Abstract
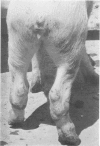
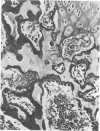
Disease in a large pig herd reared intensively and kept on sulfate-rich drinking water is described. It is the first report of diseased progeny of sows with high sulfate intake. Results of two surveys are presented, one for water with sulfate in excess of 2000 ppm and one for water with less than 1000 ppm. The management practices are described in detail. Disease of Survey I was manifested by high morbidity and mortality (50% of 600) in piglets, incoordination in piglets and some adult stock and osteopathy in piglets and weaners. In Survey II disease was less severe and restricted to piglets. Detailed histopathological studies revealed myelin deficiency in brain and spinal cord of sows and piglets, interferred endochondreal ossification of long bones of piglets and weaners, fatty changes of livers and interstitial nephritis in piglets and weaners. The changes in the nervous tissue were considered due to delayed fixation as tissue was only immersed in fixative and not perfused with it immediately after death. Similar changes have been described for pigs deficient in copper. Copper content of tissue and body fluids of pigs of this study were normal, as were the serum inorganic phosphate and total calcium levels. The bone changes observed have also been reported for rats given dextran sulfate injections, for pigs on experimental low-copper sulfate-enriched diet and for pigs reported low in copper and fed a diet supplemented with sulfide. The cause of the locomotor disturbance and mortality in piglets was not established.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cancilla P. A., Barlow R. M. Experimental copper deficiency in miniature swine. Biochemistry, histochemistry and pathology of the central nervous system. J Comp Pathol. 1970 Apr;80(2):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(70)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. W., Robinson R. J., Lorenzo A. V. Cerebrospinal fluid transport of sulfate in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):448–454. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. A., Peart K. M. Dextran sulphate osteopathy in parathyroidectomized rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Dec;52(6):684–695. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLLIS R. H., Jr, BUSH J. A., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Studies on copper metabolism. XVIII. Skeletal changes associated with copper deficiency in swine. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1955 Dec;97(6):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese G., Schmidt J. L., Mager M. An automated method for the determination of serum calcium with glyoxal bis (2-hydroxyanil). Clin Chem. 1967 Jun;13(6):515–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gipp W. F., Pond W. G., Smith S. E. Effects of level of dietary copper, molybdenum, sulfate and zinc on bodyweight gain, hemoglobin and liver copper storage of growing pigs. J Anim Sci. 1967 Jul;26(4):727–730. doi: 10.2527/jas1967.264727x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Garcia G. G., Matrone G. Copper metabolism in the early postnatal period of the piglet. J Nutr. 1967 Jun;92(2):237–244. doi: 10.1093/jn/92.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. D., Hays V. W., Cromwell G. L. Effects of copper, molybdenum and sulfate on performance, hematology and copper stores of pigs and lambs. J Anim Sci. 1971 Oct;33(4):771–779. doi: 10.2527/jas1971.334771x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcilese N. A., Ammerman C. B., Valsecchi R. M., Dunavant B. G., Davis G. K. Effect of dietary molybdenum and sulfate upon urinary excretion of copper in sheep. J Nutr. 1970 Dec;100(12):1399–1405. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.12.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEAGUE H. S., CARPENTER L. E. The demonstration of a copper deficiency in young growing pigs. J Nutr. 1951 Mar;43(3):389–399. doi: 10.1093/jn/43.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman J., Carnes W. H. Cardiovascular studies on copper-deficient Swine: x. The fine structure of the defective elastic membranes. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jul;51(1):117–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]