Abstract
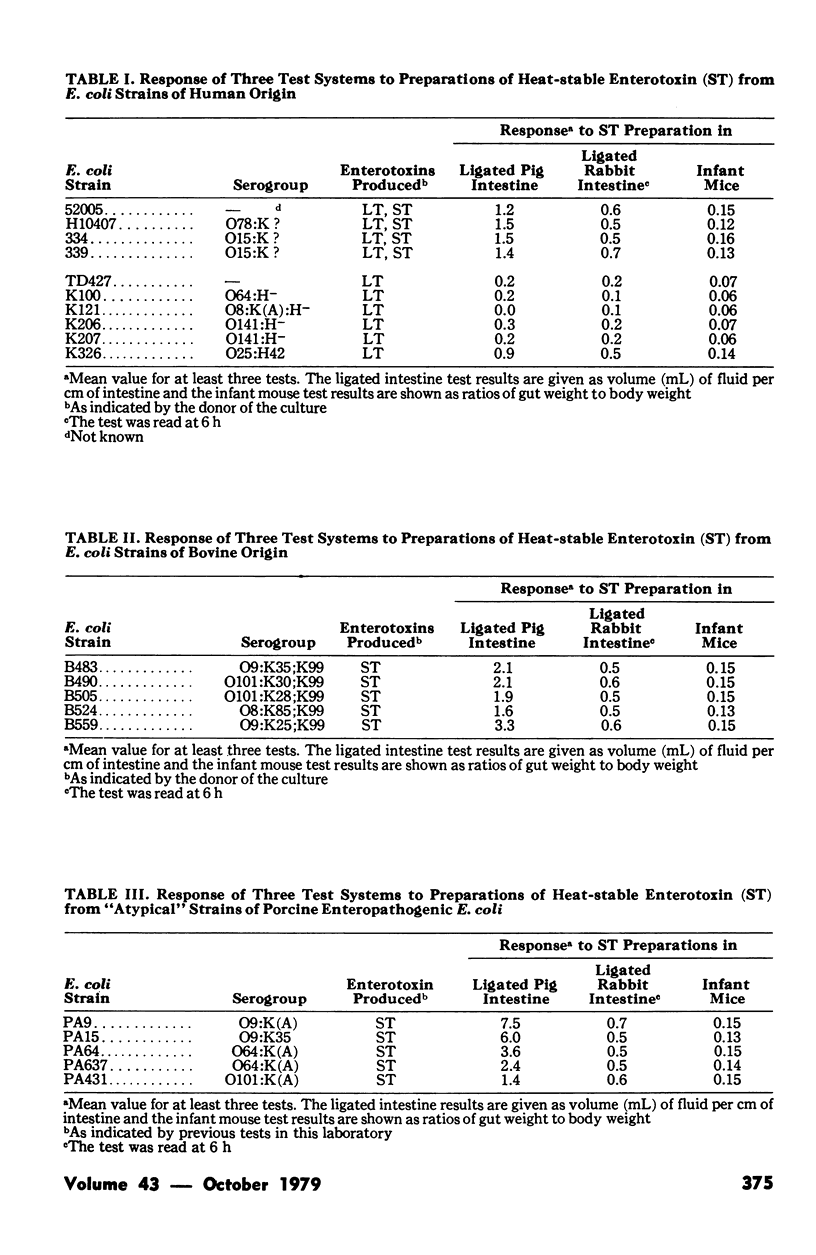
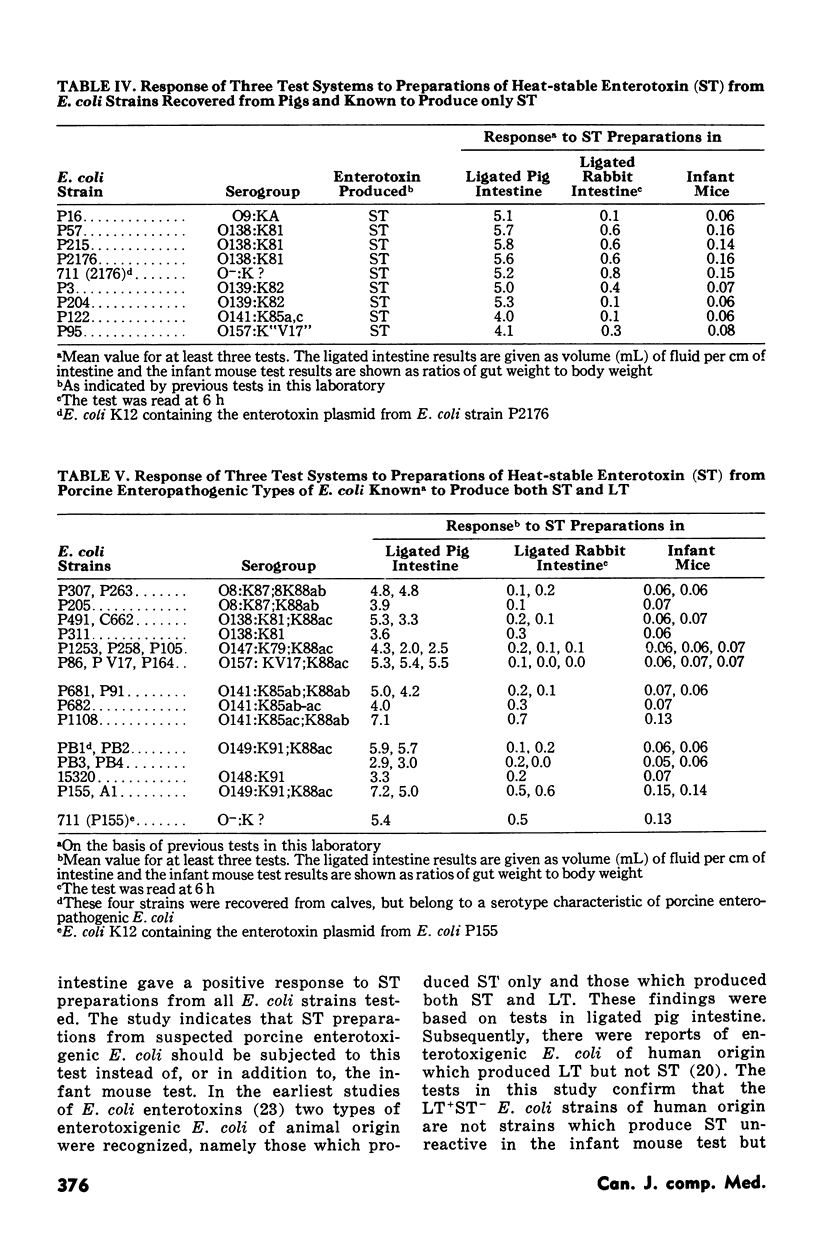
A study was undertaken to evaluate the response of different test systems to preparations of heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) derived from Eschericihia coli strains recovered from diarrheal disease of humans, pigs and calves. Sterile broth culture supernatants of enterotoxigenic strains of E. coli were heated at 65°C for 30 minutes and tested for the presence of heat-stable enterotoxin. Three test systems, namely, ligated intestine of weaned pigs, ligated intestine of rabbits and the infant mouse test were used in attempts to detect ST in the culture supernatants. Two patterns of reaction were observed in response to ST-containing preparations: either the preparation elicited a response in the three tests or the preparation elicited a reaction only in the ligated pig intestine. A response in all three tests were observed for 5/5 human ST-producing E. coli, 5/5 bovine enterotoxigenic E. coli, 5/5 “atypical” porcine enterotoxigenic E. coli, 3/3 St+LT- porcine E. coli of serogroup O138:K81 and 4/24 LT+ST+ porcine E. coli. A response only in the ligated pig intestine was obtained with 5/5 ST+LT- porcine E. coli belonging to serogroups other than O138:K81 and to 20/24 ST+LT+ E. coli from pigs. The results are consistent with the view that there are two kinds of ST, one of which (ST1) reacts in all three tests and the other (ST2) which reacts only in the ligated pig intestine. The findings underscore the limitations of the infant mouse test as a means of detecting ST in porcine isolates of E. coli, since the test fails to detect ST produced by a large number of these E. coli strains. There appeared to be a relationship between kind(s) of ST produced and the animal species from which the producing organism was recovered.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceska M., Grossmüller F., Effenberger F. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay method for determination of Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):347–352. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.347-352.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Agterberg C. M., Jansen W. H., Frik J. F. Serological identification of pig enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains not belonging to the classical serotypes. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):549–555. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.549-555.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Stevens J. B., Craven J. A. A study of Escherichia coli strains isolated from pigs with gastro-intestinal disease. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Jul;35(3):258–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C., So M., Falkow S. The enterotoxin plasmids of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):40–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linggood M. A., Ingram P. L. The effect of oral immunisation with heat stable Escherichia coli antigens on the sensitivity of pigs to enterotoxins. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Jul;25(1):113–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Morris G. K., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Creech W. B., Kapikian A. Z., Gangarosa E. J. Travelers' diarrhea in Mexico. A prospective study of physicians and family members attending a congress. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 10;294(24):1299–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606102942401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Development of resistance with age by swine intestine to effects of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):220–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L., Newman F. S., Warren G. R., Catlin J. E., Anderson C. K. Calf ligated intestinal segment test to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):588–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.588-591.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Kaminsky D. C., Sack R. B., Wamola I. A., Orskov F., Orskov I., Slack R. C., Arthur R. R., Kapikian A. Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea of travelers: a prospective study of American Peace Corps volunteers. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1977 Aug;141(2):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Merson M. H., Wells J. G., Sack R. B., Morris G. K. Diarrhoea associated with heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90958-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaswamy G., Gyles C. L. The prevalence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the feces of calves with diarrhea. Can J Comp Med. 1976 Jul;40(3):241–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The effect of cell-free fluids prepared from cultures of human and animal enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli on ligated intestinal segments of rabbits and pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):403–409. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O. Studies on Escherichia coli in pigs. IV. Reactions of Escherichia coli strains in the ligated intestine test. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1973 Sep;20(7):558–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1973.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Greenberg H. B., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):439–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



