Abstract
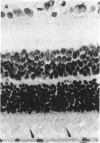
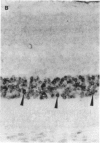
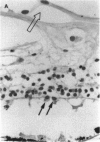
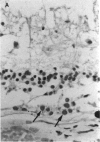
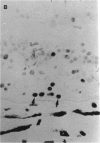
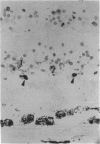
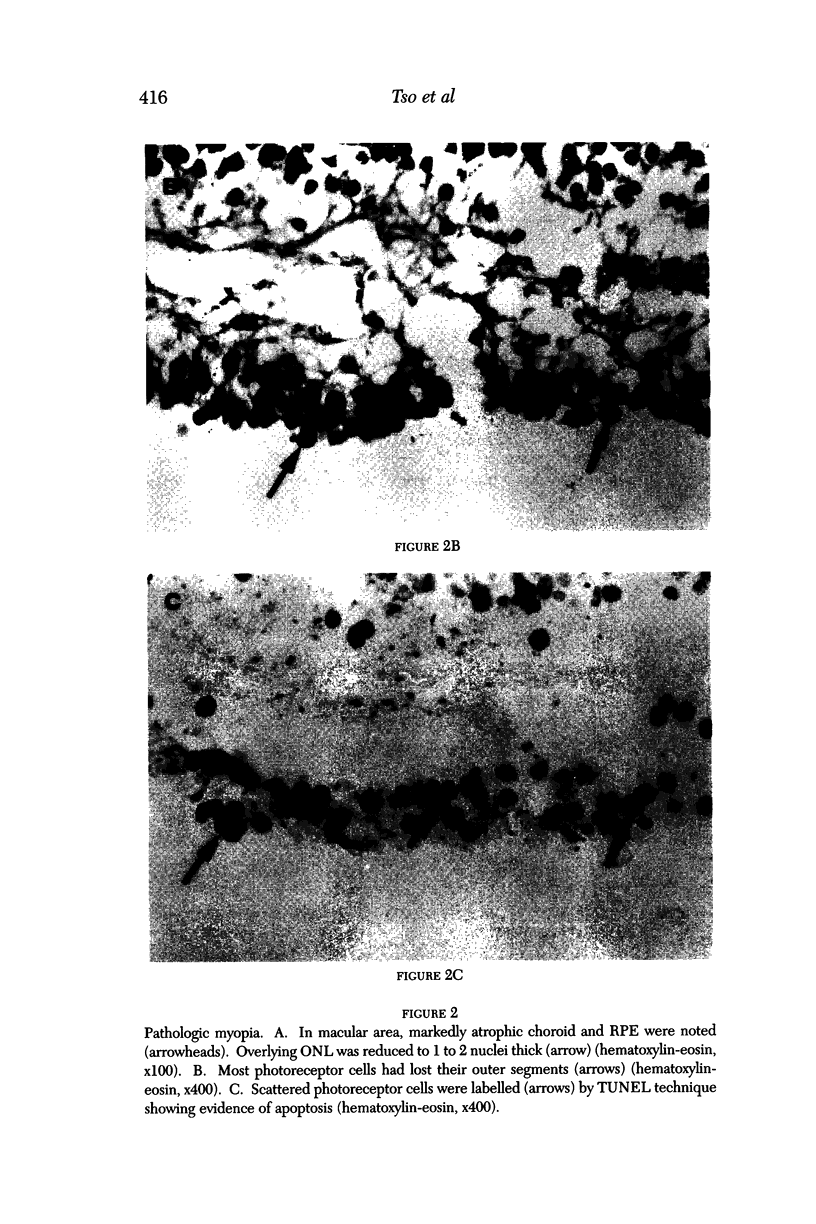
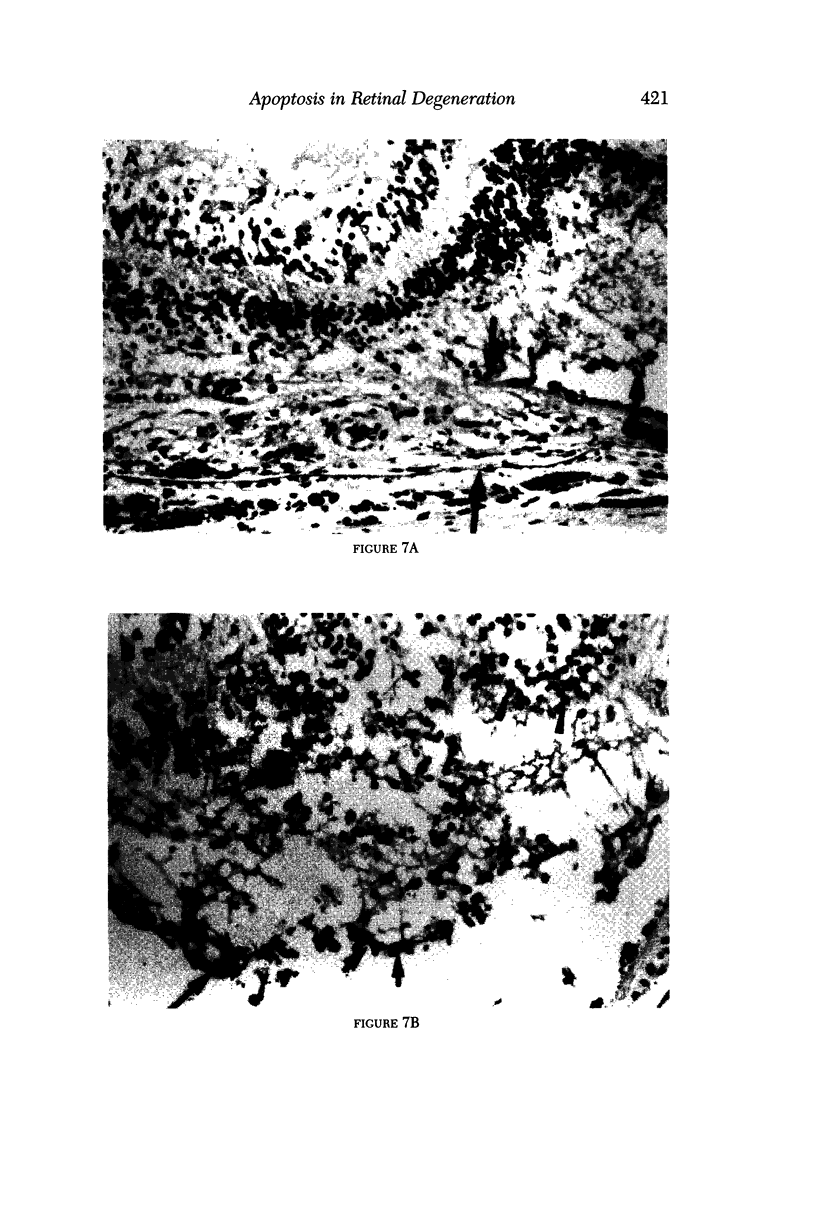
PURPOSE: This paper examined the role of apoptosis in human retinal degenerations including pathologic myopia, age-related macular degeneration, serous retinal detachment, retinal lattice, and paving stone degenerations. METHOD: Thirty-seven enucleated human eyes with 1 of the above-mentioned retinal degenerations were studied by histopathology and by TdT-mediated biotin-dUTP nicked-end labelling (TUNEL) technique. RESULTS: Tunnel labelling characteristic DNA fragmentation of apoptosis was observed in photoreceptor cells in 2 of the 4 eyes with pathologic myopia and in 4 of 16 eyes with age-related macular degeneration, 2 of which were exudative and 2 of which were atrophic. However, only a few scattered photoreceptor cells were labelled in 4 of 8 eyes with serous retinal detachment secondary to malignant melanoma of the choroid. Moreover, none of the photoreceptors cells in the 4 eyes with retinal lattice degeneration and 6 eyes with retinal paving stone degeneration were labelled. CONCLUSIONS: Apoptosis is 1 of the important pathways of photoreceptor cell degeneration in pathologic myopia and age-related macular degeneration.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. C. Retinal photoreceptor dystrophies LI. Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995 May;119(5):543–562. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchi E. R., Bernauer W., Daicker B. Cell death and disposal in retinoblastoma: an electron microscopic study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994 Nov;232(11):635–645. doi: 10.1007/BF00171377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Lai W. W., Edward D. P., Tso M. O. Apoptotic photoreceptor cell death after traumatic retinal detachment in humans. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995 Jul;113(7):880–886. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1995.01100070054025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. Q., Hao Y., Wong F. Apoptosis: final common pathway of photoreceptor death in rd, rds, and rhodopsin mutant mice. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90072-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook B., Lewis G. P., Fisher S. K., Adler R. Apoptotic photoreceptor degeneration in experimental retinal detachment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995 May;36(6):990–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktorovich E. G., Steinberg R. H., Yasumura D., Matthes M. T., LaVail M. M. Photoreceptor degeneration in inherited retinal dystrophy delayed by basic fibroblast growth factor. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):83–86. doi: 10.1038/347083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foos R. Y., Simons K. B. Vitreous in lattice degeneration of retina. Ophthalmology. 1984 May;91(5):452–457. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(84)34266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuks Z., Persaud R. S., Alfieri A., McLoughlin M., Ehleiter D., Schwartz J. L., Seddon A. P., Cordon-Cardo C., Haimovitz-Friedman A. Basic fibroblast growth factor protects endothelial cells against radiation-induced programmed cell death in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1994 May 15;54(10):2582–2590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovitz-Friedman A., Balaban N., McLoughlin M., Ehleiter D., Michaeli J., Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z. Protein kinase C mediates basic fibroblast growth factor protection of endothelial cells against radiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 May 15;54(10):2591–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin D. B., Curtin B. J. Peripheral chorioretinal lesions and axial length of the myopic eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 May;81(5):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson P. E., Knox D. L., Green W. R. Ischemic ocular inflammation. A clinicopathologic case report. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971 Sep;86(3):274–280. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1971.01000010276007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namiki M. [Quantification of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and transforming growth factor (TGF alpha) in rabbit aqueous humor after intraocular lens implantation]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1994 Apr;98(4):334–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portera-Cailliau C., Sung C. H., Nathans J., Adler R. Apoptotic photoreceptor cell death in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):974–978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. R., Streeten B. W. The surface morphology of retinal breaks and lattice retinal degeneration. A scanning electron microscopic study. Ophthalmology. 1986 Feb;93(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(86)33759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeten B. W., Bert M. The retinal surface in lattice degeneration of the retina. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Dec;74(6):1201–1209. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90743-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. O. Pathogenetic factors of aging macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 1985 May;92(5):628–635. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(85)33992-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. O., Zhang C., Abler A. S., Chang C. J., Wong F., Chang G. Q., Lam T. T. Apoptosis leads to photoreceptor degeneration in inherited retinal dystrophy of RCS rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 May;35(6):2693–2699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]