Abstract
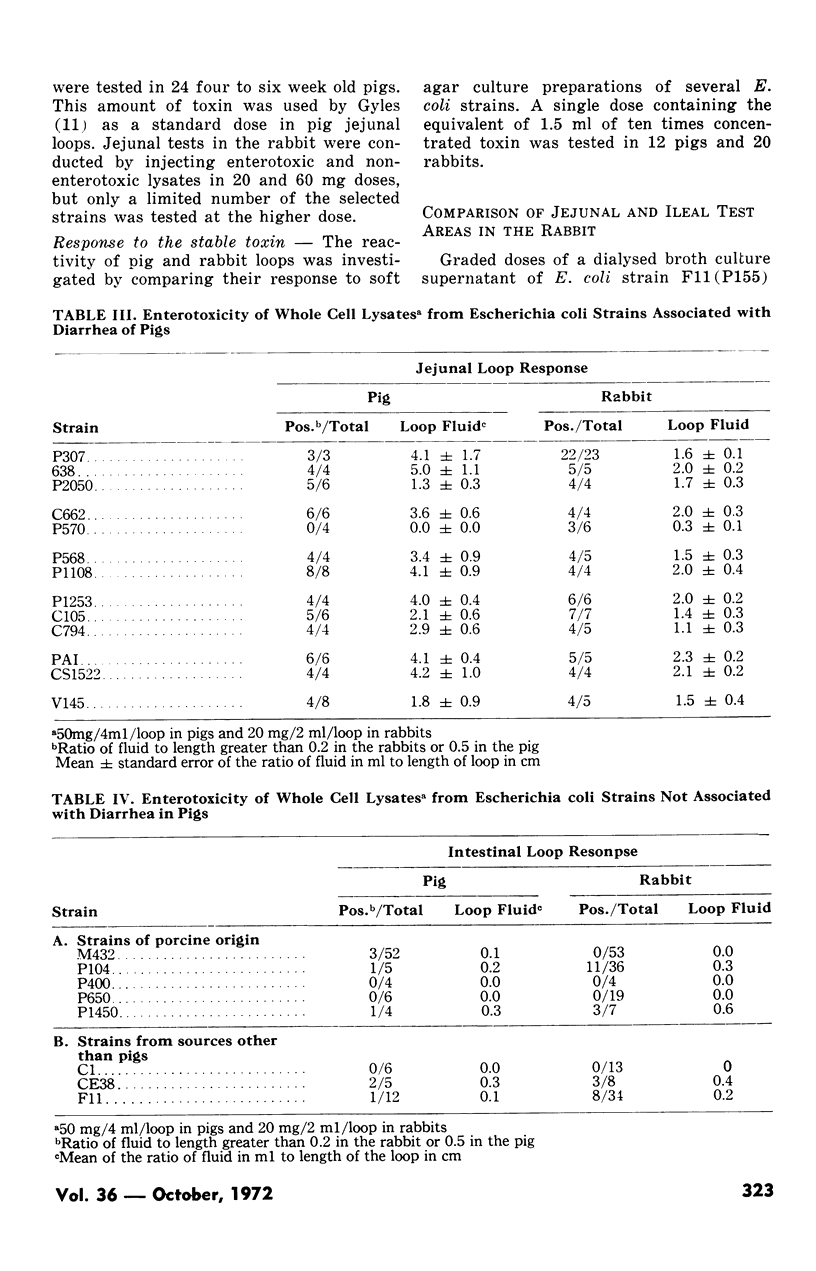
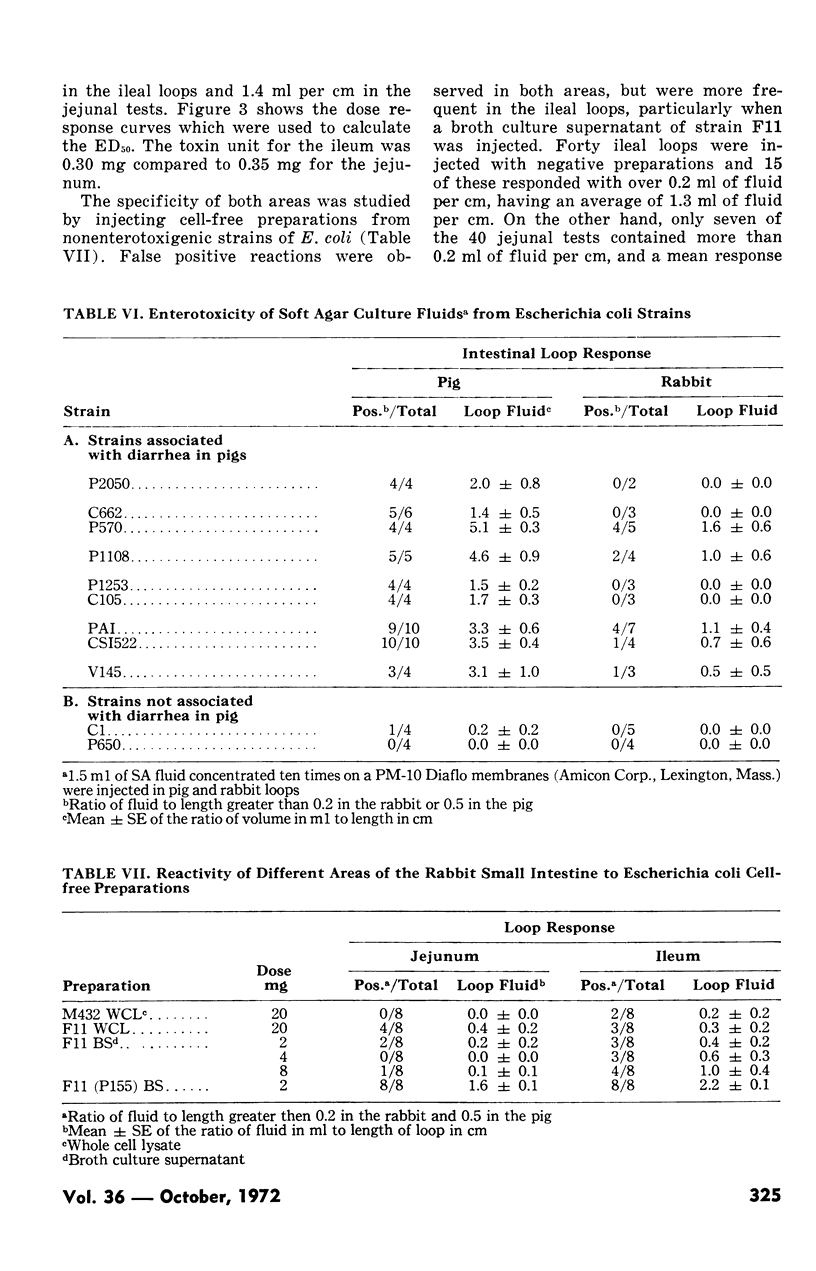
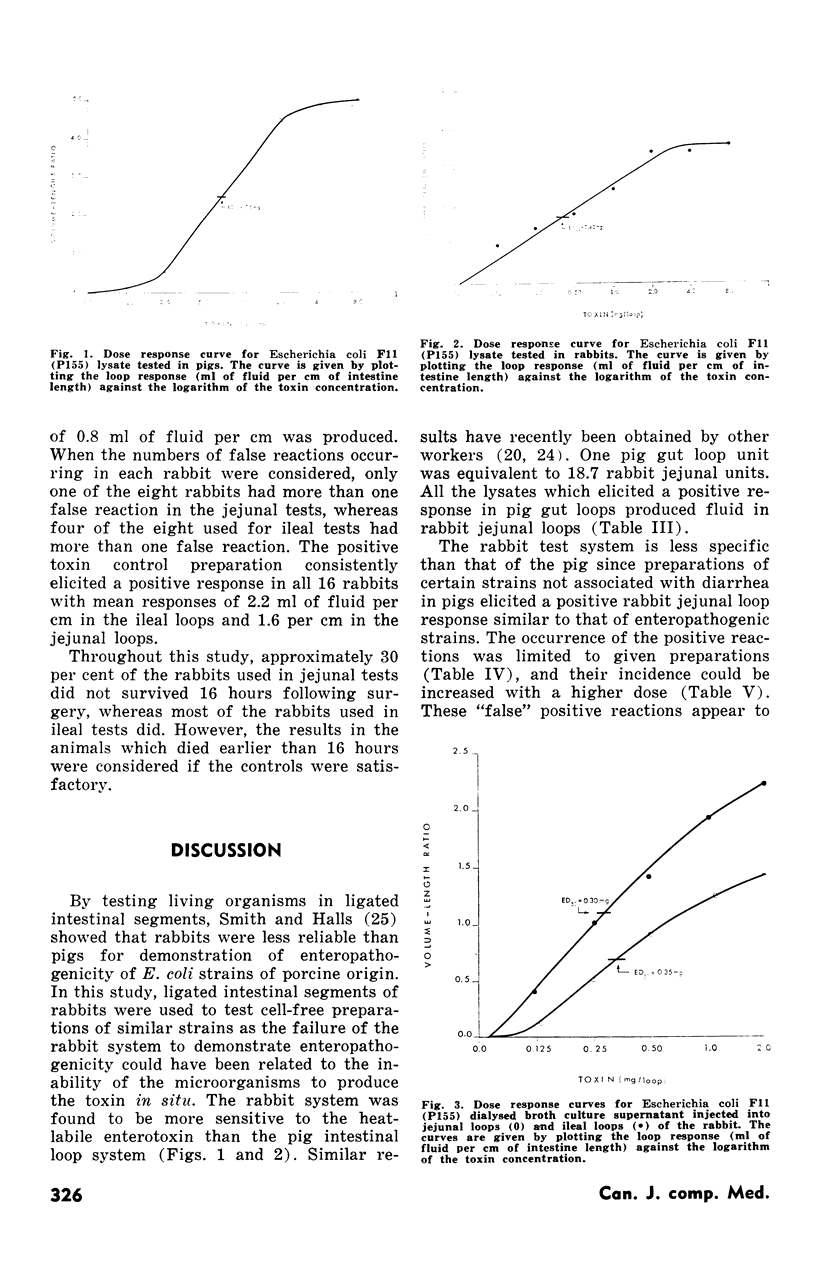
A comparison was made between segments of pig and rabbit small intestine in their response to heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) preparations from porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Either whole cell lysates or dialysed broth culture supernatants were used as sources of LT and soft agar culture fluids as a source of ST. Whole cell lysates of all thirteen LT-producing E. coli strains tested regularly elicited fluid accumulation in rabbit gut loops. Whole cell lysates of certain E. coli strains considered to be nonenteropathogenic in pigs could also elicit a positive response in rabbit gut loops. When graded doses of LT were tested in pig and rabbit gut loops, the rabbit was more sensitive and is therefore considered preferable to the pig for quantitation of LT. In the rabbit, upper (jejunal) and lower (ileal) small intestine were compared for their response to LT and it was found that ileal loops were twice as sensitive but more prone to false positive reactions. When soft agar culture fluids of several enteropathogenic E. coli strains were tested in the rabbit, the response was inconsistent, and it was concluded that the rabbit is unsuitable for the assay of the heat-stable enterotoxin.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARM H. G., FLOYD T. M., FABER J. E., HAYES J. R. USE OF LIGATED SEGMENTS OF RABBIT SMALL INTESTINE IN EXPERIMENTAL SHIGELLOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:803–809. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.803-809.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachman U., Basu S., Pickett M. J. Vibrio cholerae: production of toxin by a nonpathogenic strain. J Infect Dis. 1970 Dec;122(6):540–543. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.6.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows W., Musteikis G. M. Cholera infection and toxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Apr;116(2):183–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., BHATTACHARYA K., SARKAR J. K. A study of the pathogenicity of strains of Bacterium coli from acute and chronic enteritis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):201–209. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N. Enterotoxicity of bacteria-free culture-filtrate of Vibrio cholerae. Nature. 1959 May 30;183(4674):1533–1534. doi: 10.1038/1831533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., GHOSE M. L., SEN A. Activities of bacteria-free preparations from Vibrio cholerae. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:373–380. doi: 10.1002/path.1700790219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Ileal loop fluid accumulation and production of diarrhea in rabbits by cell-free products of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):86–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.86-94.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Sugiyama H., Strong D. H. Rabbit ileal loop response to strains of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1560–1566. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1560-1566.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. Escherichia coli in ligated segments of pig intestine. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):189–194. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Liu P. V. An enterotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):97–98. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch G. J., Burrows W. Experimental cholera in the rabbit ligated intestine: ion and water accumulation in the duodenum, ileum and colon. J Infect Dis. 1968 Oct;118(4):349–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNAUGHT W., ROBERTS G. B. Enteropathogenic effects of strains of Bacterium coli isolated from cases of gastro-enteritis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):155–158. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen N. O., Sautter J. H. Infection of ligated intestinal loops with hemolytic Escherichia coli in the pig. Can Vet J. 1968 Apr;9(4):90–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The effect of cell-free fluids prepared from cultures of human and animal enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli on ligated intestinal segments of rabbits and pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):403–409. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Observations by the ligated intestinal segment and oral inoculation methods on Escherichia coli infections in pigs, calves, lambs and rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):499–529. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Bettelheim K. A. The action of chloroform-killed suspensions of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on ligated rabbit-gut segments. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):309–313. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


