Abstract
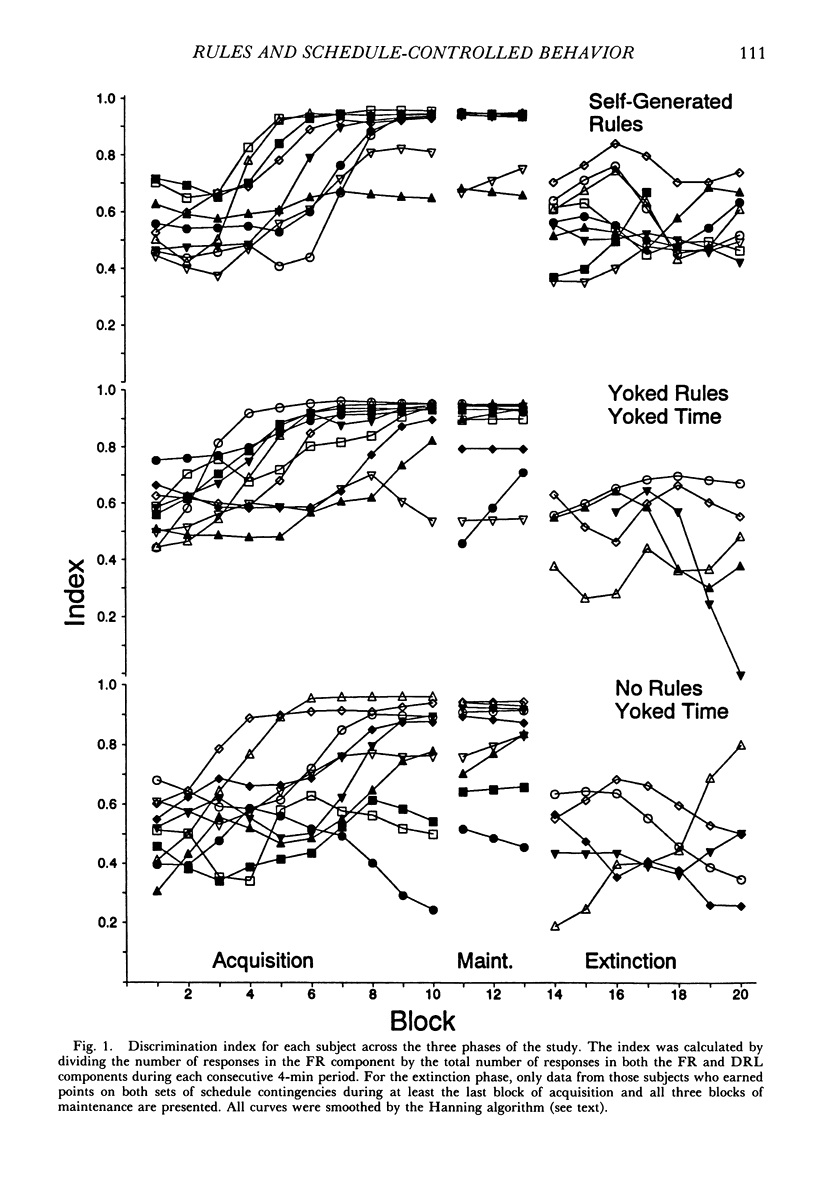
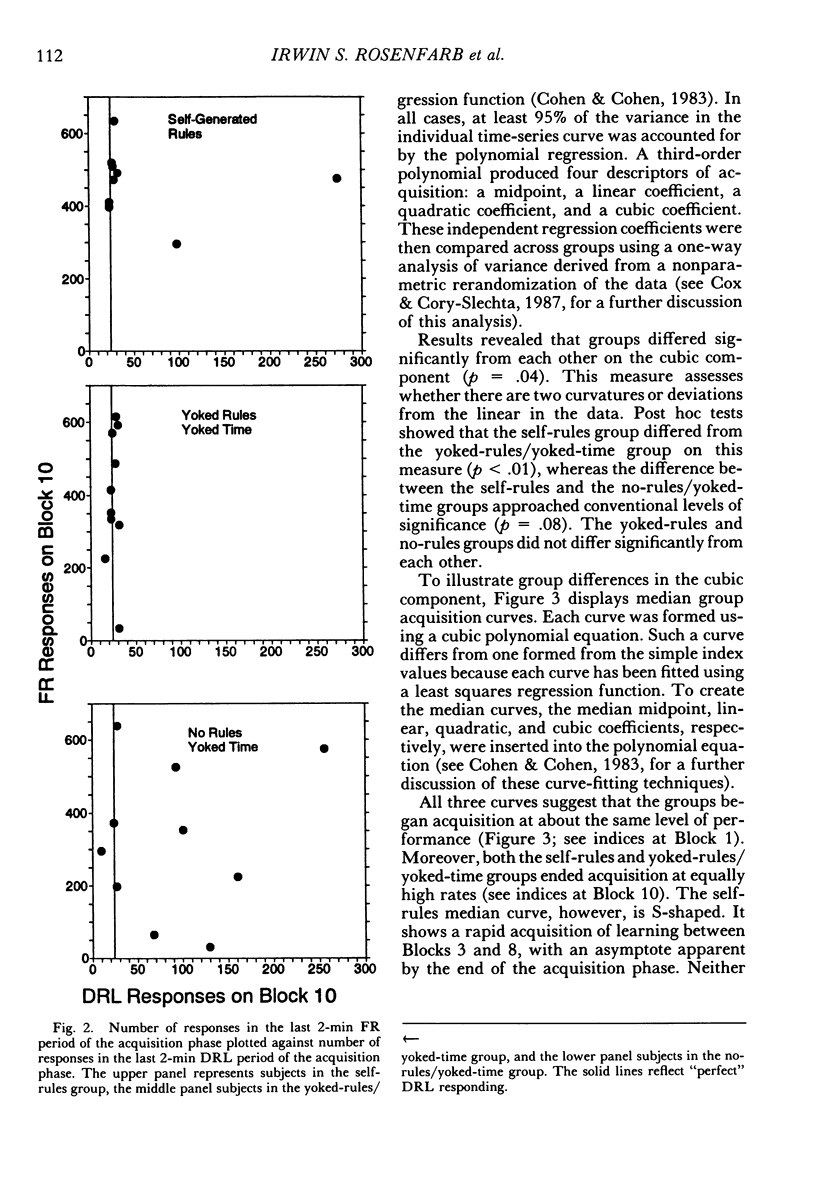
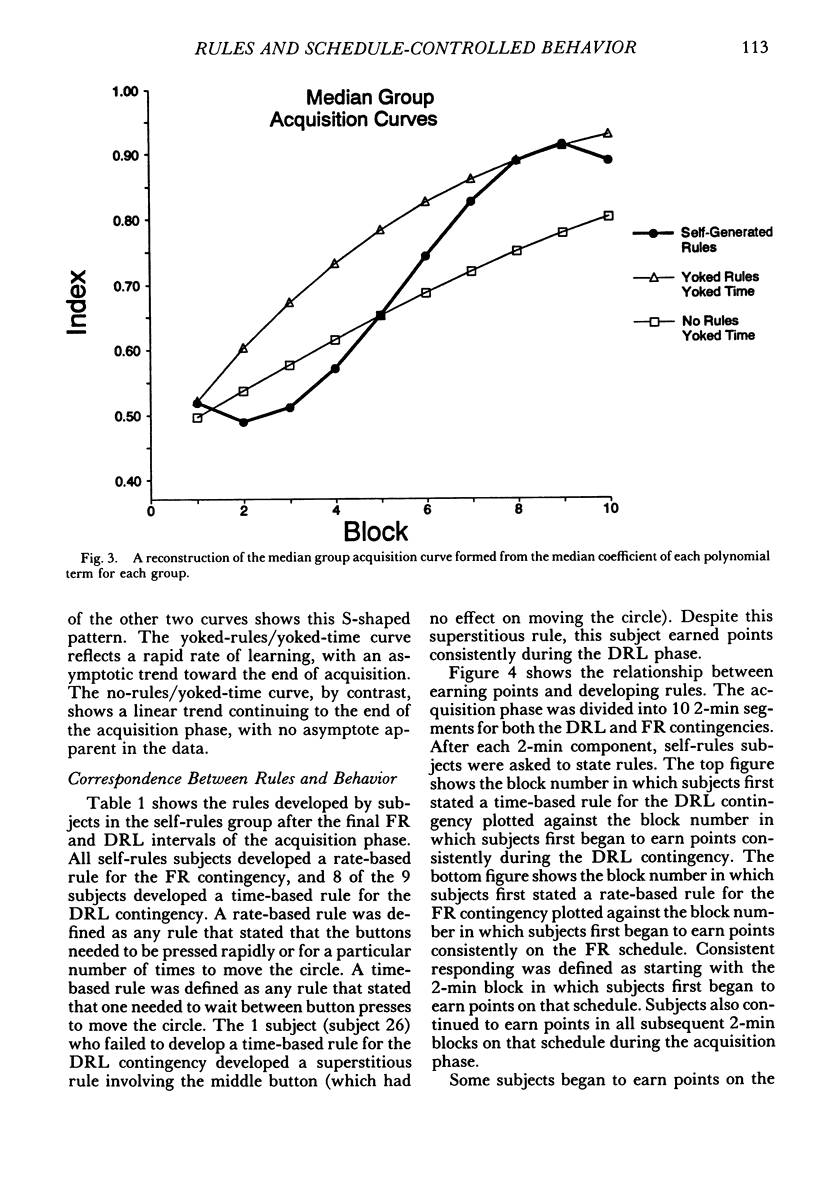
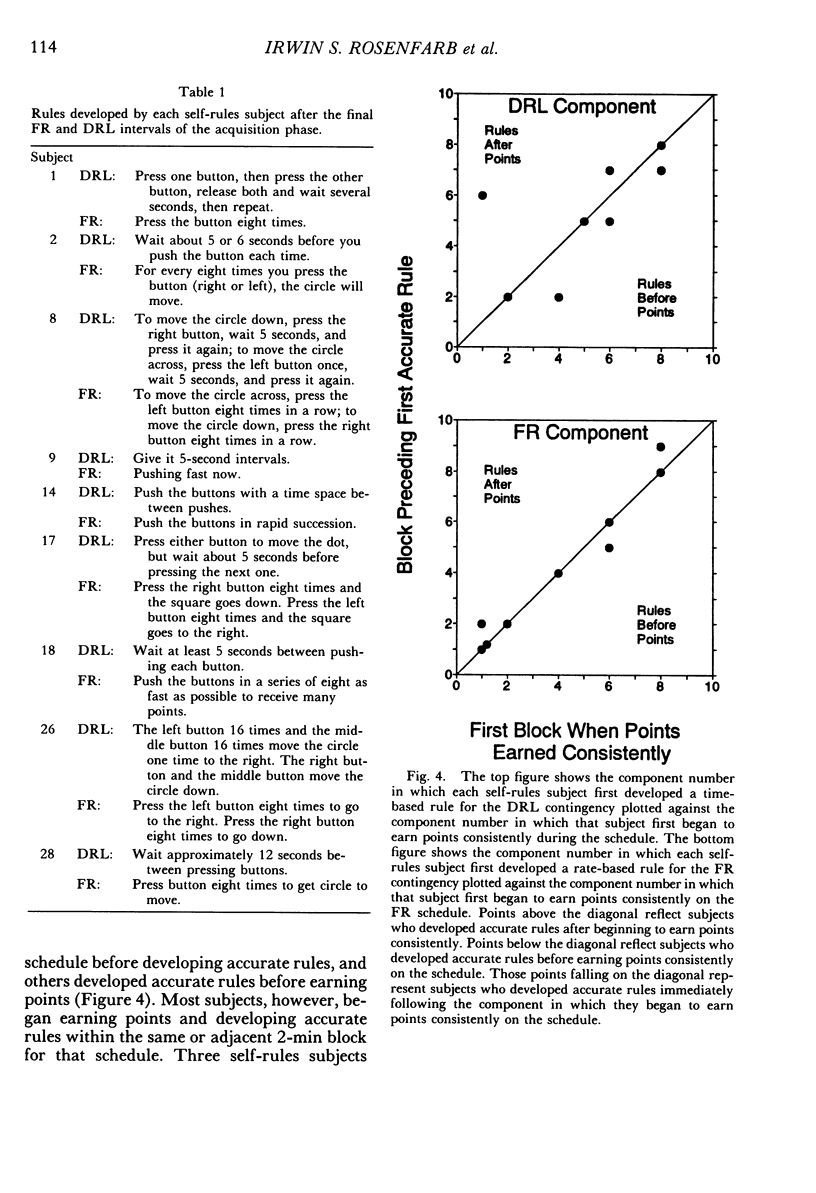
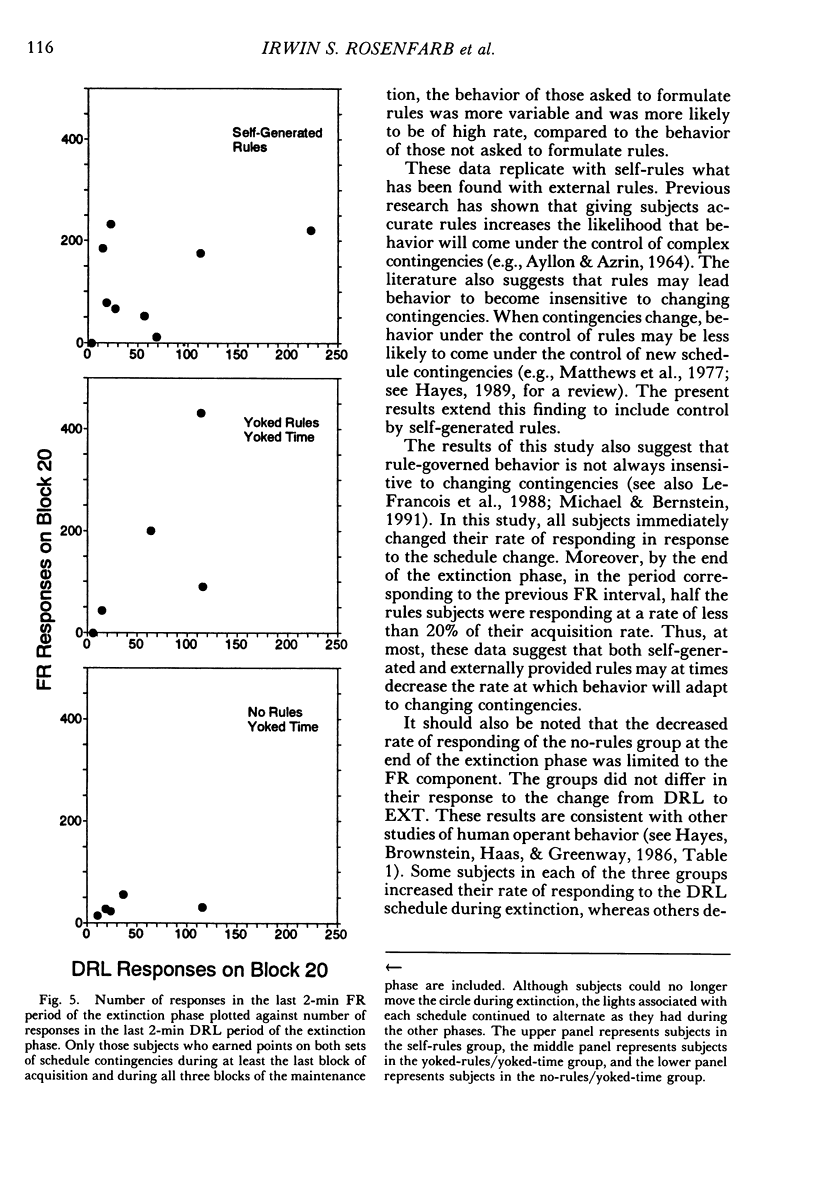
College students responded under a multiple differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate 5-s fixed-ratio 8 schedule, with components alternating every 2 min. After 40 programmed minutes of acquisition and 12 min of maintenance, without notice, both schedules changed to extinction for 28 min. During acquisition, between alternations of the multiple schedule, some subjects were asked to develop rules describing the schedule contingencies. Other subjects were given these same rules between alternations, and a third group neither received nor were asked to develop rules. By the end of the acquisition phase, self-generated-rule subjects were more likely to show schedule-typical behavior than were subjects not asked to generate rules. The behavior of those given rules was similar to those asked to generate rules at the end of acquisition, but yoked-rule subjects acquired schedule-typical behavior at a quicker rate. By the end of extinction, during the period corresponding to the previous fixed-ratio interval, all no-rule subjects who had earned points during acquisition and maintenance were responding at a rate of less than 30 responses per minute. Only 3 of the 9 self-generated-rule subjects and 2 of the 5 yoked-rule subjects were similarly responding at this low rate. Results suggest that asking subjects to develop self-rules facilitates acquisition, but can retard extinction. Results also suggest that self-generated rules function similarly to external rules.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYLLON T., AZRIN N. H. REINFORCEMENT AND INSTRUCTIONS WITH MENTAL PATIENTS. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jul;7:327–331. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams D. B., Wilson G. T. Self-monitoring and reactivity in the modification of cigarette smoking. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1979 Apr;47(2):243–251. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.47.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Kaufman A., Stauber K. A. Effects of instructions and reinforcement-feedback on human operant behavior maintained by fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):701–712. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Matthews B. A., Shimoff E. Instructed versus shaped human verbal behavior: Interactions with nonverbal responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Nov;38(3):233–248. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.38-233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C., Cory-Slechta D. A. Analysis of longitudinal "time series" data in toxicology. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1987 Feb;8(2):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(87)90114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchfield T. S., Perone M. Verbal self-reports of delayed matching to sample by humans. J Exp Anal Behav. 1990 May;53(3):321–344. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1990.53-321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizio M. Contingency-shaped and rule-governed behavior: instructional control of human loss avoidance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Jan;31(1):53–70. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.31-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H. A comparison of several procedures for eliminating behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:399–406. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. C., Brownstein A. J., Haas J. R., Greenway D. E. Instructions, multiple schedules, and extinction: Distinguishing rule-governed from schedule-controlled behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Sep;46(2):137–147. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.46-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. C., Brownstein A. J., Zettle R. D., Rosenfarb I., Korn Z. Rule-governed behavior and sensitivity to changing consequences of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 May;45(3):237–256. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois J. R., Chase P. N., Joyce J. H. The effects of a variety of instructions on human fixed-interval performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 May;49(3):383–393. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. A., Shimoff E., Catania A. C., Sagvolden T. Uninstructed human responding: sensitivity to ratio and interval contingencies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 May;27(3):453–467. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael R. L., Bernstein D. J. Transient effects of acquisition history on generalization in a matching-to-sample task. J Exp Anal Behav. 1991 Jul;56(1):155–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1991.56-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. TEMPORALLY SPACED RESPONDING BY PIGEONS: DEVELOPMENT AND EFFECTS OF DEPRIVATION AND EXTINCTION. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Nov;7:415–421. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. Development of complex, stereotyped behavior in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Mar;33(2):153–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.33-153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoff E., Catania A. C., Matthews B. A. Uninstructed human responding: Sensitivity of low-rate performance to schedule contingencies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Sep;36(2):207–220. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.36-207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger C. D., DeNike L. D. Descriptive behaviorism versus cognitive theory in verbal operant conditioning. Psychol Rev. 1966 Jul;73(4):306–326. doi: 10.1037/h0023454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


