Abstract
Objective:
To present the case of a college football player with acute, atraumatic, exercise-induced compartment syndrome in the leg.
Background:
Acute, atraumatic, exercise-induced compartment syndrome is an infrequently reported cause of leg pain in the athlete. If left untreated, acute compartment syndrome can cause muscle necrosis.
Differential Diagnosis:
Chronic exertional compartment syndrome, medial tibial syndrome, stress fracture.
Treatment:
Treatment consists of compartment fasciotomy.
Uniqueness:
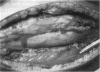
This previously healthy, but unconditioned, athlete developed severe anterolateral left leg pain after two days of fall practice in which he was unable to run a mile in 7.5 minutes. Physical examination by the team physician revealed acute compartment syndrome, and an emergency anterolateral compartment fasciotomy was performed. Second-look débridement performed 48 hours later revealed no significant change in the necrotic appearance of the anterior compartment soft tissue. Therefore, the dead muscle was completely débrided, and a free-flap latissumus dorsi graft was used for coverage of the wound. With recovery, strength returned to normal in the lateral compartment but remained 0/5 in the anterior compartment. The patient had persistent sensory loss in the distributions of the superficial and deep peroneal nerves.
Conclusions:
Although much less common than the more frequent causes of leg pain (ie, chronic exertional compartment syndrome, medial tibial syndrome, stress fracture), acute compartment syndrome is potentially more devastating. When the increased intracompartmental pressure within a closed tissue space exceeds capillary perfusion pressure, tissue perfusion is decreased, the soft tissue becomes ischemic, and cells die. The most important clinical diagnostic signs of compartment syndrome are pain with passive stretching of the compartment and pain out of proportion to the results of the physical examination.
Keywords: leg pain, fasciotomy, rhabdomyolysis
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arciero R. A., Shishido N. S., Parr T. J. Acute anterolateral compartment syndrome secondary to rupture of the peroneus longus muscle. Am J Sports Med. 1984 Sep-Oct;12(5):366–367. doi: 10.1177/036354658401200505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better O. S., Stein J. H. Early management of shock and prophylaxis of acute renal failure in traumatic rhabdomyolysis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 22;322(12):825–829. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003223221207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black K. P., Schultz T. K., Cheung N. L. Compartment syndromes in athletes. Clin Sports Med. 1990 Apr;9(2):471–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelberman R. H., Garfin S. R., Hergenroeder P. T., Mubarak S. J., Menon J. Compartment syndromes of the forearm: diagnosis and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981 Nov-Dec;(161):252–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppenstall R. B., Sapega A. A., Scott R., Shenton D., Park Y. S., Maris J., Chance B. The compartment syndrome. An experimental and clinical study of muscular energy metabolism using phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988 Jan;(226):138–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb A. B., Ibrahim A. A. Acute peroneal compartment syndrome in a well conditioned athlete: report of a case. Am J Sports Med. 1977 Jul-Aug;5(4):154–157. doi: 10.1177/036354657700500403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens M. A., Moeyersoons J. P. Acute and recurrent effort-related compartment syndrome in sports. Sports Med. 1990 Jan;9(1):62–68. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199009010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson G. O., Clement D. B., McKenzie D. C., Taunton J. E., Lloyd-Smith D. R., MacIntyre J. G. Stress fractures in athletes. A study of 320 cases. Am J Sports Med. 1987 Jan-Feb;15(1):46–58. doi: 10.1177/036354658701500107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHale K. M., Prahinski J. R. Acute exertional compartment syndrome occurring after performance of the army physical fitness test. Orthop Rev. 1994 Sep;23(9):749–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael R. H., Holder L. E. The soleus syndrome. A cause of medial tibial stress (shin splints). Am J Sports Med. 1985 Mar-Apr;13(2):87–94. doi: 10.1177/036354658501300202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mubarak S. J., Gould R. N., Lee Y. F., Schmidt D. A., Hargens A. R. The medial tibial stress syndrome. A cause of shin splints. Am J Sports Med. 1982 Jul-Aug;10(4):201–205. doi: 10.1177/036354658201000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mubarak S. J., Owen C. A. Double-incision fasciotomy of the leg for decompression in compartment syndromes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977 Mar;59(2):184–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedowitz R. A., Hargens A. R., Mubarak S. J., Gershuni D. H. Modified criteria for the objective diagnosis of chronic compartment syndrome of the leg. Am J Sports Med. 1990 Jan-Feb;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1177/036354659001800106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorabeck C. H., Castle G. S., Hardie R., Logan J. Compartmental pressure measurements: an experimental investigation using the slit catheter. J Trauma. 1981 Jun;21(6):446–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorabeck C. H., Clarke K. M. The pathophysiology of the anterior tibial compartment syndrome: an experimental investigation. J Trauma. 1978 May;18(5):299–304. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197805000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorabeck C. H. The treatment of compartment syndromes of the leg. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984 Jan;66(1):93–97. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.66B1.6693486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan G. W., Matsen F. A., 3rd Fasciotomy in the treatment of the acute compartment syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976 Jan;58(1):112–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer S. R., Martin D. F., Stanish W. D., Michael R. H. Chronic compartment syndrome caused by aberrant fascia in an aerobic walker. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1991 Mar;23(3):304–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]