Abstract
3H-labelled Pseudomonas endotoxin was incubated in vitro with blood from nontolerant and endotoxin tolerant calves. Formed elements were separated from serial samples of the incubated mixtures.
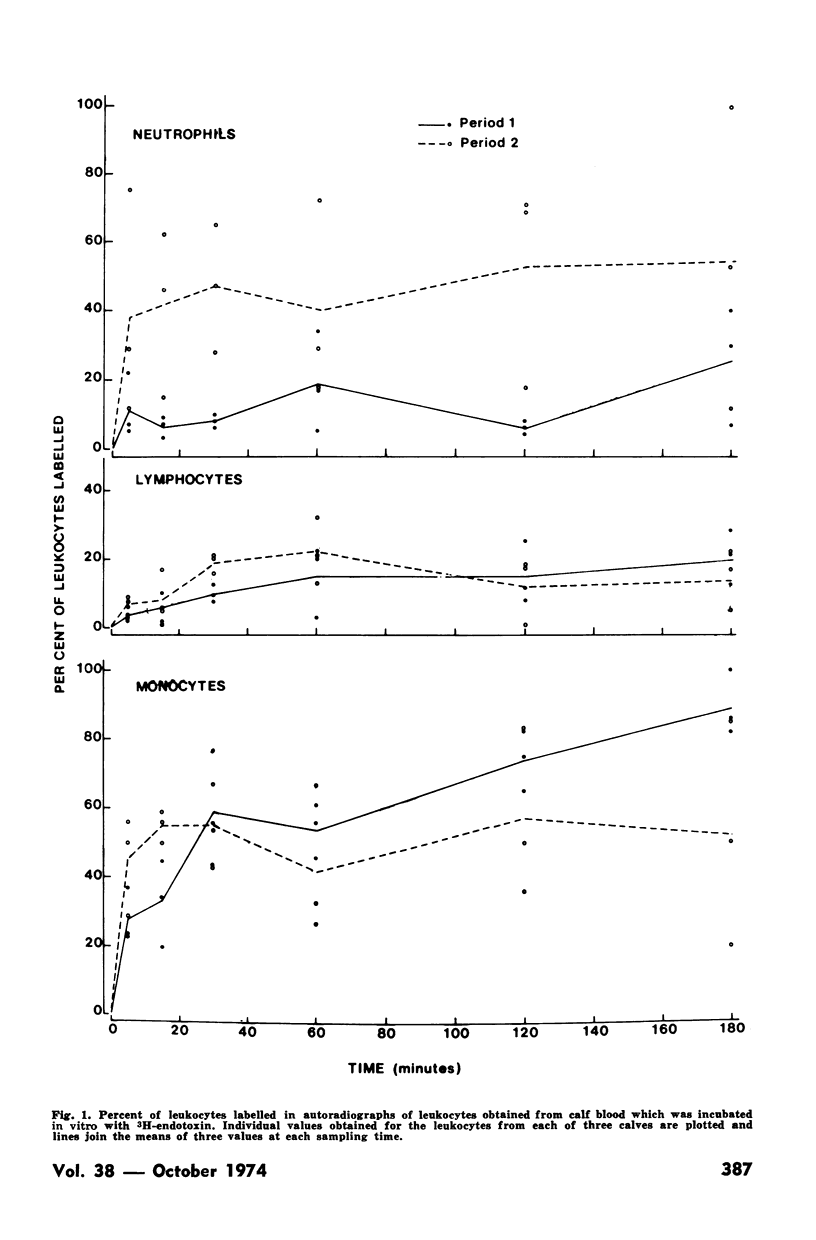
The labelled endotoxin became associated with neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, platelets and erythrocytes. Association of 3H-endotoxin with formed elements of the blood occurred during the first five minutes of incubation and did not significantly change over the course of a three hour incubation period. Tolerance did not result in increased uptake of 3H-endotoxin by formed elements of the blood. Tolerance of calves to endotoxin is apparently not due to increased uptake of endotoxin by formed elements of the blood.
The Limulus amebocyte lysate assay was unreliable for the detection of endotoxin which was present in calf blood in vitro and requires further modification.
Full text
PDF


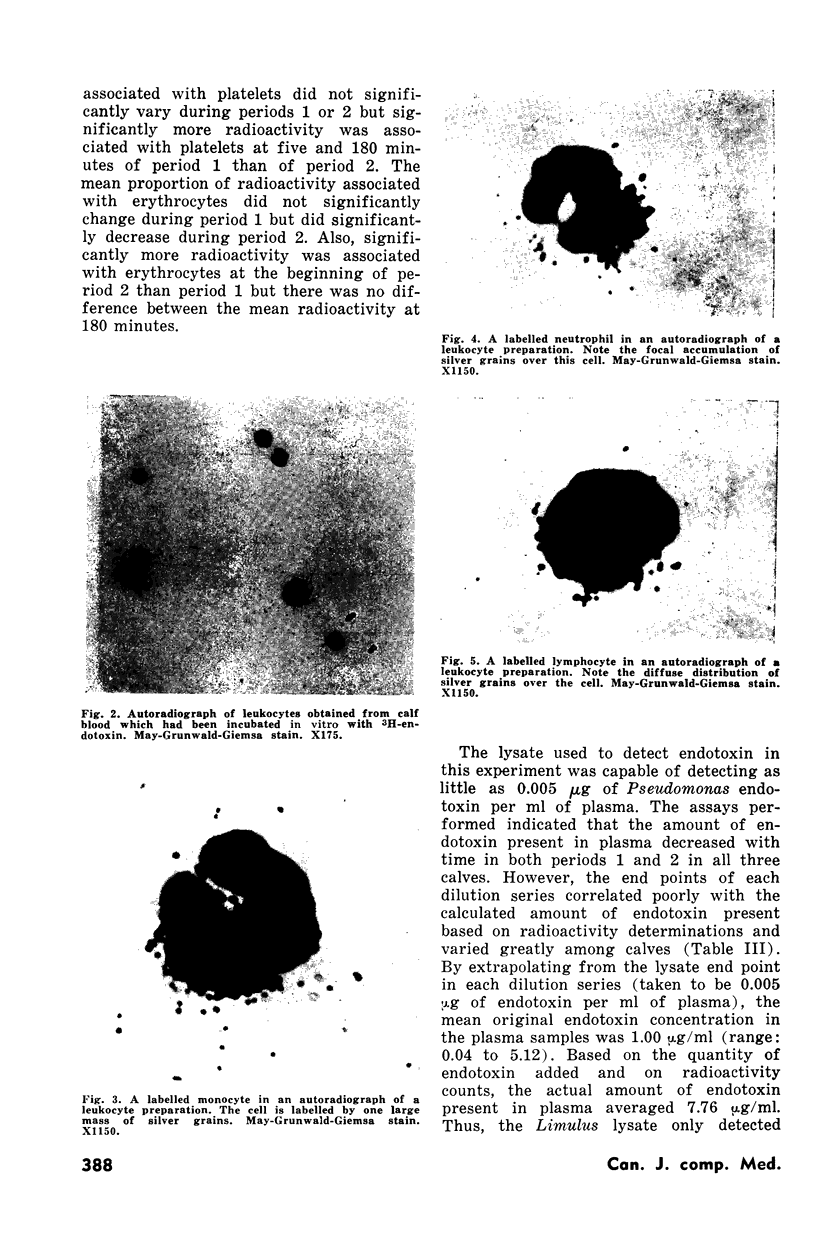
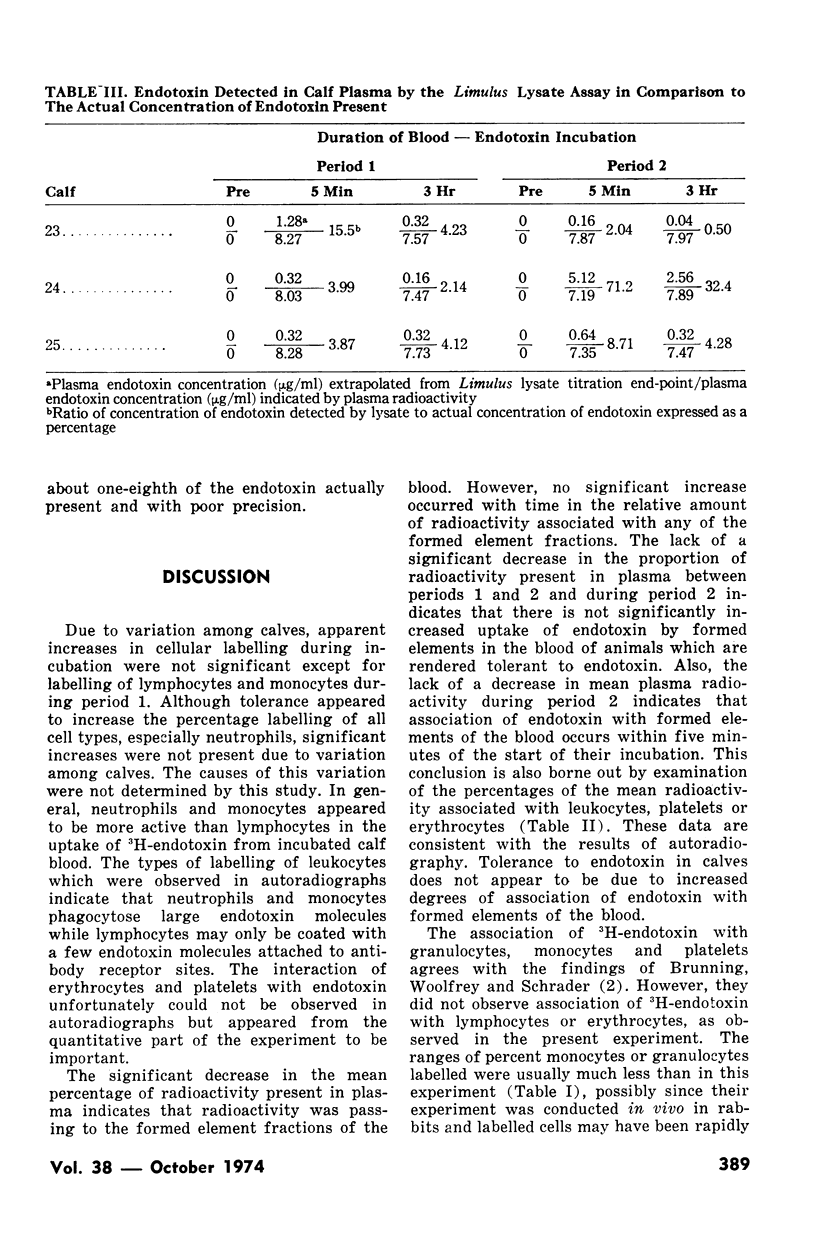

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUNNING R. D., WOOLFREY B. F., SCHRADER W. H. STUDIES WITH TRITIATED ENDOTOXIN. II. ENDOTOXIN LOCALIZATION IN THE FORMED ELEMENTS OF THE BLOOD. Am J Pathol. 1964 Mar;44:401–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berczi I., Bertók L., Bereznai T. Comparative studies on the toxicity of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in various animal species. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):1070–1071. doi: 10.1139/m66-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. F., Levin J., Wagner H. N., Jr Quantitative comparison of in vitro and in vivo methods for the detection of endotoxin. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Bang F. B. Clottable protein in Limulus; its localization and kinetics of its coagulation by endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Poore T. E., Young N. S., Margolis S., Zauber N. P., Townes A. S., Bell W. R. Gram-negative sepsis: detection of endotoxemia with the limulus test. With studies of associated changes in blood coagulation, serum lipids, and complement. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Jan;76(1):1–7. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Tomasulo P. A., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in human blood and demonstration of an inhibitor. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):903–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez L. A., Quintiliani R., Tilton R. C. Clinical experience on the detection of endotoxemia with the limulus test. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jan;127(1):102–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxie M. G., Valli V. E., Lumsden J. H. Studies with radioactive endotoxin. II. Clearance of 3H-labelled endotoxin from the blood of calves. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Oct;38(4):367–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxie M. G., Valli V. E., Robinson G. A., Truscott R. B., McSherry B. J. Studies with radioactive endotoxin. I. Clearance of 51Cr-labelled endotoxin from the blood of calves. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Oct;38(4):347–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Wolff S. M. Cellular localization of carbon-14 endotoxin in cultured leucocytes. Nature. 1966 Aug 13;211(5050):767–768. doi: 10.1038/211767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold R. B., Fine J. A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):334–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Corona R. R., Skarnes R., Tamakuma S., Fine J. The Limulus coagulation test for endotoxin. A comparison with other assay methods. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):599–601. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Galanos C., Kinsky S., Bradshaw R. A., Wessler S., Lüderitz O., Sarmiento M. E. Picogram-sensitive assay for endotoxin: gelation of Limulus polyphemus blood cell lysate induced by purified lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]