Abstract
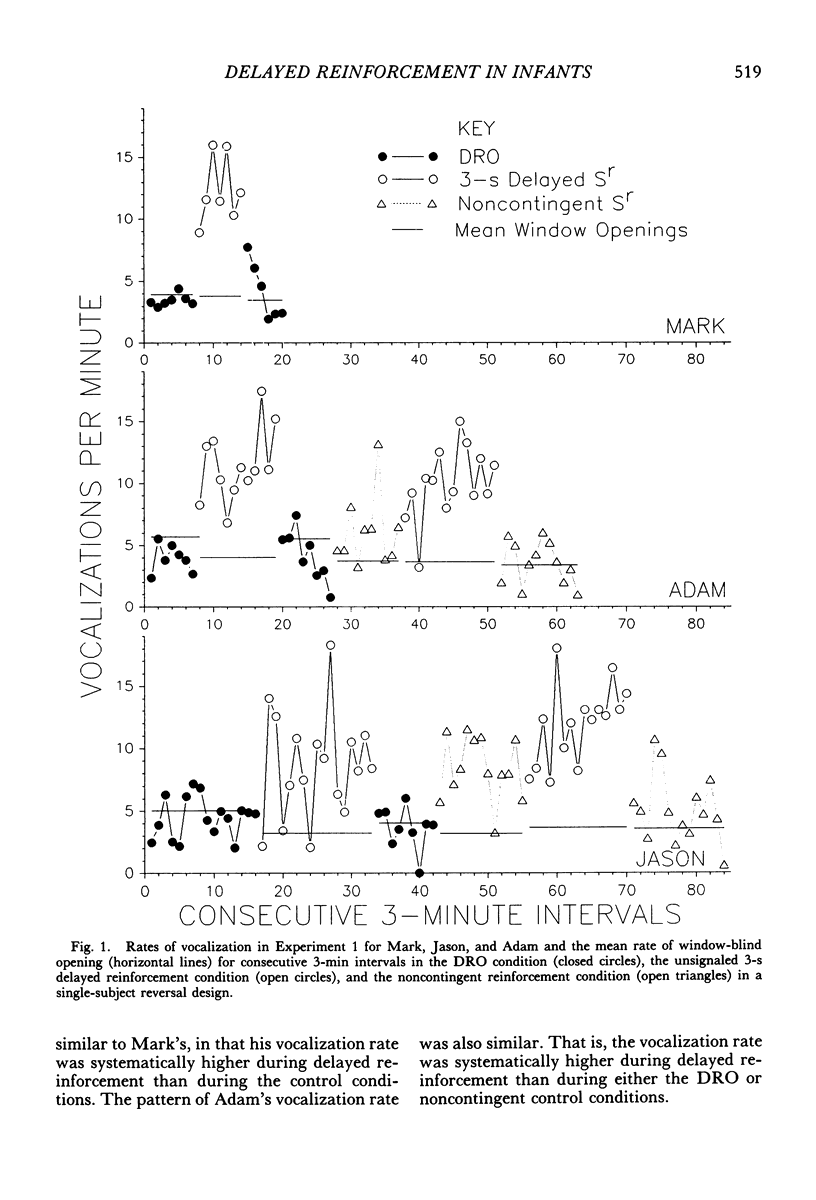
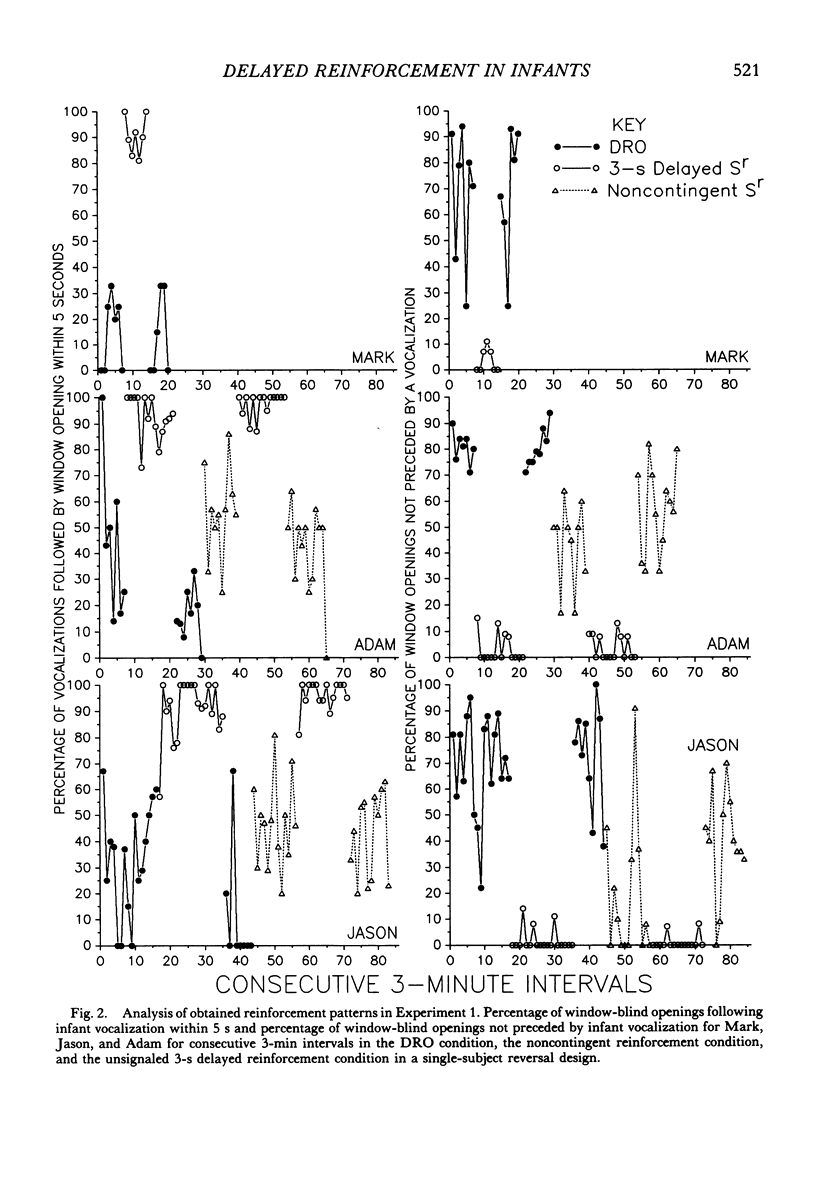
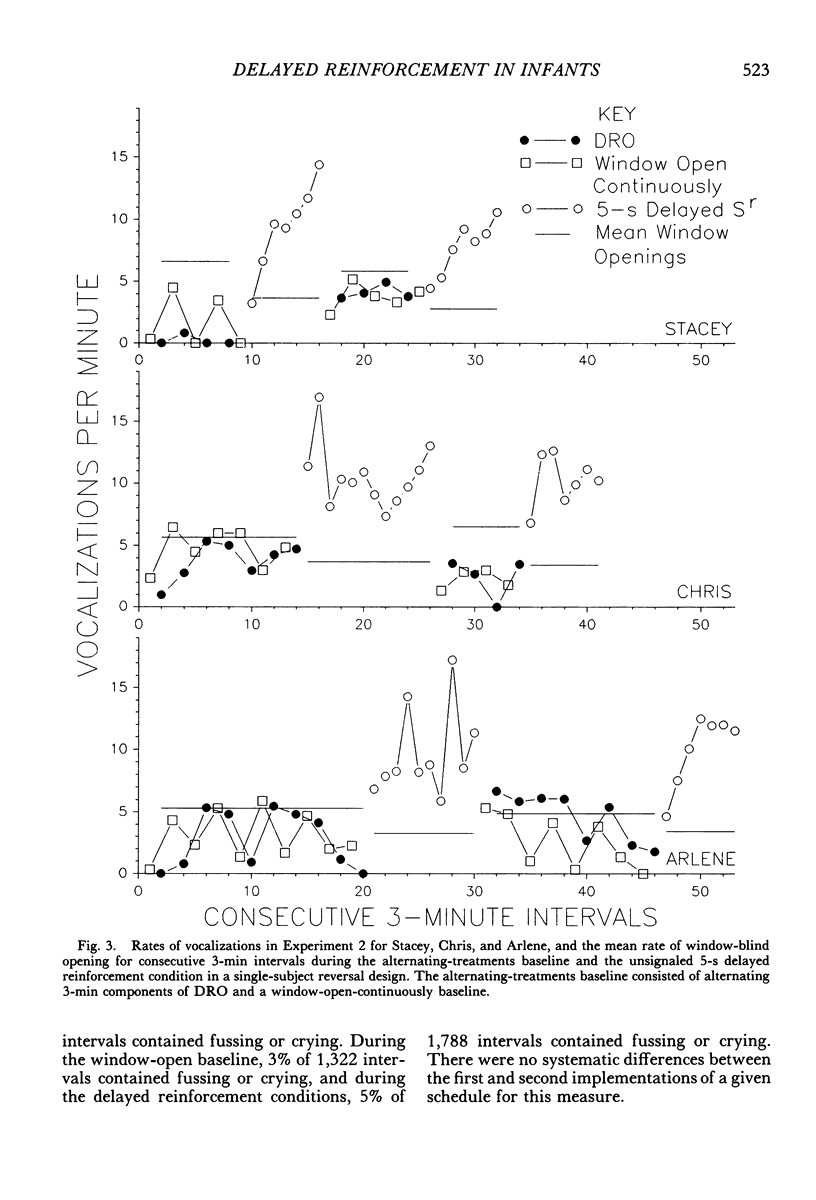
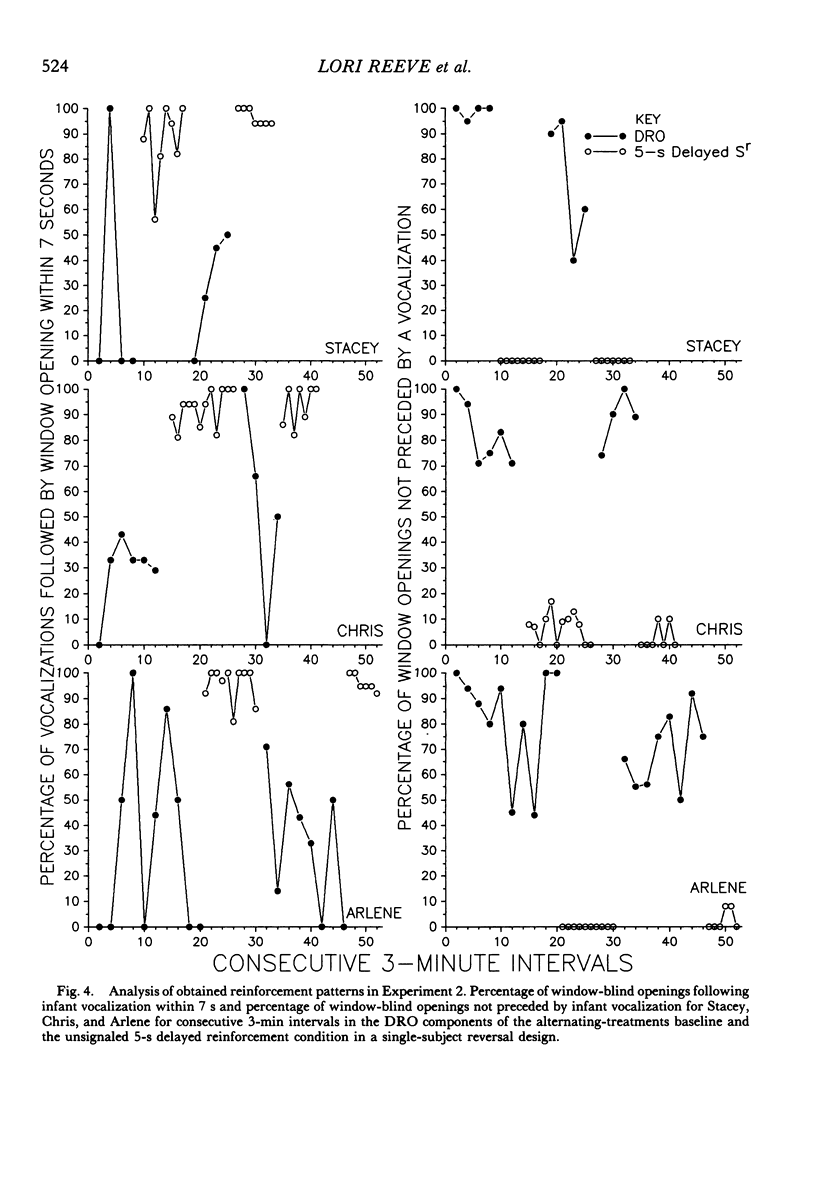
This study is an exploration of the parameters of delayed reinforcement with 6 infants (2 to 6 months old) in two experiments using single-subject repeated-reversal designs. In Experiment 1, unsignaled 3-s delayed reinforcement was used to increase infant vocalization rate when compared to a differential-reinforcement-of-other-than-vocalization condition and a yoked, no-contingency comparison condition. In Experiment 2, unsignaled 5-s delayed reinforcement was used to increase infant vocalization rate when compared to an alternating-treatments comparison condition. The alternating-treatments comparison consisted of 3-min components of differential reinforcement of other behavior and 3-min components of a nontreatment baseline. Successful conditioning was obtained in both experiments. These results contrast with those of previous infancy researchers who did not obtained conditioning with delays of 3 s and who attributed their findings to the limitations of the infant's memory capacity. We present an alternative conceptual framework and methodology for the analysis of delayed reinforcement in infants.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZZI R., FIX D. S., KELLER F. S., ROCHAESILVA M. I. EXTEROCEPTIVE CONTROL OF RESPONSE UNDER DELAYED REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:159–162. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. Free-operant behavior under conditions of delayed reinforcement. I. CRF-type schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:221–234. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B., HAMMER C. VARIABLES DETERMINING THE EFFECTS OF DELAY IN REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jul;8:243–254. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B. Sustained behavior under delayed reinforcement. J Exp Psychol. 1953 Apr;45(4):218–224. doi: 10.1037/h0062158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson S., Lattal K. A. Response-reinforcer relations and the maintenance of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 Nov;48(3):383–393. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.48-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattal K. A. Combinations of response-reinforcer dependence and independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Sep;22(2):357–362. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar W. S., Watson J. S. The effect of delayed feedback on infant learning reexamined. Child Dev. 1979 Sep;50(3):747–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. H., Hanford P. V., Zimmerman J. Effects of different delay of reinforcement procedures on variable-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):141–146. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulson C. L., Nunes L. R. The infant vocal-conditioning literature: a theoretical and methodological critique. J Exp Child Psychol. 1988 Dec;46(3):438–450. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(88)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramey C. T., Ourth L. L. Delayed reinforcement and vocalization rates of infants. Child Dev. 1971 Mar;42(1):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve L., Reeve K. F., Brown A. K., Brown J. L., Poulson C. L. Effects of delayed reinforcement on infant vocalization rate. J Exp Anal Behav. 1992 Jul;58(1):1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1992.58-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. W. A comparison of signaled and unsignaled delay of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Mar;35(2):145–152. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaal D. W., Branch M. N. Responding of pigeons under variable-interval schedules of signaled-delayed reinforcement: effects of delay-signal duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1990 Jan;53(1):103–121. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1990.53-103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaal D. W., Branch M. N. Responding of pigeons under variable-interval schedules of unsignaled, briefly signaled, and completely signaled delays to reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jul;50(1):33–54. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.50-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore O. J., Lattal K. A. Dependency, temporal contiguity, and response-independent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Jan;27(1):119–125. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. The effects of unsignalled delayed reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Nov;26(3):441–449. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


