Abstract
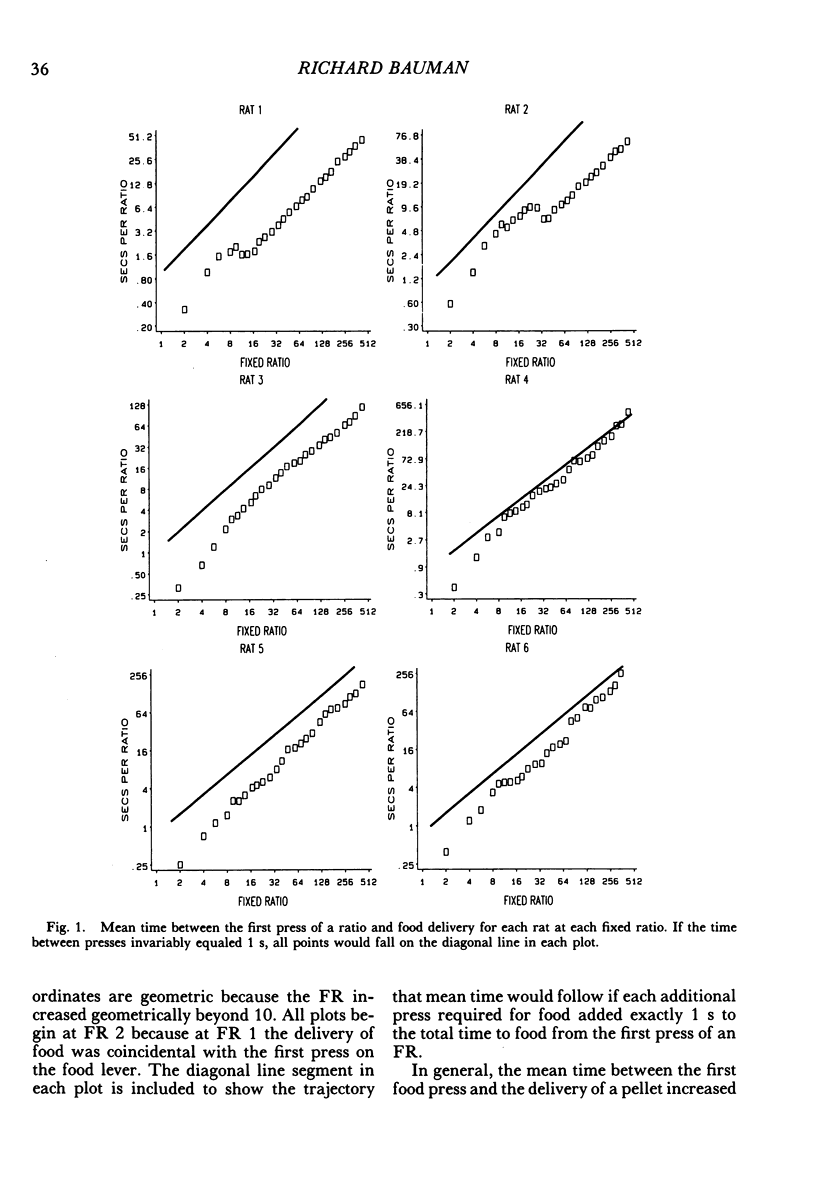
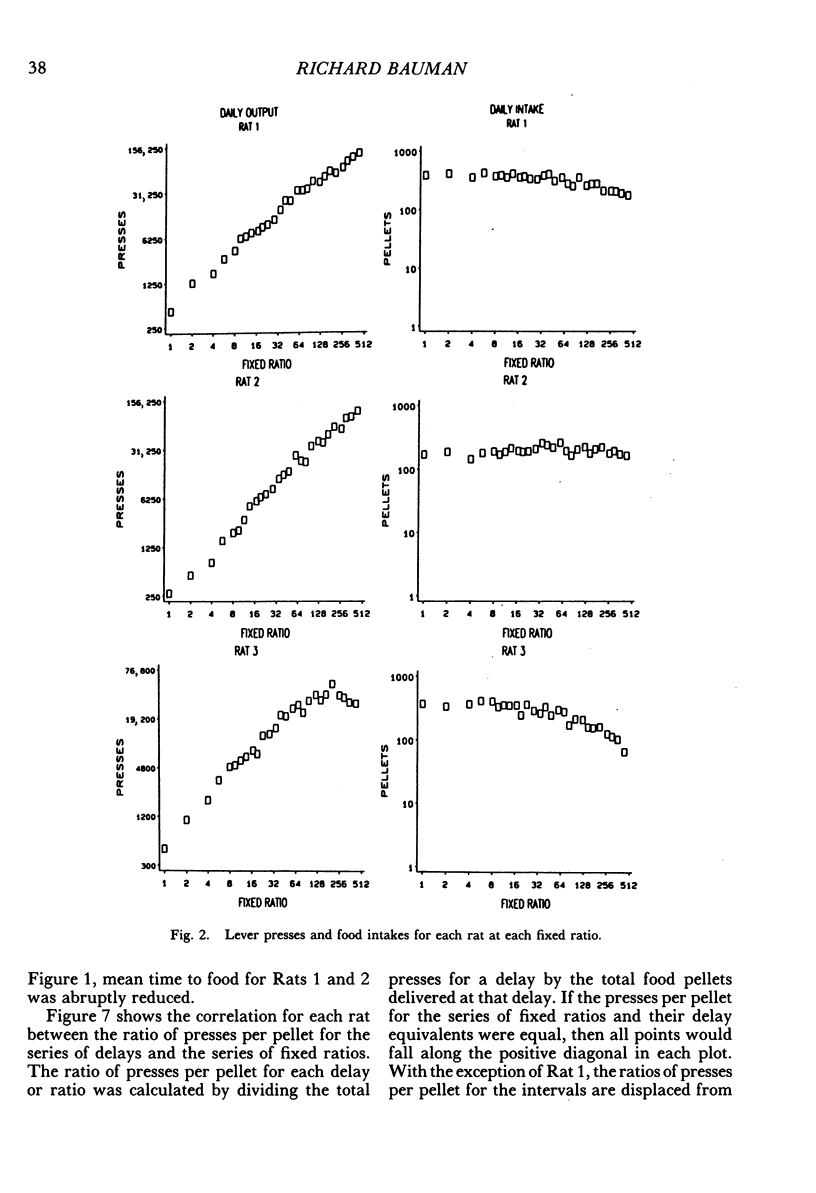
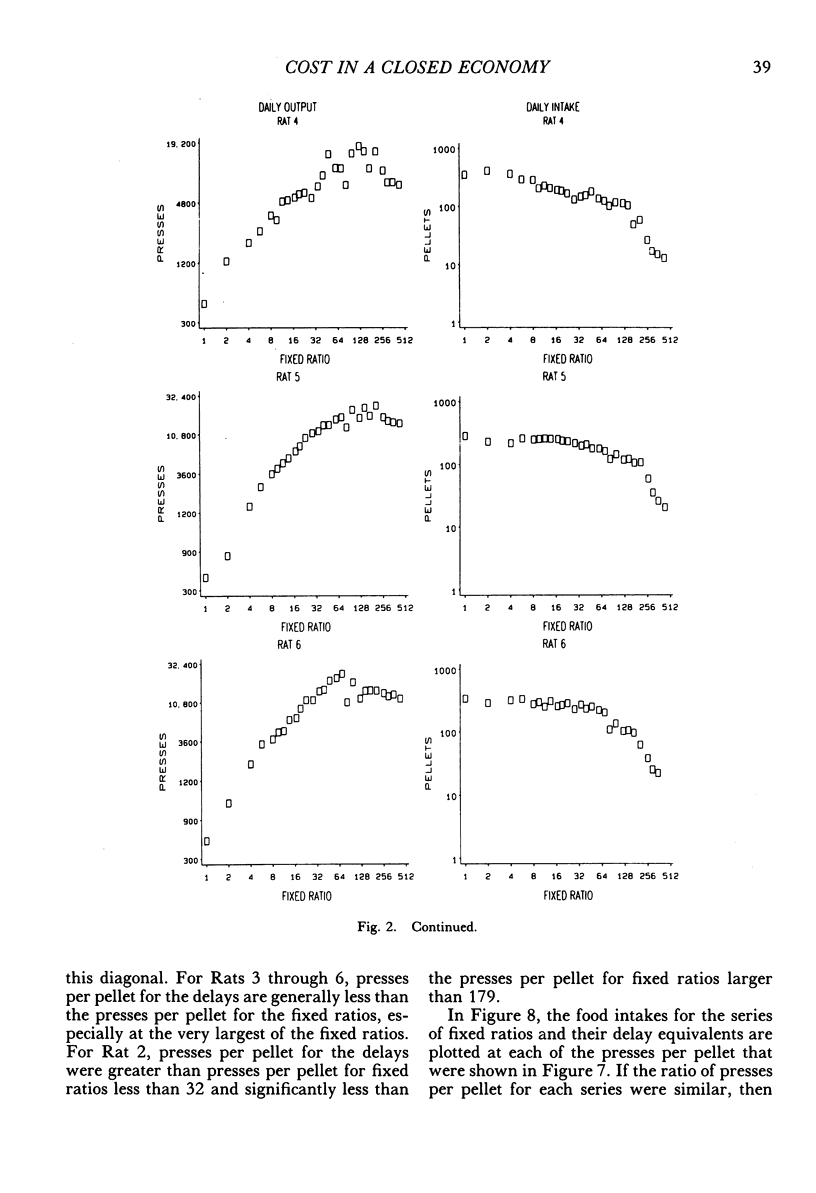
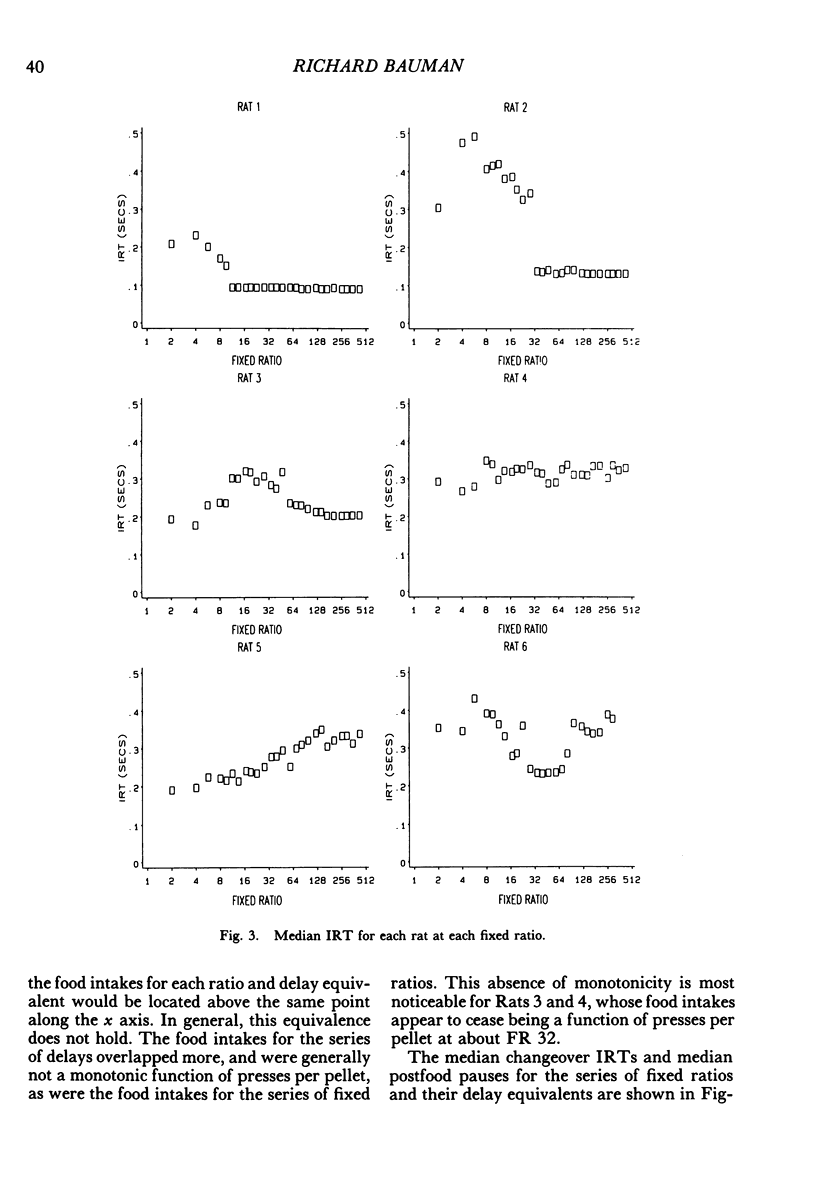
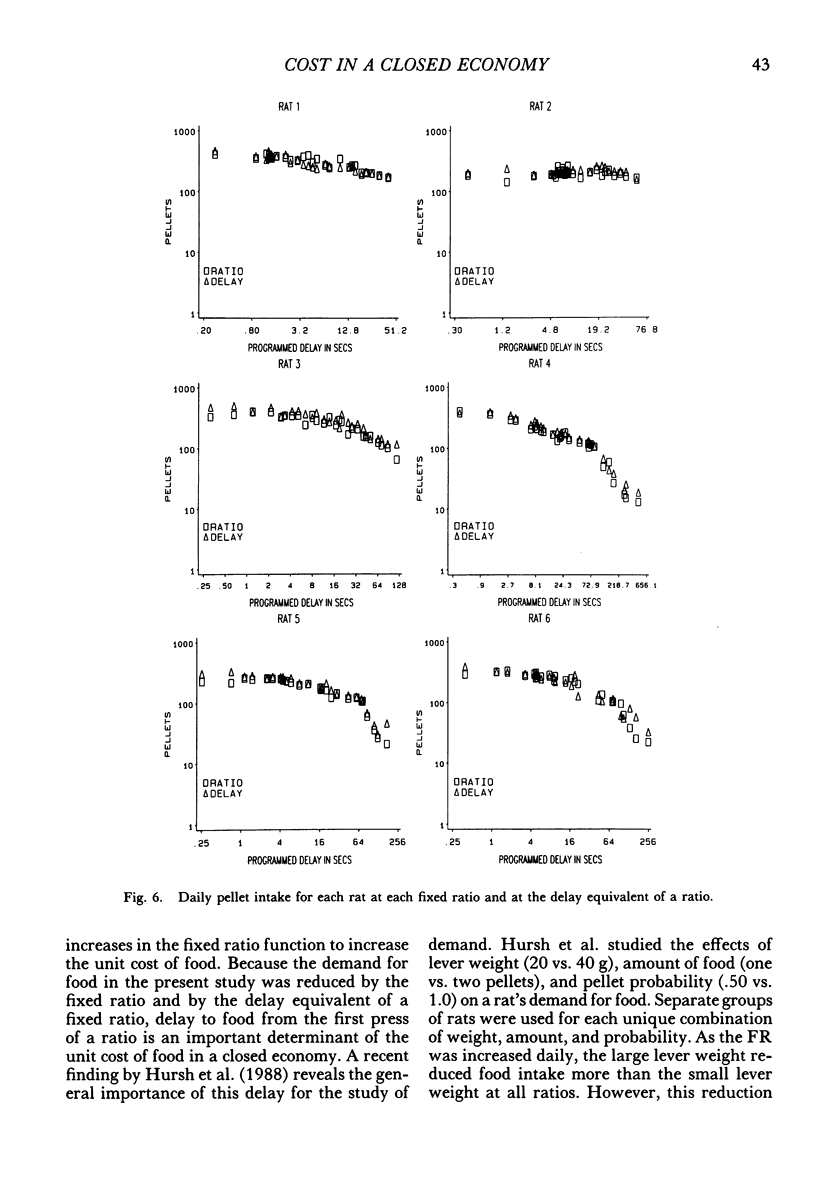
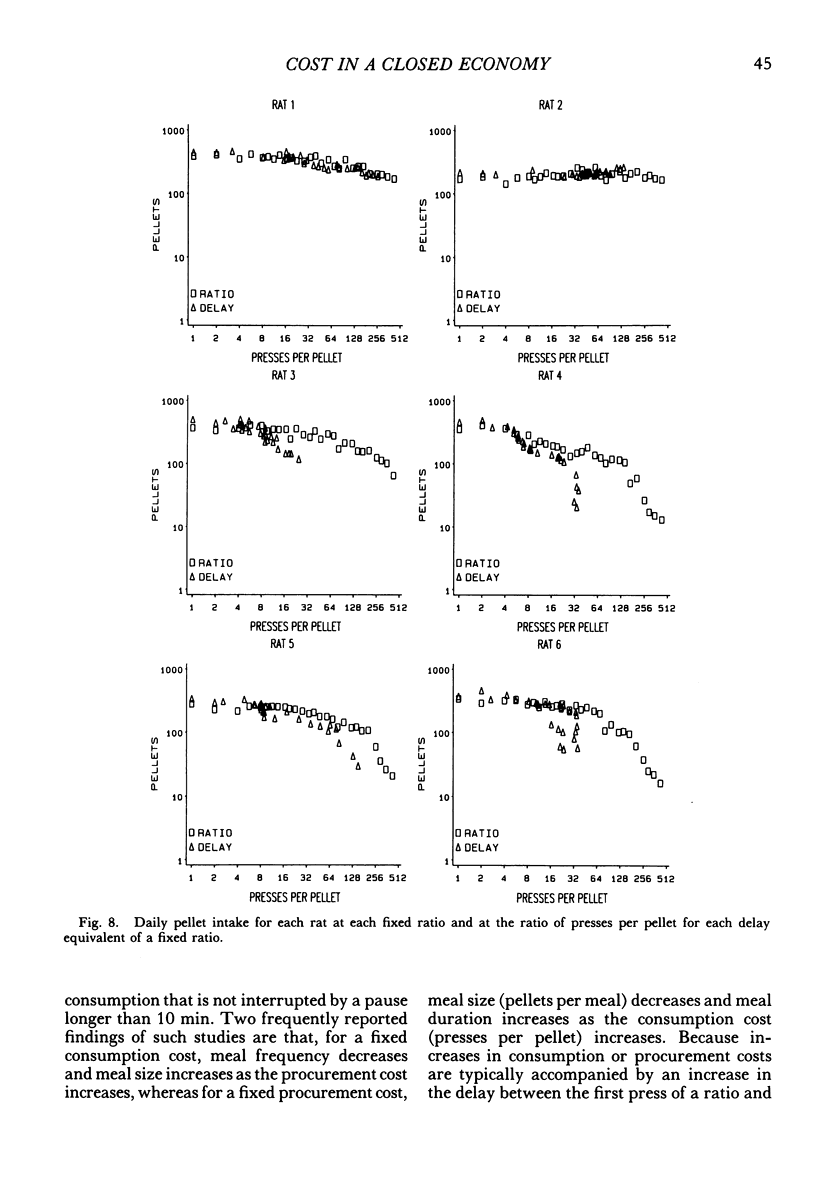
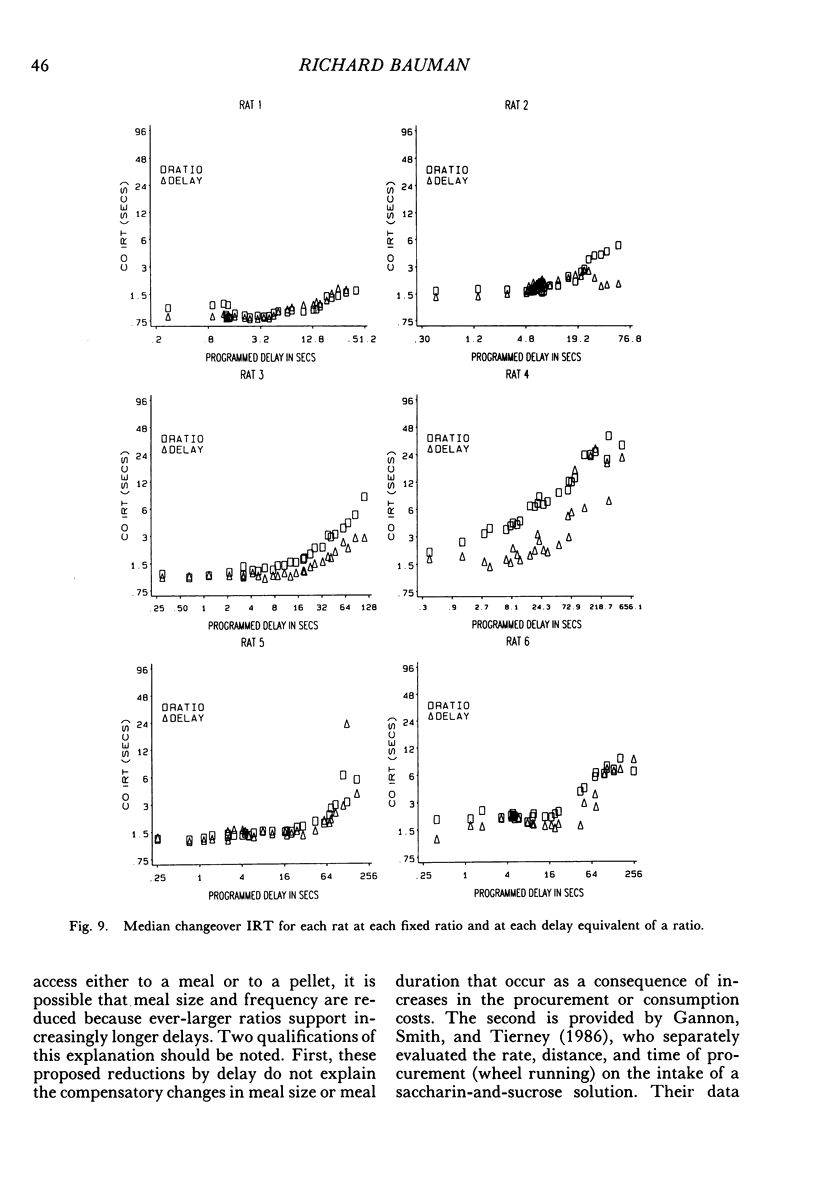
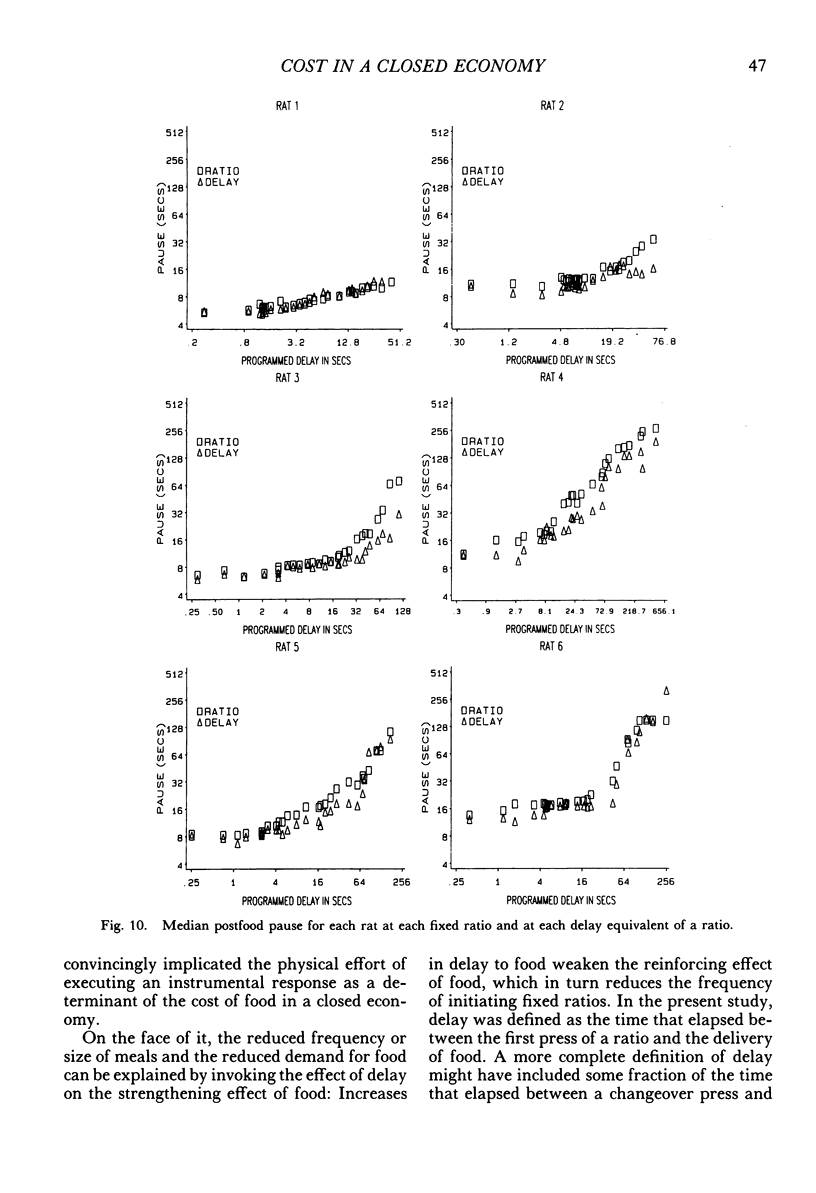
Rats lived in individual chambers in which the only food available was delivered for lever pressing. During Stage I, a fixed number of presses was required for each food pellet. As this fixed ratio of presses per food pellet was increased daily, a rat's daily intake of food was reduced. During Stage II, the cost of a food pellet was increased by replacing each fixed ratio with its interval equivalent. Each interval was a rat's mean time between the first press of a ratio and the delivery of a pellet during Stage I. During Stage II, only two presses were every required for a food pellet: The first press initiated a delay and the second activated the pellet dispenser after that delay elapsed. Food intakes for the series of fixed ratios and a rat's series of delay equivalents were very similar when plotted as a function of delay, but not when plotted as a function of presses per pellet. Consequently, the fixed ratio reduced food intake because larger ratios increased delay to food from the first press of a ratio. Observations and an analysis of interresponse times further revealed that as the fixed ratio increased, and local as well as overall rate of food intake decreased, lever pressing became more stereotyped. Because this increased stereotypy resulted in greatly increased rates of lever pressing, delay to food was minimized, and perhaps more importantly, so too was the reduction of a rat's baseline daily intake.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONITIS J. J. Response variability in the white rat during conditioning, extinction, and reconditioning. J Exp Psychol. 1951 Oct;42(4):273–281. doi: 10.1037/h0060407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier G. H., Johnson D. F., Hill W. L., Kaufman L. W. The economics of the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Sep;46(2):113–136. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.46-113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerman D. A., Lanson R. N. Variability of response location for pigeons responding under continuous reinforcement, intermittent reinforcement, and extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):73–80. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon K. N., Smith H. V., Tierney K. J. Effects of rate and distance of procurement wheel-running on saccharin-and-sucrose solution drinking by non-deprived rats. Physiol Behav. 1986;36(3):539–543. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(86)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R. Behavioral economics. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Nov;42(3):435–452. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.42-435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R. Economic concepts for the analysis of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):219–238. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R., Raslear T. G., Shurtleff D., Bauman R., Simmons L. A cost-benefit analysis of demand for food. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Nov;50(3):419–440. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.50-419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. F., Collier G. H. Caloric regulation and patterns of food choice in a patchy environment: the value and cost of alternative foods. Physiol Behav. 1987;39(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(87)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


