Abstract
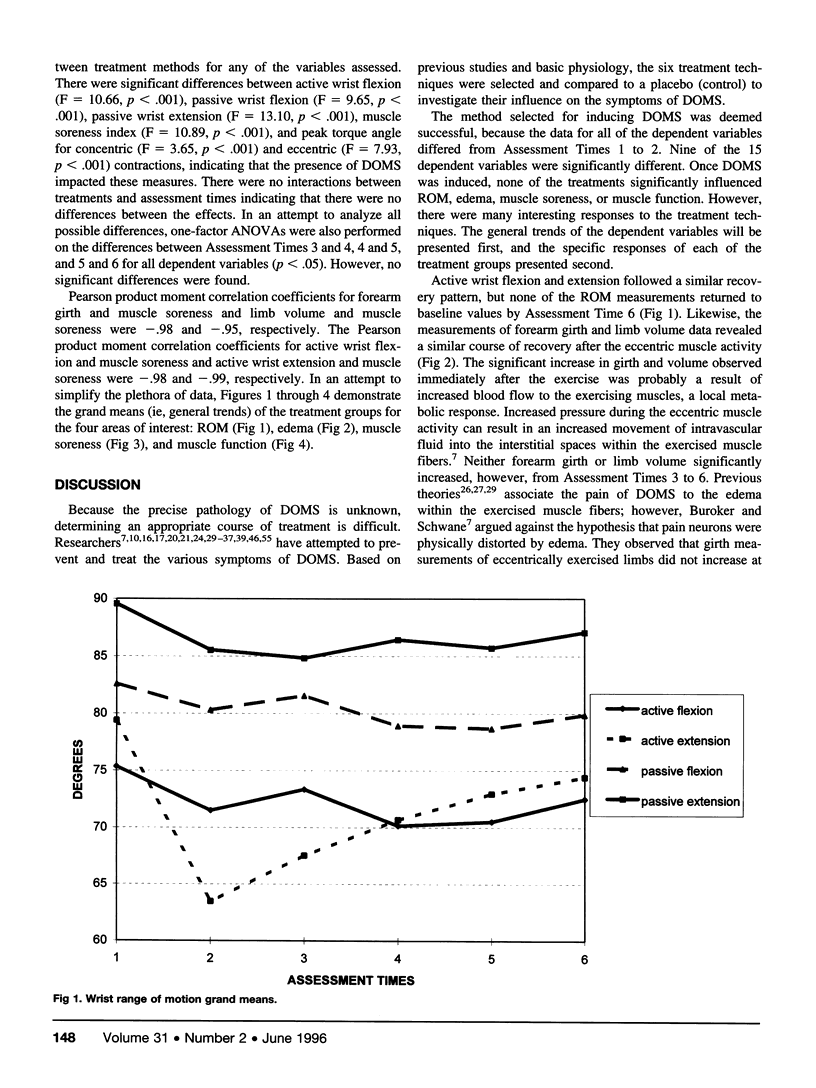
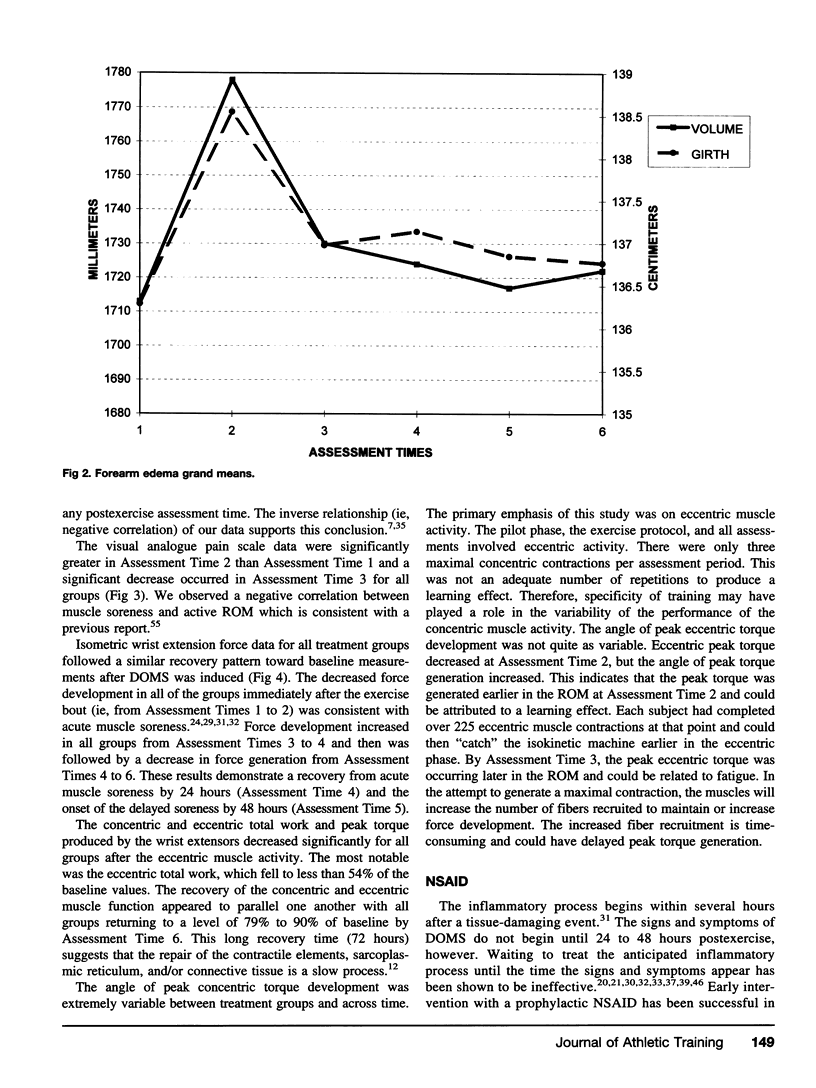
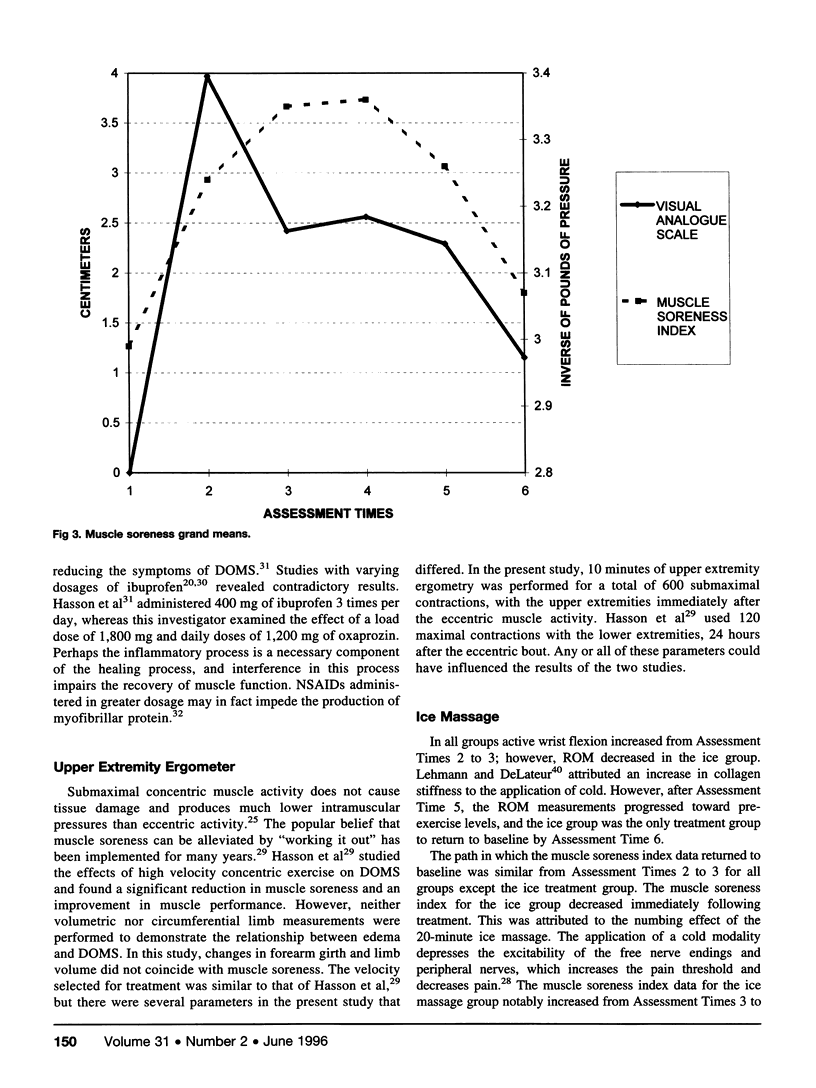
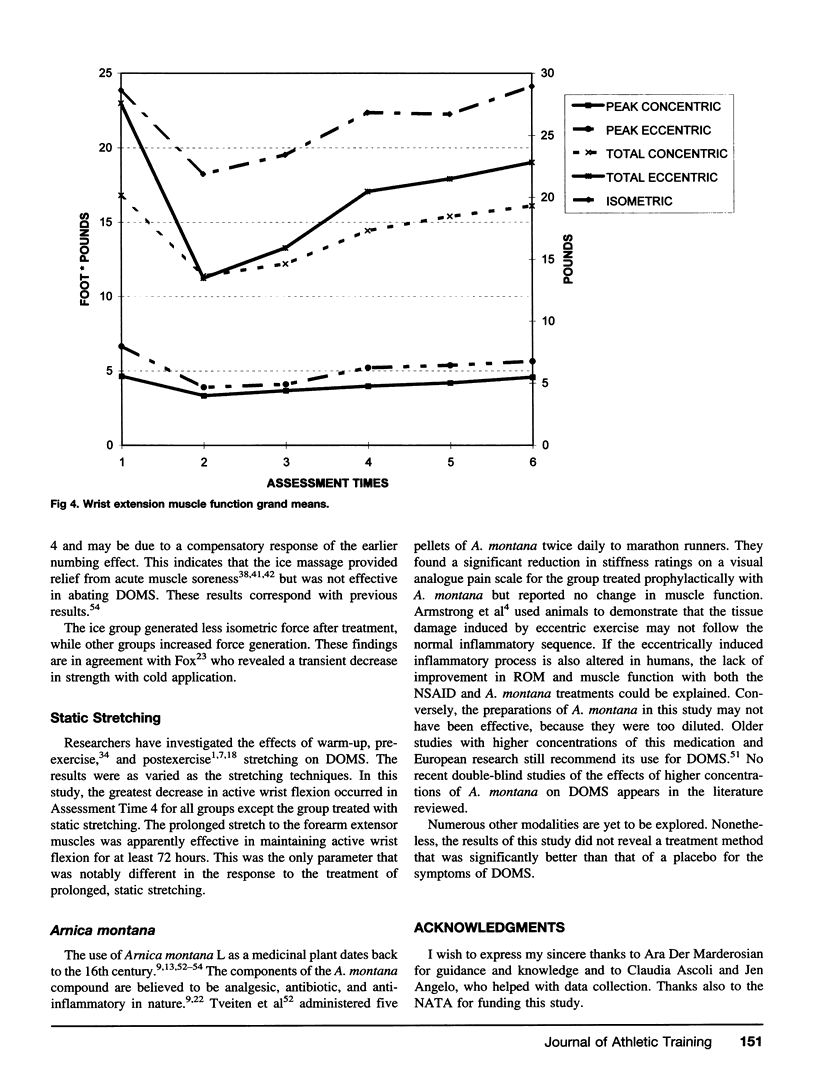
Eccentric activities are an important component of physical conditioning and everyday activities. Delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) can result from strenuous eccentric tasks and can be a limiting factor in motor performance for several days after exercise. An efficacious method of treatment for DOMS would enhance athletic performance and hasten the return to activities of daily living. The purpose of this study was to identify a treatment method which could assist in the recovery of DOMS. In the selection of treatment methods, emphasis was directed toward treatments that could be rendered independently by an individual, therefore making the treatment valuable to an athletic trainer in team setting. DOMS was induced in 70 untrained volunteers via 15 sets of 15 eccentric contractions of the forearm extensor muscles on a Lido isokinetic dynamometer. All subjects performed a pilot exercise bout for a minimum of 9 weeks before data collection to assure that DOMS would be produced. Data were collected on 15 dependent variables: active and passive wrist flexion and extension, forearm girth, limb volume, visual analogue pain scale, muscle soreness index, isometric strength, concentric and eccentric wrist total work, concentric and eccentric angle of peak torque. Data were collected on six occasions: pre- and post-induced DOMS, 20 minutes after treatment, and 24, 48, and 72 hours after treatment. Subjects were randomly assigned to 1 of 7 groups (6 treatment and 1 control). Treatments included a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, high velocity concentric muscle contractions on an upper extremity ergometer, ice massage, 10-minute static stretching, topical Amica montana ointment, and sublingual A. montana pellets. A 7 × 6 ANOVA with repeated measures on time was performed on the delta values of each of the 15 dependent variables. Significant main effects (p < .05) were found for all of the dependent variables on time only. There were no significant differences between treatments. Therefore, we conclude that none of the treatments were effective in abating the signs and symptoms of DOMS. In fact, the NSAID and A. montana treatments appeared to impede recovery of muscle function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E. Observations on experimental muscular soreness. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1956;2(2):109–116. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1956.2.issue-1-4.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham W. M. Factors in delayed muscle soreness. Med Sci Sports. 1977 Spring;9(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. B. Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscular soreness: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1984 Dec;16(6):529–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. B., Ogilvie R. W., Schwane J. A. Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jan;54(1):80–93. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. C., Azen S. P., Lin C. M., Spence C., Baron C., Lee L. Reliability of goniometric measurements. Phys Ther. 1978 Nov;58(11):1355–1360. doi: 10.1093/ptj/58.11.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes W. C., Clarkson P. M., White J. S., Hsieh S. S., Frykman P. N., Maughan R. J. Delayed onset muscle soreness following repeated bouts of downhill running. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Sep;59(3):710–715. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.3.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone C. D., Leggin B. G., Callamaro J. J. Effects of ultrasound and trolamine salicylate phonophoresis on delayed-onset muscle soreness. Phys Ther. 1991 Sep;71(9):666–678. doi: 10.1093/ptj/71.9.666a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson P. M., Byrnes W. C., McCormick K. M., Turcotte L. P., White J. S. Muscle soreness and serum creatine kinase activity following isometric, eccentric, and concentric exercise. Int J Sports Med. 1986 Jun;7(3):152–155. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson P. M., Tremblay I. Exercise-induced muscle damage, repair, and adaptation in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jul;65(1):1–6. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denegar C. R., Perrin D. H. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, cold, and a combination treatment on pain, decreased range of motion, and strength loss associated with delayed onset muscle soreness. J Athl Train. 1992;27(3):200–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly A. E., Maughan R. J., Whiting P. H. Effects of ibuprofen on exercise-induced muscle soreness and indices of muscle damage. Br J Sports Med. 1990 Sep;24(3):191–195. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.24.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly A. E., McCormick K., Maughan R. J., Whiting P. H., Clarkson P. M. Effects of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug on delayed onset muscle soreness and indices of damage. Br J Sports Med. 1988 Mar;22(1):35–38. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.22.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX R. H. Local cooling in man. Br Med Bull. 1961 Jan;17:14–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis K. T., Hoobler T. Effects of aspirin on delayed muscle soreness. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1987 Sep;27(3):333–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J. Muscle soreness after exercise: implications of morphological changes. Int J Sports Med. 1984 Apr;5(2):57–66. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sfakianos P. N., Hargens A. R. Muscle soreness and intramuscular fluid pressure: comparison between eccentric and concentric load. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Dec;61(6):2175–2179. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.6.2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridén J., Sjöström M., Ekblom B. A morphological study of delayed muscle soreness. Experientia. 1981 May 15;37(5):506–507. doi: 10.1007/BF01986165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines J. A survey of recent developments in cold therapy. Physiotherapy. 1967 Jul;53(7):222–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasson S. M., Daniels J. C., Divine J. G., Niebuhr B. R., Richmond S., Stein P. G., Williams J. H. Effect of ibuprofen use on muscle soreness, damage, and performance: a preliminary investigation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993 Jan;25(1):9–17. doi: 10.1249/00005768-199301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasson S. M., Wible C. L., Reich M., Barnes W. S., Williams J. H. Dexamethasone iontophoresis: effect on delayed muscle soreness and muscle function. Can J Sport Sci. 1992 Mar;17(1):8–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasson S., Mundorf R., Barnes W., Williams J., Fujii M. Effect of pulsed ultrasound versus placebo on muscle soreness perception and muscular performance. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1990;22(4):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High D. M., Howley E. T., Franks B. D. The effects of static stretching and warm-up on prevention of delayed-onset muscle soreness. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1989 Dec;60(4):357–361. doi: 10.1080/02701367.1989.10607463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isabell W. K., Durrant E., Myrer W., Anderson S. The effects of ice massage, ice massage with exercise, and exercise on the prevention and treatment of delayed onset muscle soreness. J Athl Train. 1992;27(3):208–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers H., Keizer H. A., Verstappen F. T., Costill D. L. Influence of a prostaglandin-inhibiting drug on muscle soreness after eccentric work. Int J Sports Med. 1985 Dec;6(6):336–339. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1025866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Kieckhefer G. M. Measuring human responses using visual analogue scales. West J Nurs Res. 1989 Feb;11(1):128–132. doi: 10.1177/019394598901100111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. F., Warren C. G., Scham S. M. Therapeutic heat and cold. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974 Mar-Apr;(99):207–245. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197403000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newham D. J., Mills K. R., Quigley B. M., Edwards R. H. Pain and fatigue after concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jan;64(1):55–62. doi: 10.1042/cs0640055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson N. H., Takolander R., Bergqvist D. Lower limb oedema after arterial reconstructive surgery. Influence of preoperative ischaemia, type of reconstruction and postoperative outcome. Acta Chir Scand. 1989 Apr-May;155(4-5):259–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. D., McGrath P. A., Rafii A., Buckingham B. The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain. 1983 Sep;17(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(83)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. M., Miller P. J., Roettger R. F. Goniometric reliability in a clinical setting. Elbow and knee measurements. Phys Ther. 1983 Oct;63(10):1611–1615. doi: 10.1093/ptj/63.10.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talag T. S. Residual muscular soreness as influenced by concentric, eccentric, and static contractions. Res Q. 1973 Dec;44(4):458–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulesius O., Norgren L., Gjöres J. E. Foot-volumetry, a new method for objective assessment of edema and venous function. Vasa. 1973;2(4):325–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tveiten D., Bruseth S., Borchgrevink C. F., Løhne K. Effekt av Arnica D 30 ved hard fysisk anstrengelse. En dobbeltblind randomisert undersøkelse under Oslo Maraton 1990. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1991 Dec 10;111(30):3630–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willuhn G. Untersuchungen über die Inhaltsstoffe von Arnica-Arten. V. Gehalt und Gehaltsschwankungen an atherischem Ol in den verschiedenen Organen von Arnica-Arten. Planta Med. 1972 May;21(3):221–245. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1099547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yackzan L., Adams C., Francis K. T. The effects of ice massage on delayed muscle soreness. Am J Sports Med. 1984 Mar-Apr;12(2):159–165. doi: 10.1177/036354658401200214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



