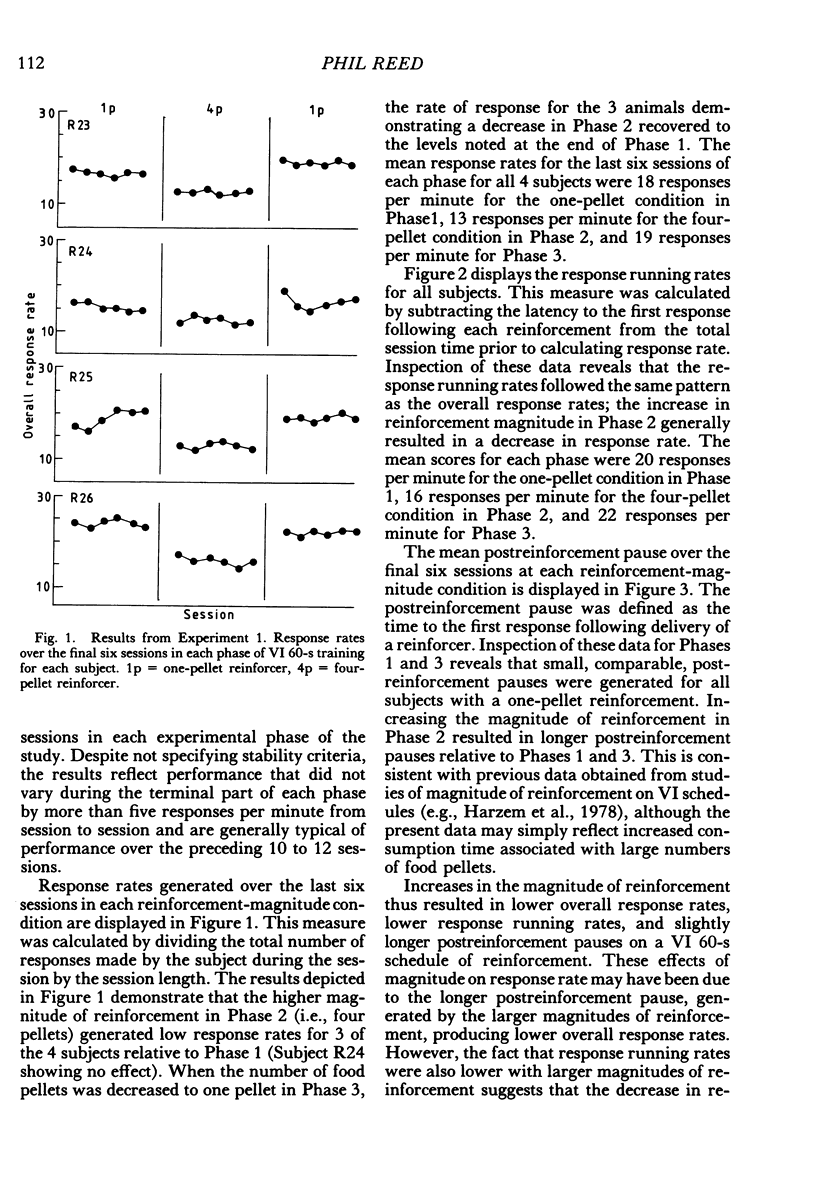
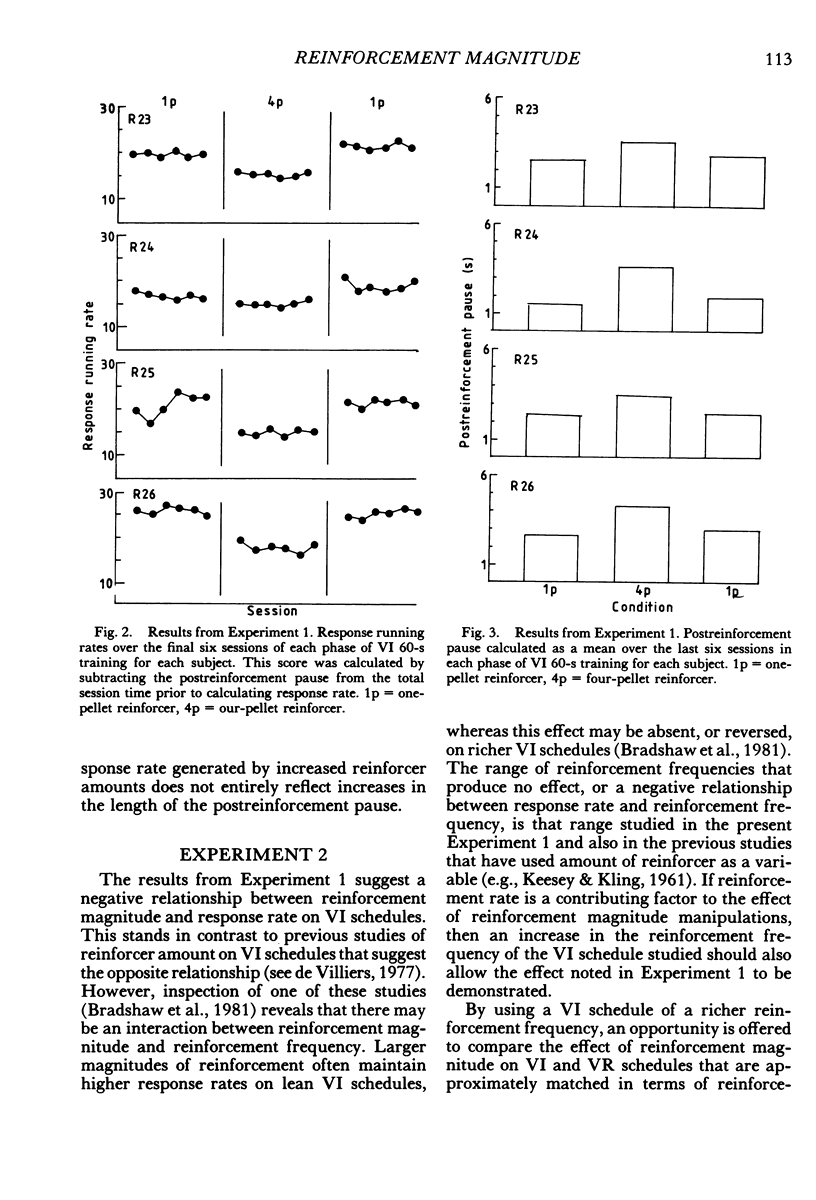
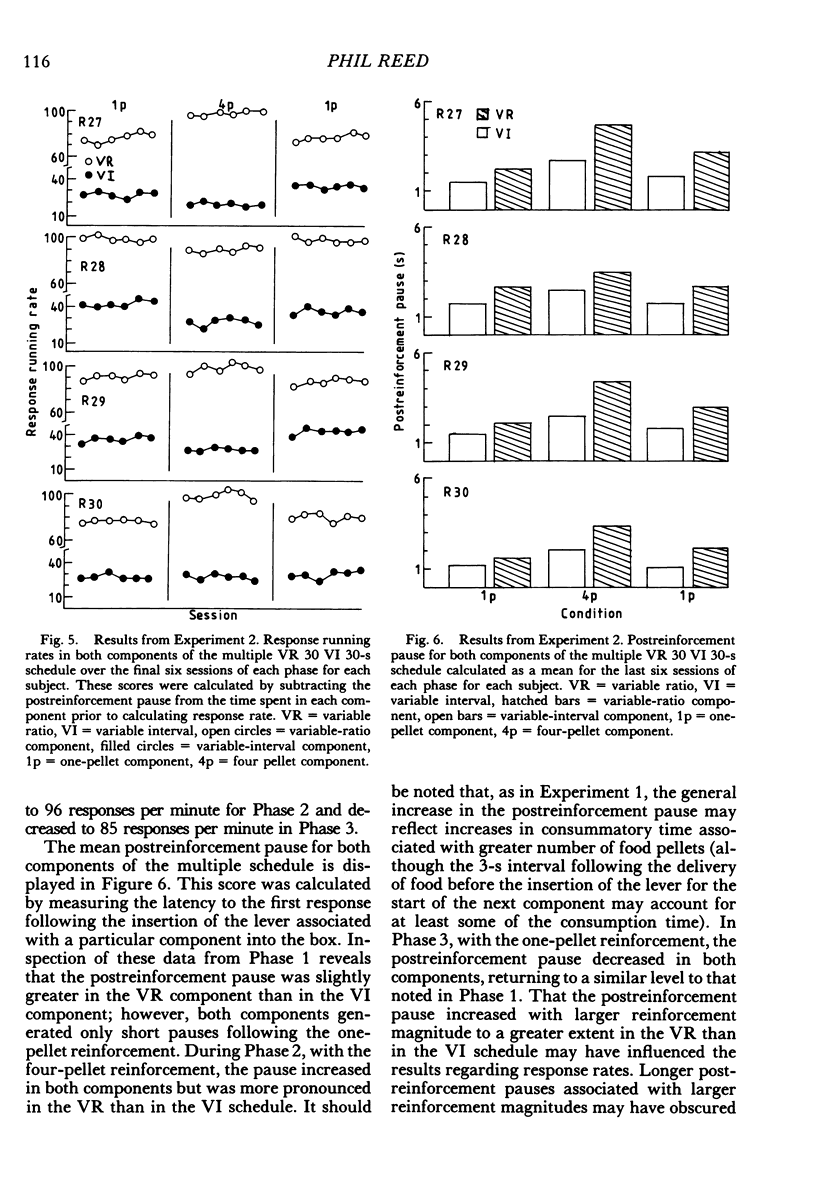
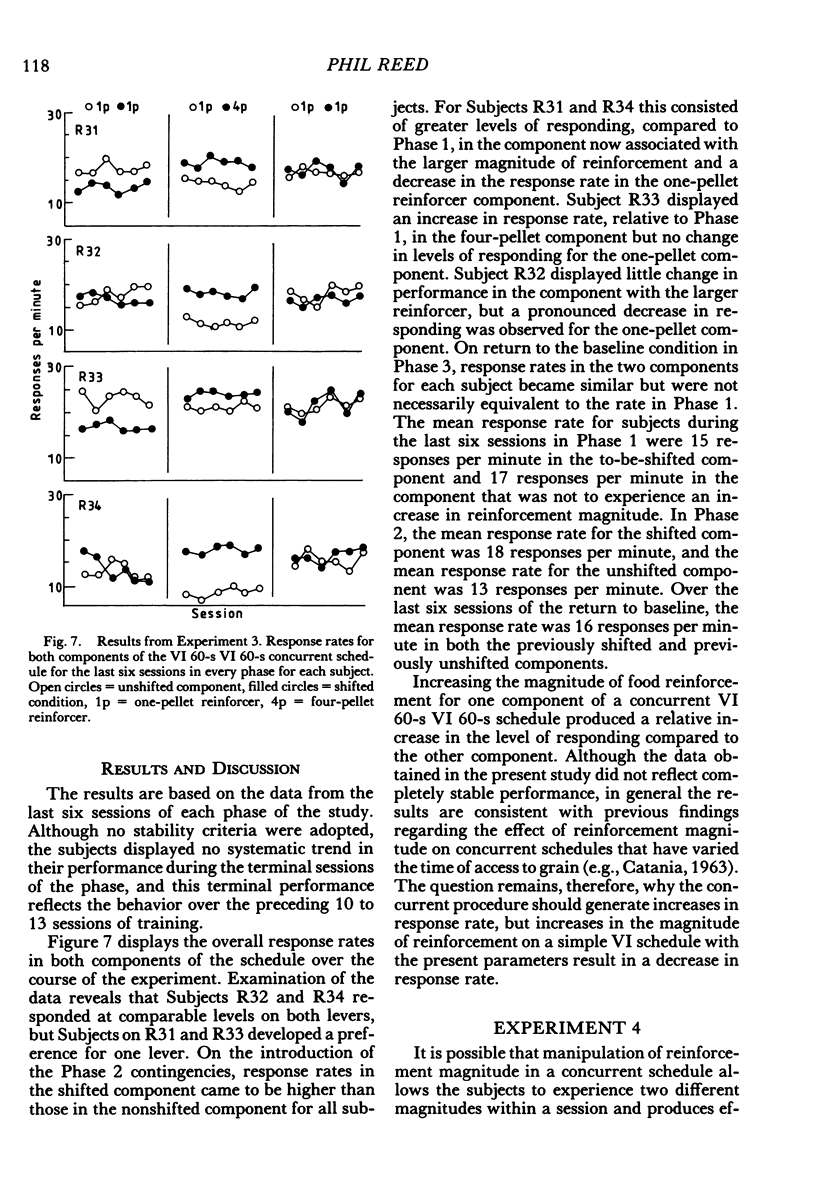
Abstract
Four experiments examined the effects of increasing the number of food pellets given to hungry rats for a lever-press response. On a simple variable-interval 60-s schedule, increased number of pellets depressed response rates (Experiment 1). In Experiment 2, the decrease in response rate as a function of increased reinforcement magnitude was demonstrated on a variable-interval 30-s schedule, but enhanced rates of response were obtained with the same increase in reinforcement magnitude on a variable-ratio 30 schedule. In Experiment 3, higher rates of responding were maintained by the component of a concurrent variable-interval 60-s variable-interval 60-s schedule associated with a higher reinforcement magnitude. In Experiment 4, higher rates of response were produced in the component of a multiple variable-interval 60-s variable-interval 60-s schedule associated with the higher reinforcement magnitude. It is suggested that on simple schedules greater reinforcer magnitudes shape the reinforced pattern of responding more effectively than do smaller reinforcement magnitudes. This effect is, however, overridden by another process, such a contrast, when two magnitudes are presented within a single session on two-component schedules.
Keywords: reinforcement magnitude, variable-interval schedules, variable-ratio schedules, concurrent schedules, multiple schedules, response shaping, contrast, lever press, rat
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakely E., Schlinger H. Determinants of pausing under variable-ratio schedules: Reinforcer magnitude, ratio size, and schedule configuration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jul;50(1):65–73. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.50-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw C. M., Ruddle H. V., Szabadi E. Relationship between response rate and reinforcement frequency in variable-interval schedules: II. Effect of the volume of sucrose reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 May;35(3):263–269. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E., Bevan P. Relationship between response rate and reinforcement frequency in variable-interval schedules: the effect of the concentration of sucrose reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 May;29(3):447–452. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskist W., Oliveira-Castro J., Bennett R. Some effects of response-correlated increases in reinforcer magnitude on human behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jan;49(1):87–94. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTTMAN N. Operant conditioning, extinction, and periodic reinforcement in relation to concentration of sucrose used as reinforcing agent. J Exp Psychol. 1953 Oct;46(4):213–224. doi: 10.1037/h0061893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. D., Eskew R. T. Graded differential reinforcement: Response-dependent reinforcer amount. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Jan;41(1):27–34. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.41-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRY D. P. The effect of correlated amount of reward on performance on a fixed-interval schedule of reinforcement. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1962 Jun;55:387–391. doi: 10.1037/h0046507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRY D. P., VAN-TOLLER C. PERFORMANCE ON A FIXED-RATIO SCHEDULE WITH CORRELATED AMOUNT OF REWARD. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:207–209. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harzem P., Lowe C. F., Priddle-Higson P. J. Inhibiting function of reinforcement: magnitude effects on variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jul;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. Formal properties of the matching law. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):159–164. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEESEY R. E., KLING J. W. Amount of reinforcement and free-operant responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:125–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. R. Incentive theory: IV. Magnitude of reward. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):407–417. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell R. W. The effect of reinforcement magnitude upon responding under fixed-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jul;12(4):605–608. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Relativity of response rate and reinforcement frequency in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:179–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P., Wright J. E. Effects of magnitude of food reinforcement on free-operant response rates. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jan;49(1):75–85. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRIER A. M. Comparison of two methods of investigating the effect of amount of reward on performance. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1958 Dec;51(6):725–731. doi: 10.1037/h0038761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuriff G. E. A comparison of variable-ratio and variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 May;13(3):369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


