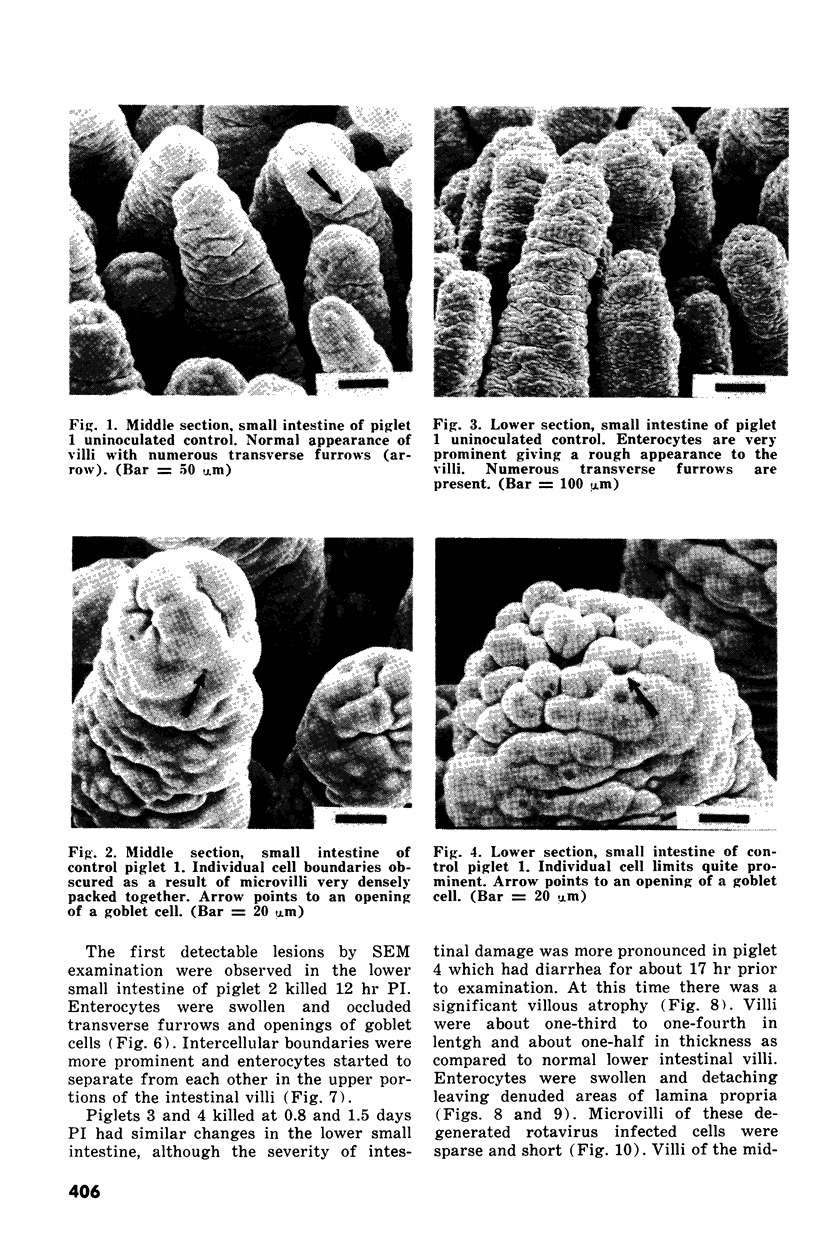
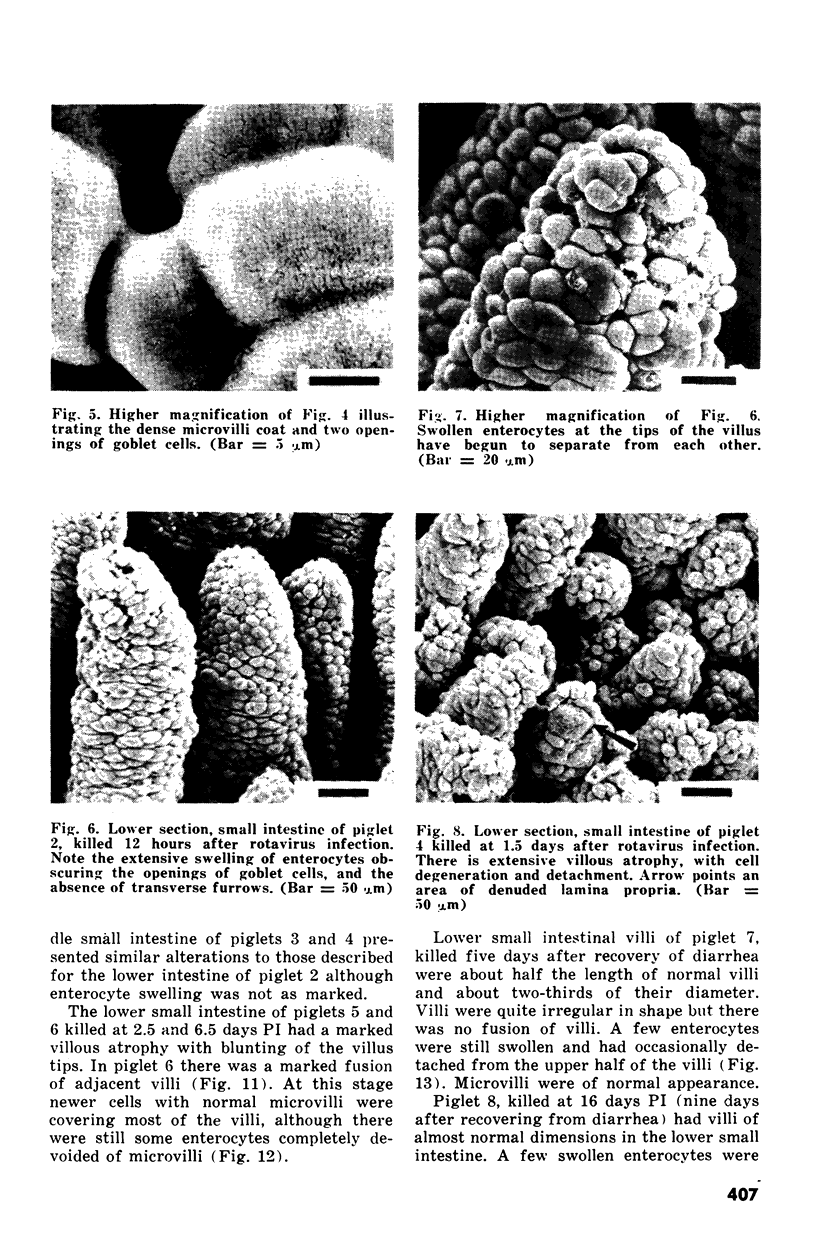
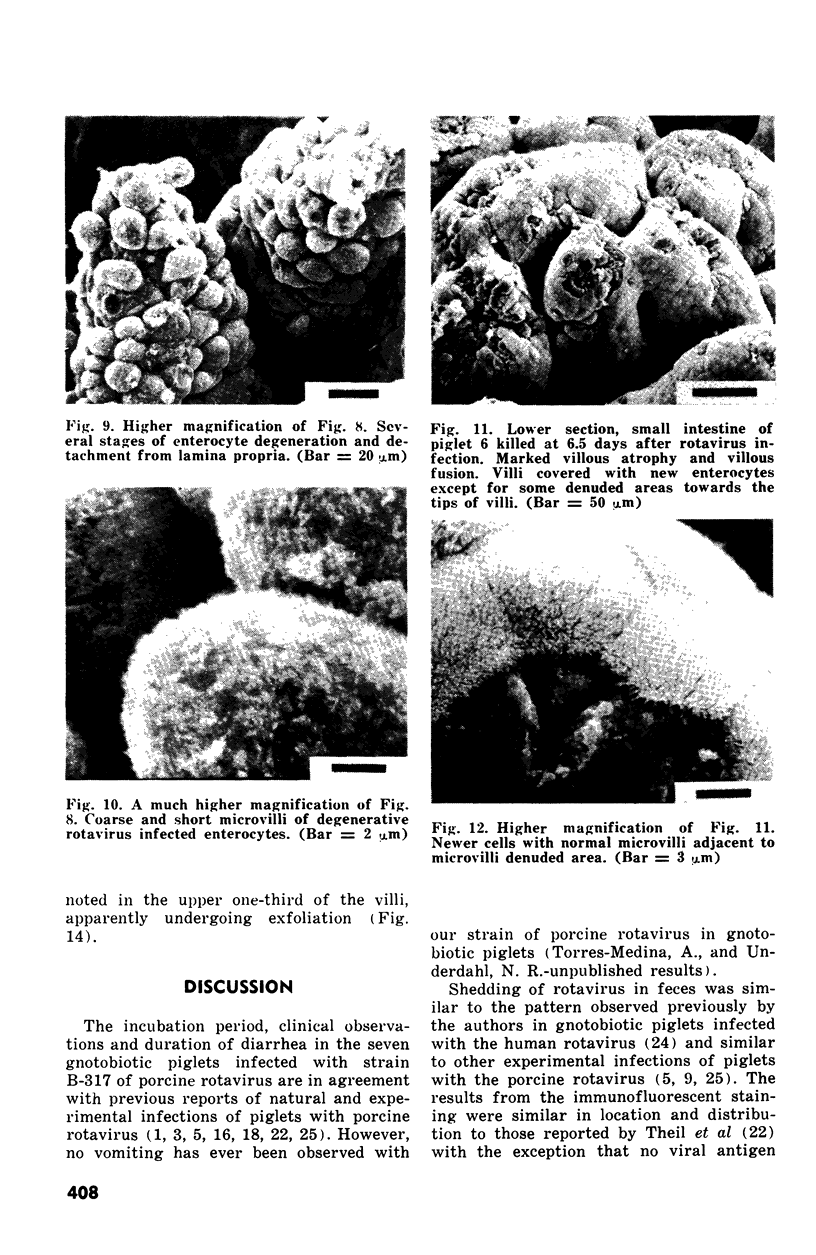
Abstract
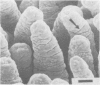
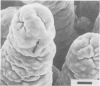
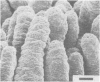
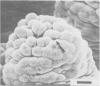
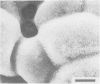
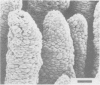
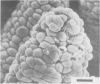
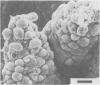
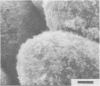
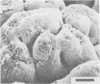
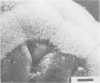
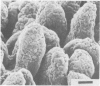
The development of intestinal lesions caused by the porcine rotavirus were studied in six day old gnotobiotic piglets by scanning electron microscopy. The onset of diarrhea followed an incubation period of 17 to 31 hr. The first detectable lesion was observed in the ileum at 12 hr postinfection, a few hours before the onset of diarrhea. At this time enterocytes appeared swollen and began to separate from each other. Seventeen hours after the onset of diarrhea, lesions were quite severe jejunum and ileum. Enterocytes were detaching from the lamina propria leaving denuded areas. Microvilli were sparse on the cell surfaces and there was marked villous atrophy. Regeneration of ileal mucosa was evident at 4.8 days after the onset of diarrhea. Nine days after recovery from diarrhea the intestinal villi had returned to near its normal structure but there remained some evidence of mucosal damage.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Saif L. J., Cross R. F., Agnes A. G., Theil K. W. Rotavirus as a cause of diarrhea in pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Woode G. N., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H. Transmission of human rotaviruses to gnotobiotic piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):565–569. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chap H., Perret B., Mauco G., Simon M. F., Douste-Blazy L. Organization and role of platelet membrane phospholipids as studied with purified phospholipases. Agents Actions. 1979 Oct;9(4):400–406. doi: 10.1007/BF01970668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Lucas M. Detection of rotavirus in experimentally infected piglets. Res Vet Sci. 1977 Jan;22(1):124–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. A., Bridger J. C., Chandler R. L., Woode G. N. Gnotobiotic piglets experimentally infected with neonatal calf diarrhoea reovirus-like agent (Rotavirus). Vet Pathol. 1976;13(3):197–210. doi: 10.1177/030098587601300304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W., Mock R. Reovirus-like agent associated with fatal diarrhea in neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):816–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.816-825.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W. Role of rotavirus (reo-like) in weanling diarrhea of pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):454–458. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.454-458.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W. The calf reo-like virus (rotavirus) vaccine: an ineffective immunization agent for rotaviral diarrhea of piglets. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Jan;43(1):90–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malick L. E., Wilson R. B. Modified thiocarbohydrazide procedure for scanning electron microscopy: routine use for normal, pathological, or experimental tissues. Stain Technol. 1975 Jul;50(4):265–269. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Newman L. E. Scanning electron, light, and immunofluorescent microscopy of intestine of gnotobiotic calf infected with reovirus-like agent. Am J Vet Res. 1977 May;38(5):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Newman L. E., Stair E. L., Jr Scanning electron, light, and immunofluorescent microscopy of intestine of gnotobiotic calf infected with calf diarrheal coronavirus. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Dec;36(12):1719–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Newman L. E., Stair E. L. Scanning electron, light, and transmission electron microscopy of intestine of gnotobiotic calf. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):985–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Petric M., Szymanski M. T. Propagation of infantile gastroenteritis virus (orbi-group) in conventional and germfree piglets. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1276–1280. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1276-1280.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Pathological changes in the small intestine of neonatal pigs infected with a pig reovirus-like agent (rotavirus). J Comp Pathol. 1977 Jul;87(3):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(77)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Ultrastructural changes in small intestinal epithelium of neonatal pigs infected with pig rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1979;59(1-2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01317902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prozesky L., Theodoridis A. Diarrhoea in pigs induced by rotavirus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1977 Dec;44(4):275–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Craven J. A., Williams I. Letter: Demonstration of reovirus-like particles in intestinal contents of piglets with diarrhoea. Aust Vet J. 1975 Nov;51(11):536–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1975.tb06917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Hughes J. H. Immune electron microscopy of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and rotavirus (reovirus-like agent) of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Bohl E. H. Morphogenesis of porcine rotavirus in porcine kidney cell cultures and intestinal epithelial cells. J Gen Virol. 1978 May;39(2):205–217. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Cross R. F., Kohler E. M., Agnes A. G. Pathogenesis of porcine rotaviral infection in experimentally inoculated gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Feb;39(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Medina A., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Underdahl N. R., Kapikian A. Z. Diarrhea caused in gnotobiotic piglets by the reovirus-like agent of human infantile gastroenteritis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):22–27. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Medina A., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Underdahl N. R., Kapikian A. Z. Patterns of shedding of human reovirus-like agent in gnotobiotic newborn piglets with experimentally-induced diarrhea. Intervirology. 1976;7(4-5):250–255. doi: 10.1159/000149957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Williams I. H. Diarrhoea in piglets inoculated with rotavirus. Aust Vet J. 1978 Apr;54(4):188–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdahl N. R., Mebus C. A., Stair E. L., Twiehaus M. J. The effect of cytopathogenic transmissible gastroenteritis-like viruses and-or Escherichia coli on germfree pigs. Can Vet J. 1972 Jan;13(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J., Hall G. A., Jones J. M., Jackson G. The isolation of reovirus-like agents (rota-viruses) from acute gastroenteritis of piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):203–209. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]