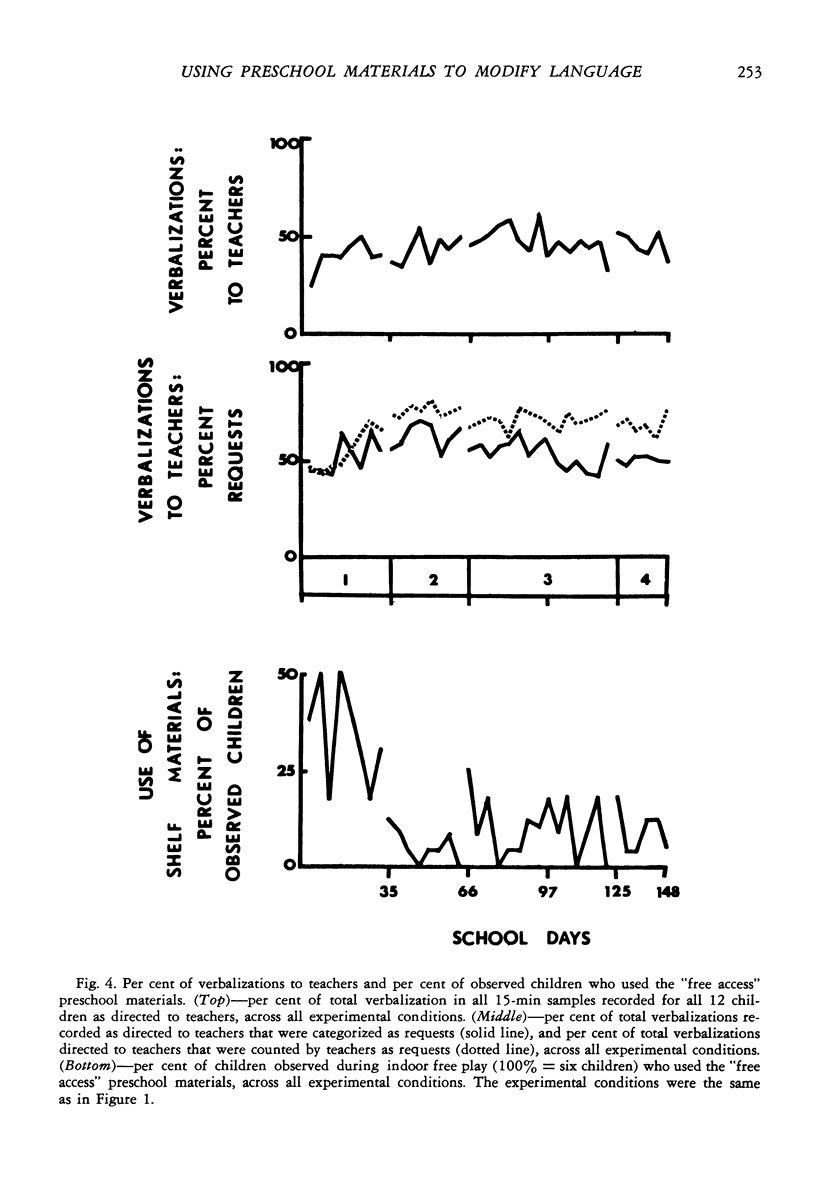
Although language remediation programs have generally been conducted with the use of special materials in structured group settings, traditional preschool practice emphasizes “incidental teaching” incorporated into children's free play. To determine if incidental teaching practices could be effective in improving children's speech, this study investigated the spontaneous speech of 12 disadvantaged children during free-play periods over eight months of a preschool program. Whenever the children selected a preschool play material, they were prompted and required to ask for it, first by name (noun), then by name plus a word that described the material (adjective-noun combination), then by use of a color adjuctive-noun combination, and finally by requesting the material and describing how they were going to use it (compound sentence). As each requirement was made, the children's general use of that aspect of language markedly increased, but little change was noted in the amount or nature of the children's interactions with teachers or their use of a set of materials to which they had free access. This study demonstrates that preschool free-play periods can be powerful “incidental teaching” periods by capitalizing on moments when children seek new play materials.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen K. E., Henke L. B., Harris F. R., Baer D. M., Reynolds N. J. Control of hyperactivity by social reinforcement of attending behavior. J Educ Psychol. 1967 Aug;58(4):231–237. doi: 10.1037/h0024905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell J. Collateral social development accompanying reinforcement of outdoor play in a preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):167–173. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. V., Lund D., Jackson D. Effects of teacher attention on study behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):1–12. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. M., Risley T. R. Establishing use of descriptive adjectives in the spontaneous speech of disadvantaged preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):109–120. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds N. J., Risley T. R. The role of social and material reinforcers in increasing talking of a disadvantaged preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):253–262. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigler E., Butterfield E. C. Motivational aspects of changes in IQ test performance of culturally deprived nursery school child children. Child Dev. 1968 Mar;39(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


