Abstract
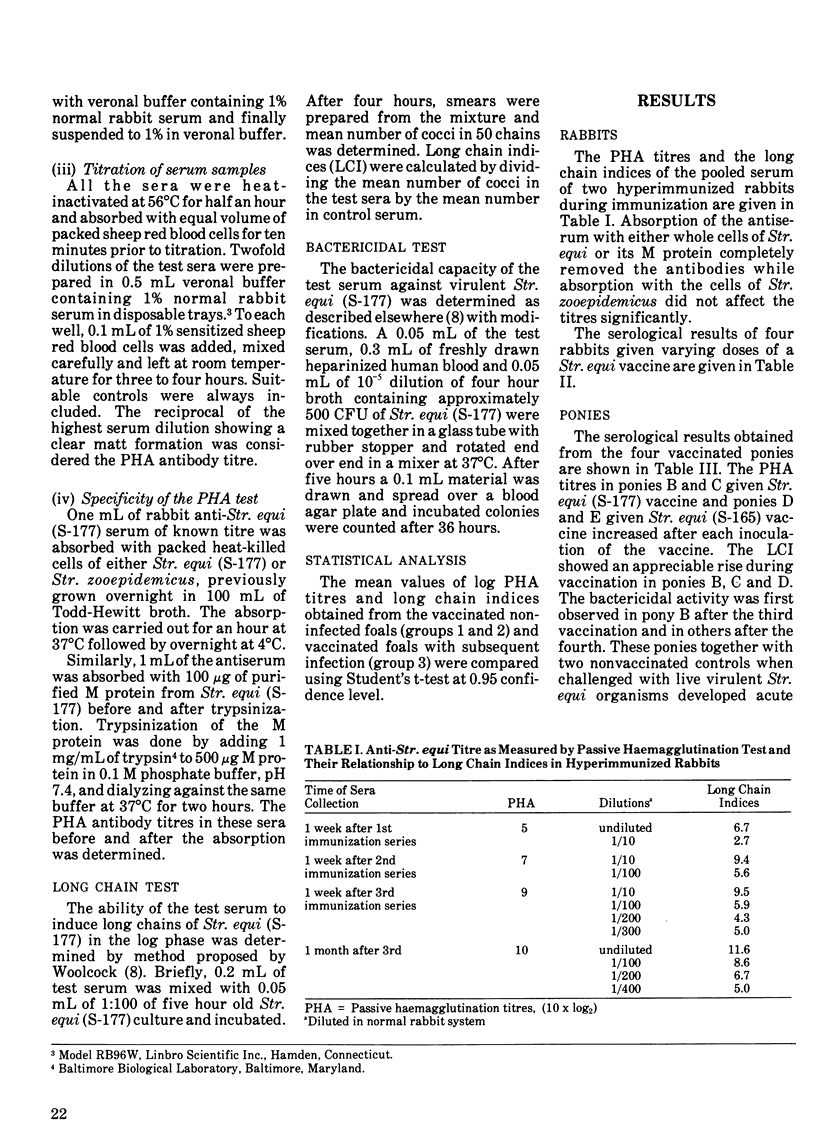
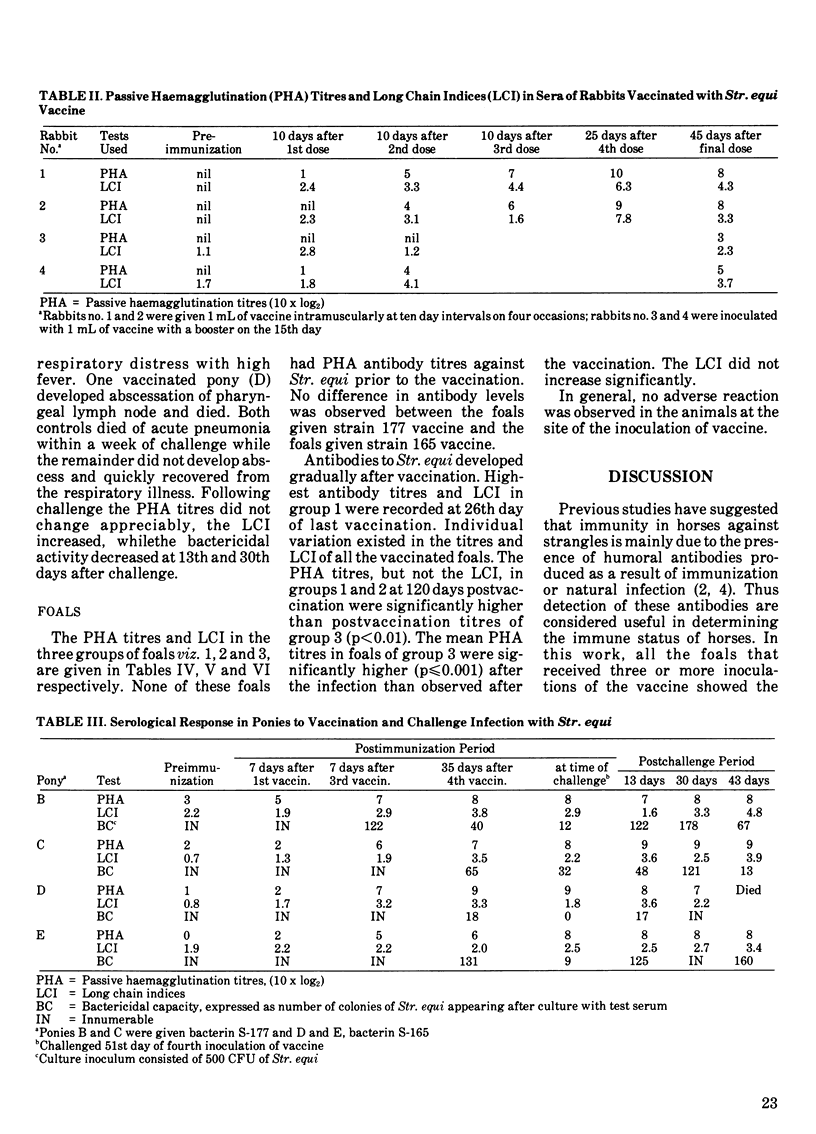
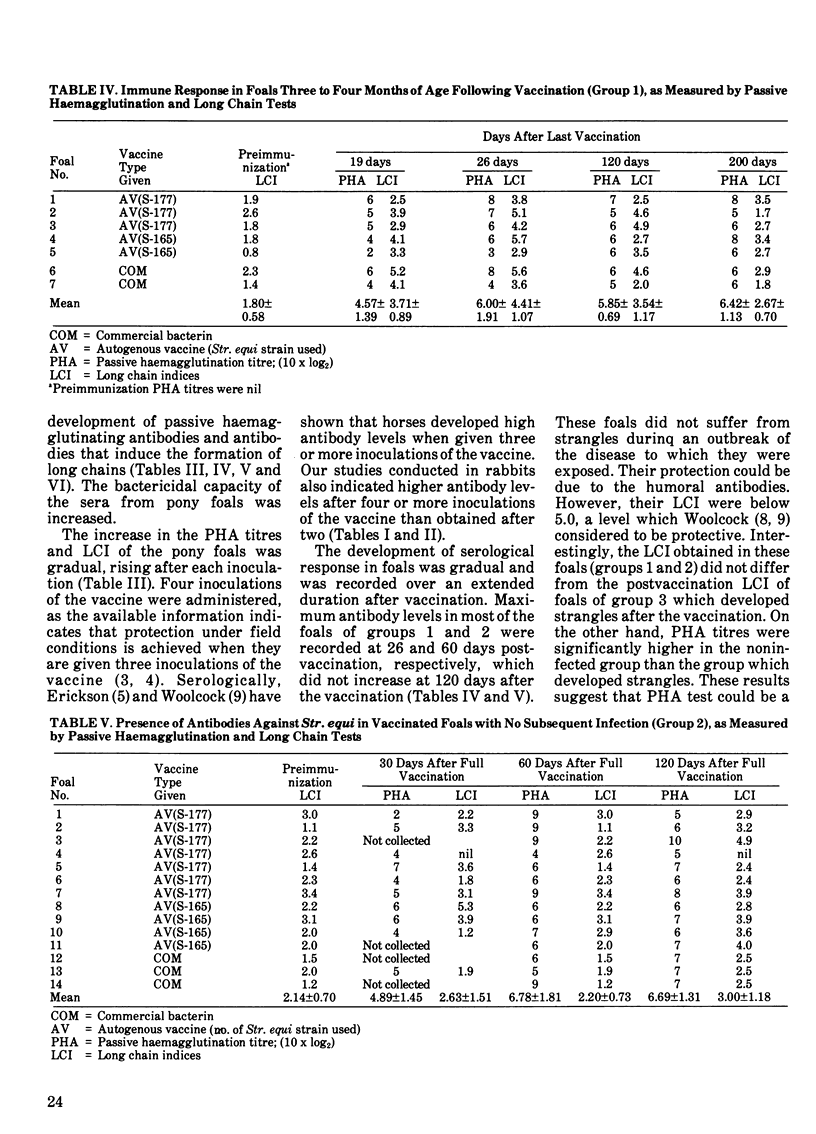
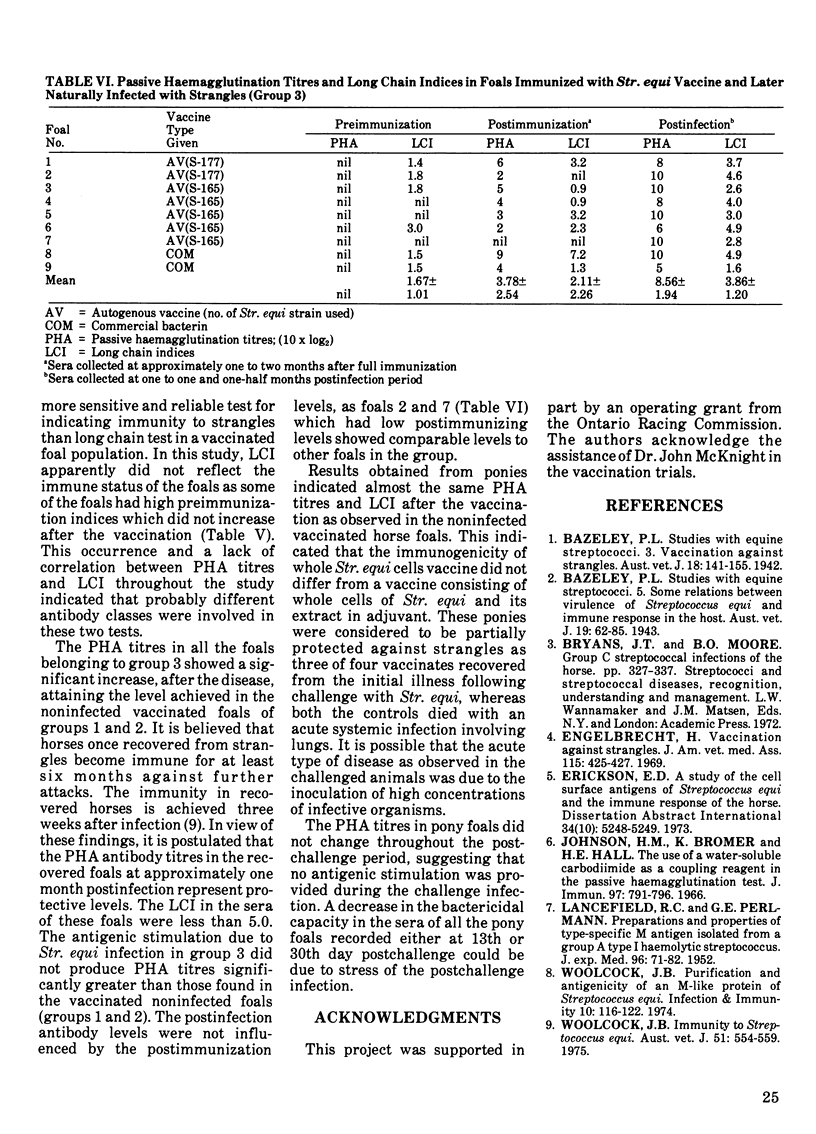
A group of 100 foals was given either a commercial bacterin or an autogenous vaccine consisting of whole cells and an acid extract of Streptococcus equi. During the study, some of the foals developed clinical strangles. Various sets of sera were collected from these foals prevaccination, during vaccination, postvaccination and postinfection. The serological response of these foals was measured by passive haemagglutination and long chain tests. In foals which remained healthy, the highest titres were reached within one to two months postvaccination with a passive haemagglutination 10 x log2 mean titre of 6.78 and the long chain indices of 4.41. These levels persisted for 120 days postvaccination. Those foals which had clinical strangles exhibited lower passive haemagglutination titres (3.78) at one to two months postimmunization, but rose significantly after recovery. Four ponies immunized with formalinized Str. equi bacterin showed a partial protection against the challenge infection. The passive haemagglutination titres, long chain indices and serum bactericidal activity in these ponies were highest at 35 days postvaccination but did not increase after infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engelbrecht H. Vaccination against strangles. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):425–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Brenner K., Hall H. E. The use of a wate-soluble carbodiimide as a coupling reagent in the passive hemagglutination test. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):791–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B. Immunity to Streptococcus equi. Aust Vet J. 1975 Dec;51(12):554–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1975.tb09379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B. Purification and antigenicity of an M-like protein of Streptococcus equi. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.116-122.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


