Abstract
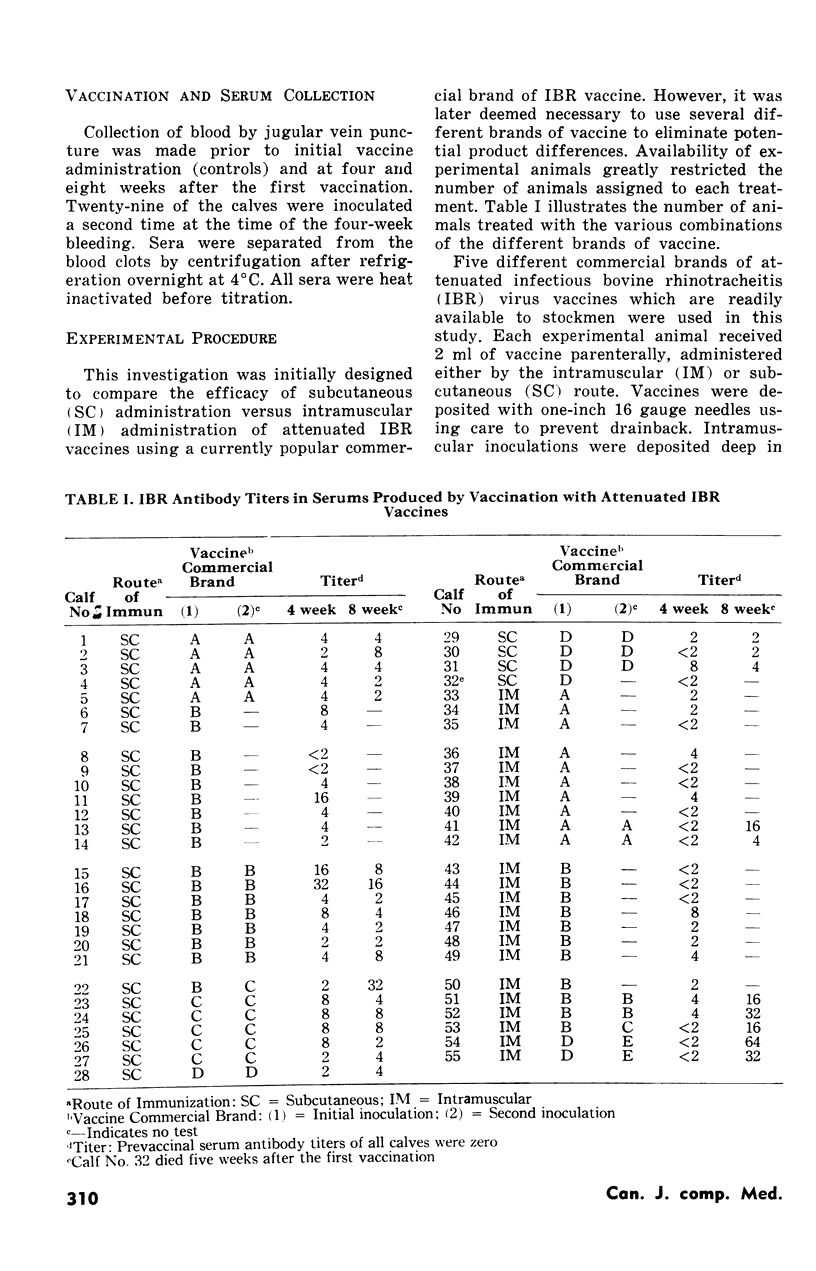
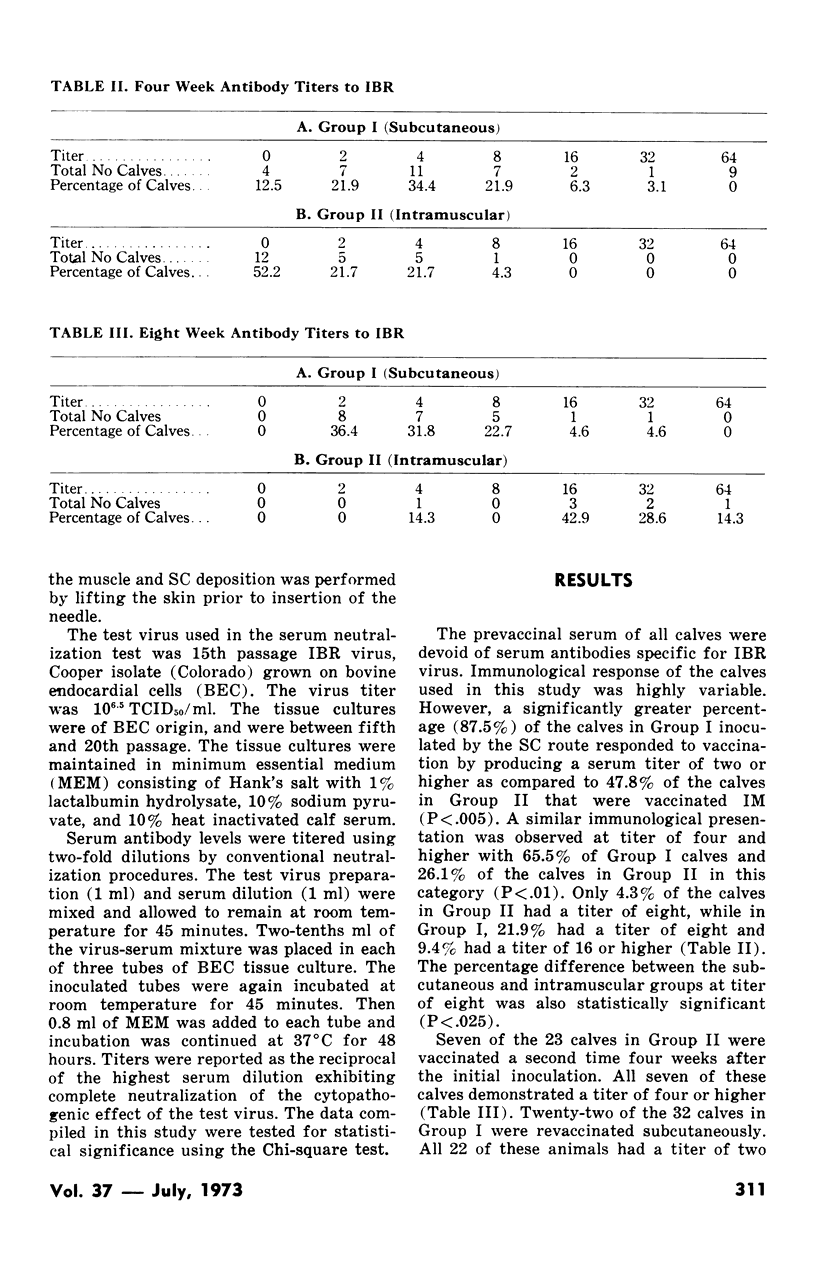
The serum antibody response of calves vaccinated against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis by the intramuscular route was compared to calves vaccinated subcutaneously. Immunological response in the calves as determined by serum neutralization tests was highly variable; however, a significantly greater percentage (87.5%) of the calves inoculated subcutaneously responded to vaccination by producing a four-week post-vaccinal serum titer of two or higher as compared to only 47.8% of the calves that were vaccinated intramuscularly. Of those calves that were vaccinated a second time, all maintained or had produced titers of two or higher within four weeks after the second immunization. However, the existing circulating serum antibody titers resulting from the first vaccination of nine of 22 calves were lowered by repeat vaccination.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER J. A., GILLESPIE J. H., SHEFFY B. E., MARSHALL V. Simultaneous immunization of cattle against leptospirosis, virus diarrhea, and infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. Cornell Vet. 1958 Apr;48(2):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T. L. Duration of immunity in heifers inoculated with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Jan 1;160(1):51–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fastier L. B. Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis--a summary of the disease and its control with emphasis on New Zealand conditions. N Z Vet J. 1967 Mar;15(3):41–42. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1967.33685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHRS R. F. A SEROLOGICAL COMPARISON OF WINTER DYSENTERY WITH BOVINE VIRUS DIARRHEA AND INFECTIOUS BOVINE RHINOTRACHEITIS. INCIDENCE OF WINTER DYSENTERY IN VACCINATED ANIMALS. Cornell Vet. 1965 Jul;55:505–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeely R. A., Merritt A. M., Steraly E. L. Abortion in a dairy herd vaccinated for infectious bovine rhinotracheitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1968 Sep 15;153(6):657–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKercher D. G., Crenshaw G. L. Comparative efficacy of intranasally and parenterally administered infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccines. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Dec 1;159(11):1362–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKercher D. G., Saito J. K., Crenshaw G. L., Bushnell R. B. Complications in cattle following vaccination with a combined bovine viral diarrhea-infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1968 Jun 1;152(11):1621–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARZ A. J., YORK C. J., ZIRBEL L. W., ESTELA L. A. Modification of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus in tissue culture and development of a vaccine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Nov;96(2):453–458. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. D., Volenec F. J., Paton I. M. Intranasal vaccination against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis: studies on early onset of protection and use of the vaccine in pregnant cows. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Dec 1;159(11):1370–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUSCHEK F., CHOW T. L. Immunogenicity of 2 infectious bovine rhinotracheitis vaccines. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1961 Jul 15;139:236–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


