Abstract
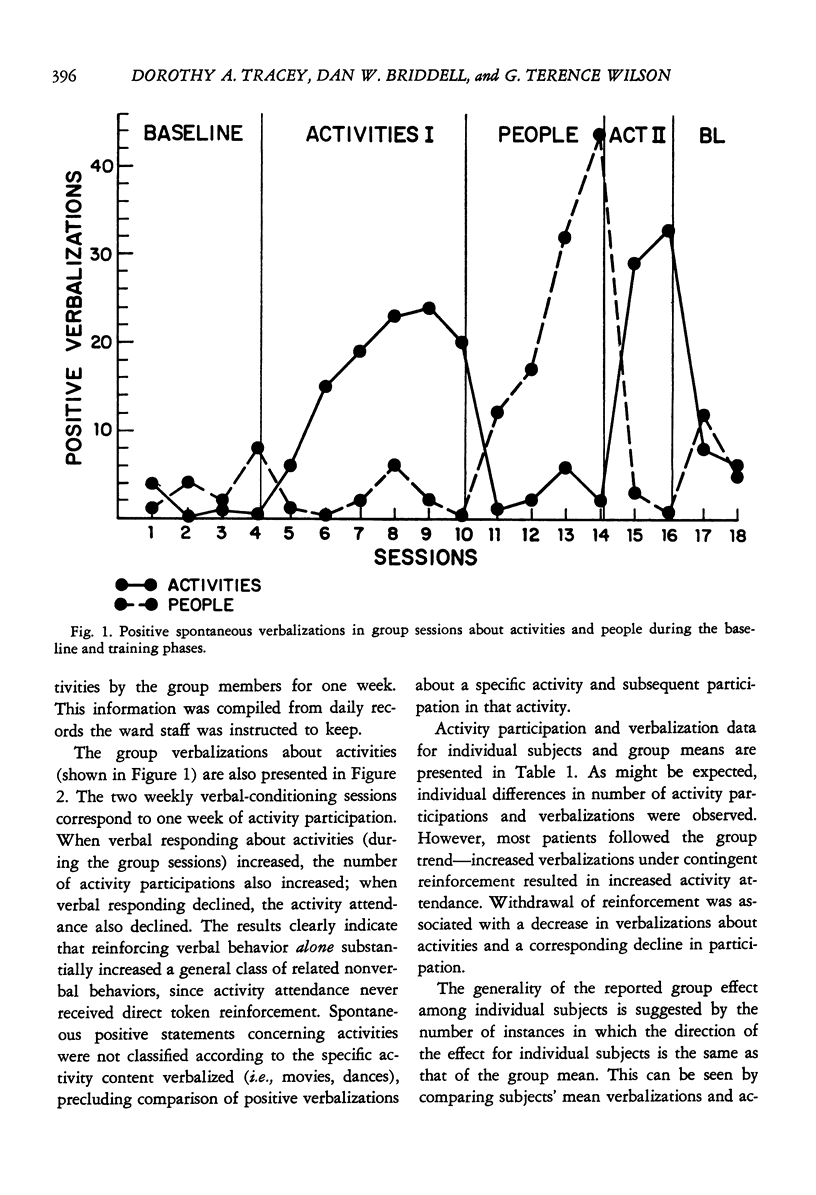
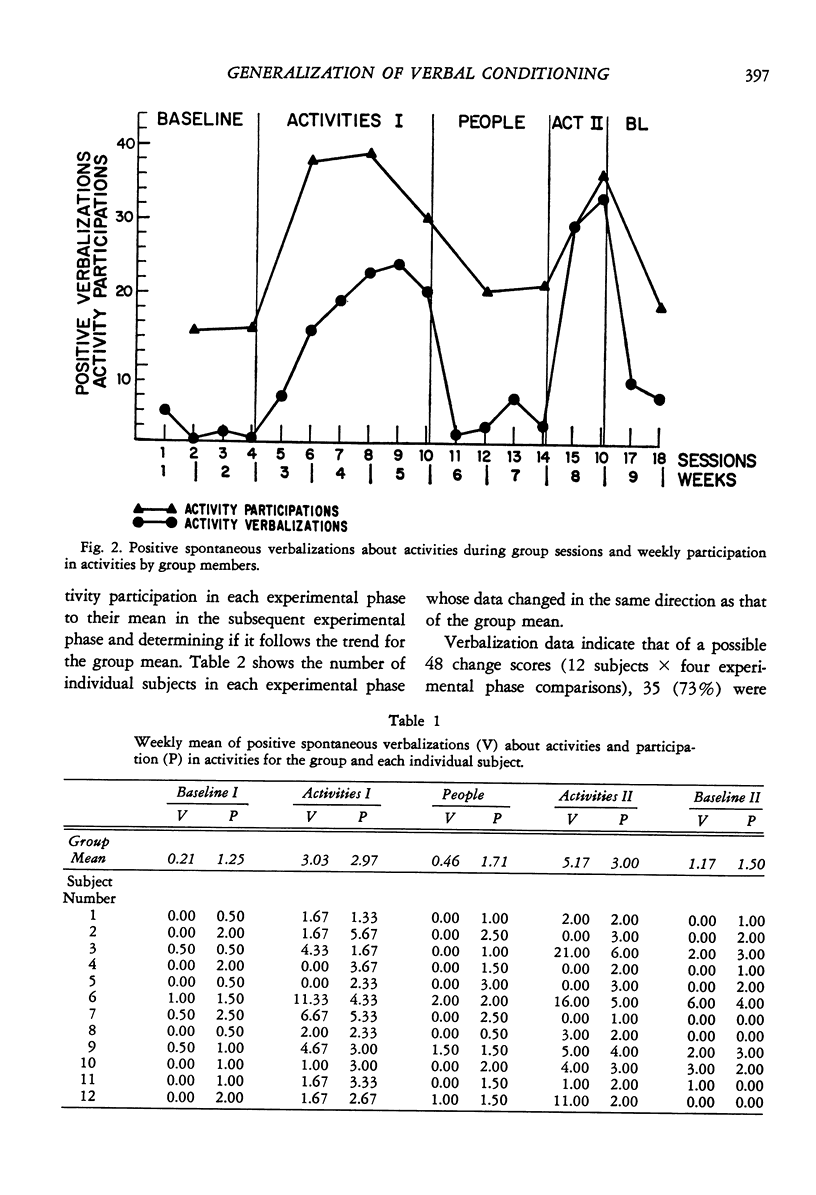
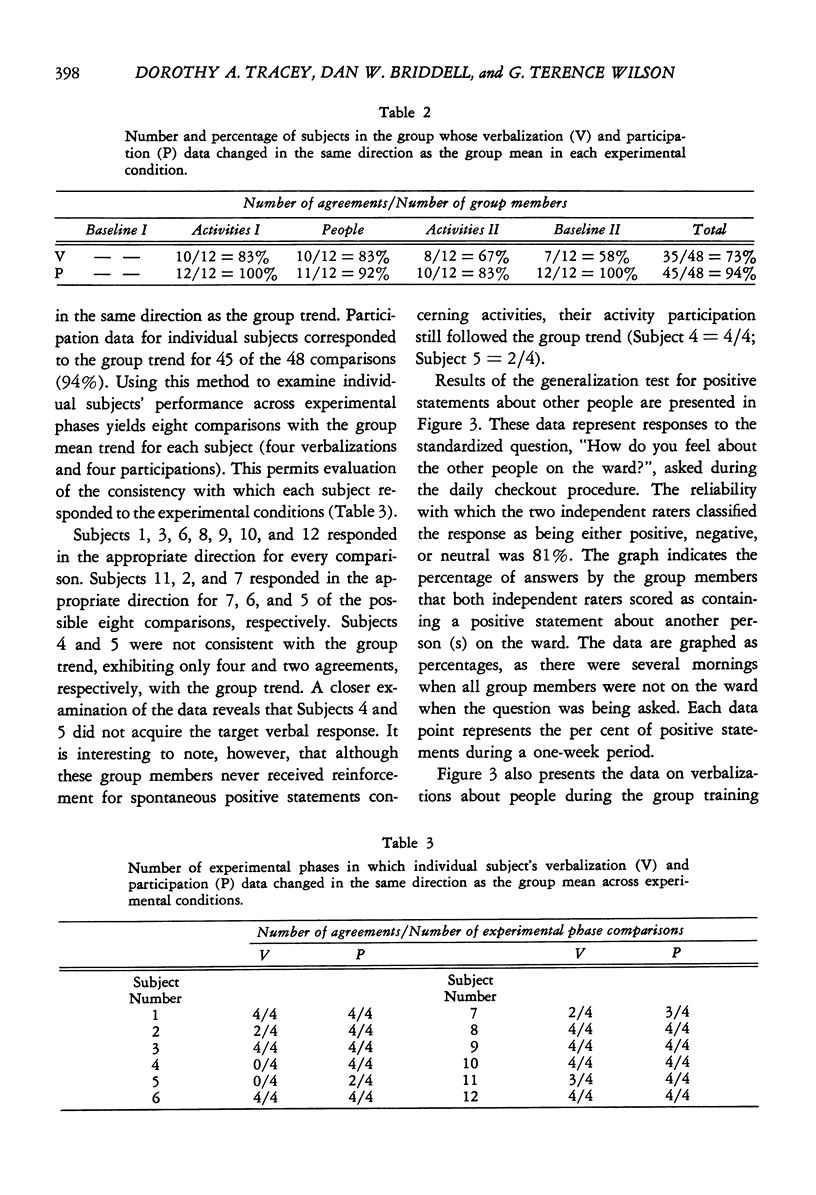
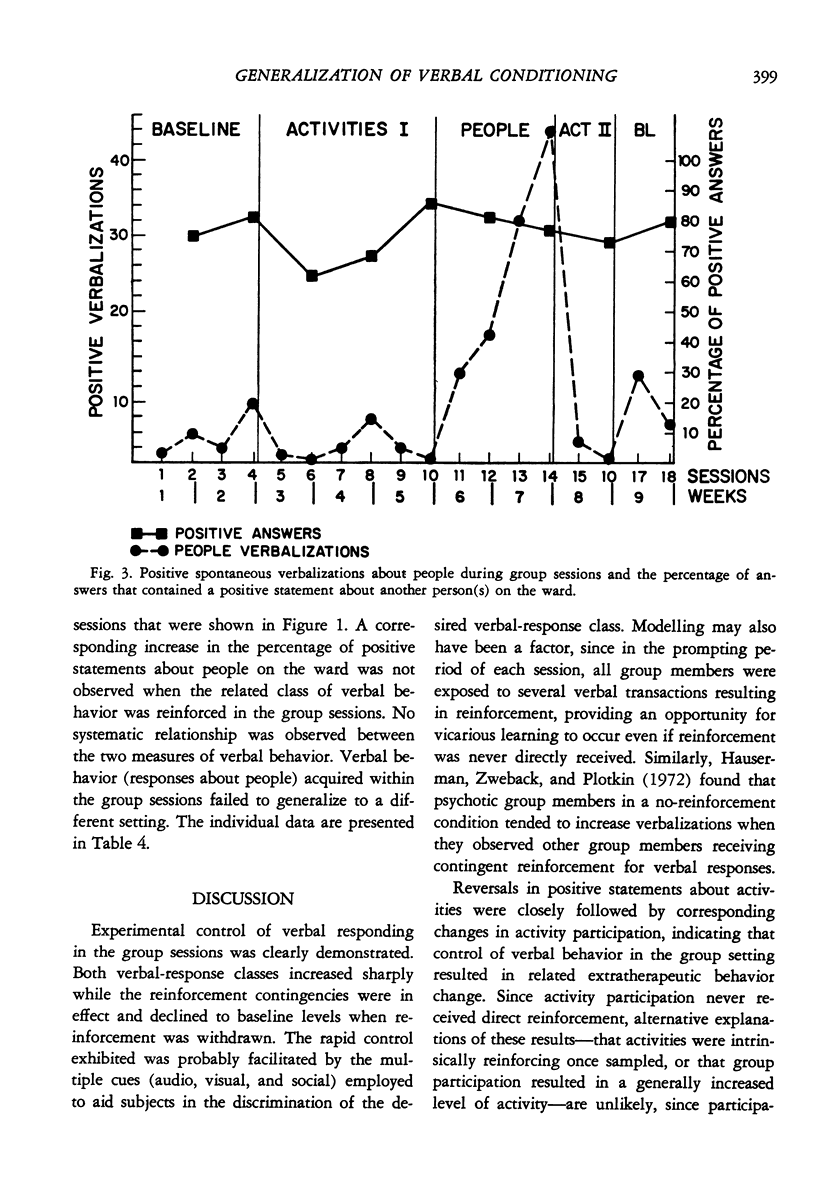
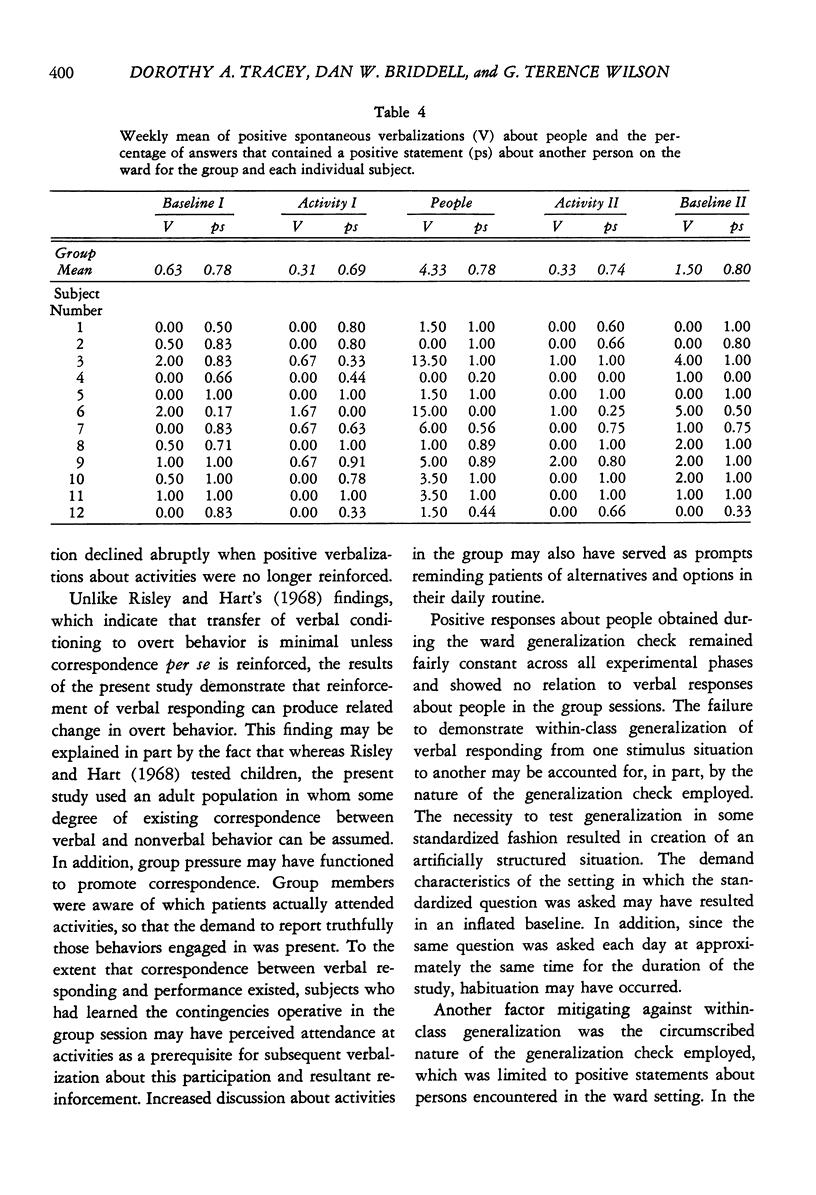
Twelve chronic hospitalized female patients received token reinforcement contingent on two separate classes of verbalizations: (a) positive statements about optional activities available in the hospital setting, and (b) positive statements about people. Cross-class generalization of reinforced verbal responses about activities to overt behavior was tested by actual participation in activities; within-class generalization of verbal responses about people to verbalizations in another stimulus setting was assessed in a structured interview situation. A multiple baseline design with contingency reversals was employed to demonstrate experimental control of both classes of verbalizations in the group sessions. Positive statements about activities generalized to actual participation in activities, while generalization of positive statements about people to verbalization in the extragroup setting did not occur.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DINOFF M., HORNER R. F., KURPIEWSKI B. S., RICKARD H. C., TIMMONS E. O. Conditioning verbal behavior of a psychiatric population in a group therapy-like situation. J Clin Psychol. 1960 Oct;16:371–372. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(196010)16:4<371::aid-jclp2270160406>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauserman N., Zweback S., Plotkin A. Use of concrete reinforcement to facilitate verbal initiations in adolescent group therapy. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1972 Feb;38(1):90–96. doi: 10.1037/h0032410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVAAS O. I. CONTROL OF FOOD INTAKE IN CHILDREN BY REINFORCEMENT OF RELEVANT VERBAL BEHAVIOR. J Abnorm Psychol. 1964 Jun;68:672–678. doi: 10.1037/h0047612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVAAS O. I. Interaction between verbal and nonverbal behavior. Child Dev. 1961 Jun;32:329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1961.tb05031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman R. P., Teigen J., Patterson R., Baker V. Reducing delusional speech in chronic, paranoid schizophrenics. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Spring;6(1):57–64. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichenbaum D. H. The effects of instructions and reinforcement on thinking and language behavior of schizophrenics. Behav Res Ther. 1969 Feb;7(1):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(69)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS J. M. Operant conditioning in a Quasi-therapy setting. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1960 Mar;60:247–252. doi: 10.1037/h0041188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T. R., Hart B. Developing correspondence between the non-verbal and verbal behavior of preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Winter;1(4):267–281. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczyk R. G., Kent R. N., Diament C., O'leary K. D. Measuring the reliability of observational data: a reactive process. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Spring;6(1):175–184. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN J. A. MODIFICATION OF NONVERBAL BEHAVIOR THROUGH REINFORCEMENT OF RELATED VERBAL BEHAVIOR. Child Dev. 1964 Sep;35:717–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1964.tb05211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truax C. B. Reinforcement and nonreinforcement in Rogerian psychotherapy. J Abnorm Psychol. 1966 Feb;71(1):1–9. doi: 10.1037/h0022912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLMANN L. P., KRASNER L., COLLINS B. J. Modification of behavior through verbal conditioning: effects in group therapy. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1961 Jan;62:128–132. doi: 10.1037/h0048368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. I., Blanton R. L. Verbal conditioning in a psychotherapeutic situation. Behav Res Ther. 1968 Feb;6(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(68)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


