Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate molecular and phenotypic methods for the identification of nonhemolytic streptococci. A collection of 148 strains consisting of 115 clinical isolates from cases of infective endocarditis, septicemia, and meningitis and 33 reference strains, including type strains of all relevant Streptococcus species, were examined. Identification was performed by phylogenetic analysis of nucleotide sequences of four housekeeping genes, ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA; by PCR analysis of the glucosyltransferase (gtf) gene; and by conventional phenotypic characterization and identification using two commercial kits, Rapid ID 32 STREP and STREPTOGRAM and the associated databases. A phylogenetic tree based on concatenated sequences of the four housekeeping genes allowed unequivocal differentiation of recognized species and was used as the reference. Analysis of single gene sequences revealed deviation clustering in eight strains (5.4%) due to homologous recombination with other species. This was particularly evident in S. sanguinis and in members of the anginosus group of streptococci. The rate of correct identification of the strains by both commercial identification kits was below 50% but varied significantly between species. The most significant problems were observed with S. mitis and S. oralis and 11 Streptococcus species described since 1991. Our data indicate that identification based on multilocus sequence analysis is optimal. As a more practical alternative we recommend identification based on sodA sequences with reference to a comprehensive set of sequences that is available for downloading from our server. An analysis of the species distribution of 107 nonhemolytic streptococci from bacteremic patients showed a predominance of S. oralis and S. anginosus with various underlying infections.
The genus Streptococcus currently consists of more than 50 species, most of which belong to one of six phylogenetic clusters that are revealed by comparative analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences. In addition to the pyogenic group, which includes the traditional pathogenic species (i.e., hemolytic streptococci), these clusters are the anginosus group, the mitis group, the salivarius group, the bovis group, and the mutans group (30, 34). Many of the species of these five clusters are major constituents of the commensal microbiota of the human oral cavity and upper respiratory tract and are occasionally implicated in various pathologies. The anginosus group, formerly called “Streptococcus milleri” in some parts of the world (16), includes three recognized species (Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus intermedius, and Streptococcus constellatus) that are primarily associated with suppurative infections of tissues of the mouth and various body sites, including the meninges (9, 37, 44, 54, 56). The mitis group currently includes 12 species, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae, Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus infantis, Streptococcus sanguinis (formerly S. sanguis), Streptococcus gordonii, Streptococcus parasanguinis (formerly S. parasanguis), Streptococcus cristatus (formerly S. crista), Streptococcus peroris, Streptococcus australis, and Streptococcus sinensis.
Although they are commensals of the upper respiratory tract, S. pneumoniae is a major cause of both local and systemic infections and several of the other mitis group streptococci have long been recognized as important etiologic agents of subacute bacterial endocarditis (2, 13); septicemia, particularly in neutropenic cancer patients (5, 6, 29); occasional cases of meningitis (8); and eye infections (1). The two species of the salivarius group associated with humans (Streptococcus salivarius and Streptococcus vestibularis) are usually considered to be of low virulence, although occasional life-threatening infections such as bacteremia and meningitis have been reported (11, 43). Some species of the bovis group, which is undergoing taxonomic reconstruction, cause endocarditis, particularly associated with colonic neoplasia (4, 20). The mutans group streptococci (primarily Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus) are considered the prime causative agents of human dental caries (22) and also cause subacute endocarditis (3).
Accurate identification of the nonhemolytic streptococci is a prerequisite for understanding the pathogenesis of the mentioned opportunistic infections and the molecular epidemiology of the increasing antibiotic resistance among some of these bacteria (47). In clinical laboratories, phenotypic test kits such as the Rapid ID 32 STREP system (Bio Mérieux, La Balme les Grottes, France) and STREPTOGRAM (Wako Pure Chemicals, Osaka, Japan) are commonly used for identification of streptococci and related genera (18, 27). The inherent problem of this approach is the large number of species relative to the limited number of biochemical traits that can be analyzed, the variability of several traits within species (33, 35, 36, 44), the poor reproducibility of some tests (12, 17, 26, 36, 44), and the lack of sufficient phenotypic data on more recently described species in the underlying databases. The last problem applies to the species S. cristatus (23), S. peroris, S. infantis (31), S. australis (55), S. sinensis (57), Streptococcus macedonicus (51), Streptococcus infantarius, Streptococcus lutetiensis, Streptococcus gallolyticus (42), and S. pseudopneumoniae (1).
Sequences of the 16S rRNA gene have been widely accepted as the most informative basis for phylogenetic analysis and identification of microorganisms. However, because of significant sequence conservation, the 16S rRNA gene is not adequate for identification of many of the Streptococcus species such as S. pneumoniae, S. pseudopneumoniae, S. mitis, and S. oralis, which exhibit more than 99% identity across species and furthermore may show misleading variation between the four rRNA operons (36). As an alternative, sequencing of other housekeeping genes has been used to identify streptococci, e.g., the genes encoding d-alanine:d-alanine ligase (ddl) (19, 32, 36), glutamate dehydrogenase (gdh) (36, 40), the β subunit of RNA polymerase (rpoB) (15), and manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (sodA) (32, 41, 42). Likewise, the sequences of the highly variable spacer region between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes and the groESL genes have been used for identification of streptococci (10, 48). It is reported that these methods enable reliable identification of Streptococcus isolates to the species level, but they have not been applied to the whole spectrum of Streptococcus species. Moreover, many streptococci are naturally competent for genetic transformation (24). To what extent recombination affects these housekeeping genes and thus the reliability of identification based on sequences of single gene loci has not been analyzed.
Recently, we reported that a PCR-based technique targeting the streptococcal glucosyltransferase gene (gtf) offers a convenient means of identifying the oral streptococcal species that produce extracellular polysaccharide, i.e., S. sanguinis, S. gordonii, S. mutans, S. sobrinus, S. salivarius, and some strains of S. oralis (28). The shortcoming of this method is that it is unable to identify other species. However, it has been suggested that the glucosyltransferase enzyme (GTF) is an important virulence factor in systemic infections, being responsible for biosynthesis of the capsule-like extracellular polysaccharide (25) and for adhesion to and invasion and killing of cultured human umbilical endothelial cells (46, 52). For this reason, it was interesting to investigate the proportion of streptococci from cases of endocarditis and septicemia that carry the gtf gene.
In the present study, sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of the four housekeeping genes ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA and PCR analysis of the gtf genes were applied to a collection of nonhemolytic streptococci isolated from patients with endocarditis, septicemia, and meningitis and to relevant type and reference strains to compare the validity of identification based on one or several gene sequences. The results were used to construct a DNA sequence database and phenotypic profiles that can facilitate exact identification of nonhemolytic streptococci and furthermore provide an update on the distribution of species of nonhemolytic streptococci in systemic infections.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and culture.
The 148 strains included in the study encompassed 101 consecutive isolates recovered from patients in hospitals in Denmark between 1980 and 1994 and submitted to the Streptococcus reference laboratory at Statens Serum Institut, Copenhagen, for examination. These strains were received from Jørgen Henrichsen (now deceased). In addition, eight Streptococcus isolates from bacteremic neutropenic patients in Switzerland were received from Patrick Francioli, Lausanne, Switzerland (6), and six isolates from the human oral cavity (35) were included. For reference purposes, 24 type and 9 reference strains were analyzed: S. sanguinis strains ATCC 10556T/SK1, SK4, and SK36 (S. sanguinis strain whose genome is currently being sequenced at Virginia Commonwealth University; www.sanguinis.mic.vcu.edu); S. oralis strains NCTC 11427T/SK23 and SK34; S. gordonii strains ATCC 10558T/SK3 and Challis/SK7; S. mitis strains NCTC 12261T/SK142, NCTC 8029/SK24, ATCC 11843/SK319, and NCTC 8031/SK320; S. pseudopneumoniae strains CCUG 49455 (ATCC BAA-960T) and CCUG 48465 (ATCC BAA-891); S. parasanguinis strains ATCC 15912T and ATCC 15911/SK968; S. australis strain ATCC 700641T/SK956; S. cristatus strain NCTC 12479T/SK231; S. peroris strain GTC 848T/SK958; S. infantis strain ATCC 27375T/SK959; S. sinensis strain CCUG 48488 (DSM 14990T); S. anginosus strain ATCC 33397T/SK52; S. constellatus strain ATCC 27823T/SK53; S. constellatus subsp. pharyngis strain CCUG 46377 (NCTC 13122T); S. intermedius strain ATCC 27335T/SK54; S. salivarius strain NCTC 8618T/SK56; S. vestibularis strain ATCC 49125T/SK227; S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus strain CCUG 35224 (ACM3611T); S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus strain CCUG 39970 (ACA-DC 206T); S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus strain CCUG 46150 (CIP 107122T); S. infantarius subsp. infantarius strain CCUG 43820 (NCDO 599T); S. infantarius subsp. coli strain CCUG 47831 (NCDO 964T); S. lutetiensis strain CCUG 46149 (CIP 106849T); and S. mutans strain NCTC 10449T/SK28. The strains designated ATCC, NCTC, and CCUG were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, the National Collection of Type Cultures (Colindale, London, England), and the Culture Collection of the University of Göteborg, Göteborg, Sweden, respectively, and the SK strains were from our own culture collection (35, 36).
The isolates were routinely cultured in Todd-Hewitt broth (TH; Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Mich.) and on 5% defibrinated horse blood agar (Statens Serum Institut, Copenhagen, Denmark).
Nomenclature.
Trüper and De Clari (50) corrected the long-standing names S. sanguis, S. parasanguis, and S. crista to S. sanguinis, S. parasanguinis, and S. cristatus, respectively, for reasons of Latin grammar. Although we consider these changes an unnecessary source of confusion and a direct violation of the principles of the International Code of Bacterial Nomenclature, we have adopted the corrected names in this paper according to the recent ruling of the Judicial Commission of the International Committee of the Taxonomy of Bacteria (53).
Preparation of DNA for PCR.
DNA was extracted from the bacteria by alkaline lysis (56). Individual strains were inoculated on 5% defibrinated horse blood agar and incubated at 37°C for 18 h in a 5% CO2-enriched atmosphere. The bacterial colonies were scraped from the agar with a sterile disposable plastic loop (1 mm in diameter) and suspended in 100 μl of sterile ultrapure water. Then 20 μl of the bacterial suspension and 80 μl of 0.05 M sodium hydrate were gently mixed in a microcentrifuge tube. This mixture was incubated at 60°C for 45 min and then 9.2 μl of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.0) was added to neutralize the pH. The prepared solution was used as the template DNA for the PCR analyses.
PCR primers.
Oligonucleotide primers used to amplify fragments of the genes ddl, gdh, rpoB, sodA, and gtf were designed on the basis of conserved sequences identified by aligning relevant sequences of Streptococcus species obtained at the GenBank nucleotide database (Table 1). The species-specific gtf primers used were reported previously (28).
TABLE 1.
PCR primers used to amplify ddl, gdh, rpoB, sodA, and gtf gene sequences
| Target gene | Primer name | Primer sequencea | Annealing temp (°C) | Expected size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddl | ddl-F | 5′-GCYATGGATAAAATYACRAC-3′ | 50 | 563 |
| ddl-R | 5′-CCACTGGKTRAARCCTGGCAGRGT-3′ | |||
| gdh | gdh-F | 5′-CGTGGYGGCTAYTATGACC-3′ | 50 | 642 |
| gdh-R | 5′-CYTCRTCCCAGTGRCTRAARTTRG-3′ | |||
| rpoB | rpoB-F | 5′-AARYTIGGMCCTGAAGAAAT-3′ | 50 | 742 |
| rpoB-R | 5′-TGIARTTTRTCATCAACCATGTG-3′ | |||
| sodA | sodA-F | 5′-TRCAYCATGAYAARCACCAT-3′ | 50 | 438 |
| sodA-R | 5′-ARRTARTAMGCRTGYTCCCARACRTC-3′ | |||
| gtf | gtf_uni-F | 5′-GAAACTGTTGATGGCTATTTGACAGC-3′ | 50 | 678 |
| gtf_uni-R | 5′-CATTGACATTATCCACCGCATCGACACG-3′ |
I, inosine; Y, C or T; R, A or G; K, G or T; M, A or C.
PCR analyses.
All PCR mixtures contained 10 μl of Eppendorf HotmasterMix (Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany), 10 μl of a 200-fold dilution of the preparation of template DNA described above, and a 0.4 μM concentration of each primer supplemented with sterile ultrapure water to a total volume of 25 μl. Amplification was performed with a Mastercycler gradient (Eppendorf) using the following parameters: an initial denaturing step at 94°C for 5 min, and 30 cycles of a denaturing step at 94°C for 30 s, a primer-annealing step at the appropriate temperature for 30 s, an extension step at 72°C for 30 s, and a final extension step at 72°C for 5 min. The primer-annealing temperature was optimized for each primer set (Table 1) (28). The PCR products were analyzed by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis after staining with ethidium bromide.
Sequencing of ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA.
Amplicons of four housekeeping genes obtained by PCR were purified with Wizard minicolumns (Promega Co., Madison, WI). The gene fragments were sequenced on both strands using the same primers and the Thermo Sequence Dye Terminator cycle sequencing premix kit (Amersham Bioscience AB, Uppsala, Sweden) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The following program was used: 30 cycles of denaturation at 96°C for 30 s, primer annealing at 45°C for 15 s, and extension at 60°C for 4 min. The products of the sequencing reaction were examined with an automatic DNA sequencer (ABI Prism 310 genetic analyzer; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA).
Phylogenetic analyses of ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA.
The Clustal X software (49) downloaded from http://www.ebi.ac.uk was used to align the sequences for each gene separately and as concatenated sequences in the order rpoB, sodA, ddl, and gdh. Phylogenetic analysis by the neighbor-joining algorithm (45) was conducted using MEGA version 3 (38). Missing sequences as a result of lack of a PCR amplification product of genes that may be missing or present in a significantly different sequence variant were dealt with as gaps of the same length. The corresponding parameter of the neighbor-joining algorithm was set at “pairwise deletion.” The model used was “nucleotide: Kimura two-parameter.”
Criteria for identification based on the sequences of the four housekeeping genes.
Unequivocal clustering with a single type strain and other well-described reference strains of a particular species in the unrooted phylogenetic tree based on concatenated sequences of the four housekeeping genes was taken as evidence of conclusive identification of that species. Deviations from this identification based on phylogenetic analysis of single gene loci were recorded. The single strain of Gemella haemolysans, from which only one of the four housekeeping genes was successfully amplified, was assigned to that species based on a 100% similarity to the corresponding gene sequence (rpoB) of the type strain.
PCR analysis of gtf.
As the first screening, PCR analysis with universal gtf primers, which were able to amplify all streptococcal gtf genes without regard to species, was carried out. Next, PCR analyses with six sets of species-specific gtf primers were performed on each isolate that was positive in the first-screen PCR. By the results of this PCR analysis, the isolate was identified according to the species that possessed the targeted gtf gene.
Phenotypic examination and identification.
The Rapid ID 32 STREP kit (Bio Mérieux, La Balme les Grottes, France) was inoculated from a suspension of bacteria grown anaerobically for 2 days on blood agar according to the manufacturer's instructions using an ATB1574 automatic dispenser (Vitek Systems, Bio Mérieux). After incubation for 4 hours at 37°C, the reactions were read and processed by an ATB expression system (Vitek Systems). Phenotypic analysis using the STREPTOGRAM kit (Wako Pure Chemicals, Osaka, Japan) was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions. Identification was achieved after 20 h by visual comparison of color reactions with the color plate included by the manufacturer.
Identifications obtained by the two kits were classified into three levels: (i) good identification, i.e., the first suggestion supported by a score ≥80% of relative probability; (ii) acceptable identification, the first suggestion supported by a score ≤80% of relative probability; (iii) no identification (“unacceptable profile”) or no suggestion supported by a probability of >50%. Each result was compared with the corresponding identification based on phylogenetic analysis of concatenated sequences of the four housekeeping genes.
For comparative purposes all strains were also tested for the ability to hydrolyze arginine using a traditional tube test as described previously (35).
RESULTS
PCR amplification and sequence determination of ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA genes.
PCR of the ddl, gdh, rpoB, sodA, and gtf genes yielded a single amplified band at approximately 560, 640, 740, 440, and 680 bp, respectively. The rates of successful amplifications with the ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA primers were 80.2, 70.0, 100, and 96.6%, respectively (see below for each species). Sequences covering 292, 431, 517, and 390 bp, respectively, of the four amplified genes were used in the analyses. The GenBank accession numbers of sequences determined for the reference strains in this study are shown in Table 2 together with numbers for reference sequences extracted from GenBank. The nucleotide sequences determined for clinical isolates have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers AB199330 to AB199446 (ddl), AB199447 to AB199548 (gdh), AB199914 to AB200046 and AB218984 (rpoB), and AB200047 to AB200167 and AB218985 (sodA). All sequences are also available for downloading as packages of either single loci or concatenated sequences at http://www.immi.au.dk/service/download/kilian.
TABLE 2.
Accession numbers of housekeeping gene sequences of reference strains extracted from public databases
| Taxon | Reference strain | ddl | gdh | rpoB | sodA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mitis group | |||||
| S. mitis | ATCC 12261T | U69164a | SMT1633b | SMT1463b | Z95909a |
| S. pneumoniae | R6 | NT02SP1638b | NT02SP1223b | NT021922b | NT02SP0735b |
| S. pneumoniae | TIGR4 | SP1671b | SP1243b | SP1961b | SP0766b |
| S. pseudopneumoniae | CCUG 49455T | AB199333c | AB199449c | AB199917c | AB200048c |
| S. oralis | NCTC 11427T | AB199332c | AB199448c | AF535168a | Z95911a |
| S. infantis | ATCC 700799T | AB199334c | NRd | AB199918c | AB022546a |
| S. australis | ATCC 700641T | NRd | NRd | AB199916c | AY386219a |
| S. parasanguinis | CCUG 30417T | NRd | AB199450c | AB199919c | Z95913a |
| S. cristatus | ATCC 12479T | AB199335c | AB199451c | AB199920c | AB021548a |
| S. gordonii | ATCC 10558T | U69163a | NRd | AB199921c | Z95905a |
| S. peroris | GTC848T | AB199337c | NRd | AB199922c | AB021545a |
| S. sanguinis | ATCC 10556T | AB199330c | AB199449c | AB199914c | Z95918a |
| S. sinensis | CCUG 48488T | AB199338c | AB199452c | AB199923c | AY386220a |
| Anginosus group | |||||
| S. anginosus | ATCC 33397T | AB199339c | AB199453c | AF535183a | Z95895a |
| S. intermedius | ATCC 27335T | AB199340c | NRd | AF535190a | Z95908a |
| S. constellatus subsp. constellatus | ATCC 27823T | AB199341c | AB199454c | AF535184a | Z95897a |
| S. constellatus subsp. pharyngis | CCUG 46377T | AB199342c | AB199455c | AB199924c | AB200049c |
| Salivarius group | |||||
| S. salivarius | NCTC 8618T | NRd | NRd | AF535169a | Z95916a |
| Bovis group | |||||
| “S. bovis” | NCTC 8177 | U69162a | NRd | AF535189a | Z95896a |
| S. infantarius subsp. infantarius | CCUG 43820T | NRd | NRd | AY315155a | AJ297184a |
| S. infantarius subsp. colie | CCUG 47831T | NRd | NRd | AB199925c | AJ306978a |
| S. lutetiensise | CCUG 46149T | NRd | NRd | AF535190a | AJ297189a |
| S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus | CCUG 35224T | AB199343c | NRd | AY315154a | AJ297183a |
| S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | CCUG 46150T | NRd | NRd | AY315157a | AJ297195a |
| S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus | CCUG 39970T | NRd | NRd | AY315156a | AJ297186a |
| Mutans group | |||||
| S. mutans | NCTC 10449T | AB199344c | NRd | AF535168a | AB200050c |
| S. mutans | UA159 | NT02SM0588b | NRd | NT02SM1951b | NT02SM0619b |
| Pyogenic group | |||||
| S. pyogenes | SF370 | NT01SP1170b | NRd | NT01SP0079b | NT01SP1158b |
| S. agalactiae | NEM316 | NT04SA0897b | NRd | NT04SA0218b | NT04SA0918b |
GenBank accession number.
TIGR locus name in the genome database of TIGR.
Accession number of a sequence determined in this study.
NR, no reference sequence available.
S. infantarius subsp. coli and S. lutetiensis are synonyms for the same species according to Poyart et al. (42).
Identification of strains based on phylogenetic analysis.
Of the 147 strains examined, 145 were identified as belonging to the genus Streptococcus. The two remaining strains were identified as Enterococcus faecalis and Gemella haemolysans based on 100% similarity of the sequences of rpoB and sodA to sequences of those two species detected in a nucleotide BLAST search (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/Blast.cgi).
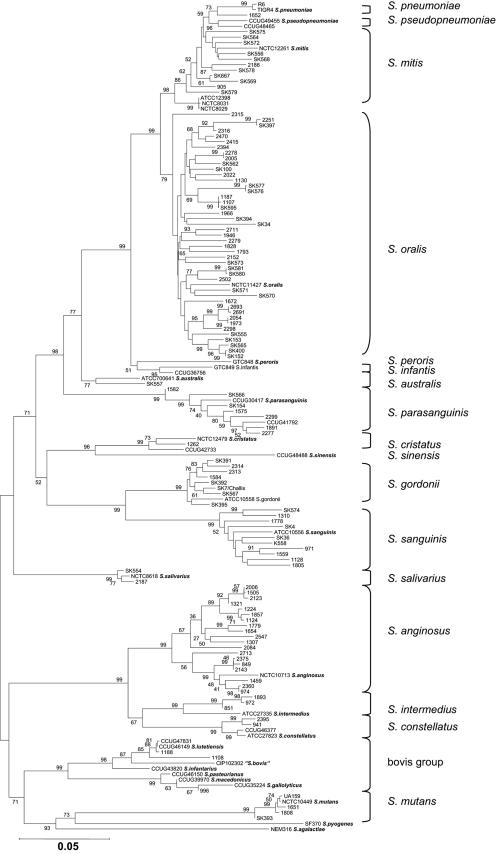
The concatenated sequence of the four housekeeping genes rpoB, sodA, ddl, and gdh consisted of 1,630 bp. Phylogenetic analysis of the concatenated sequences resulted in the tree shown in Fig. 1. The tree revealed clear separation of all currently recognized species supported by significant bootstrap values. Some clusters showed an unexpected degree of sequence variation. This was most striking in the clusters containing the type and reference strains of S. anginosus and S. parasanguinis. This situation may reflect the existence of yet unrecognized species within some of the clusters. However, with a few potential exceptions, all strains could be assigned with confidence to currently recognized species. This was considered the conclusive identification of the strains.
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic tree based on concatenated sequences of four housekeeping genes, rpoB, sodA, ddl, and gdh. The tree was based on the neighbor-joining method. The value on each branch is the estimated confidence limit (expressed as a percentage) for the position of the branch as determined by bootstrap analysis. Only values exceeding 50% are shown. The scale bar (neighbor-joining [NJ] distance) represents a 5% difference in nucleotide sequence.
The phylogenetic trees based on separate analyses of ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA likewise showed distinct clusters that could be correlated with individual species (not shown). However, identifications based on these analyses revealed some deviations from the conclusive identification based on analysis of the concatenated sequences. Thus, identification of a total of eight strains (5.5%), including three type strains of the anginosus group of species, deviated from the conclusive identification (Table 3). The deviating results were based mainly on ddl and rpoB gene sequences, whereas no deviation was observed in results obtained by analysis of the sodA gene. No strain possessed more than one deviating sequence among the four housekeeping genes examined. Apart from these problems, which can be explained by homologous recombination between species, the recently described S. pseudopneumoniae posed a problem that was visible in trees based on single loci. In each of the trees based on rpoB, gdh, and ddl, the two strains could not be distinguished with confidence from S. mitis, and in the tree based on sodA sequences, they were indistinguishable from S. pneumoniae.
TABLE 3.
Phylogenetically deviating gene sequences in eight Streptococcus strains identified according to analysis of concatenated sequences of four housekeeping genes
| Strain | Correct identity | Deviating gene | Misidentified as |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitis group | |||
| SK153 | S. oralis | ddl | S. sanguinis |
| SK36 | S. sanguinis | rpoB | S. sinensis |
| SK574 | S. sanguinis | ddl | S. gordonii |
| 1310 | S. sanguinis | ddl | S. gordonii |
| Anginosus group | |||
| SK54T | S. intermedius | rpoB | S. anginosus |
| 1893 | S. intermedius | gdh | S. anginosus |
| SK53T | S. constellatus | ddl | S. anginosus |
| CCUG 46377T | S. constellatus subsp. pharyngis | ddl | S. anginosus |
To analyze the nature of the deviating results for some of the anginosus group streptococci further, partial sequencing of 16S rRNA genes was performed for each strain belonging to the species S. intermedius and S. constellatus using the method described elsewhere (36). These results confirmed the identifications based on concatenated housekeeping genes by ≥99% similarity to the 16S rRNA gene sequences of the relevant type and reference strains in public databases (data not shown).
Rates of positive PCRs.
The percentage of PCR-positive isolates assigned to each of the Streptococcus species as described is shown in Table 4. The ddl primers failed to amplify a sequence in all strains of the species S. australis, S. salivarius, S. vestibularis, S. infantarius, S. lutetiensis, S. gallolyticus, and in some strains of S. parasanguinis, S. anginosus, and S. intermedius. The gdh PCR failed to amplify sequences in S. infantis, S. australis, S. gordonii, S. peroris, and in all members of the salivarius, bovis, and mutans groups. In contrast, the rpoB and sodA primers yielded amplicons from virtually all strains (100 and 96.6%, respectively) (Table 4).
TABLE 4.
Proportion of successful PCR amplifications of genes from 22 species of nonhemolytic streptococci using the primers listed in 1
| Taxon | Na | % of strainsb
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ddl | gdh | rpoB | sodA | gtf | gtfD | gtfT | gtfK | gtfP | gtfR | gtfG | ||
| Mitis group | ||||||||||||
| S. mitis | 16 | 100 | 63 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. pseudopneumoniae | 2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. oralis | 45 | 100 | 98 | 100 | 100 | 51 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51 | 0 |
| S. infantis | 2 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. australis | 2 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. parasanguinis | 9 | 44 | 89 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. cristatus | 3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. gordonii | 9 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| S. peroris | 1 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. sanguinis | 11 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 73 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sinensis | 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Anginosus group | ||||||||||||
| S. anginosus | 20 | 65 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. constellatus subsp. constellatus | 3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. constellatus subsp. pharyngis | 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. intermedius | 4 | 75 | 25 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Salivarius group | ||||||||||||
| S. salivarius | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. vestibularis | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Bovis group | ||||||||||||
| S. infantarius subsp. infantarius | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. infantarius subsp. coli | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. lutetiensis | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus | 2 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Mutans group | ||||||||||||
| S. mutans | 4 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other | ||||||||||||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Gemella haemolysans | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Total | 148 | 81.1 | 70.9 | 100 | 96.6 | 35.8 | ||||||
N, number of strains.
NT, not tested.
Identification of strains based on the gtf gene.
PCR analysis with the universal gtf primer set resulted in an amplicon from 53 strains (35.8%) assigned to the species S. sanguinis, S. oralis, S. gordonii, S. mutans, and S. salivarius in addition to S. infantarius subsp. infantarius and S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus. With the exception of strains of the last two taxa, all of these strains also yielded an amplicon with one of the species-specific gtf primers. No nonspecific product was observed in any of the species. The identification based on these results for gtf-positive strains was in complete agreement with the identification of the strains based on concatenated sequences and, furthermore, revealed that gtf sequences were present in all strains of S. sanguinis, S. gordonii, S. mutans, and S. salivarius. In contrast, only 51% of strains identified as S. oralis possessed a gtf gene.
Identification based on phenotypic test kits.
A total of 145 strains belonging to the genus Streptococcus as determined by DNA sequence analysis were examined with the commercial identification kit STREPTOGRAM and the Rapid ID 32 STREP system. The two kits contain 21 and 32 biochemical tests, respectively. Eleven tests are shared by the two systems and allow direct comparison of the outcomes (Tables 5 and 6). Although the overall pattern is similar, the proportion of positive reactions in individual tests shared by the two systems shows many differences. It is striking that the test for arginine hydrolysis, which is a taxonomically very informative property when determined by a standard tube test (35), shows significant differences. Less than 50% of the strains belonging to species that are invariably positive in standard tests (S. sanguinis and S. gordonii) show positive reactions with the two kits.
TABLE 5.
Physiological characteristics of strains of 22 species of nonhemolytic streptococci determined by the Rapid ID 32 Strep systema
| Species | Nb | % of strains positive
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADH | βGLU | βGAR | βGUR | αGAL | PAL | RIB | MAN | SOR | LAC | TRE | RAF | VP | APPA | βGAL | PYRA | βNAG | GTA | HIP | GLYG | PUL | MAL | MEL | SAC | MβDG | TAG | βMAN | ||
| Mitis group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. mitis | 16 | 0 | 13 | 69 | 0 | 25 | 50 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 19 | 6 | 35 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 94 | 6 | 0 | 56 | 62 | 0 | 63 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| S. pseudopneumoniae | 2 | 0 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| S. oralis | 45 | 2 | 2 | 93 | 0 | 40 | 78 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 13 | 9 | 6 | 98 | 13 | 0 | 9 | 87 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 38 | 0 | 38 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| S. infantis | 2 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sanguinis | 11 | 36 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 82 | 9 | 9 | 91 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 82 | 0 | 9 | 64 | 91 | 0 | 91 | 27 | 0 | 0 |
| S. gordonii | 9 | 44 | 89 | 100 | 0 | 11 | 100 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 78 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 78 | 67 | 11 | 67 |
| S. parasanguinis | 9 | 56 | 11 | 78 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 100 | 11 | 68 | 11 | 100 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 33 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 44 | 100 | 11 | 33 | 0 |
| S. australis | 2 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| S. cristatus | 3 | 33 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 33 | 0 |
| S. peroris | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| S. sinensis | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anginosus group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. anginosus | 20 | 75 | 95 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 100 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 60 | 80 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 95 | 0 | 100 | 80 | 0 | 15 |
| S. constellatus | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 0 | 67 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 0 |
| S. constellatus subsp. pharyngis | 1 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. intermedius | 4 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 25 | 0 | 75 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 25 | 0 | 25 |
| Bovis group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. infantarius | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. lutetiensis | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. gallolyticus | 2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| S. pasteurianus | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| S. macedonicus | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mutans group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. mutans | 4 | 0 | 75 | 50 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 25 | 100 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 75 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| Salivarius group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. salivarius | 3 | 0 | 100 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 100 | 33 | 100 | 100 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 33 | 33 | 0 | 0 |
ADH, arginine dihydrolase; βGLU, β-glucosidase; βGAR, β-galactosidase detected with p-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside as the substrate; βGUR, β-glucuronidase; αGAL, α-galactosidase; PAL, alkaline phosphatase; VP, Voges-Proskauer test; APPA, activity of alanine-phenylalanine-proline-arylamidase; βGAL, β-galactosidase detected with 2-naphthyl-β-galactopyranoside as the substrate; PYRA, pyrrolidonyl arylamidase; βNAG, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase; GTA, glycyl-tryptophan arylamidase; HIP, hydrolysis of hippurate; βMAN, β-mannosidase; RIB, MAN, SOR, LAC, TRE, RAF, GLYG, PUL, MAL, MEL, SAC, and TAG, fermentation of ribose, mannitol, sorbitol, lactose, trehalose, raffinose, glycogen, pullulan, maltose, melibiose, sucrose, and tagatose, respectively. All strains tested were negative for fermentation of melezitose, l-arabinose, d-arabitol, and cyclodextrin.
N, number of strains.
TABLE 6.
Physiological characteristics of strains of 22 species of nonhaemolytic streptococci determined by the STREPTOGRAM kita
| Species | Nb | % of strains positive
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMY | LAC | NAG | TRE | MAN | FUC | ARB | RAF | αGAL | SOR | ARA | βGAL | INU | MEL | PAL | ARG | ESC | GLN | PYRA | HIP | VP | ||
| Mitis group | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. mitis | 16 | 88 | 94 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 56 | 13 | 19 | 31 | 6 | 94 | 19 | 0 | 6 | 43 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. pseudopneumoniae | 2 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| S. oralis | 45 | 0 | 93 | 98 | 24 | 4 | 96 | 91 | 58 | 49 | 9 | 60 | 42 | 0 | 31 | 89 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| S. infantis | 2 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sanguinis | 11 | 0 | 100 | 90.9 | 100 | 0 | 82 | 73 | 18 | 55 | 63 | 9 | 0 | 82 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. gordonii | 9 | 89 | 78 | 100 | 89 | 0 | 78 | 78 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 44 | 22 | 67 | 0 | 89 | 22 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. parasanguinis | 9 | 22 | 89 | 100 | 11 | 0 | 78 | 22 | 100 | 100 | 22 | 11 | 22 | 11 | 56 | 100 | 78 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. australis | 2 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. cristatus | 3 | 0 | 67 | 33 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. peroris | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sinensis | 1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anginosus group | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. anginosus | 20 | 95 | 95 | 5 | 90 | 15 | 0 | 100 | 20 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 15 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 95 |
| S. constellatus | 3 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 67 | 67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 |
| S. constellatus subsp. pharynges | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| S. intermedius | 4 | 75 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Bovis group | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. infantarius | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| S. lutetiensis | 4 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. gallolyticus | 2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| S. macedonicus | 1 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. pasteurianus | 1 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Mutans group | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. mutans | 4 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 25 | 0 | 100 | 75 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 |
| Salivarius group | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. salivarius | 3 | 67 | 67 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 67 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 33 | 67 | 67 | 33 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67 |
NAG, N-acetylglucosaminidase detected with p-nitrophenyl-N-acetylglucosaminide as the substrate; FUC, fucopyranosidase detected with p-nitrophenyl-β-d-fucopyranoside as the substrate; αGAL, α-galactosidase detected with p-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside as the substrate; βGAL, β-galactosidase detected with 2-naphthyl-β-galactopyranoside as the substrate; PAL, alkaline phosphatase; ARG, arginine dihydrolase; ESC, hydrolysis of esculin; GLN, β-glucuronidase; PYRA, pyrrolidonyl arylamidase; HIP, hydrolysis of hippurate; VP, Voges-Proskauer test; AMY, LAC, TRE, MAN, ARB, RAF, SOR, ARA, INU, and MEL, fermentation of amygdalin, lactose, trehalose, mannitol, arbutin, raffinose, sorbitol, arabinose, inulin, and melibiose, respectively.
N, number of strains.
With reference to the conclusive identification based on phylogenetic analysis of the concatenated sequences, the rate of correct identification obtained in the two kits was calculated (Table 7). Of all 145 strains examined, 68 (47%) and 70 (48%) were correctly identified by Rapid ID 32 STREP and the STREPTOGRAM kit, respectively. The rate of incorrect identification in the two systems was 46% and 23%, respectively. STREPTOGRAM gave a “no code” response rather than an incorrect identification significantly more often than Rapid ID 32 STREP. Among 16 strains of S. mitis, only 2 (13%) and 6 (38%) strains were correctly identified by Rapid ID 32 STREP and STREPTOGRAM, respectively. Both kits correctly identified 16 (36%) of 45 strains of S. oralis. The rate of correct identification of strains of other species varied between 33 and 100%.
TABLE 7.
Comparison of conclusive identification of 145 Streptococcus strains based on phylogenetic analysis of concatenated sequences of four housekeeping genes and identifications obtained with two commercial identification kits
| Species (conclusive identification) | No. of strains | Rapid ID 32 Strep kit
|
STREPTOGRAM kit
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % with correct identification (N) | % with deviating identificationa (N) | % with no identification (N) | % with correct identification (N) | % with deviating identification (N) | % with no identification (N) | ||
| All species in database | 125 | 54 (68) | 38 (48) | 7 (9) | 56 (70) | 19 (24) | 25 (31) |
| S. mitis | 16 | 13 (2) | Total 69 (11) | 19 (3) | 38 (6) | Total 25 (4) | 38 (6) |
| S. oralis 2 (3) | S. oralis (4) | ||||||
| S. mitis 2 (2) | |||||||
| E. rhusiopathiae (2) | |||||||
| S. sanguis (2) | |||||||
| S. parasanguis (1) | |||||||
| G. morbillorum (1) | |||||||
| G. haemolysans (1) | |||||||
| S. oralis | 45 | 36 (16) | Total 62 (28) | 2 (1) | 36 (16) | Total 31 (14) | 33 (15) |
| E. rhusiopathiae (15) | S. parasanguis (6) | ||||||
| S. mitis 2 (9) | S. mitis 2 (4) | ||||||
| S. pneumoniae (1) | S. sanguis (3) | ||||||
| S. parasanguis (1) | S. mitis 1 (1) | ||||||
| S. mitis 1 (1) | |||||||
| G. vaginalis (1) | |||||||
| S. sanguinis | 11 | 64 (7) | Total 36 (4) | 0 | 82 (9) | Total 9 (1) | 9 (1) |
| S. suis I (1) | S. oralis (1) | ||||||
| G. morbillorum (1) | |||||||
| G. haemolysans (1) | |||||||
| S. mitis 2 (1) | |||||||
| S. gordonii | 9 | 78 (7) | S. mitis 2 (1) | 11 (1) | 55 (5) | Total 11 (1) | 33 (3) |
| S. oralis (1) | |||||||
| S. parasanguinis | 9 | 67 (6) | 0 | 33 (3) | 56 (5) | Total 11 (1) | 33 (3) |
| S. oralis (1) | |||||||
| S. anginosus | 20 | 100 (20) | 0 | 0 | 95 (19) | 0 | 5 (1) |
| S. intermedius | 4 | 100 (4) | 0 | 0 | 100 (20) | 0 | 0 |
| S. constellatus | 4 | 75 (3) | Total 25 (1) | 0 | 50 (2) | Total 25 (1) | 25 (1) |
| L. lactis subsp. cremoris (1) | S. vestibularis (1) | ||||||
| S. mutans | 4 | 50 (2) | Total 25 (1) | 25 (1) | 75 (3) | 0 | 25 (1) |
| S. uberis (1) | |||||||
| S. salivarius | 3 | 33 (1) | Total 68 (2) | 0 | 33 (1) | Total 68 (2) | |
| S. intermedius (2) | S. vestibularis (2) | ||||||
| Species not in database | 20 | 0 | Total 90 (18) | Total 10 (2) | 0 | Total 45 (9) | Total 55 (11) |
| S. pseudopneumoniae | 2 | 0 | S. oralis (1) | 1 | 0 | S. mitis 2 (1) | 2 |
| S. australis | 2 | 0 | S. mitis 2 | 1 | 0 | S. vestibularis (1) | 1 |
| S. cristatus | 3 | 0 | S. mitis 2 (2) | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| S. sanguis (1) | S. sanguis (2) | ||||||
| S. infantis | 2 | 0 | S. oralis (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. mitis 2 (2) | S. mitis (1) | 1 | |||||
| S. peroris | 1 | 0 | S. oralis (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. sinensis | 1 | 0 | S. oralis (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. gallolyticus | 2 | 0 | S. bovis I (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| S. pasteurianus | 1 | 0 | S. bovis II (1) | 0 | 0 | S. sanguis (1) | 1 |
| S. macedonicus | 1 | 0 | S. oralis (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| S. infantarius | 1 | 0 | S. mitis 2 (1) | 0 | 0 | S. hyointestinalis (3) | 1 |
| S. lutetiensis | 4 | 0 | S. alactolyticus (2) | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| S. mitis 2 (1) | |||||||
| S. oralis (1) | |||||||
| Total | 145 | 47 (68) | 46 (66) | 8 (11) | 48 (70) | 23 (33) | 29 (42) |
Other species included Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, Gemella morbillorum, Gemella haemolysans, Gardnerella vaginalis, and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris.
The best results were obtained with members of the anginosus group of streptococci, i.e., S. anginosus, S. intermedius, and S. constellatus. Eleven species described since 1991 (Table 7) are not included in the databases associated with the two identification kits. Eighteen of the 20 strains representing these species were assigned to other species by Rapid ID 32 STREP. Among these were strains of S. gallolyticus and S. pasteurianus, which were “correctly” identified as “S. bovis,” a species name that, however, is now considered illegitimate (42). STREPTOGRAM assigned incorrect names to nine (35%) of the 20 strains, whereas 11 (55%) remained unidentified (Table 7).
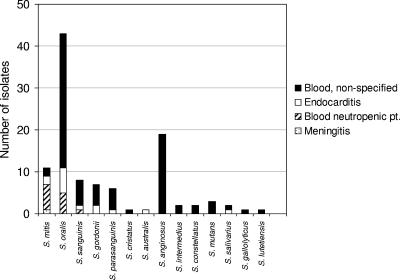
Species distribution and properties of blood isolates.
A total of 107 strains were isolated from human blood. Further information on the underlying disease was not available for 80 of these isolates. The remaining 27 strains were from patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis (n = 14) and meningitis (n = 1) and from patients suffering from neutropenia (n = 12). Figure 2 shows the species distribution of the 107 isolates according to the conclusive identification based on phylogenetic analysis of concatenated sequences of the four housekeeping genes. As shown in the figure, S. oralis accounted for 40% of all blood isolates of nonhemolytic streptococci, excluding S. pneumoniae. The second most frequently isolated species was S. anginosus (18%). Isolates from endocarditis patients belonged to S. oralis (n = 6), S. mitis (n = 2), S. gordonii (n = 2), and S. sanguinis, S. parasanguinis, S. salivarius, and S. australis (each represented by one isolate). The predominant species isolated from neutropenic patients were S. oralis (n = 6) and S. mitis (n = 5). The only other species represented in this group of patients was S. sanguinis (n = 1).
FIG. 2.
Species distribution of 111 blood isolates of nonhemolytic streptococci.
Among the 107 blood isolates, 42 (39%) produced extracellular polysaccharide as suggested by the presence of a gtf gene. Among 43 blood isolates of S. oralis, in which gtf is variably present, 22 (51%) had the gtf gene. Eight (57%) of 14 isolates from patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis produced extracellular polysaccharide.
DISCUSSION
Several factors contribute to the difficulties that are encountered in the identification of nonhemolytic streptococci by both molecular and biochemical methods. The taxonomy of this group of bacteria has been revised frequently, and many new species have been described, often without sufficient information about differential characteristics and the extent of phenotypic and genetic variation within proposed species (16, 44). Satisfactory classification of bacteria reflects their phylogenetic diversification within distinct boundaries. It has sometimes been doubted that distinct subpopulations that can be equated with species exist in the population of nonhemolytic streptococci. Nonhemolytic streptococci are naturally competent for genetic transformation (24), and there is direct evidence of interspecies homologous recombination in genes encoding transpeptidases (“penicillin-binding proteins”) in S. pneumoniae, S. mitis, and S. oralis (14, 21). However, the frequency of detectable recombination affecting penicillin-binding proteins in the natural populations of these species is undoubtedly influenced by an extraordinary selection pressure exerted by beta-lactam antibiotics. To what extent interspecies homologous recombination affects housekeeping genes in which functionally acceptable mutations are selectively neutral is not known.
The data summarized in Table 3 show that in 5.5% of the 145 Streptococcus strains examined, the phylogeny of one of the four housekeeping genes deviated from that of the other genes and revealed clear evidence of recombination with another Streptococcus species. The practical consequence of this is that these eight strains would have been misidentified if identification were based on the sequence of the affected gene alone. In five of eight strains the gene affected by recombination was ddl, in two strains it was rpoB, and in one strain it was gdh. The superoxide dismutase gene, sodA, was not affected in any of the strains examined in spite of the fact that sequences of this gene were successfully determined for all but five strains (Table 4). Thus, for unknown reasons, the frequency of deviating sequences in sodA was significantly lower than in ddl (P < 0.05).
The data in Table 3 furthermore demonstrate that recombination always occurred between members of the same phylogenetic group, i.e., either within the mitis group or within the anginosus group of species, probably determined by the requirement for sufficient sequence similarity to allow efficient integration (39). It is remarkable that 14% (n = 4) of the 28 strains belonging to the anginosus group of streptococci showed evidence of recombination affecting one of the four housekeeping genes. By comparison, only 4% (n = 4) of the 102 mitis group streptococci were affected, but with significant differences between individual species of the group. Thus, only 1 (2%) of 45 S. oralis strains showed evidence of recombination with another species, while a remarkable 27% (n = 3) of 11 S. sanguinis strains possessed deviating gene sequences apparently originating in S. gordonii or S. sinensis. These figures clearly demonstrate differences in the frequency of transfer of housekeeping gene sequences between species of nonhemolytic streptococci. Of particular practical significance is the finding that three of the four anginosus group strains with deviating sequences were type strains, which usually serve as references for gene sequence-based identification.
Recombination may also be partly responsible for the difficulties encountered in finding phenotypic traits that allow unequivocal differentiation of species of nonhemolytic streptococci. As shown in Tables 5 and 6 and by previous studies (5, 35, 36), very few characters are of differential value. Comparison of the results presented in Tables 5 and 6 furthermore demonstrates how different versions of a test for the same target character may give different results. This is even more significant when results obtained in traditional tube tests are compared with results obtained in commercially available kits such as Rapid ID 32 STREP (36). For example, the ability to hydrolyze arginine is a characteristic of all members of S. sanguinis, S. gordonii, S. parasanguinis, and S. cristatus and is therefore valuable for differentiating this group of closely related species from S. mitis, S. oralis, S. pneumoniae, and S. infantis (36). Strains previously referred to as “S. mitis biovar 2,” which are arginine hydrolase positive (35), belong to the species S. parasanguinis and to a yet unnamed taxon according to recent taxonomic studies (36). As shown in Tables 5 and 6, only a small proportion of strains (31% and 44%, respectively) belonging to S. sanguinis, S. gordonii, S. parasanguinis, and S. cristatus gave a positive result in the test for arginine hydrolysis/dihydrolase in the two commercial kits. Although these results do not necessarily invalidate the ability of the commercial kits to identify clinical isolates of these species, it is clear that the results obtained with these kits do not adequately reflect the presence or absence of particular genes and associated properties. Thus, examination of all strains by a traditional tube test (35) showed arginine hydrolase activity in all strains assigned to the species S. australis, S. parasanguinis, S. gordonii, S. sanguinis, and S. intermedius in 18 of 20 S. anginosus and in two of four S. constellatus strains.
Another problem of direct practical relevance is that the databases associated with the two commercial kits evaluated in this study are not adjusted according to the frequently changing taxonomy of this group of bacteria. As a consequence, members of species described after 1991 are not correctly identified by either of the two commercial kits (Table 7).
Combined, the problems mentioned above contributed to a rate of correct identification of the present strain collection that was below 50% for both kits. The rate of correct identification varied significantly between species. Not unexpectedly, the most significant problems were observed for S. mitis and S. oralis, of which only 13 and 36%, respectively, were correctly identified by Rapid ID 32 STREP and 38 and 36%, respectively, by STREPTOGRAM. Among all 145 strains examined 46.9% and 22.1% were incorrectly identified by the API Rapid ID 32 STREP and the STREPTOGRAM kits, respectively. The remaining 6.2% and 29.6% of the strains were unidentified by these systems, respectively (Table 7).
The results obtained in this study and in our recent taxonomic study (36) indicate that phenotypic characterization is of limited value for identification of many species of nonhemolytic streptococci.
Correct identification of nonhemolytic streptococci is to some extent achievable by partial sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene and searching for homologous sequences in public databases (7, 30). However, there are two problems with this approach. First, the method does not allow differentiation of S. mitis, S. oralis, S. pseudopneumoniae, and S. pneumoniae because of significant sequence conservation of the 16S rRNA genes in this group of bacteria and because of misleading recombinatory sequences in some versions of that gene in some strains (36). Second, many sequences in the public databases are mislabeled, either because of incorrect identification of the source strain or because of nonrecorded revised classification of the strain subsequent to deposition of the sequence. It is therefore important to restrict searches to the type strains of the species. This is an option at the database of the Ribosomal Database Project II (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/index.jsp).
Our study demonstrates that unequivocal identification of clinical isolates of nonhemolytic streptococci can be achieved by phylogenetic analysis of concatenated sequences of four housekeeping genes, ddl, gdh, rpoB, and sodA, amplified by the primer sets listed in Table 1. As the resulting identification is based on the phylogeny of the isolates as reflected in several loci distributed along the entire genome, we assume that this is as close as one can get to a correct identification, although yet unrecognized taxa may still occur, as suggested by the significant sequence divergence in some of the clusters (Fig. 1). This method can be an important tool in taxonomic studies of streptococci and may eventually replace the technically more demanding and less reproducible DNA-DNA hybridization. However, an important question is if it is feasible and biologically meaningful to define species limits according to particular thresholds of sequence similarities. Comprehensive studies of additional groups of bacteria are required to obtain an appropriate basis for such deliberations.
Multilocus sequence analysis is at present unrealistic as a general identification tool for clinical microbiology laboratories. As an alternative, our findings support the suggestion by Poyart and Kawamura and their coworkers (32, 41, 42) that sodA would be the best choice as a single informative gene. This is based on the observation that the gene could be amplified in the whole range of species, including members of related genera, and that the frequency of phylogenetically deviating sequences in this gene appears to be low. The only shortcomings of this choice are that the primers curiously failed to amplify a sequence in some S. sanguinis strains (Table 4)and that the sodA sequences of S. pseudopneumoniae and S. pneumoniae were indistinguishable.
The phylogenetic identification methods, whether based on single or multiple genes, rely on the availability of comprehensive sets of reference sequences that adequately reflect the genetic polymorphism in the respective gene loci. The sequences generated by this study may be downloaded as complete packages of sequences, either concatenated sequences or individual sequences, from www.immi.au.dk/service/download/kilian. By adding a sequence determined for a clinical isolate in the correct format and length, a phylogenetic tree showing the location of the target strain may easily be performed with the MEGA3 software (38), which can be downloaded from http://www.megasoftware.net/.
The species distribution of 107 blood isolates, the majority of which were consecutive isolates from one laboratory in Denmark, showed a clear predominance of S. oralis and S. anginosus (Fig. 2). Unfortunately, detailed clinical information about underlying diseases is lacking for the majority of the isolates. However, it is clear that S. oralis was predominant among isolates from cases of subacute bacterial endocarditis, although the number of strains is relatively limited. The species S. mitis and S. oralis were the most frequent among strains from patients with neutropenia, in agreement with previous reports (5, 29). Although these two species are among the predominant streptococci in dental plaque, their relative proportions in plaque do not adequately explain their almost exclusive occurrence in neutropenic patients. Likewise, the high proportion of S. anginosus from cases of bacteremia and its absence among isolates from known cases of endocarditis and neutropenia are hardly a coincidence. Based on the existing literature (9, 44, 54) it is conceivable that many bacteremias caused by anginosus group streptococci were associated with local suppurative infections.
There is only limited information about potential virulence factors that may explain the differential distribution of the species in various extraoral pathologies. It has been suggested that the glucosyltransferase enzyme is an important virulence factor in systemic infections due to its ability to synthesize capsule-like extracellular polysaccharide (25) and to enhance adhesion to and invasion and killing of endothelial cells in vitro (46, 52). In this study, 39% of the 107 isolates from blood possessed the gtf gene. More specifically, 51% of the blood isolates of S. oralis, in which the property is variably present, were gtf positive. The fact that a similar proportion was found in a collection of S. oralis strains mainly isolated from the oral cavity (36) does not support the hypothesis that GTF activity constitutes an advantage to the survival of viridans streptococci in the bloodstream. Our data do not exclude that GTF may be a determinant of the severity of disease, but it is unrelated to extracellular polysaccharide production, as sucrose, which is the necessary substrate, is absent in blood.
The results shown in Table 4 indicate that S. infantarius subsp. infantarius and S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus possess the gtf gene and produce extracellular polysaccharide from sucrose. These taxa were previously included in the now formally illegitimate “S. bovis,” some strains of which are known to produce extracellular polysaccharide. However, it has not been clear which of the more recently described taxa produce extracellular polysaccharide (16). This property may help in identifying clinical isolates that belong to the bovis group of streptococci.
We conclude that identification of nonhemolytic streptococci using the two commercial kits tested is not a valid approach at the present time. The shortcomings of the kits reflect the general problem of identifying these bacteria on the basis of phenotypic characterization combined with the lack of updating of the associated databases. Phylogenetic analysis of the sequences of several housekeeping genes or carefully selected single genes (e.g., sodA) with reference to a set of representative sequences will secure correct identification of clinical isolates. The principle proved its usefulness in an updated analysis of the distribution of species of nonhemolytic streptococci from bacteremic patients.
Acknowledgments
The technical help provided by Tove Findahl and Lise Hald is gratefully acknowledged.
This study was supported by the Danish Medical Research Council and by a visiting scientist stipend to T.H. within the framework of the bilateral agreement between the Danish Rectors' Conference and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 0413101).
REFERENCES
- 1.Arbique, J. C., C. Poyart, P. Trieu-Cuot, G. Quesne, G. C. Mda, A. G. Steigerwalt, R. E. Morey, D. Jackson, R. J. Davidson, and R. R. Facklam. 2004. Accuracy of phenotypic and genotypic testing for identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae and description of Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:4686-4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baddour, L. M. 1994. Virulence factors among gram-positive bacteria in experimental endocarditis. Infect. Immun. 62:2143-2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Banas, J. A. 2004. Virulence properties of Streptococcus mutans. Front. Biosci. 9:1267-1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bassetti, M., G. Secchi, S. Borziani, G. Melica, A. Cassottana, L. Martinelli, S. Chierchia, and D. Bassetti. 2004. Successful treatment of four-valve native endocarditis caused by Streptococcus bovis. Int. J. Cardiol. 97:159-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beighton, D., A. D. Carr, and B. A. Oppenheim. 1994. Identification of viridans streptococci associated with bacteraemia in neutropenic cancer patients. J. Med. Microbiol. 40:202-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bochud, P. Y., P. Eggiman, T. Calandra, G. Van Melle, L. Saghafi, and P. Francioli. 1994. Bacteremia due to viridans streptococcus in neutropenic patients with cancer: clinical spectrum and risk factors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 18:25-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bosshard, P. P., S. Abels, M. Altwegg, E. C. Böttger, and R. Zbinden. 2004. Comparison of conventional and molecular methods for identification of aerobic catalase-negative gram-positive cocci in the clinical laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:2065-2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cabellos, C., P. F. Viladrich, J. Corredoira, R. Verdaguer, J. Ariza, and F. Gudiol. 1999. Streptococcal meningitis in adult patients: current epidemiology and clinical spectrum. Clin. Infect. Dis. 28:1104-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chang, W. N., J. J. Wu, C. R. Huang, Y. C. Tsai, C. C. Chien, and C. H. Lu. 2002. Identification of viridans streptococcal species causing bacterial meningitis in adults in Taiwan. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 21:393-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen, C. C., L. J. Teng, S. Kaiung, and T. C. Chang. 2005. Identification of clinically relevant viridans streptococci by sequence analysis of the 16S-23S ribosomal DNA spacer region. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:2651-2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Conangla, G., L. Rodriguez, C. Alonso-Tarres, A. Avila, and A. G. de la Campa. 2004. Streptococcus salivarius meningitis after spinal anesthesia. Neurologia 19:331-333. (In Spanish.) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Coykendall, A. L. 1989. Classification and identification of the viridans streptococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2:315-328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Douglas, C. W. I., J. Heath, K. K. Hampton, and F. E. Preston. 1993. Identity of viridans streptococci isolated from cases of infective endocarditis. J. Med. Microbiol. 39:179-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dowson, C. G., T. J. Coffey, C. Kell, and R. A. Whiley. 1993. Evolution of penicillin resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae; the role of Streptococcus mitis in the formation of a low affinity PBP2B in S. pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 9:635-643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Drancourt, M., V. Roux, P. E. Fournier, and D. Raoult. 2004. rpoB gene sequence-based identification of aerobic gram-positive cocci of the genera Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Gemella, Abiotrophia, and Granulicatella. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:497-504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Facklam, R. 2002. What happened to the streptococci: overview of taxonomic and nomenclature changes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15:613-630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Facklam, R., G. S. Bosley, D. Rhoden, A. R. Franklin, N. Weaver, and R. Schulman. 1985. Comparative evaluation of the API 20S and AutoMicrobic gram-positive identification systems for non-beta-hemolytic streptococci and aerococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 21:535-541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.French, G. L., H. Talsania, J. R. Charlton, and I. Phillips. 1989. A physiological classification of viridans streptococci by use of the API-20STREP system. J. Med. Microbiol. 28:275-286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Garnier, F., G. Gerbaud, P. Courvalin, and M. Galimand. 1997. Identification of clinically relevant viridans group streptococci to the species level by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:2337-2341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gold, J. S., S. Bayar, and R. R. Salem. 2004. Association of Streptococcus bovis bacteremia with colonic neoplasia and extracolonic malignancy. Arch. Surg. 139:760-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hakenbeck, R., A. König, I. Kern, M. van der Linden, W. Keck, D. Billot-Klein, R. Legrand, B. Schoot, and L. Gutmann. 1998. Acquisition of five high-Mr penicillin-binding protein variants during transfer of high-level β-lactam resistance from Streptococcus mitis to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 180:1831-1840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hamada, S., and H. D. Slade. 1980. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Rev. 44:331-384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Handley, P., A. Coykendall, D. Beighton, J. M. Hardie, and R. A. Whiley. 1991. Streptococcus crista sp. nov., a viridans streptococcus with tufted fibrils, isolated from the human oral cavity and throat. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 41:543-547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Håvarstein, L. S., R. Hakenbeck, and P. Gaustad. 1997. Natural competence in the genus Streptococcus: evidence that streptococci can change pherotype by interspecies recombinational exchanges. J. Bacteriol. 179:6589-6594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Heraief, E., M. P. Glauser, and L. R. Freedman. 1982. Natural history of aortic valve endocarditis in rats. Infect. Immun. 37:127-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hillman, J. D., S. W. Andrews, S. Palner, and P. Strashenko. 1989. Adaptative changes in a strain of Streptococcus mutans during colonization of the human oral cavity. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2:231-239. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hinnebusch, C. J., D. M. Nikolai, and D. A. Bruckner. 1991. Comparison of API Rapid Strep, Baxter MicroScan Rapid Pos ID Panel, BBL Minitek Differential Identification System, IDS RapID STR System, and Vitek GPI to conventional biochemical tests for identification of viridans streptococci. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 96:459-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hoshino, T., M. Kawaguchi, N. Shimizu, N. Hoshino, T. Ooshima, and T. Fujiwara. 2004. PCR detection and identification of oral streptococci in saliva samples using gtf genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 48:195-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jacobs, J. A., H. C. Schouten, E. E. Stobberingh, and P. B. Soeters. 1995. Viridans streptococci isolated from the bloodstream. Relevance of species identification. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22:267-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kawamura, Y., X. G. Hou, F. Sultana, H. Miura, and T. Ezaki. 1995. Determination of 16S rRNA sequences of Streptococcus mitis and Streptococcus gordonii and phylogenetic relationships among members of the genus Streptococcus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45:406-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kawamura, Y., X. G. Hou, Y. Todome, F. Sultana, K. Hirose, S. E. Shu, T. Ezaki, and H. Ohkuni. 1998. Streptococcus peroris sp. nov. and Streptococcus infantis sp. nov., new members of the Streptococcus mitis group, isolated from human clinical specimens. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48:921-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kawamura, Y., R. A. Whiley, S.-E. Shu, T. Ezaki, and J. M. Hardie. 1999. Genetic approaches to the identification of the mitis group with the genus Streptococcus. Microbiology 145:2605-2613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kikuchi, K., T. Enari, K. Totsuka, and K. Shimizu. 1995. Comparison of phenotypic characteristics, DNA-DNA hybridization results, and results with a commercial rapid biochemical and enzymatic reaction system for identification of viridans group streptococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:1215-1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kilian, M. 2005. Streptococcus and Lactobacillus, p. 833-881. In P. Borriello, P. R. Murray, and G. Funke (ed.), Topley and Wilson's microbiology and microbial infections. Hodder Arnold Health Sciences, New York, N.Y.
- 35.Kilian, M., L. Mikkelsen, and J. Henrichsen. 1989. Taxonomic studies of viridans streptococci: description of Streptococcus gordonii sp. nov. and emended descriptions of Streptococcus sanguis (White and Niven 1946), Streptococcus oralis (Bridge and Sneath 1982), and Streptococcus mitis (Andrewes and Horder 1906). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39:471-484. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kilian, M., K. Poulsen, and U. B. S. Sørensen. Inter-species recombination and extreme intra-species diversification confuses the taxonomy of mitis group streptococci. Submitted for publication.
- 37.Kitada, K., M. Inoue, and M. Kitano. 1997. Experimental endocarditis induction and platelet aggregation by Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus constellatus and Streptococcus intermedius. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 19:25-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kumar, S., K. Tamura, and M. Nei. 2004. MEGA3: integrated software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 5:150-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lawrence, J. G. 2002. Gene transfer in bacteria: speciation without species? Theor. Popul. Biol. 61:449-460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Okwumabua, O., M. O'Connor, and E. Shull. 2003. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay specific for Streptococcus suis based on the gene encoding the glutamate dehydrogenase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 218:79-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Poyart, C., G. Quesne, S. Coulon, P. Berche, and P. Trieu-Cuot. 1998. Identification of streptococci to species level by sequencing the gene encoding the manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase. J. Clin. Microbiol. 36:41-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Poyart, C., G. Quesne, and P. Trieu-Cuot. 2002. Taxonomic dissection of the Streptococcus bovis group by analysis of manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase gene (sodA) sequences: reclassification of ‘Streptococcus infantarius subsp. coli’ as Streptococcus lutetiensis sp. nov. and of Streptococcus bovis biotype 11.2 as Streptococcus pasteurianus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52:1247-1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ruoff, K. L., S. I. Miller, C. V. Garner, M. J. Ferraro, and S. B. Calderwood. 1989. Bacteremia with Streptococcus bovis and Streptococcus salivarius: clinical correlates of more accurate identification of isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 27:305-308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ruoff, K. L., R. A. Whiley, and D. Beighton. 2003. Streptococcus, p. 405-421. In P. R. Murray, E. J. Baron, J. H. Jorgensen, M. A. Pfaller, and R. H. Yolken (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 8th ed. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
- 45.Saitou, N., and M. Nei. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4:406-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Stinson, M. W., S. Alder, and S. Kumar. 2003. Invasion and killing of human endothelial cells by viridans group streptococci. Infect. Immun. 71:2365-2372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Teng, L. J., P. R. Hsueh, S. W. Ho, and K. T. Luh. 1998. Antimicrobial susceptibility of viridans group streptococci in Taiwan with an emphasis on the high rates of resistance to penicillin and erythromycin in Streptococcus oralis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 41:621-627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Teng, L. J., P. R. Hsueh, J. C. Tsai, P. W. Chen, J. C. Hsu, H. C. Lai, C. N. Lee, and S. W. Ho. 2002. groESL sequence determination, phylogenetic analysis, and species differentiation for viridans group streptococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:3172-3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Thompson, J. D., T. J. Gibson, F. Plewniak, F. Jeanmougin, and D. G. Higgins. 1997. The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:4876-4882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Trüper, H. G., and L. De Clari. 1997. Taxonomic note: necessary correction of specific epithets formed as substantives (nouns) “in apposition.” Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47:908-909. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tsakalidou, E., E. Zoidou, B. Pot, L. Wassill, W. Ludwig, L. A. Devriese, G. Kalantzopoulos, K. H. Schleifer, and K. Kersters. 1998. Identification of streptococci from Greek Kasseri cheese and description of Streptococcus macedonicus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48:519-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Vacca-Smith, A. M., C. A. Jones, M. J. Levine, and M. W. Stinson. 1994. Glucosyltransferase mediates adhesion of Streptococcus gordonii to human endothelial cells in vitro. Infect. Immun. 62:2187-2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Vos, P., H. G. Trüper, and B. J. Tindall. 2005. Judicial Commission of the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes Xth International (IUMS) Congress of Bacteriology and Applied Microbiology. Minutes of the meetings, 28, 29, and 31 July and 1 August 2002, Paris, France. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55:525-532 [Google Scholar]
- 54.Whiley, R. A., D. Beighton, T. G. Winstanley, H. Y. Fraser, and J. M. Hardie. 1992. Streptococcus intermedius, Streptococcus constellatus, and Streptococcus anginosus (the Streptococcus milleri group): association with different body sites and clinical infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30:243-244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Willcox, M. D., H. Zhu, and K. W. Knox. 2001. Streptococcus australis sp. nov., a novel oral streptococcus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1277-1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Woo, P. C., A. M. Fung, S. K. Lau, S. S. Wong, and K. Y. Yuen. 2001. Group G beta-hemolytic streptococcal bacteremia characterized by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:3147-3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Woo, P. C., D. M. Tam, K. W. Leung, S. K. Lau, J. L. Teng, M. K. Wong, and K. Y. Yuen. 2002. Streptococcus sinensis sp. nov., a novel species isolated from a patient with infective endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:805-810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]