Abstract
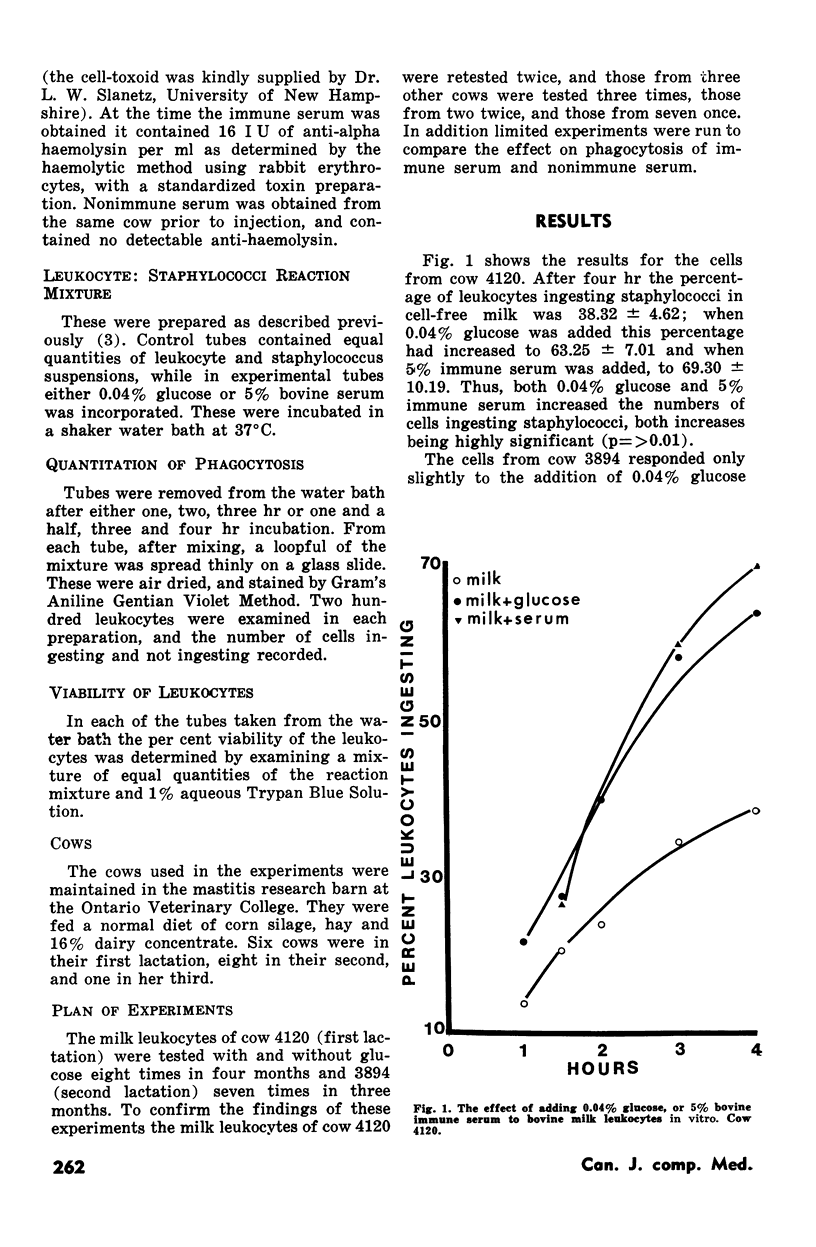
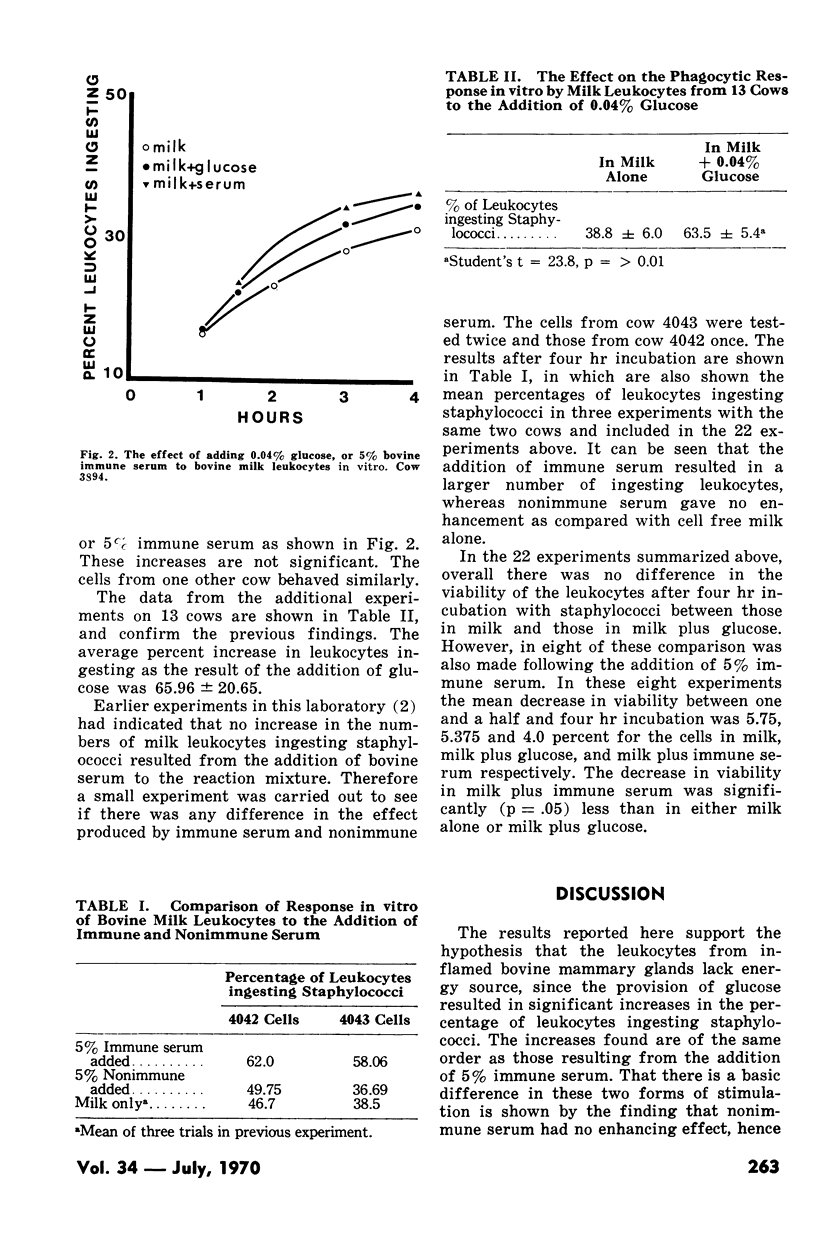
The data presented show a highly significant increase in numbers of bovine milk leukocytes, obtained from mammary glands of 13 cows irritated by sterile distilled water, which ingested staphylococci in four hr when 0.04% glucose was added to the leukocyte: staphylococci mixture. This increase was of the same order as that resulting from the addition of 5% of bovine anti-staphylococcal serum containing 16 I U of anti-alpha haemolysin. Nonimmune serum produced no enhancement. Cells from two other cows did not respond to either glucose or immune serum.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANDT L. ADHESIVENESS TO GLASS AND PHAGOCYTIC ACTIVITY OF NEUTROPHILIC LEUKOCYTES IN MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASES. Scand J Haematol. 1965;2:126–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1965.tb01288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent G. M., Newbould F. H. Phagocytosis and related phenomena in polymorphonuclear leukocytes from cow's milk. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Jul;33(3):214–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbould F. H. Some effects of the source of bovine milk leucocytes and strain of staphylococcus on their interaction in vitro. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1967 Dec;31(12):303–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


