Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants (SCVs) are believed to account in part for the persistence of S. aureus during chronic infections. Little is understood about the gene expression profile that may explain the phenotype and distinguish SCVs from prototype S. aureus strains. In this study, DNA array transcriptional profiles of clinical SCVs isolated from the airways of cystic fibrosis patients were obtained and compared to those obtained from a laboratory-derived SCV strain (i.e., a respiratory-deficient hemB mutant) and prototype S. aureus strains. The genes commonly up-regulated in both hemB and clinical SCVs were found to be implicated in fermentation and glycolysis pathways. The well-known virulence regulator agr was not activated in SCVs, and such strains had low levels of alpha-toxin (hla) gene expression. Clinical SCVs also had a transcriptional signature of their own. Of striking interest is that many genes, most of them under the positive control of the alternate sigma factor SigB, were specifically up-regulated and differed in that way from that seen in prototype S. aureus and the hemB mutant. Since SigB influences up-regulation of adhesin type genes while indirectly down-regulating exoproteins and toxins, we evaluated the internalization and persistence of SCVs in mammalian cells. Results showed that clinical SCVs persisted much more efficiently in cells than the hemB and prototype strains and that a sigB mutant was a poor persister. Thus, it appears that the agr locus plays a minor role in the regulation of the virulon of SCVs, unlike SigB, which may have a key role in intracellular persistence.
Staphylococcus aureus is an important animal and human pathogen that causes multiple types of serious infections with high morbidity rates. It possesses multiple virulence factors that affect host defenses, permit colonization and destruction of tissues, and induce sepsis syndromes (2). The agr (accessory gene regulator) locus is one of the virulence regulators that control passage from the colonization to the invasion phase (12, 34).
However, the presence of a bacterial subpopulation constituted of small-colony variants (SCVs) is believed to account in part for the increased persistence of the pathogen during chronic or difficult-to-treat infections (1, 31, 43, 48, 50). S. aureus SCVs exhibit distinctive phenotypic characteristics on agar, like very small-sized colonies, markedly reduced hemolysin production, and the absence of pigmentation (29).
Clinical SCV isolates can be unstable, revert to the wild-type phenotype, and carry unknown mutations (30). Therefore, S. aureus hemB mutants, which are genetically defined stable mutant strains for the electron transport chain that present typical characteristics of clinical SCVs, were used by us and others for in vitro and in vivo studies (5, 13, 23, 49). Based on in vitro assays carried out with these S. aureus hemB mutants, the SCV phenotype showed an extended capacity to invade epithelial cells and to remain intracellular (13, 47, 49). These novel properties are related to the increased expression of fibronectin-binding protein adhesins and to the diminished expression of α-hemolysin, respectively (46, 47). Additionally, the hemB mutants and clinical SCVs were found to be more resistant to a number of antibiotics in vitro, for the most part to aminoglycosides (6). We also found an increased persistence of the hemB mutant in a mouse mastitis model during antibiotic therapy with the beta-lactam antibiotic cephapirin, while no resistance was observed for this mutant towards cephapirin in vitro (13). Altogether, and despite their reduced ability to colonize tissues in animal models of infection (5, 13, 23), these results show that SCVs can be more invasive, more persistent within eucaryotic cells, and less susceptible to antibiotic treatment than their non-SCV wild-type counterpart. Since they are often unstable, it is possible that a pool of intracellular S. aureus SCVs that are protected from antibiotics and host immune responses may eventually provoke the resurgence and/or the persistence of the infection.
The respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients, especially at a young age, is frequently colonized by S. aureus, which is, along with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Haemophilus influenzae, a major pathogen in this life-threatening disease (38). The presence of SCVs has been associated with the chronic form of S. aureus infection in CF patients (24, 26). The SCV phenotype is the result of an altered metabolic state and an atypical pattern of gene expression, which in turn provide a marked advantage over “normal” S. aureus strains for long-term colonization. To tackle chronic infection, a better understanding of the S. aureus SCV altered metabolic state and virulence properties is necessary. Gene expression profiling experiments will allow the identification of specific genes that are important for the survival or virulence of SCVs and will ultimately permit the identification of specific targets for therapy. Using DNA arrays and clinical S. aureus SCV isolates from CF patients, expression profiling experiments were carried out in the present study. A wild-type prototype strain and its isogenic hemB mutant were also included for comparison. As expected, we found that particular genes are differentially expressed in SCVs compared to the normal phenotype. Evidence showing that the Agr system is not activated in SCVs and that the alternative sigma factor SigB greatly influences the virulon of clinical SCVs is presented. This SigB activity appears to be of crucial importance for the intracellular persistence of S. aureus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains.
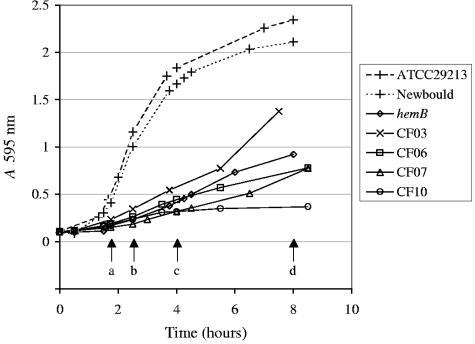
Staphylococcus aureus Newbould 305 (ATCC 29740) and its isogenic hemB mutant (13) were used as a representative control pair for the wild-type (normal prototype) and SCV phenotypes, respectively. An isogenic mutant of S. aureus Newbould, in which the sigB gene was disrupted by homologous recombination, was also constructed by using the temperature-sensitive pBT2 plasmid and a strategy previously described (42), which was similar to that employed for the construction of the hemB mutant (13). In addition to strain Newbould, another S. aureus prototype strain (ATCC 29213) was also used. Clinical S. aureus isolates from CF patients were isolated from sputum and throat swab samples. Four clinical SCVs (CF03, CF06, CF07, and CF10) were found in samples from 17 CF patients collected in the years 2003 and 2004 at the CF clinic of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke (Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada). Clinical SCV isolates were found based on their phenotypic traits: hemolysis, gentamicin resistance, and colony morphology on Mueller-Hinton agar or tryptic soy agar (TSA) with 5% sheep blood (Table 1). Clinical SCVs were primarily discriminated by their slow-growth phenotype (Fig. 1). Care was also taken to ensure that no reversion of SCVs to the normal phenotype occurred throughout the study by limiting the number of passages on agar to one, by visual inspection of colonies, and by surveying the growth rate of cultures in broth. Auxotrophy of SCVs for hemin (1 μg/ml), menadione (1 μg/ml), and thymidine (100 μg/ml), alone or in combination, was evaluated by comparison of colony sizes obtained on supplemented and unsupplemented TSA plates.
TABLE 1.
Characteristics of prototype and SCV strains used in this studya
| Characteristic | Strain
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 29213 | Newbould | hemB | CF03 | CF06 | CF07 | CF10 | |
| Colony size | Large | Large | Small | Small | Small | Small | Small |
| Pigmentation | Yellow | Beige | White | White | Beige | White | White |
| β-Hemolysis | + | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| PFGE pattern | A | D | D′ | NT | A | B | A |
| Agr type | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MIC (μg/ml) | |||||||
| Gentamicin | 0.5 | 0.25-0.5 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | >8 |
| SMX/TMPa | 0.06/1.2 | 0.06/1.2 | 0.5/9.5 | 0.06/1.2 | 0.12/2.4 | 0.25/4.8 | 0.5/9.5 |
| TMP | ND | 2 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 8 |
| Erythromycin | 0.5 | 0.25 | >16 | >4 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Oxacillin | 0.12-0.25 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 1 |
| Rifampicin | 0.008-0.015 | 0.008-0.015 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.03 | 0.015 | 0.06 |
| Vancomycin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Lysostaphin | ND | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
SMX/TMP, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (1/19); ND, not determined; NT, not typeable. A + or − indicates the presence or absence, respectively, of β-hemolysis.
FIG. 1.
Growth characteristics of prototype and SCV strains. The time points a to d were specifically studied. Time points a (1 h 45 min) and c (4 h), and b (2 h 30 min) and d (8 h), were defined as the representatives of the early and late exponential phases of growth for the prototype and SCV strains, respectively.
Agr typing.
Genomic DNA was extracted from each strain with the GenElute bacterial DNA kit (Sigma-Aldrich, Oakville, Canada). Multiplex PCR of the agr locus were conducted as described elsewhere previously (28).
Antibiotic MIC.
MICs of antibiotics for S. aureus were evaluated by a broth microdilution method as recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (formerly NCCLS) (33), except that the incubation period was extended to 48 h to allow SCVs to reach maximal growth.
PFGE.
All Staphylococcus aureus strains and isolates used in this study were subtyped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) separation of SmaI-digested genomic DNA. Briefly, once the cells were cast in 1.3% Incert agarose (Cambrex, Rockland, ME) plugs, the cell wall was digested with a lysis solution (50 mg/ml lysozyme, 5 U/ml lysostaphin, 20 μg/ml RNase, 6 mM Tris, pH 6.0, 1 M NaCl, 100 mM EDTA, pH 7.6, 0.5% Brij 35, 0.2% sodium desoxycholate acid, 0.5% N-lauryl sarcosine) for 4 h at 37°C. The plugs were then treated with proteinase K (500 mM EDTA, pH 7.6, 0.1% N-lauryl sarcosine, 100 μg/ml proteinase K) for 16 h at 50°C. The genomic DNA was digested for 3 h with SmaI (New England Biolabs, Pickering, Ontario, Canada) at 25°C. The plugs were electrophoresed on a Rotaphor instrument (Biometra, Goettingen, Germany) at 155 V in a 1% agarose gel (Pulse Field Certified Agarose; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) in 0.5× Tris-borate-EDTA buffer at 16°C. Pulsing was set to a ramp time from 60 to 10 s (logarithmic) for 24 h and a reorientation of 120° to 110° (linear).
Preparation of RNA for DNA array experiments.
Cultures grown overnight were used to inoculate brain heart infusion broth at an A595 of 0.1. The cells were grown aerobically at 35°C with shaking and were harvested during the early and late exponential phases of growth for RNA preparation. The prototype and SCV cells were collected at equivalent growth phases (Fig. 1). For the prototype strains (Newbould and ATCC 29213), the early exponential phase was achieved at an A595 of 0.4 (1 h 45 min postinoculation), whereas the late exponential phase was reached at an A595 of 1.8 (4 h postinoculation). For hemB and clinical SCVs, the early exponential phase was achieved at an A595 of 0.2 to 0.25 (2 h 30 min postinoculation), and the late exponential phase was reached after 8 h (A595, 1.0) as evaluated and generalized from the shape of growth curves shown in Fig. 1. Cells were treated with RNAprotect (QIAGEN, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada), and the RNA was extracted from the pellets after bacterial lysis with lysostaphin (200 μg/ml) (1 h at room temperature) using the RNeasy Mini kit and the RNase-free DNase set (QIAGEN).
DNA array probe synthesis.
Fluorescent probes were generated through an aminoallyl cDNA labeling procedure. Briefly, 2.5 μg of total RNA was mixed with 5 μg of random hexamers and 1 μl of the appropriate RNA spike from the Lucidea Universal Scorecard (Amersham Biosciences, Baie D'Urfι, Quebec, Canada). This mixture was denatured at 70°C for 10 min. Reverse transcription was started by adding reverse transcriptase buffer (Invitrogen, Burlington, Canada), 10 mM dithiothreitol, deoxynucleotide triphosphate mix [final concentration, 500 μM dATP, dCTP, and dGTP; 300 μM dTTP; and 200 μM 5-(3-aminoallyl)-2-dUTP (aadUTP) (Sigma-Aldrich)], and 400 U of Superscript II reverse transcriptase to the RNA preparation, and the reaction was allowed to occur for 2 h at 42°C. The RNA was hydrolyzed after transcription by the addition of 200 mM NaOH and 100 mM EDTA at 65°C for 15 min. The reaction mixture was neutralized with 333 μM HEPES, pH 7.5. The cDNAs were purified before fluorescent labeling through three passages onto a Microcon YM30 (Millipore, Nepean, Ontario, Canada). The resulting aadUTP cDNA was coupled separately to N-hydroxysuccinimide-Cy3 (test strain, hemB and clinical SCVs) and N-hydroxysuccinimide-Cy5 (prototype strain, Newbould or ATCC 29213) (Fluorolink Cy3/5 monoreactive packs; Amersham Biosciences) in the presence of 100 μM NaHCO3, pH 9.0, for 1 h at room temperature. The reaction mixtures were quenched with 1.25 μM hydroxylamine for 15 min at room temperature. The fluorescent cDNAs were purified by using a QIAquick PCR purification kit (QIAGEN), giving particular attention to three washing steps with PE buffer before elution in EB buffer (provided with the kit). The probes were dosed separately at 550 nm (Cy3), 650 nm (Cy5), and 260 nm to determine the percentage of incorporation of the dyes and the amount of cDNA produced. Thereafter, equal amounts of the probes were combined and dried down by using an Eppendorf Vacufuge.
DNA array printing.
Our microarrays contained a selection of 460 genes implicated in different cellular processes such as virulence (biofilm genes, adhesins, toxins, and homologs of such genes), secretion, general stress responses, sensory/regulator systems, antibiotic resistance, iron transport, and general biosynthesis. Genes were first amplified by PCR using Sigma (Oakville, Ontario, Canada) Genosys primers designed for the methicillin-resistant S. aureus COL strain and other primers designed using Primer 3 software. PCR products were then purified (QIAquick PCR purification kit; QIAGEN), precipitated, suspended at a concentration of 150 ng/μl in 50% dimethyl sulfoxide, and printed in triplicates on GAPS II slides (Corning, Inc., Corning, NY) by using the SpotBot personal microarrayer (TeleChem International, Sunnyvale, CA) or with the help of the Microarray printing platform of the Biotechnology Research Institute of Montreal (Montreal, Quebec, Canada). Control spots were obtained from the Lucidea Universal Scorecard (Amersham Biosciences).
DNA array hybridization and analysis.
The probes (200 pmol of each fluorophore incorporated at a rate of 8%) were suspended in 20 μl of hybridization buffer (5× SSC [1× SSC is 0.15 M NaCl plus 0.015 M sodium citrate], 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 25% formamide, 100 μg/ml mouse COT1 DNA [Invitrogen]). The prehybridization, hybridization, and washing steps were done as prescribed for Corning GAPS II slides. Hybridization signals for each spot were quantified with the ScanArrayExpress microarray scanner and ScanArrayExpress software V 2.2.0.0022 (Perkin-Elmer, Wellesley, MA). The intensity of each dye was adjusted using the signal of the control spots from Lucidea Universal Scorecard, and data were submitted to Lowess normalization. Only signals showing an intensity that was three times above the background were analyzed. Ratios of Cy3 (test strain) to Cy5 (prototype strain) for three separate experiments were obtained and averaged. Only genes with expression ratios showing a ≥2-fold increase (or decrease, as indicated by a minus sign) for three out of four clinical SCV strains and a P value of <0.05 for at least one clinical SCV were considered.
Real-time PCR.
Cells were collected at 1 h 45 min, 2 h 30 min, 4 h, and 8 h (Fig. 1). RNA was extracted as mentioned above but with a second passage on the RNeasy Mini kit and the RNase-free DNase set (QIAGEN) to avoid any genomic DNA contamination of the samples. One microgram of total RNA was reverse transcribed with 0.5 mM deoxynucleotide triphosphate, 50 ng random hexamers, and 200 U of Invitrogen Superscript II reverse transcriptase according to the manufacturer's recommendations. RNA was denatured, and the cDNAs were purified with the QIAquick PCR purification kit (QIAGEN). One microliter of the cDNA preparation was amplified on the Stratagene MX3000P Real-Time PCR instrument with the Full Velocity SYBR Green QPCR Master mix (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) and 100 nM of the primers listed in Table 2. Reaction mixtures were denatured for 10 min at 95°C, followed by 35 cycles of 30 s at 95°C, 1 min at 60°C, and 1 min at 72°C. A dissociation curve was done to insure the specificity of the reaction. The kinetic of expression of each gene was calculated for each strain by using the cycle threshold (CT) of the 1-h 45-min time point as the calibrator (n-fold expression = 2−ΔCT, where ΔCT represents the difference between the CT of each time and the CT at 1 h 45 min). Also, the difference in real-time PCR between the test strain and prototype strain Newbould or ATCC 29213 was determined for the early and late exponential phases (n-fold expression = 2−ΔCT, where ΔCT represents the difference between the CT of each strain and the CT of the prototype strain).
TABLE 2.
Primers used for real-time PCR experiments
| ORFa (COL) | Gene | Description | Primer | Position in genome | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 672 | sarA | Staphylococcal accessory regulator A | 672-RT-FWD | 700164 | CAAACAACCACAAGTTGTTAAAGC |
| 672-RT-REV | 699992 | TGTTTGCTTCAGTGATTCGTTT | |||
| 723 | Antigenic surface protein, SsaA like | 723-RT-FWD | 748476 | GCTGGTTCAGCATCATCTCA | |
| 723-RT-REV | 748308 | TTGTACCACCTGATCCACCA | |||
| 787 | Conserved protein, Csb29 | 787-RT-FWD | 810624 | TGTTCAAAACGCTGAAAACG | |
| 787-RT-REV | 810474 | GGTCGTTTCGCCAGAATATG | |||
| 1173 | hla | α-Hemolysin | 1173-RT-FWD | 1180976 | AATGAATCCTGTCGCTAATGCCGC |
| 1173-RT-REV | 1180708 | CTGAAGGCCAGGCTAAACCACTTT | |||
| 2022 | hld | δ-Hemolysin, RNA III | 2022-RT-FWD | 2082870 | TAATTAAGGAAGGAGTGATTTCAATG |
| 2022-RT-REV | 2082771 | TTTTTAGTGAATTTGTTCACTGTGTC | |||
| 2088 | Exotoxin, SceD like | 2088-RT-FWD | 2152102 | AACGTGAATCAGGTGGCAAT | |
| 2088-RT-REV | 2151938 | ATTTTACTGCTGCGGCATCT | |||
| 2173 | asp23 | Alkaline shock protein 23 | 2173-RT-FWD | 2255791 | TCGCTGCACGTGAAGTTAAA |
| 2173-RT-REV | 2255660 | CAGCAGCTTGTTTTTCACCA | |||
| 2580 | Hypothetical protein | 2580-RT-FWD | 2644065 | GGGCAGAGTTGATTCATTGG | |
| 2580-RT-REV | 2643876 | TCATGACGTTCACCTCTTCG |
ORF, open reading frame.
Cell internalization and persistence studies.
Mammalian cells (bovine epithelial MAC-T cells) (22) were grown in complete medium composed of Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10% inactivated fetal bovine serum, antibiotics, hydrocortisone (5 μg/ml), and insulin (5 μg/ml). Cells were incubated in humidified air with 5% CO2 at 37°C and split twice weekly 1:5 by trypsinization. Twenty-four hours before the invasion assay, MAC-T cells were seeded in 24-well culture plates (1.5 × 105 cells/well) in complete medium. The complete medium was replaced by the invasion medium (complete medium with 1% serum and without antibiotic) 16 h before the invasion assay. For invasion, bacterial inocula were prepared by suspending (in cold phosphate-buffered saline) bacteria grown overnight on TSA plates containing 5% sheep blood. Bacterial cells were washed two times in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline and suspended in the invasion medium supplemented with 0.5% bovine serum albumin to obtain a multiplicity of infection of 1 to 10. The invasion assay was carried out as follows. Confluent MAC-T cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were washed two times with Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS), and bacteria were added in a final volume of 500 μl. Invasion was allowed for 90 min (5% CO2, 37°C), and the wells were then emptied and washed with HBSS. One milliliter of a lysostaphin solution (10 μg/ml in invasion medium) was added to kill extracellular bacteria (13), and the 24-well plates were further incubated in the presence of lysostaphin for a total of 24 h. Table 1 shows that the strains used in this study had similar susceptibilities to lysostaphin. Following three washes with HBSS, cells were detached with 100 μl of trypsin and lysed for 10 min by the addition of 900 μl of sterile water containing 0.05% Triton X-100. The cell lysates were serially diluted 10-fold and plated on agar for CFU determination. Invasion and persistence were evaluated as the relative percentage of the initial inoculum found within cells for each strain and compared to that obtained for S. aureus Newbould to which an arbitrary value of 100% was attributed. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way analysis of variance followed by the Dunnett multiple-comparisons test.
RESULTS
Four SCVs were found in 17 CF patient isolates collected during the years 2003 and 2004 (i.e., 23%, as reported previously by others [39]). The phenotypic characteristics of the strains used in this study are summarized in Table 1. Typical of the SCV phenotype, hemB and strains isolated from CF patients were small-sized colonies and were nonhemolytic on blood agar plates and showed generally less pigmentation (29). Also, typical of respiratory-deficient mutants, the SCVs of this study showed an elevated MIC of gentamicin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic that needs the integrity of the electrochemical potential of the bacterial membrane for penetration and optimal activity (14). Accordingly, we found that supplemental hemin or menadione reverted the small-size-colony phenotype for strains hemB or CF03 and CF07, respectively (data not shown). None of the SCVs were complemented by thymidine.
Before we proceeded to the full-scale transcriptional profile analysis of SCV strains with DNA arrays, we validated the choice of the comparator strain Newbould. Strain Newbould was chosen because we already had constructed its isogenic hemB mutant, which behaved as a typical SCV (13). The Newbould-hemB pair would therefore serve as a good reference for data collected from clinical SCVs isolated from CF patients. Also, Newbould typically behaves like a virulent prototype strain of S. aureus. Typically, in prototype S. aureus strains grown to the exponential phase in vitro, the agr locus is induced through a two-component, quorum-sensing system that controls the expression of RNA III (the transcript of hld, δ-hemolysin), a regulatory RNA that promotes the expression of several exotoxins (e.g., α-hemolysin [hla]) and proteolytic enzymes, while it negatively affects the expression of cell surface proteins involved in colonization (e.g., fibrinogen-binding proteins [fnbA] and protein A [spa]) (9). Thus, by using a low-density array with representative genes of known transcriptional modulation, we demonstrated that the transcriptional profile of hemB was practically identical when this SCV was compared to either the prototype strain Newbould or S. aureus ATCC 29213 (Table 3). Interestingly, Table 3 indicates that, compared to prototype strains, the Agr system and SigB were not active in hemB as deduced from the relative level of transcripts detected for hld (change of −5- to −8-fold versus prototype strains), fnbA (+8- to +10-fold), and asp23 (about −4.5-fold versus prototype strains), the latter being a known indicator of SigB activity (9). Therefore, in the subsequent DNA array analyses with clinical SCVs, we paid specific attention to the Agr system and SigB activity (see Table 4 to Table 7).
TABLE 3.
Expression ratios for selected genes as evaluated by DNA arrays for SCV strain hemB compared to that obtained for the prototype strains ATCC 29213 and Newbould
| ORF (COL) | Gene | Class | Description | Known modulation | Reference | Fold changea
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hemB/ ATCC 29213 | hemB/ Newbould | ||||||
| 222 | ldh | Biosynthesis/metabolism | l-Lactate dehydrogenase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 100.0 | 52.3 |
| 660 | adh | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Alcohol dehydrogenase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 50.0 | 30.9 |
| 205 | pflA | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Formate-lyase-activating enzyme, putative | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 37.5 | 25.5 |
| 220 | hmp | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Flavohemoprotein | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 23.1 | 27.5 |
| 2657 | arcA | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Arginine deiminase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 17.6 | 30.9 |
| 2656 | arcB | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Aspartate/ornithine carbamoyltransferase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 12.0 | 15.3 |
| 839 | pgk | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Phosphoglycerate kinase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 2.6 | 2.2 |
| 840 | tpiA | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Triosephosphate isomerase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| 838 | gap | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 1.9 | 1.3 |
| 842 | eno | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Enolase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 1.7 | 1.5 |
| 2117 | fba | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, class II | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| 1745 | pyk | Biosynthesis/metabolism | Pyruvate kinase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| 2022 | hld | Virulence | δ-Hemolysin, RNA III | Up-regulated by Agr | 9 | −8.0 | −5.3 |
| 2511 | fnbA | Virulence | Fibronectin-binding protein A | Down-regulated by Agr | 9 | 8.6 | 10.9 |
| 2563 | clpC | Stress-associated gene | SigA-dependent stress genes | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 6.8 | 3.7 |
| 2173 | asp23 | Stress-associated gene | Alkaline shock protein 23 | Up-regulated by sigB | 9 | −4.6 | −4.4 |
Expression ratios (hemB/indicated prototype strain, both strains in the early exponential phase of growth as shown in Fig. 1). A decrease is indicated by a minus sign.
TABLE 4.
Expression ratios of genes commonly up-regulated in hemB and at least three clinical SCVs
| ORF (COL) | Gene | Description | Known modulation and characteristic(s) | Reference(s) | Fold changea
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hemB | CF03 | CF06 | CF07 | CF10 | |||||
| Virulence-associated genes | |||||||||
| 2511 | fnbA | Fibronectin-binding protein A | Down-regulated by Agr; Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 10.9 | 2.0 | 8.3 | 3.1 | 1.2 |
| 2676 | Proteins with cell-sorting signals | 3.2 | 6.6 | 1.7 | 5.6 | 4.0 | |||
| Biosynthesis/transport/metabolism-associated genes | |||||||||
| 205 | pflA | Formate-lyase-activating enzyme | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 25.5 | 2.3 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 2.0 |
| 220 | hml | Flavohemoprotein | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 27.5 | 3.8 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 2.5 |
| 222 | ldh | l-Lactate dehydrogenase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 52.3 | 131.0 | 63.0 | 79.4 | 72.1 |
| 301 | Formate/nitrite transporter protein | Down-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | 12.8 | 21.8 | 40.5 | 32.9 | 36.8 | |
| 494 | nuoF | NADH dehydrogenase I, F subunit | 7.4 | 7.4 | 6.0 | 7.8 | 9.0 | ||
| 660 | adh | Alcohol dehydrogenase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 30.9 | 7.8 | 4.3 | 5.6 | 7.6 |
| 839 | pgk | Phosphoglycerate kinase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics | 27 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| 841 | pgm | Phosphoglycerate mutase | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.8 | ||
| 1932 | Transglycosylase domain protein | 5.4 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 5.2 | |||
| 1984 | aldA | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | 2.7 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 4.5 | ||
| 2363 | l-Lactate permease | Down-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | 10.3 | 17.3 | 17.4 | 18.6 | 11.2 | |
| 2369 | Disulfide reductase | 3.1 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 3.5 | |||
| 2398 | nirB | Nitrite reductase, large subunit | 5.2 | 6.7 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 3.3 | ||
| 2399 | nirR | Transcriptional regulator | Down-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 3.7 |
| 2656 | arcB | Aspartate/ornithine carbamoyltransferase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 27 | 15.3 | 11.1 | 17.9 | 20.7 | 16.9 |
| 2657 | arcA | Arginine deiminase | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 27 | 30.9 | 23.6 | 66.9 | 39.7 | 50.0 |
| Stress-associated genes | |||||||||
| 1368 | katA | Catalase | 2.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.5 | ||
| 1777 | htrA | Serine protease HtrA | 3.9 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 3.8 | ||
| 2385 | Heat shock protein, Hsp20 family | 2.1 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 5.3 | |||
| 2563 | clp | ATP-dependent protease | Up-regulated in hemB proteomics; up-regulated by SigB | 9, 27 | 3.7 | 6.0 | 6.6 | 1.0 | 5.3 |
Expression ratios (SCV test strain/Newbould, both strains in the early exponential phase of growth) showing a ≥2-fold increase for hemB and at least three clinical SCVs are listed.
TABLE 7.
Expression ratios of genes specifically down-regulated in at least three clinical SCVs
| ORF (COL) | Gene | Description | Known modulation and characteristics | Reference | Fold changea
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hemB | CF03 | CF06 | CF07 | CF10 | |||||
| Virulence-associated genes | |||||||||
| 478 | Exotoxin 3 | 6.6 | −3.6 | −2.3 | −6.4b | −6.2 | |||
| 1168 | fib | Fibrinogen-binding protein | 3.0 | −2.5 | −1.6 | −2.2 | −2.6 | ||
| 1173 | hla | α-Hemolysin | Up-regulated by Agr; down-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.8 | −1.6 | −2.4 | −2.2b | −4.3 |
| Biosynthesis/transport/metabolism-associated genes | |||||||||
| 688 | mntC | Manganese ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein | −1.4 | −1.8 | −2.9 | −8.1 | −2.3 | ||
| 689 | mntB | Manganese ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein | −1.5 | −1.6 | −2.5 | −6.4 | −2.1 | ||
| 1052 | menD | Carboxylate synthase | −1.2 | −2.8 | −1.8 | −5.0 | −3.1 | ||
| 1140 | isdA | Heme transport, cell wall LPXTG protein | Down-regulated in biofilm | 7 | 1.9 | −2.8 | −1.7 | −2.5 | −2.1 |
| 2166 | htsB | Heme transport ABC transporter, permease | −1.0 | −2.9 | −1.5 | −2.7 | −2.3 | ||
Expression ratios (SCV test strain/Newbould, both strains in the early exponential phase of growth) showing a ≥2-fold decrease in at least three clinical SCVs (but not hemB) are listed. A decrease is indicated by a minus sign.
Calculated with a biological duplicate, not a triplicate like the other values.
Because we compared different clinical strains of different genetic backgrounds (i.e., different Agr types and PFGE banding patterns) (Table 1), we decided to be relatively permissive in the DNA array analysis. In other words, up- and down-regulated genes that are reported in Tables 4 to 7 showed a ≥2-fold increase (or decrease, indicated by a minus sign) in at least three of the four clinical SCVs and a P value of <0.05 in at least one SCV. In this way, we hoped to capture major transcriptional trends common to all SCVs despite their genetic divergence, and that distinguished them from prototype S. aureus strains. There was no apparent correlation between the PFGE banding patterns or Agr types of strains (Table 1) and the transcriptional profiles obtained from DNA array experiments (see Tables 4 to 7). Instead, SCVs demonstrated a certain homogeneity in transcriptomes. Hence, Table 4 shows the up-regulated genes (≥2-fold) common to the hemB mutant and at least three out of four of the CF strains, whereas Table 5 shows the up-regulated genes specifically expressed by the CF strains but not by hemB. Data show that many of the overall common genes shown in Table 4 demonstrated the respiratory deficiency of the clinical SCVs by the strong up-regulation of fermentation pathways as previously reported in a proteomic analysis of a hemB mutant (27). Very interestingly, many of the specific genes up-regulated by CF strains (Table 5) were recently found to be part of the SigB regulon (9, 19) and/or up-regulated in biofilms (7). Thus, even though the agr locus is down-regulated (as seen by the decreased expression of hld and agrB) (Table 6), the transcriptomes revealed that SigB influenced the up-regulation of many virulence genes in clinical SCVs, notably the capsular biosynthesis genes, surface-associated proteins (e.g., SA0723 and ClfA), and some toxins (e.g., SA2088) (Table 5). In addition to SigB, Tables 4 to 5 also show an up-regulation of sarA, another known regulator of virulence (34). Besides, Table 7 shows genes that are specifically down-regulated in CF strains, and these data also support the noninduction of agr by showing a down-regulation of α-hemolysin (hla) in those strains.
TABLE 5.
Expression ratios of genes specifically up-regulated in at least three clinical SCVs
| ORF (COL) | Gene | Description | Known modulation and characteristic(s) | Reference(s) | Fold changea
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hemB | CF03 | CF06 | CF07 | CF10 | |||||
| Virulence-associated genes | |||||||||
| 136 | cap5A | Cap5A protein | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 9 | 1.3 | 3.7 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 39.7 |
| 140 | cap5E | Cap5E protein | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 9 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 45.4 |
| 141 | cap5F | Cap5F protein | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 9 | 1.6 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 32.9 |
| 142 | cap5G | Cap5G, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 9 | 1.3 | 4.3 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 23.2 |
| 148 | cap5M | Cap5M, galactosyltransferase | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 9 | −1.2 | 5.0 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 14.8 |
| 149 | cap5N | Cap5N, UDP-glucose-4-epimerase | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 7, 9 | −1.3 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 12.0 |
| 150 | cap5O | Cap5O, UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosaminuronate dehydrogenase | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in biofilm | 9 | −1.1 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 9.4 |
| 672 | sarA | Staphylococcal accessory regulator A | Up-regulated by SigB; important in biofilm | 7, 9 | −1.1 | 1.9 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 3.9 |
| 723 | Antigenic surface protein, SsaA like | Up-regulated early by SigB; antigenic | 9, 18 | 1.0 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 3.4 | |
| 856 | clfA | Clumping factor A | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −2.0 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 3.2 |
| 921 | Possible hemolysin | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 4.2 | |
| 2088 | Exotoxin, SceD like | Up-regulated early by SigB | 9 | 1.4 | 27.8 | 12.0 | 14.1 | 79.4 | |
| Biosynthesis/transport/metabolism-associated genes | |||||||||
| 97 | sirC | Iron compound ABC transporter, permease | −2.2 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 3.5 | 3.0 | ||
| 306 | ABC transporter, ATP-binding protein | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 4.0 | 1.4 | 6.9 | |
| 457 | Conserved protein, Csb12 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 3.5 | 2.8 | 3.7 | |
| 617 | Hexulose 6P synthase, Csb4 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.4 | 3.1 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.8 | |
| 787 | Conserved protein, Csb29 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −1.7 | 4.4 | 4.0 | 5.2 | 7.8 | |
| 1680 | csbD | Conserved protein, Csb8 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −2.3 | 2.8 | 3.2 | 2.1 | 6.8 |
| 1933 | Csb3 ThiJ/PfpI family protein | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.5 | 3.1 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.8 | |
| 2114 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, Csb24 | Up-regulated by SigB; up-regulated in SigB proteomics | 9, 19 | 1.2 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 4.1 | |
| 2136 | Conserved protein, Csb9 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −1.8 | 6.8 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 11.8 | |
| 2321 | Oxidoreductase dehydrogenase/reductase, Csb28 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.4 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 13.8 | 25.5 | |
| 2379 | Conserved protein, Csb19 | Up-regulated in SigB proteomics | 19 | −1.1b | 3.0 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 9.8 | |
| 2576 | crtN | Squalene desaturase | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −1.9 | 1.2 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 2.5 |
| 2577 | crtM | Dehydrosqualene synthase | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −2.1 | 1.6 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 4.0 |
| 2580 | Hypothetical protein | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −1.4 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 2.0b | 4.4 | |
| Stress-associated genes | |||||||||
| 541 | spoVG | Stage V sporulation protein G homolog | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | 1.0 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 5.1 |
| 620 | proP | Osmoprotectant proline transporter | Up-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 3.0 | 2.9 |
| 2173 | asp23 | Alkaline shock protein 23 | Up-regulated by SigB | 9 | −4.4 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 4.5 | 4.7 |
| Cell wall-associated genes | |||||||||
| 247 | lrgA | Holin-like LrgA, murein hydrolase | Down-regulated by SigB | 9 | −2.8 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.5 | 3.2 |
| 248 | lrgB | Holin-like LrgB, murein hydrolase | Down-regulated by SigB | 9 | −3.2 | 2.4 | 3.7 | 3.1 | 3.4 |
| 263 | lytM | Peptidoglycan hydrolase | Up-regulated early by SigB | 9 | −1.4 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 2.7 | 2.4 |
| 1062 | atl | Bifunctional autolysin | Up-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | −1.3 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 3.1 |
Expression ratios (SCV test strain/Newbould, both strains in the early exponential phase of growth) showing a twofold increase in at least three clinical SCVs (but not hemB) are listed. A decrease is indicated by a minus sign.
Calculated with a biological duplicate, not a triplicate like the other values.
TABLE 6.
Expression ratios of genes commonly down-regulated in hemB and at least three clinical SCVs
| ORF (COL) | Gene | Description | Known modulation and characteristic(s) | Reference(s) | Fold changea
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hemB | CF03 | CF06 | CF07 | CF10 | |||||
| Virulence-associated genes | |||||||||
| 209 | coa | Coagulase | Down-regulated by Agr; up-regulated by Rot | 9, 40 | −4.5 | −5.6 | −4.1 | −3.4 | −22.6 |
| 857 | Staphylocoagulase, putative | −8.4 | −13.0 | −4.9 | −13.9 | −13.9 | |||
| 860 | nuc | Thermonuclease precursor | Down-regulated by SigB | 9 | −1.7 | −2.1 | −2.0 | −3.9 | 2.3 |
| 1164 | Protein with cell wall sorting signal | −2.2 | −2.3 | −1.3 | −3.0 | −6.3 | |||
| 1357 | Thermonuclease, putative | −4.0 | −3.4 | −2.4 | −2.9 | −8.8 | |||
| 2022 | hld | δ-Hemolysin, RNA III | Up-regulated by Agr | 9 | −5.3 | −10.8 | −5.6 | −6.7 | −15.2 |
| 2023 | agrB | Accessory gene regulatory protein B | Up-regulated by Agr | 9 | −3.0 | −3.6 | −3.5 | −2.0 | −6.1 |
| 2291 | Antigenic surface protein, SsaA like | Up-regulated early by SigB; immunoreactive | 9, 18 | −2.5 | −3.6 | −2.2 | −2.8 | −8.2 | |
| Biosynthesis/transport/metabolism-associated genes | |||||||||
| 6 | gyrA | DNA gyrase, A subunit | −2.0 | −2.4b | −2.0 | −2.0 | −4.6 | ||
| 18 | purA | Adenylsuccinate synthetase | −4.8 | −6.7 | −4.6 | −5.8 | −13.0 | ||
| 159 | ABC transporter, permease | −3.4 | −2.2 | −2.0 | 1.0 | −3.1 | |||
| 1103 | pdhB | Pyruvate dehydrogenase component | −2.6 | −3.6 | −3.2 | −4.3 | −4.4 | ||
| 1371 | guaC | GMP reductase | Up-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | −6.2 | −8.7 | −6.1 | −7.9 | −16.1 |
| 1373 | Conserved protein | Up-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | −2.4 | −3.2 | −2.5 | −2.9 | −1.6 | |
| 1468 | Membrane protein | −2.1 | −2.0 | −1.8 | −2.2 | −3.2 | |||
| 1640 | Oxygen-independent coproporphyrinogen III oxidase | −2.3 | −2.5 | −1.6 | −2.1 | −4.5 | |||
| 2213 | rpoA | DNA-directed RNA polymerase, alpha subunit | −2.5 | −2.5 | −2.2 | −2.5 | −4.9 | ||
| 2242 | Xanthine/uracil permease | Up-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | −3.3 | −3.0 | −2.3 | −3.0 | −4.2 | |
| 2293 | NAD/NADP octopine/nopaline dehydrogenase, Csb22 | −3.3 | −2.4 | −1.8 | −2.2 | −2.2 | |||
| 2340 | gltS | Sodium:glutamate symporter | Up-regulated in laboratory-derived VRSA | 32 | −3.3 | −2.7 | −3.6 | −2.6 | −5.1 |
| Stress-associated genes | |||||||||
| 1637 | dnaK | DnaK protein | −2.0 | −2.1 | −2.3 | −3.3 | 1.5 | ||
| 1639 | hrcA | Heat-inducible transcription repressor | −1.8 | −2.1 | −2.7 | −3.7 | 1.5 | ||
| 2016 | groEL | SigA-dependent stress genes | −1.6 | −2.1 | −2.8 | −3.2 | 1.2 | ||
| 2437 | bcr | Bicyclomycin resistance protein | −1.7 | −2.0 | −1.7 | −2.2 | −2.0 | ||
| Cell wall-associated genes | |||||||||
| 699 | pbp4 | Penicillin-binding protein 4 | −2.5 | −1.0 | −2.3 | −2.7 | −2.5 | ||
Expression ratios (SCV test strain/Newbould, both strains in the early exponential phase of growth) showing a twofold decrease for hemB and at least three clinical SCVs are listed. A decrease is indicated by a minus sign.
Calculated with a biological duplicate, not a triplicate like the other values.
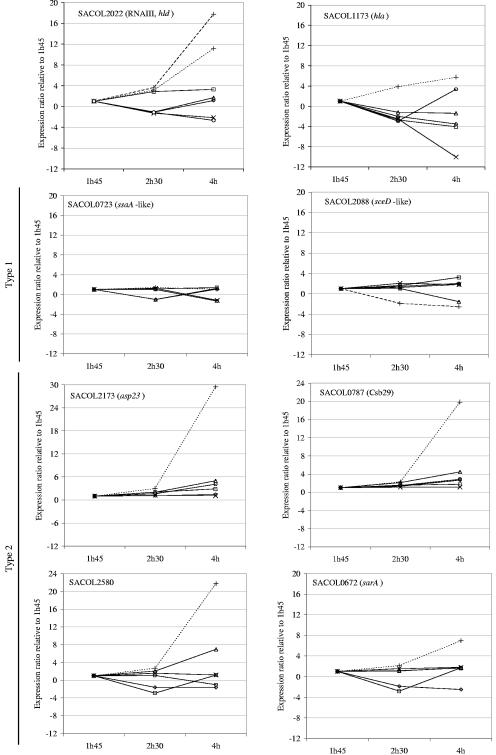
Note that transcriptional results obtained from DNA arrays (Tables 4 to 7) were used to compare RNA isolated from the early exponential phase of growth (see Materials and Methods) and that the phenomenon seen in SCVs isolated from CF patients (i.e., noninduction of Agr and increased activity of SigB) might have been transient. For this reason, and also to validate DNA array results, we have performed real-time PCR experiments to monitor the expression kinetics of key genes. Figure 2 shows that, compared to the early exponential phase (1 h 45 min postinoculation), the levels of expression of hld (RNA III) and hla associated with the Agr system increase over time for the prototype strains, whereas it is mostly stable or decreased over time for the clinical SCVs. Also, we showed that the genes SA0787, SA2580, and sarA followed the same kinetic of expression as that of a well-known marker of SigB activity (asp23), i.e., a stable or a slight up-regulation of the four genes over time for the clinical SCVs and a much stronger gene expression in the late exponential phase of growth for the prototype strain Newbould. Besides, among genes specifically up-regulated in clinical SCVs (Table 5), the expression levels of two genes (SA0723 and SA2088) were also studied by real-time PCR (Fig. 2). In this case, the genes were stably expressed over time for all strains. Consequent to that type of kinetic (arbitrarily called type 1) (Fig. 2), the latter up-regulated genes, seen specifically in clinical SCVs, remained expressed at levels superior to that observed in the prototype strain throughout the growth phases (Table 8). Indeed, Table 8 compiles and summarizes the levels of gene expression in SCVs by reporting the ratios of gene expression (SCV test strain/prototype strain) at the early and late exponential phases of growth. Table 8 also includes the reported effect of SigB on the genes of interest (9). Except for hld (RNA III), all the gene studied were part of the SigB regulon either by being up-regulated in the early or late exponential phases of growth or by being indirectly down-regulated (9). Table 8 clearly shows that Agr was not activated and that the α-hemolysin gene was not expressed in any of the SCVs at any time points, while genes known to be up-regulated by SigB late in the exponential phase of prototype strains (asp23, SA0787, SA2580, and sarA) are overexpressed in clinical SCVs (relative to the prototype strain) in the early exponential phase but not later in time. In contrast, and as mentioned above, genes that showed a type 1 kinetic in our real-time PCR tests and that were shown to be up-regulated only very early by SigB in prototype strains (9) were strongly overexpressed in all SCVs at all time points (Table 8). Finally, it was very interesting that although hemB and clinical SCVs shared many up-regulated metabolic genes (Table 4), and Agr was not activated in any of the SCVs including hemB (Table 8), SigB activity was not as strongly detected in hemB (Tables 5 and 8).
FIG. 2.
Expression pattern of selected genes over time in prototype (broken lines) and SCV (solid lines) strains as determined by real-time PCR. The kinetic of expression of each gene was calculated for each strain by using the CT of the 1-h 45-min (1h45) time point as the calibrator. Some kinetic types were assigned to SigB-regulated genes for which expression was relatively maintained through time (type 1) and those that were prominently up-regulated at a later time point in prototype S. aureus (type 2). Symbol representation is as shown in Fig. 1.
TABLE 8.
Expression ratios for selected genes as evaluated by DNA arrays and real-time PCR in the early and late exponential phases of growth for the indicated strains compared to prototype strain Newboulde
| ORF (COL) | ORF (N315) | Gene | Description | SigB regulationa | Kinetic typeb | Method | Phasec | Fold changed
|
Interpretation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hemB | CF03 | CF06 | CF07 | CF10 | |||||||||
| Agr markers | |||||||||||||
| 2022 | SAS065 | hld | δ-Hemolysin, RNA III | Not influenced | Array | Early | −5.3 | −10.8 | −5.6 | −6.7 | −15.2 | Agr not activated in any of the SCVs | |
| Real-timef | Early | −6,562.2 | −225.9 | −19.4 | −167.7 | −116.9 | Agr not activated in any of the SCVs | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | −57,052.0 | −8.5 | −288.0 | −59.3 | −661.7 | Agr not activated in any of the SCVs | ||||||
| 1173 | 1007 | hla | α-Hemolysin | Down-late | Array | Early | 1.8 | −1.6 | −2.4 | −1.9 | −4.3 | hla not up-regulated in any of the SCVs | |
| Real-time | Early | 1.2 | −2.7 | −7.8 | −6.1 | −11.2 | hla not up-regulated in any of the SCVs | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | −7.5 | −3.8 | −119.4 | −82.7 | −14.2 | hla not up-regulated in any of the SCVs | ||||||
| Known SigB markers | |||||||||||||
| 2173 | 1984 | asp23 | Alkaline shock protein 23 | Up-late | 2 | Array | Early | −4.4 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 4.6 | 4.7 | SigB activity detected early in CF strains but not in hemB |
| Real-time | Early | −2.6 | 23.0 | 29.2 | 5.1 | 32.9 | SigB activity detected early in CF strains but not in hemB | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | −34.1 | −4.2 | −1.3 | −2.3 | −2.4 | SigB activity detected later in Newbould | ||||||
| 787 | 681 | Conserved protein, Csb29 | Up-late | 2 | Array | Early | −1.7 | 4.4 | 4.0 | 5.2 | 7.8 | SigB activity detected early in CF strains but not in hemB | |
| Real-time | Early | 2.9 | 54.7 | 110.6 | 54.6 | 92.4 | SigB activity detected early in CF strains but not in hemB | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | −5.6 | 1.3 | 5.3 | 5.0 | 2.2 | SigB activity detected later in Newbould | ||||||
| CF up-regulated proteins | |||||||||||||
| 2580 | 2352 | Hypothetical protein | Up-late | 2 | Array | Early | −1.4 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 4.4 | Detected early in CF strains but not in hemB, follows SigB markers | |
| Real-time | Early | −3.6 | 4.8 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 9.5 | Detected early in CF strains but not in hemB, follows SigB markers | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | −33.2 | −25.8 | −6.7 | −7.1 | −11.5 | Detected later in Newbould, follows SigB markers | ||||||
| 723 | 620 | Antigenic surface protein, SsaA like | Up-early | 1 | Array | Early | 1.0 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 3.4 | Up-regulation of a surface protein gene in CF strains | |
| Real-time | Early | 2.7 | 5.2 | 4.3 | 6.9 | 5.3 | Up-regulation of a surface protein gene in all SCVs | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | 4.3 | 4.8 | 11.8 | 11.7 | 9.6 | Up-regulation of a surface protein gene in all SCVs | ||||||
| 2088e | 1898 | Exotoxin, SceD like | Up-early | 1 | Array | Early | 1.4 | 27.8 | 12.0 | 14.1 | 79.4 | Up-regulation of an exotoxin gene in CF strains | |
| Real-time | Early | 1.5 | 42.2 | 62.0 | 38.3 | 85.6 | Up-regulation of an exotoxin gene in CF strains | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | 6.5 | 152.7 | 1,807.8 | 377.4 | 1,458.2 | Up-regulation of an exotoxin gene in all SCVs | ||||||
| Other regulator | |||||||||||||
| 672 | 573 | sarA | Staphylococcal accessory regulator A | Up-late | 2 | Array | Early | −1.1 | 1.9 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 3.9 | Detected early in CF strains but not in hemB, follows SigB markers |
| Real-time | Early | 1.3 | 7.2 | 3.2 | 9.4 | 15.8 | Detected early in CF strains but not in hemB, follows SigB markers | ||||||
| Real-time | Late | −3.2 | −3.0 | −1.3 | −2.1 | −1.1 | Detected later in Newbould, follows SigB markers | ||||||
Genes that were shown to be up- or down-regulated by SigB in prototype strains by Bischoff et al. (9). Up-late refers to those genes typically up-regulated in the postexponential phase of growth, and Up-early refers to a smaller set of genes transiently up-regulated in the early phase of growth, i.e., 1 to 3 hours postinoculation.
The kinetic of gene expression over time refers to that exemplified in Fig. 2.
Samples were obtained in the early or late exponential phase of growth as described in the legend of Fig. 1.
Expression ratios (SCV test strain/Newbould). A decrease is indicated by a minus sign.
The expression ratios evaluated by real-time PCR for the gene SACOL 2088 were calculated for the test SCV versus prototype strain ATCC 29213 instead of Newbould.
Real-time, real-time PCR.
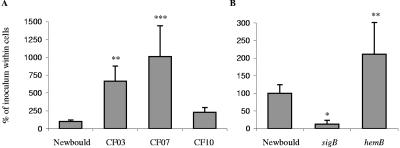
Because it is usually accepted that the Agr system controls the passage from the colonization to the invasion and tissue destruction phases (12, 34) and that SigB helps the up-regulation of adhesin type genes while indirectly down-regulating exoproteins and toxins (9), we hypothesized that SCVs, and in particular clinical SCVs, would be better equipped to adhere and to be internalized by mammalian cells. Indeed, Fig. 3 shows intracellular persistence data collected with the different test strains. These experiments measured the combined ability of bacteria to adhere to mammalian cells and to be internalized by these cells within 90 min as well as to persist inside the cells for a total period of 24 h. Figure 3A shows that clinical SCV strains CF03 and CF07 were much more habilitated to persist in mammalian cells than the prototype strain. This was also observed for strain CF10, although not at a statistically significant level (also note that strain CF06 was not tested). Because SigB was most likely involved in this phenotype, a Newbould isogenic sigB mutant was created and tested (Fig. 3B). Results show that the sigB mutant was drastically impaired in its ability to persist within mammalian cells, whereas the hemB mutant showed an elevated capacity of persistence (Fig. 3B) although not to the level of the clinical SCVs (Fig. 3A) in which we showed high SigB activity (Table 8).
FIG. 3.
Bacterial invasion and persistence within mammalian cells. S. aureus strains were incubated with MAC-T cells for 90 min to allow invasion. Cell monolayers were then washed, and lysostaphin was added to the medium to kill extracellular bacteria. Adherent eucaryotic cells were incubated for a total of 24 h in the presence of lysostaphin. Persistent intracellular bacteria were then quantified after eukaryotic cells were washed and lysed. Values on the graph indicate the relative percentages of the initial inoculum found within cells for each strain, and these were compared to that obtained for S. aureus Newbould (100%). Standard deviations and statistical significance compared to the corresponding S. aureus Newbould results are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).
DISCUSSION
With the accessibility of DNA microarray and proteomic technologies, a number of recent studies have reported the transcriptional profiles of global regulator mutants to improve our understanding of the S. aureus regulatory circuits agr and sarA (16), sigB (9, 19), and rot (40). Although these studies reported very useful lists of hundreds of genes that are part of the respective regulons (unique and overlapping), they failed to identify the virulence factors or regulatory circuits that directly contribute to specific infections. In the present study, using a subgenome DNA array, we could demonstrate the influence of some of S. aureus regulatory circuits in clinical strains isolated from CF patients.
It is generally accepted that the regulation of the S. aureus virulon, which includes an exhaustive list of adhesins, toxins, and degradative enzymes as well as appropriate metabolic functions, allows adaptation to multiple environments during infection and that different infection types require different virulence factors. This is supported by the finding that experimental approaches like signature-tagged mutagenesis (15) and size marker identification technology (8) identified a wide variety of infection type-specific essential genes in S. aureus. Interestingly, there are more and more examples of infections in which the action of the agr locus seems unimportant or specifically suppressed. For example, agr mutants were found to have a competitive advantage over agr+ in abscesses or wounds but not in systemic infections (41). Also in agreement with the present work were the observations that the agr transcript was absent in sputum from CF patients (21) and, just recently, that the Agr quorum-sensing system failed to be activated in thymidine-dependent SCVs isolated from CF patients subjected to long-term therapy with the antibiotic combination trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (25). We have shown here not only that the Agr system is not activated in SCVs but also that the alternative sigma factor SigB is importantly responsible for the expression of a large part of the virulon and consequently the phenotypic properties of clinical SCVs isolated from CF patients.
The role of SigB was demonstrated in biofilm formation on medical devices (4, 7, 37), and sigB or rsbU (positive regulator of sigB) mutants have altered regulatory roles of sarA and agr in the expression of several virulence factors (10, 11, 20). Delineation of regulatory circuits involved in S. aureus virulence is difficult. Regulators such as agr, sar, and sae combine both activation and repression. Other regulators include sarH1 (44), srrAB (staphylococcal respiratory response) (35), rot (40), the not-entirely-elucidated L2 ribosomal protein-derived RAP-TRAP quorum-sensing system (12), and the interaction of sigma factors with different regulatory loci and promoters (9). The interplay of these regulators is therefore not completely understood. In fact, Novick (34) previously elaborated a hypothetical “black box” model of the regulation of the S. aureus virulon, in which the transcriptional regulators are linked to environmental signals through several unknown black boxes. Besides agr that is stimulated by quorum sensing, an environmental signal like low oxygen pressure has been found to activate the two-component sensor regulator system srrAB, which in turn down-regulates agr (35). Other signals known to modulate virulence gene expression include NaCl, sucrose, magnesium, temperature, and CO2. Since we have determined that SCVs had distinctive transcriptomes in studies performed in vitro, it is tempting to speculate that part of the clinical SCV phenotype arose from mutations in some regulatory circuits allowing S. aureus to survive and persist in CF patient lungs. For example, allowing expression of a capsular material that protects against phagocytosis (39, 45) would certainly help the persistence of S. aureus in the airways of patients. We showed evidence that the capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis genes were fully expressed in clinical SCVs grown in vitro (Table 5), similarly to that reported for bacteria found in biofilms (7). It is also possible that the respiratory deficiency, for example, consequent to a mutation in heme biosynthesis genes like in our hemB mutant, is sufficient to restrict the quorum-sensing activation of the Agr system because of a low cell density and to activate the SigB regulon because of the low energy production. However, we have clearly shown that although both hemB and the clinical SCVs commonly overexpressed a series of genes indicative of respiratory deficiency (Table 4), only clinical SCVs were shown to actively express a large part of the SigB regulon (Tables 5 and 8). In fact, this finding is in contrast to that reported previously by Kahl et al. (25), who isolated SCVs that were thymidine auxotrophs and who failed to show the overexpression of asp23, an indicator of SigB activity. In that regard, the SCVs reported previously by Kahl et al. more closely resemble our hemB mutant. Further work is thus needed to determine how the SigB regulon is activated in some types of clinical SCVs and not others. One possibility for explaining the lack of detection of SigB activity in the SCVs reported previously by Kahl et al. is the kinetic of gene expression over time. Indeed, we have shown that SigB activity is strong and evident for our clinical SCVs in the early exponential phase of growth and that this distinction is attenuated over time compared to prototype strains in which SigB is active in the late exponential phase of growth (Fig. 2 and Table 8). Interestingly, this is only true for SigB-regulated genes that were shown to be up-regulated in the late exponential phase of growth (9), i.e., our type 2 kinetic, whereas genes that were shown to be up-regulated by SigB in the early phase of growth and following a type 1 kinetic (e.g., SA0723 and SA2088) were shown to be stably overexpressed over time in our SCVs compared to those found in prototype strains (Fig. 2 and Table 8).
One important consequence of the SigB activity appears to be the up-regulation of a multitude of surface-expressed proteins and adhesins and the down-regulation of a variety of exotoxins (9). Hence, our clinical SCVs might indeed be better equipped to adhere to eukaryotic cells (through a variety of adhesins), to be internalized more efficiently, and to persist more within cells than S. aureus prototype strains due to the lack of production of certain exotoxins. Indeed, a link between the presence of S. aureus SCVs and persistent and recurring infections, especially in cases of human osteomyelitis and pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis, has been proposed (36, 50). We have also demonstrated the ability of a hemB mutant to persist more than its isogenic counterpart under antibiotic pressure in vivo (13). It has been suggested that the increased intracellular persistence of SCVs is probably a consequence of the lowered amount of alpha-toxin (hla) produced (3, 46), while higher invasiveness is the result of increased production of fibronectin-binding proteins (17, 47). Here, we showed that the hla transcript was indeed remarkably diminished in SCVs and that genes coding for a variety of known adhesins and cell surface proteins were expressed in clinical SCVs (e.g., fnbA, clfA, SA0723, etc.). Accordingly, we have also shown that SCVs persist more within eukaryotic cells and that clinical SCVs that showed high SigB activity were even more efficient in this way than hemB or the S. aureus prototype strain (Fig. 3). Moreover, we have shown that a sigB mutant of strain Newbould was drastically altered in its ability to persist within mammalian cells. This was also in agreement with the increased hemolytic activity of the sigB mutant observed on blood agar plate (data not shown). However, in the present study, we were not able to really distinguish if SCV strains adhered more to eukaryotic cells or if the internalization process was more efficient than that of prototype strains, since we have only measured the overall persistence of S. aureus within intact cells. The role of SigB in each of the steps of this cellular process will have to be further investigated with, for example, a sigB mutant created in a SCV background. Besides, the role in infection and the consequence of the overexpression of the SceD-like exotoxin gene in all SCVs tested (particularly in strains CF06 and CF10) remain to be determined. It is possible that the expression of this exotoxin diminishes the relative ability of CF10 to persist within cells compared to CF03 and CF07, which seemed to express this gene much less than that observed for strain CF10 in the late exponential phase of growth (Table 8).
In conclusion, we have shown that the Agr system was not activated in clinical SCVs and that the alternative sigma factor SigB may contribute to the overall phenotype of SCVs by up-regulating a large part of the S. aureus virulon. Of specific interest are some SigB-targeted genes that remain expressed at levels superior to that observed in the prototype strain throughout the growth phases. These genes may play a role in the persistence of SCVs in CF patients and patients with other types of chronic infections and represent interesting targets for therapeutic intervention.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant MOP-57701 to F.M. from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research.
REFERENCES
- 1.Abele-Horn, M., B. Schupfner, P. Emmerling, H. Waldner, and H. Goring. 2000. Persistent wound infection after herniotomy associated with small colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Infection 28:53-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Archer, G. L. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus: a well-armed pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:1179-1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Balwit, J. M., P. van Langevelde, J. M. Vann, and R. A. Proctor. 1994. Gentamicin-resistant menadione and hemin auxotrophic Staphylococcus aureus persist within cultured endothelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 170:1033-1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bateman, B. T., N. P. Donegan, T. M. Jarry, M. Palma, and A. L. Cheung. 2001. Evaluation of a tetracycline-inducible promoter in Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo and its application in demonstrating the role of sigB in microcolony formation. Infect. Immun. 69:7851-7857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bates, D. M., C. von Eiff, P. J. McNamara, G. Peters, M. R. Yeaman, S. A. Bayer, and R. A. Proctor. 2003. Staphylococcus aureus menD and hemB mutants are as infective as the parent strains, but the menadione biosynthetic mutant persists within the kidney. J. Infect. Dis. 187:1654-1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Baumert, N., C. von Eiff, F. Schaaff, G. Peters, R. A. Proctor, and H. G. Sahl. 2002. Physiology and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants. Microb. Drug Resist. 8:253-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Beenken, K. E., P. M. Dunman, F. McAleese, D. Macapagal, E. Murphy, S. J. Projan, J. S. Blevins, and M. S. Smeltzer. 2004. Global gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 186:4665-4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Benton, B. M., J. P. Zhang, S. Bond, C. Pope, T. Christina, L. Lee, K. M. Winterberg, M. B. Schmid, and J. M. Buysse. 2004. Large-scale identification of genes required for full virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 186:8478-8489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bischoff, M., P. Dunman, J. Kormanec, D. Macapagal, E. W. Mounts, B. Berger-Bachi, and S. Projan. 2004. Microarray-based analysis of the Staphylococcus aureus σB regulon. J. Bacteriol. 186:2085-2099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bischoff, M., J. M. Entenza, and P. Giachino. 2001. Influence of a functional sigB operon on the global regulators sar and agr in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 183:5171-5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Blevins, J. S., K. E. Beenken, M. O. Elasri, B. K. Hurlburt, and M. S. Smeltzer. 2002. Strain-dependent differences in the regulatory roles of sarA and agr in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 70:470-480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bronner, S., H. Monteil, and G. Prévost. 2004. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus: complexity and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 28:183-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brouillette, E., A. Martinez, B. J. Boyll, N. E. Allen, and F. Malouin. 2004. Persistence of a Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variant under antibiotic pressure in vivo. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 41:35-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bryan, L. E., and S. Kwan. 1983. Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 23:835-845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Coulter, S. N., W. R. Schwan, E. Y. Ng, M. H. Langhorne, H. D. Ritchie, S. Westbrock-Wadman, W. O. Hufnagle, K. R. Folger, A. S. Bayer, and C. K. Stover. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus genetic loci impacting growth and survival in multiple infection environments. Mol. Microbiol. 30:393-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dunman, P. M., E. Murphy, S. Haney, D. Palacios, G. Gucker-Kellogg, S. Wu, E. L. Brown, R. J. Zagursky, D. Shlaes, and S. J. Projan. 2001. Transcription profiling-based identification of Staphylococcus aureus genes regulated by the agr and/or sarA loci. J. Bacteriol. 183:7341-7353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dziewanowska, K., J. M. Patti, C. F. Deobald, K. W. Bayles, W. R. Trumble, and G. A. Bohach. 1999. Fibronectin binding protein and host cell tyrosine kinase are required for internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 67:4673-4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Etz, H., D. B. Minh, T. Henics, A. Dryla, B. Winkler, C. Triska, A. P. Boyd, J. Sollner, W. Schmidt, U. von Ahsen, M. Buschle, S. R. Gill, J. Kolonay, H. Khalak, C. M. Fraser, A. von Gabain, E. Nagy, and A. Meinke. 2002. Identification of in vivo expressed vaccine candidate antigens from Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:6573-6578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gertz, S., S. Engelmann, R. Schmid, A.-K. Ziebandt, K. Rischer, C. Scharf, J. Hacker, and M. Hecker. 2000. Characterization of the σB regulon in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 182:6983-6991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Giachino, P., S. Engelmann, and M. Bischoff. 2001. σB activity depends on RsbU in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 183:1843-1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goerke, C., S. Campana, M. G. Bayer, G. Doring, K. Botzenhart, and C. Wolz. 2000. Direct quantitative transcript analysis of the agr regulon of Staphylococcus aureus during human infection in comparison to the expression profile in vitro. Infect. Immun. 68:1304-1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huynh, H. T., G. Robitaille, and J. D. Turner. 1991. Establishment of bovine mammary epithelial cells (MAC-T): an in vitro model for bovine lactation. Exp. Cell Res. 197:191-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jonsson, I.-M., C. von Eiff, R. A. Proctor, G. Peters, C. Ryden, and A. Tarkowski. 2003. Virulence of a hemB mutant displaying the phenotype of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variant in a murine model of septic arthritis. Microb. Pathog. 34:73-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kahl, B. C., K. Becker, A. W. Friedrich, J. Clasen, B. Sinha, C. von Eiff, and G. Peters. 2003. agr-dependent bacterial interference has no impact on long-term colonization of Staphylococcus aureus during persistent airway infection of cystic fibrosis patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:5199-5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kahl, B. C., G. Belling, P. Becker, I. Chatterjee, K. Wardecki, K. Hilgert, A. L. Cheung, G. Peters, and M. Herrmann. 2005. Thymidine-dependent Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants are associated with extensive alterations in regulator and virulence gene expression profiles. Infect. Immun. 73:4119-4126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kahl, B. C., M. Herrmann, A. S. Everding, H. G. Koch, K. Becker, E. Harms, R. A. Proctor, and G. Peters. 1998. Persistent infection with small colony variant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 177:1023-1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kohler, C., C. von Eiff, G. Peters, R. A. Proctor, M. Hecker, and S. Engelmann. 2003. Physiological characterization of a heme-deficient mutant of Staphylococcus aureus by a proteomic approach. J. Bacteriol. 185:6928-6937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lina, G., F. Boutite, A. Tristan, M. Bes, J. Etienne, and F. Vandenesch. 2003. Bacterial competition for human nasal cavity colonization: role of staphylococcal agr alleles. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69:18-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Looney, W. J. 2000. Small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 57:317-322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Massey, R. C., A. Buckling, and S. J. Peacock. 2001. Phenotypic switching of antibiotic resistance circumvents permanent costs in Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Biol. 11:1810-1814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McNamara, P. J., and R. A. Proctor. 2000. S. aureus small colony variants, electron transport and persistent infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 14:117-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mongodin, E., J. Finan, M. W. Climo, A. Rosato, S. Gill, and G. L. Archer. 2003. Microarray transcription analysis of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates resistant to vancomycin. J. Bacteriol. 185:4638-4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.NCCLS. 2003. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standard M7-A6. NCCLS, Wayne, Pa.
- 34.Novick, R. P. 2003. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 48:1429-1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pragman, A. A., J. M. Yarwood, T. J. Tripp, and P. M. Schlievert. 2004. Characterization of virulence factor regulation by SrrAB, a two-component system in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 186:2430-2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Proctor, R. A., O. Vesga, M. F. Otten, S. P. Koo, M. R. Yeamen, H. G. Sahl, and A. S. Bayer. 1996. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants cause persistent and resistant infections. Chemotherapy 42:47-52.8751266 [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rachid, S., K. Ohlsen, U. Wallner, J. Hacker, M. Hecker, and W. Ziebuhr. 2000. Alternative transcription factor σB is involved in regulation of biofilm expression in a Staphylococcus aureus mucosal isolate. J. Bacteriol. 183:6824-6826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Renders, N., H. Verbrugh, and A. van Belkum. 2001. Dynamics of bacterial colonization in the respiratory tract of patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 1:29-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sadowska, B., A. Bonar, C. von Eiff, R. A. Proctor, M. Chmiela, W. Rudnicka, and B. Rozalska. 2002. Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus, isolated from airways of cystic fibrosis patients, and their small colony variants. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 32:191-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Said-Salim, B., P. M. Dunman, F. M. McAleese, D. Macapagal, E. Murphy, P. J. McNamara, S. Arvidson, T. J. Foster, S. J. Projan, and B. N. Kreiswirth. 2003. Global regulation of Staphylococcus aureus genes by Rot. J. Bacteriol. 185:610-619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schwan, W. R., M. H. Langhorne, H. D. Ritchie, and C. K. Stover. 2003. Loss of hemolysin expression in Staphylococcus aureus agr mutants correlates with selective survival during mixed infection in murine abscesses and wounds. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 38:23-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Singh, V. K., J. L. Schmidt, R. K. Jayaswal, and B. J. Wilkinson. 2003. Impact of sigB mutation on Staphylococcus aureus oxacillin and vancomycin resistance varies with parental background and method of assessment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 21:256-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Spearman, P., D. Lakey, S. Jotte, A. Chernowitz, S. Claycomb, and C. Stratton. 1996. Sternoclavicular joint septic arthritis with small-colony variant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 26:13-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tegmark, K., A. Karlsson, and S. Arvidson. 2000. Identification and characterization of SarH1, a new global regulator of virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 37:398-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Thakker, M., J.-S. Park, V. Carey, and J. C. Lee. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus serotype 5 capsular polysaccharide is antiphagocytic and enhances bacterial virulence in a murine bacteremia model. Infect. Immun. 66:5183-5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vann, J. M., and R. A. Proctor. 1988. Cytotoxic effects of ingested Staphylococcus aureus on bovine endothelial cells: role of S. aureus alpha-hemolysin. Microb. Pathog. 4:443-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vaudaux, P., P. Francois, C. Bisognano, W. L. Kelley, D. P. Lew, J. Schrenzel, R. A. Proctor, P. J. McNamara, G. Peters, and C. von Eiff. 2002. Increased expression of clumping factor and fibronectin-binding proteins by hemB mutants of Staphylococcus aureus expressing small colony variant phenotypes. Infect. Immun. 70:5428-5437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.von Eiff, C., K. Becker, D. Metze, G. Lubritz, J. Hockmann, T. Schwarz, and G. Peters. 2001. Intracellular persistence of Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants within keratinocytes: a cause for antibiotic treatment failure in a patient with Darier's disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32:1643-1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.von Eiff, C., C. Heilmann, R. A. Proctor, C. Woltz, G. Peters, and F. Gotz. 1997. A site-directed S. aureus hemB mutant is a small-colony variant which persists intracellularly. J. Bacteriol. 179:4706-4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.von Eiff, C., R. A. Proctor, and G. Peters. 2000. Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants: formation and clinical impact. Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 115:44-49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]