Abstract
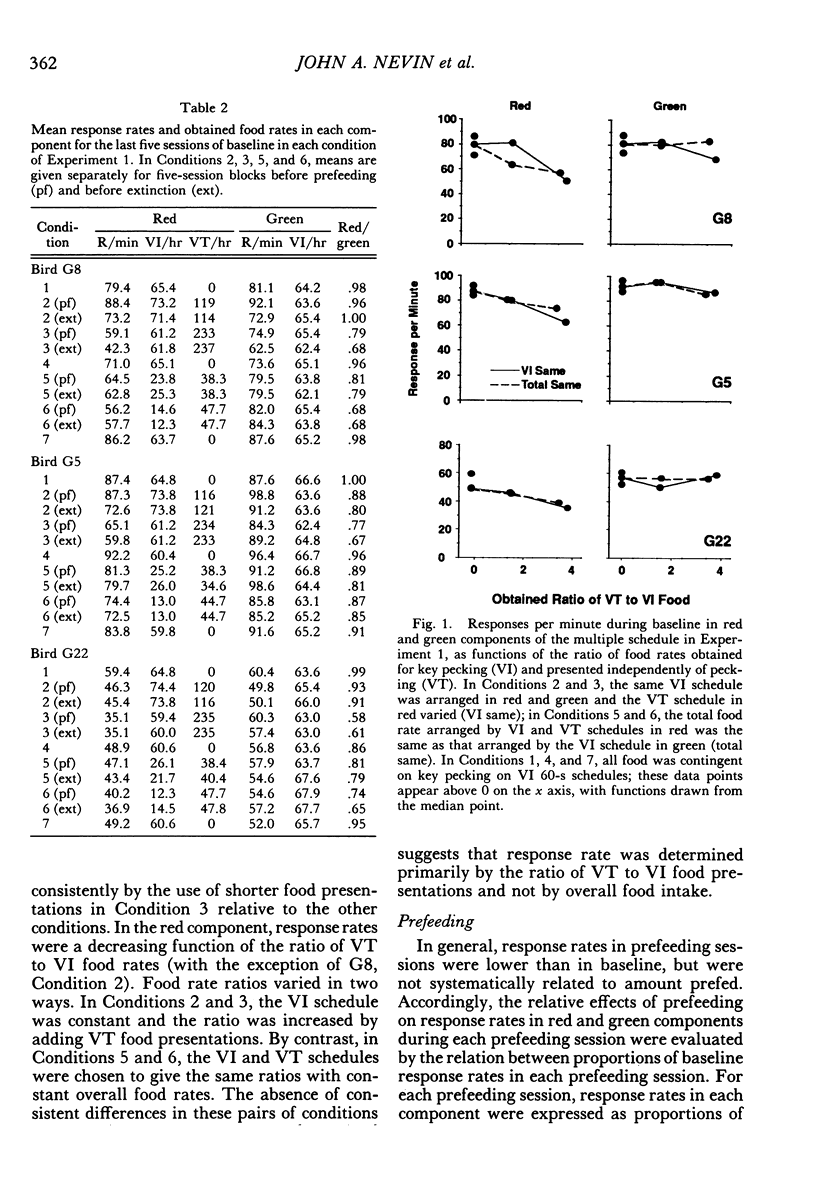
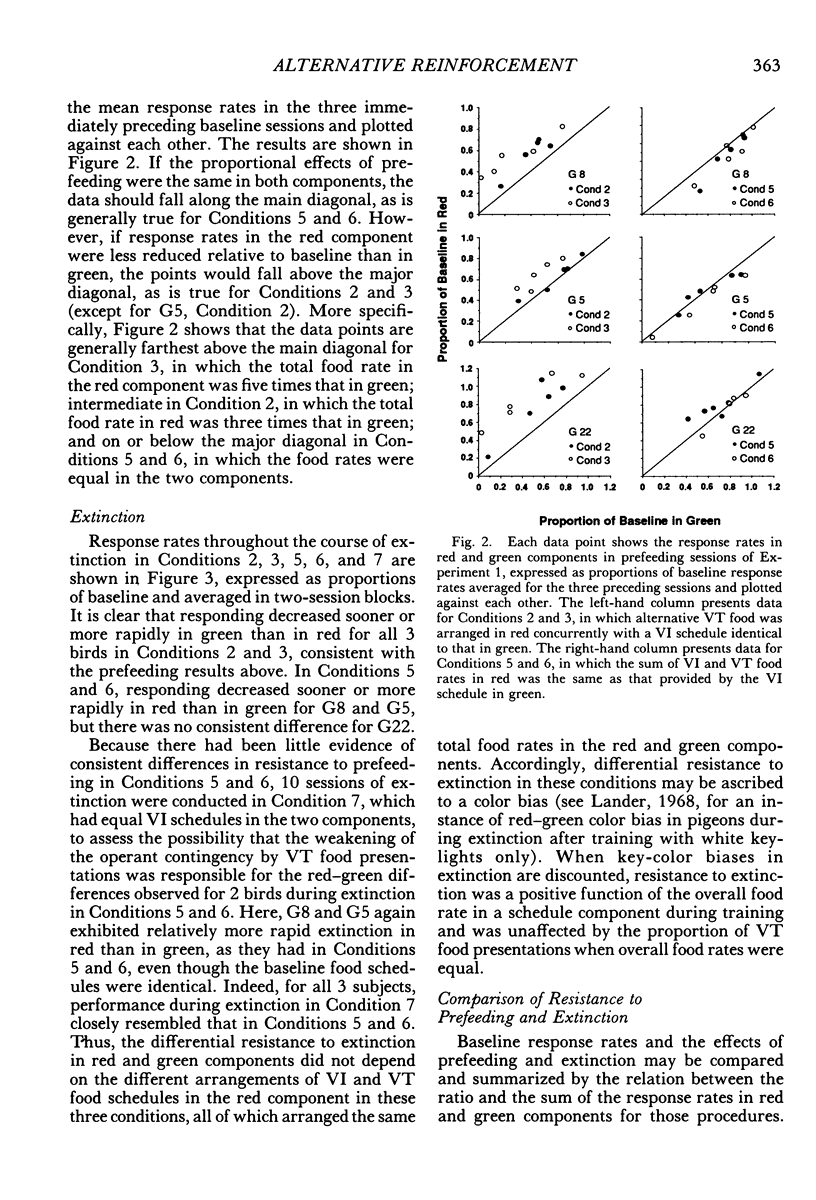
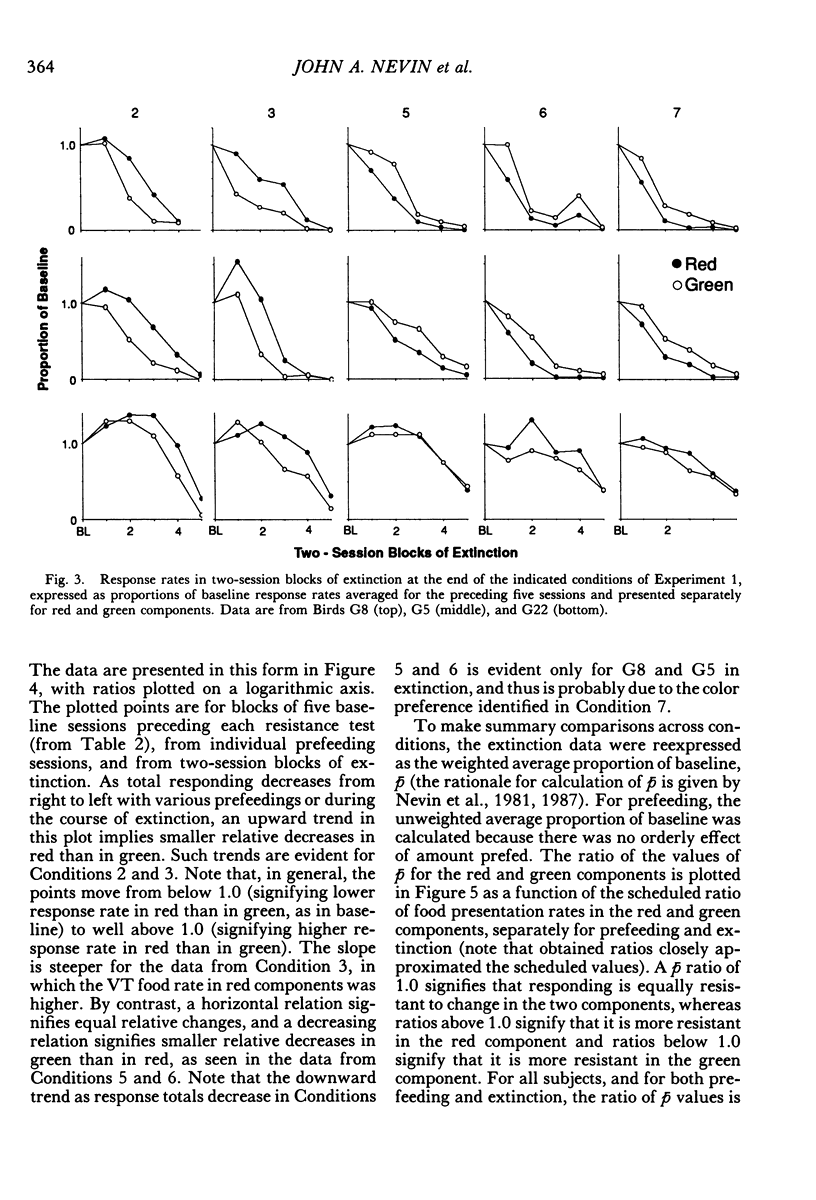
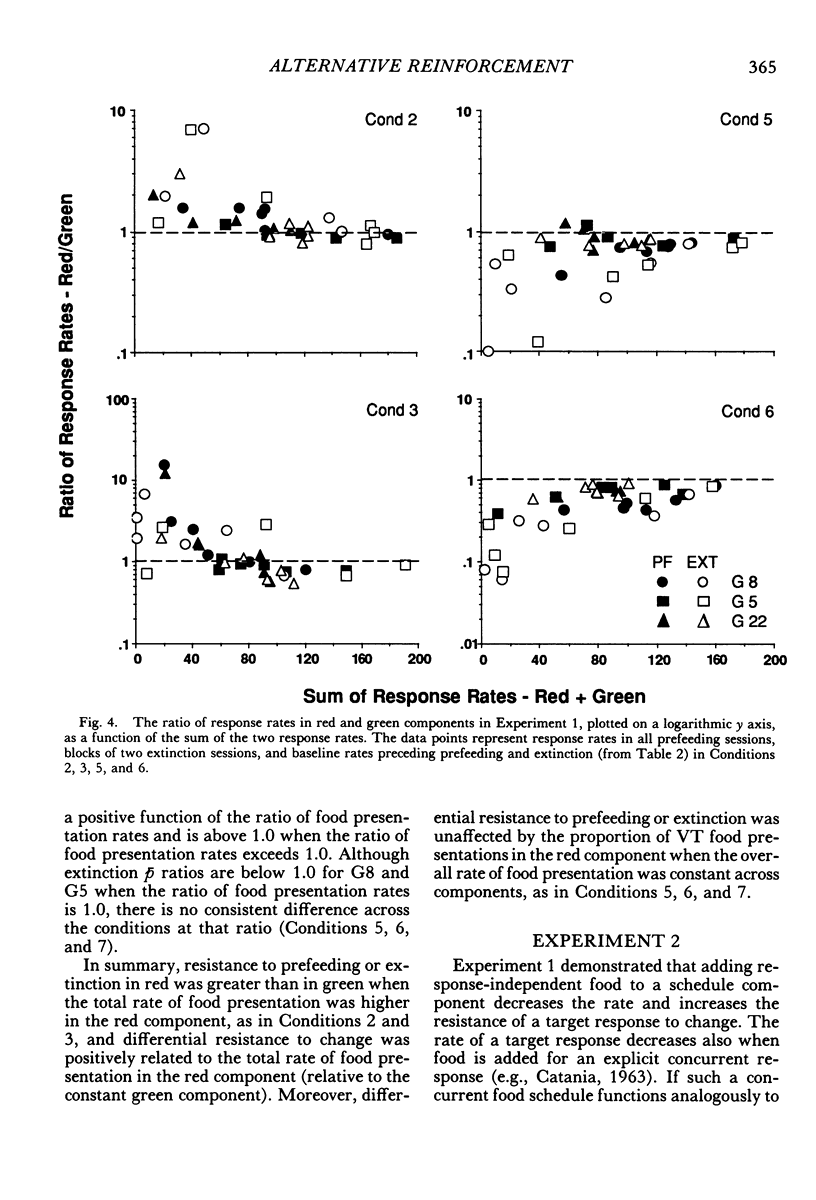
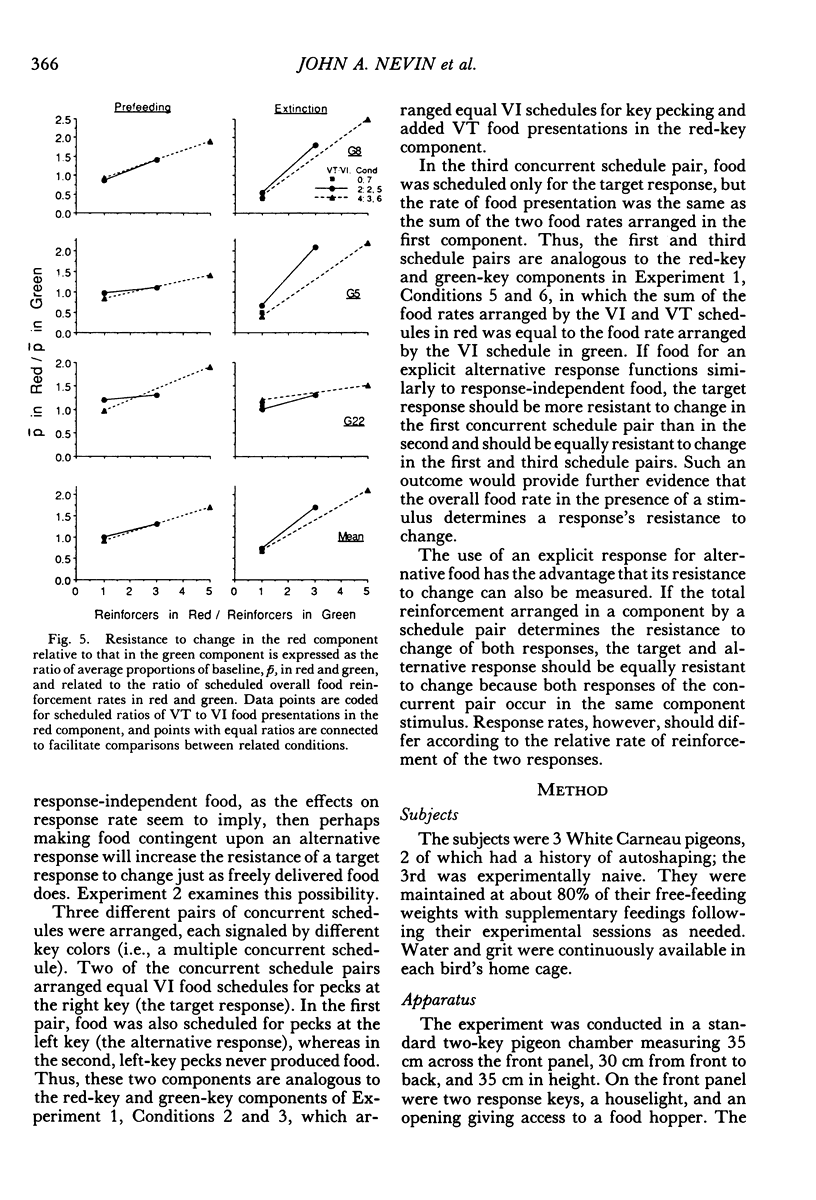
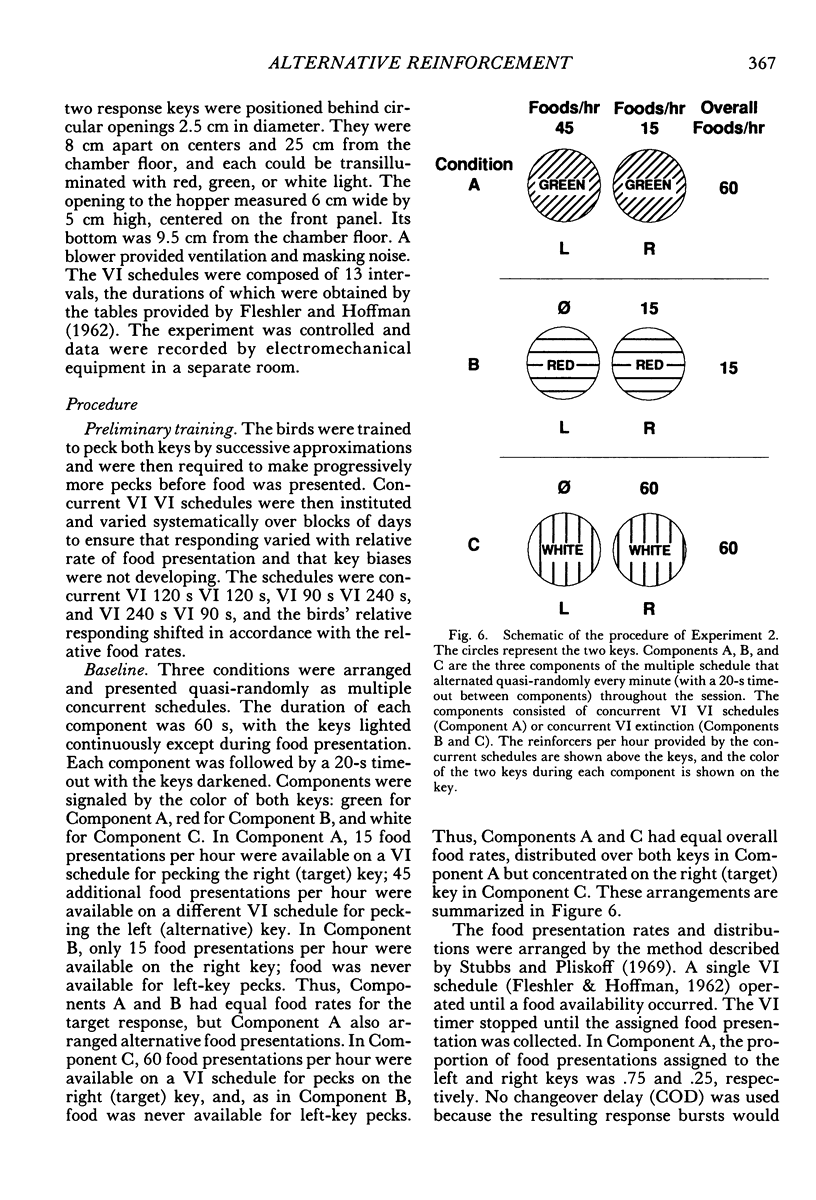
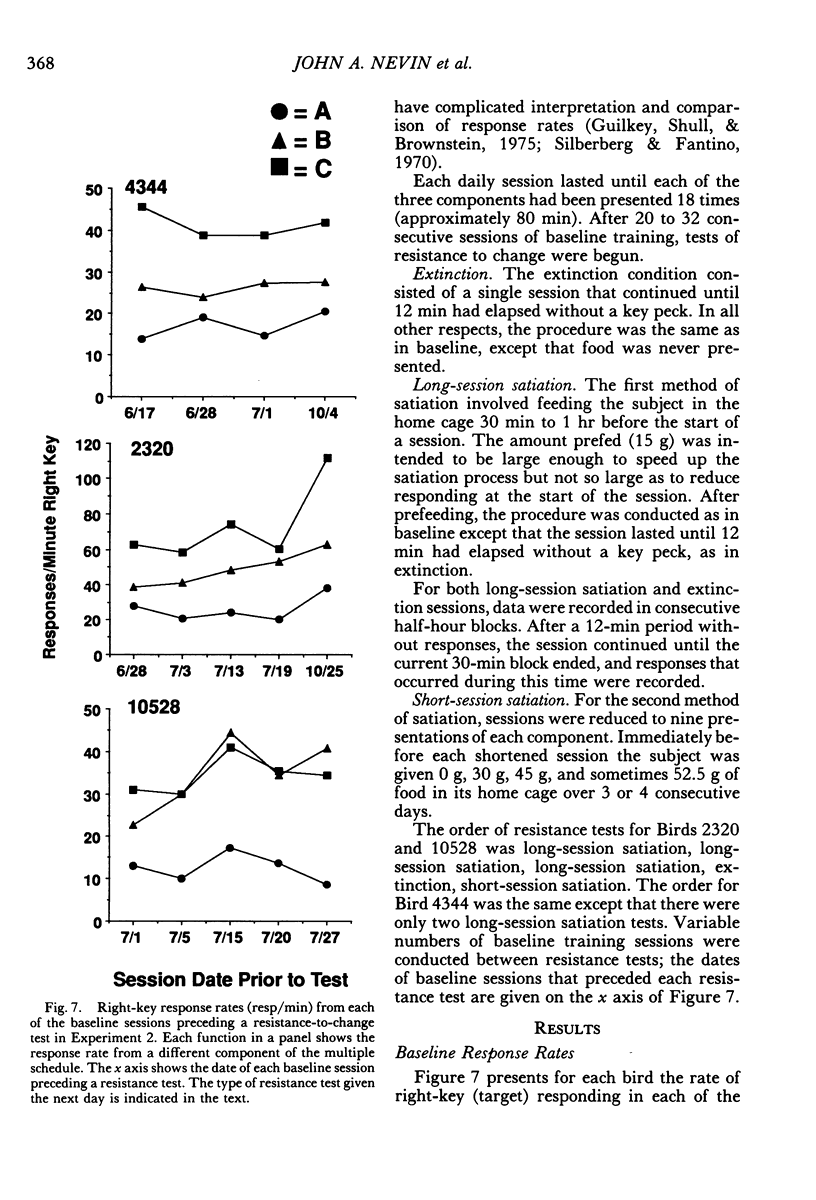
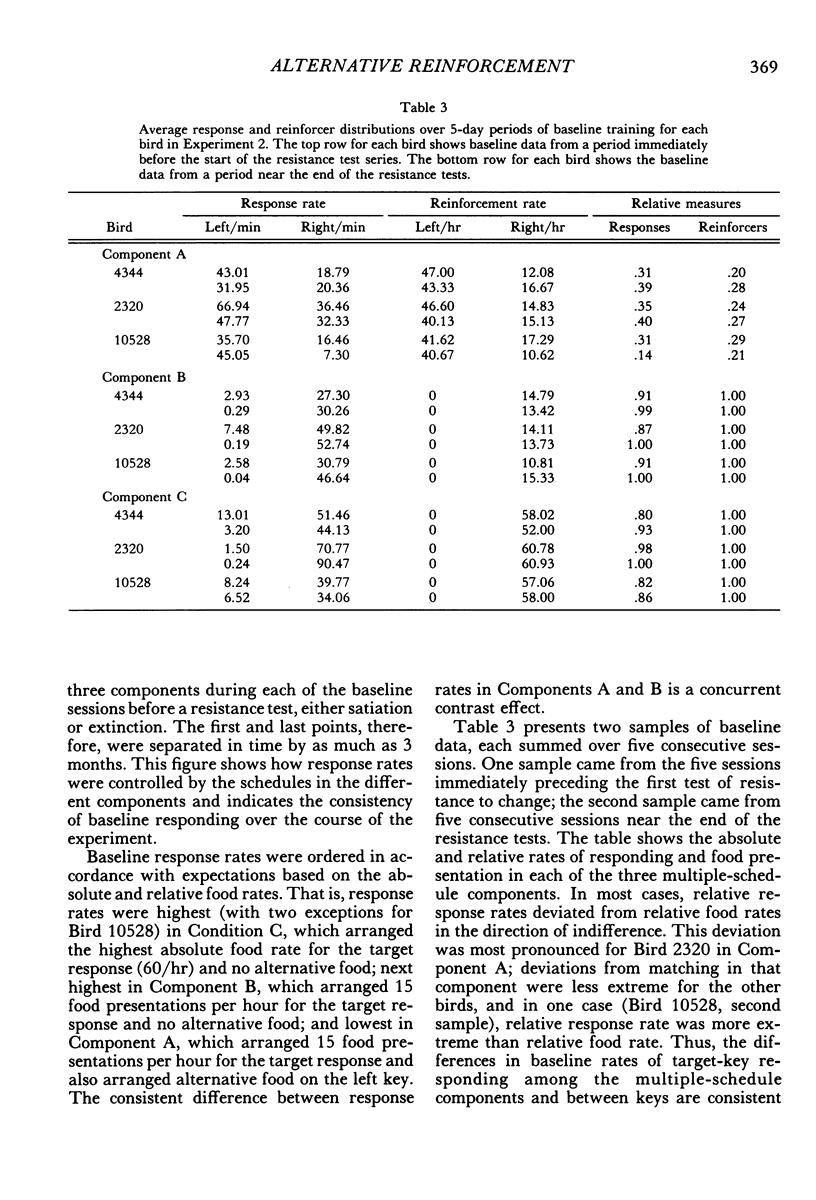
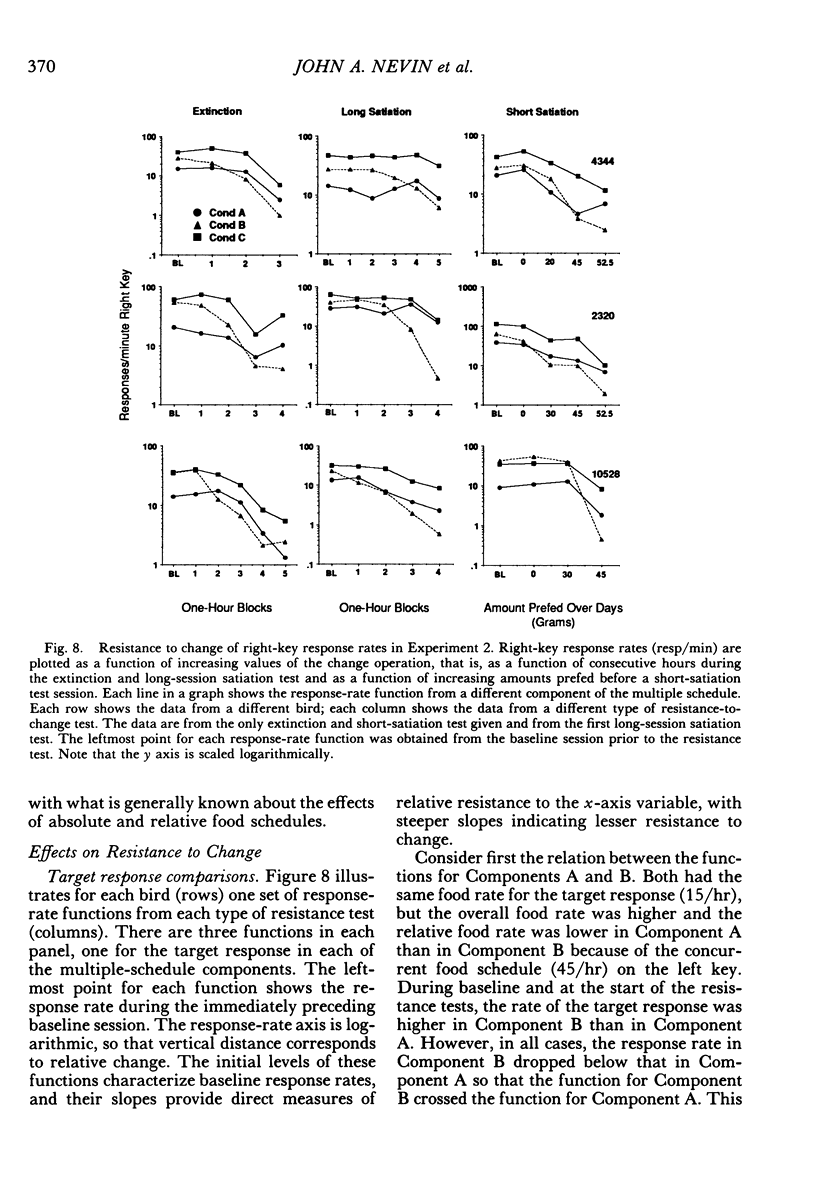
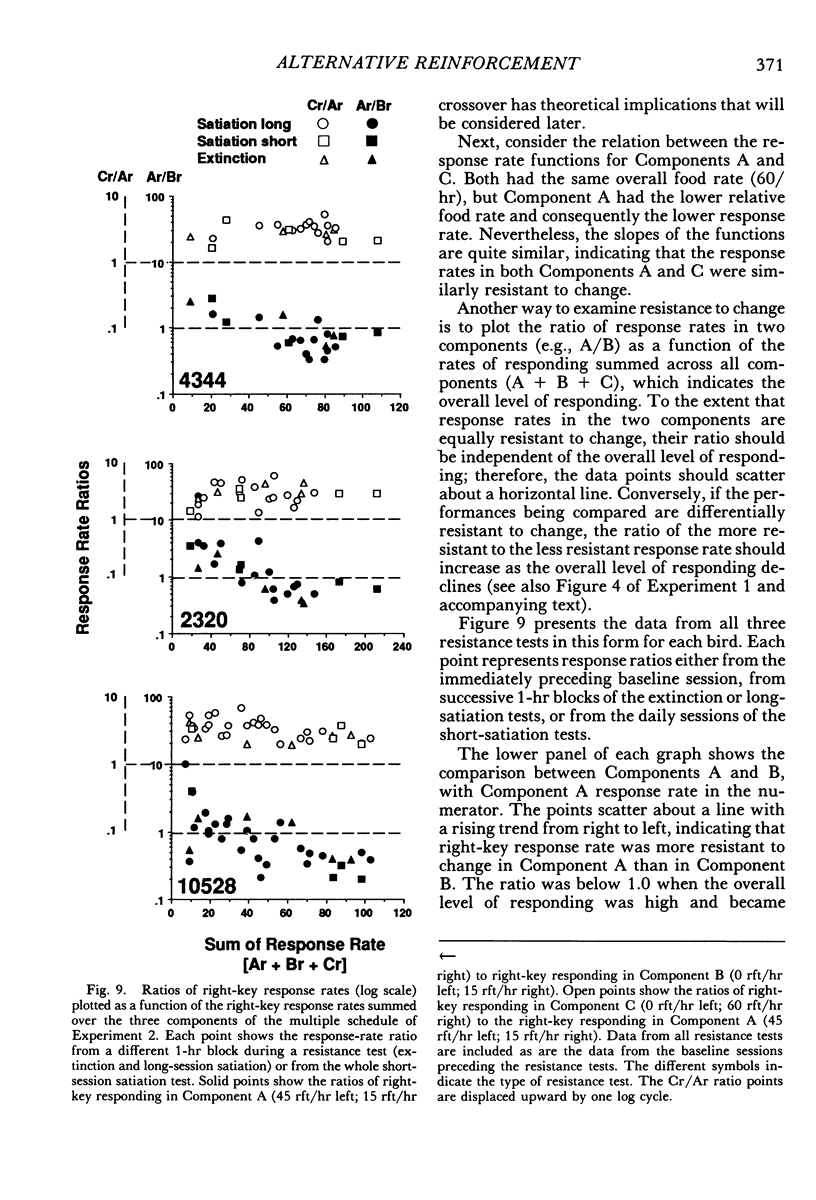
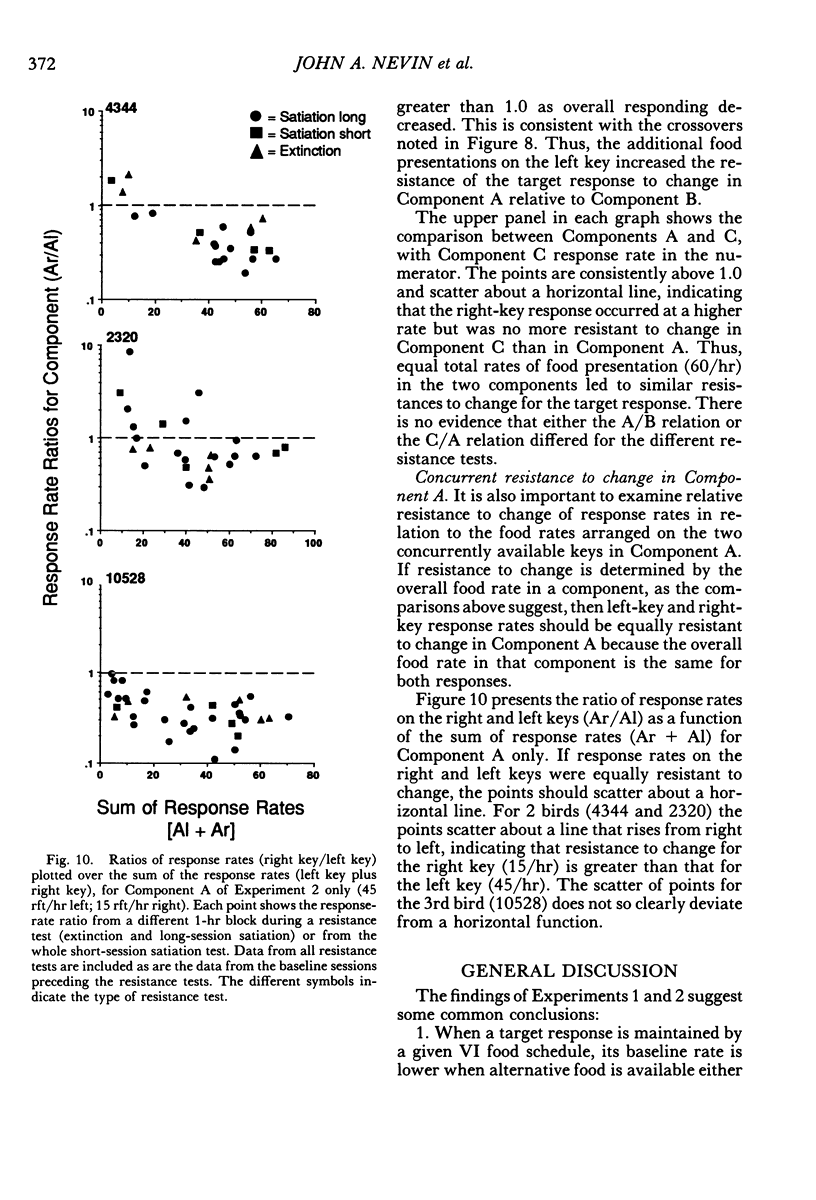
Two multiple-schedule experiments with pigeons examined the effect of adding food reinforcement from an alternative source on the resistance of the reinforced response (target response) to the decremental effects of satiation and extinction. In Experiment 1, key pecks were reinforced by food in two components according to variable-interval schedules and, in some conditions, food was delivered according to variable-time schedules in one of the components. The rate of key pecking in a component was negatively related to the proportion of reinforcers from the alternative (variable-time) source. Resistance to satiation and extinction, in contrast, was positively related to the overall rate of reinforcement in the component. Experiment 2 was conceptually similar except that the alternative reinforcers were contingent on a specific concurrent response. Again, the rate of the target response varied as a function of its relative reinforcement, but its resistance to satiation and extinction varied directly with the overall rate of reinforcement in the component stimulus regardless of its relative reinforcement. Together the results of the two experiments suggest that the relative reinforcement of a response (the operant contingency) determines its rate, whereas the stimulus-reinforcement contingency (a Pavlovian contingency) determines its resistance to change.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Matching, undermatching, and overmatching in studies of choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Sep;32(2):269–281. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boakes R. A., Halliday M. S., Poli M. Response additivity: effects of superimposed free reinforcement on a variable-interval baseline. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Mar;23(2):177–191. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein A. J., Pliskoff S. S. Some effects of relative reinforcement rate and changeover delay in response-independent concurrent schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):683–688. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess I. S., Wearden J. H. Superimposition of response-independent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Jan;45(1):75–82. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C. Concurrent performances: inhibition of one response by reinforcement of another. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):731–744. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath S. J., Fields L., Malott M. K., Grossett D. Response rate, latency, and resistance to change. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Mar;39(2):267–274. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT T. F. Fundamental dimensional properties of the operant. Psychol Rev. 1958 Sep;65(5):272–282. doi: 10.1037/h0044071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbon J., Berryman R., Thompson R. L. Contingency spaces and measures in classical and instrumental conditioning. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):585–605. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilkey M., Shull R. L., Brownstein A. J. Response-rate invariance in concurrent schedules: effects of different changeover contingencies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jul;24(1):43–52. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.24-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond L. J. The effect of contingency upon the appetitive conditioning of free-operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Nov;34(3):297–304. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G. Stimulus bias in the absence of food reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):711–714. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE W. H., SKINNER B. F. Some factors involved in the stimulus control of operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Jan;1:103–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon R. C., Shull R. L. Resistance to change produced by access to fixed-delay versus variable-delay terminal links. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Jul;46(1):79–92. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.46-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerson J., Hale S. Choice in transition: A comparison of melioration and the kinetic model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Mar;49(2):291–302. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Interval reinforcement of choice behavior in discrete trials. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):875–885. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Response strength in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):389–408. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Smith L. D., Roberts J. Does contingent reinforcement strengthen operant behavior? J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 Jul;48(1):17–33. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.48-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pear J. J., Rector B. L. Constituents of response rates. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Nov;32(3):341–362. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Effects of alternative reinforcement: does the source matter? J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):231–241. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla R. A. Probability of shock in the presence and absence of CS in fear conditioning. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1968 Aug;66(1):1–5. doi: 10.1037/h0025984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla R. A., Solomon R. L. Two-process learning theory: Relationships between Pavlovian conditioning and instrumental learning. Psychol Rev. 1967 May;74(3):151–182. doi: 10.1037/h0024475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKINNER B. F. Are theories of learning necessary? Psychol Rev. 1950 Jul;57(4):193–216. doi: 10.1037/h0054367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg A., Fantino E. Choice, rate of reinforcement, and the changeover delay. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):187–197. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Royalty P. A test of the melioration theory of matching. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1989 Apr;15(2):99–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


