Abstract
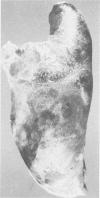
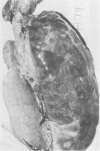
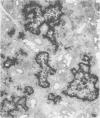
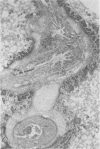
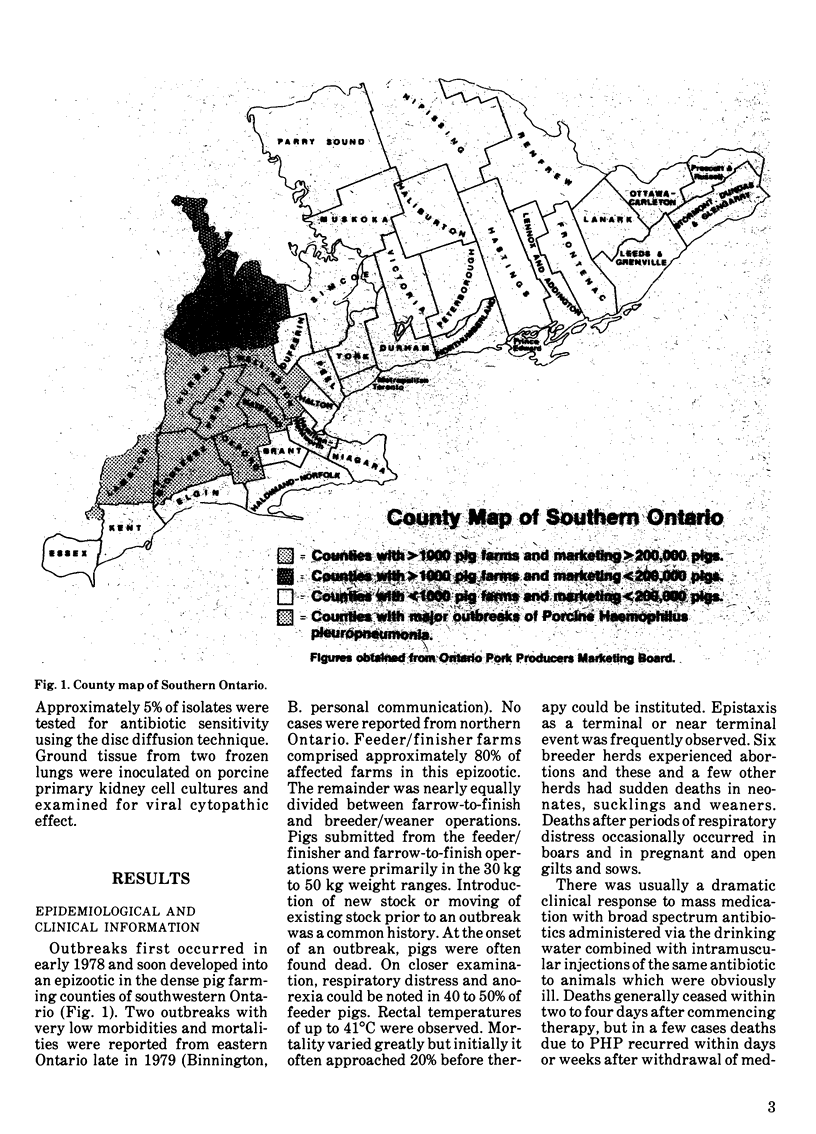
A fibrinous necrotizing pleuropneumonia with a predominant mononuclear cell infiltrate commenced January 1978. The pneumonia, caused by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae assumed epizootic proportions and affected mainly feeder pigs in the intensive pig rearing area of southwestern Ontario. A few abortions occurred. Winter storms, recent transportation and other potentially stressful situations were associated with herd outbreaks. Broad spectrum antibiotics were usually effective in stopping deaths.
Full text
PDF
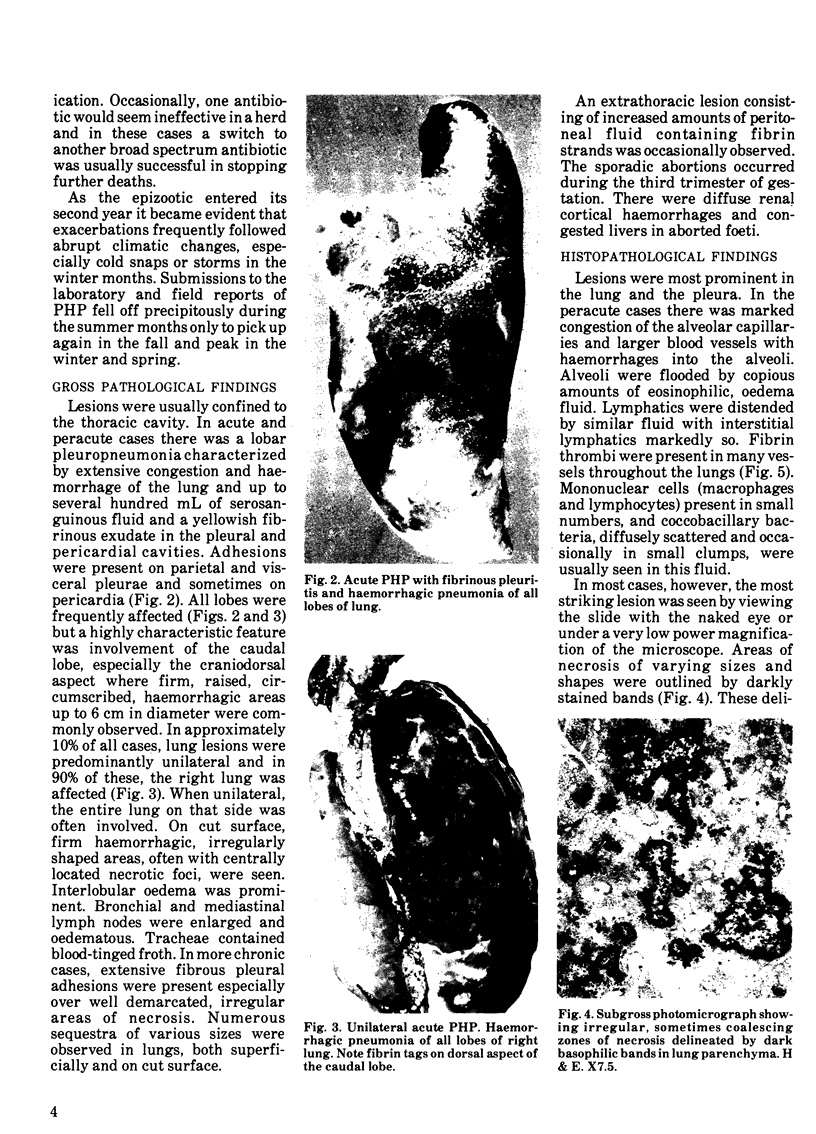



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson M. L., Thomson R. G., Valli V. E. The bovine alveolar macrophage. II. In vitro studies with Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Jul;42(3):368–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberstein E. L., Gunnarsson A., Hurvell B. Cultural and biochemical criteria for the identification of haemophilus spp from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bacterial endotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:67–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C., Yamamoto K., Konishi S., Ogata M. Isolation and antigenic characterization of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus from porcine pneumonia. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1978 Feb;40(1):103–107. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.40.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Jr, Sangster L. T., Cooper J. A. Haemophilus parahaemolyticus associated with pleuropneumonia in Georgia swine. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1978 Nov;73(11):1444–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. C., Thomson R. G., Wilkie B. N. Pulmonary lesions induced by Pasteurella hemolytica in cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Apr;41(2):219–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A. Evaluation of different antigens in the complement-fixation test for diagnosis of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae (parahaemolyticus) infections in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Nov;40(11):1564–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A., Hurvell B., Biberstein E. L. Serologic studies of porcine strains of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus (pleuropneumoniae): antigenic specificity and relationship between serotypes. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Aug;39(8):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häni H., König H., Nicolet J., Scholl E. Zur Haemophilus-Pleuropneumonie beim Schwein. V. Pathomorphologie. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1973 May;115(5):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häni H., König H., Nicolet J., Scholl E. Zur Haemophilus-Pleuropneumonie beim Schwein. VI. Pathogenese. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1973 May;115(5):205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little T. W., Harding J. D. The comparative pathogenicity of two porcine haemophilus species. Vet Rec. 1971 May 22;88(21):540–545. doi: 10.1136/vr.88.21.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. J., Wilkie B. N. Interaction between Pasteurella haemolytica and bovine alveolar macrophages: cytotoxic effect on macrophages and impaired phagocytosis. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jan;41(1):18–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylrea P. J., Fraser G., Macqueen P., Lambourne D. A. Pleuropneumonia in pigs caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Aust Vet J. 1974 Jun;50(6):255–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb05292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J. Sur l'hémophilose du porc. I. Identification d'un agent fréquent: Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1968;31(4):215–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. An outbreak of pleuropneumonia among a group of baconers. Pathological and bacteriological observations. Nord Vet Med. 1973 Oct;25(10):492–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Mandrup M. Pleuropneumonia in swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. A study of the epidemiology of the infection. Nord Vet Med. 1977 Nov;29(11):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Pleuropneumonia of swine caused by Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Studies on the protection obtained by vaccination. Nord Vet Med. 1976 Jul-Aug;28(7-8):337–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTISON I. H., HOWELL D. G., ELLIOT J. A haemophilus-like organism isolated from pig lung and the associated pneumonic lesions. J Comp Pathol. 1957 Oct;67(4):320–330. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(57)80031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radostits O. M., Ruhnke H. L., Losos G. J. An Outbreak of Meningitis in Swine Caused by Haemophilus Species of Bacterium. Can Vet J. 1963 Oct;4(10):265–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer B., Moffatt R. E., Greenfield J., Agar J. L., Majka J. A. Porcine Hemophilus parahemolyticus pneumonia in Saskatchewan. I. Natural occurrence and findings. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Apr;38(2):99–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson R. G., Ruhnke H. L. Haemophilus Septicemia in Piglets. Can Vet J. 1963 Oct;4(10):271–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Kierstead M. Haemophilus parahemolyticus associated with abortion in swine. Can Vet J. 1976 Aug;17(8):222–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]