Abstract
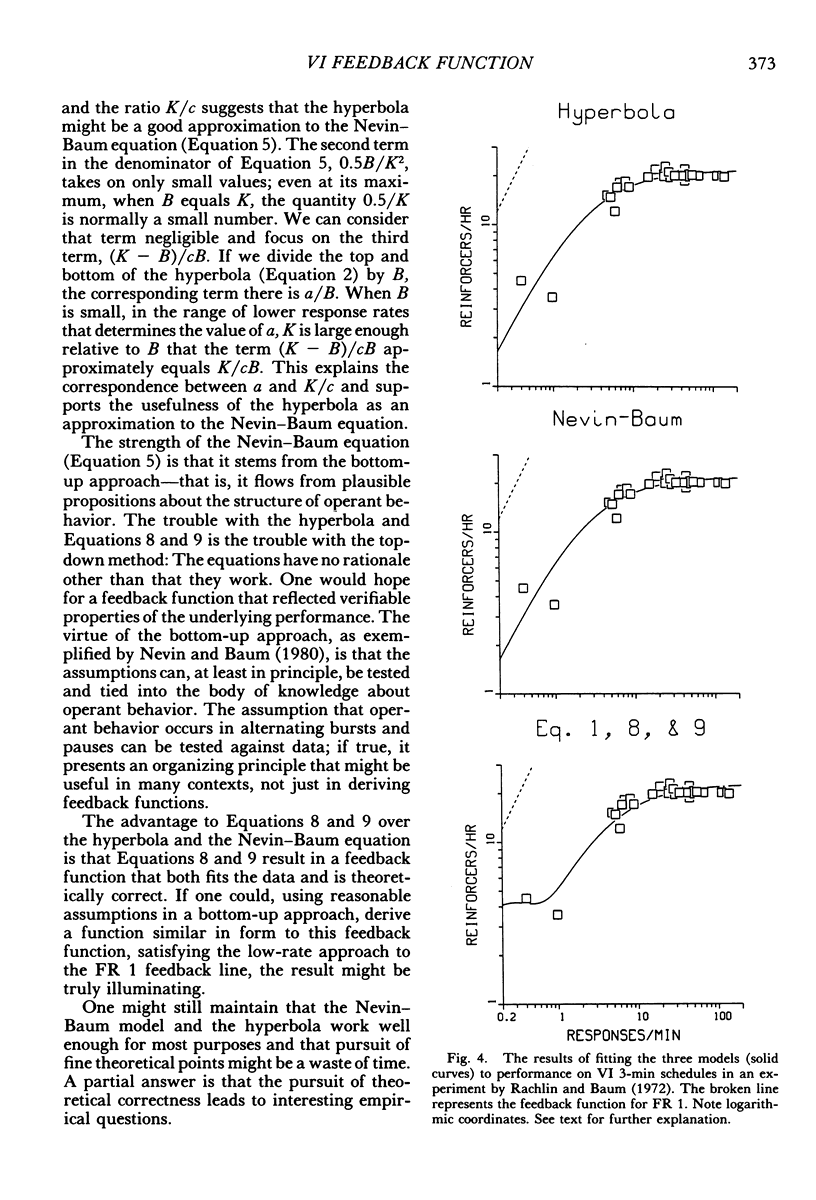
Finding a theoretically sound feedback function for variable-interval schedules remains an important unsolved problem. It is important because interval schedules model a significant feature of the world: the dependence of reinforcement on factors beyond the organism's control. The problem remains unsolved because no feedback function yet proposed satisfies all the theoretical and empirical requirements. Previous suggestions that succeed in fitting data fail theoretically because they violate a newly recognized theoretical requirement: The slope of the function must approach or equal 1.0 at the origin. A function is presented that satisfies all requirements but lacks any theoretical justification. This function and two suggested by Prelec and Herrnstein (1978) and Nevin and Baum (1980) are evaluated against several sets of data. All three fitted the data well. The success of the two theoretically incorrect functions raises an empirical puzzle: Low rates of reinforcement are coupled with response rates that seem anomalously high. It remains to be discovered what this reflects about the temporal patterning of operant behavior at low reinforcement rates. A theoretically and empirically correct function derived from basic assumptions about operant behavior also remains to be discovered.
Keywords: feedback function, variable-interval schedules, molar relations
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. Optimization and the matching law as accounts of instrumental behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Nov;36(3):387–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.36-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. The correlation-based law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Jul;20(1):137–153. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. Time-based and count-based measurement of preference. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 Jul;26(1):27–35. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.26-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. Interresponse time as a function of continuous variables: a new method and some data. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6(2):237–246. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell J. J., Kessel R. A multivariate rate equation for variable-interval performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Mar;31(2):267–283. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.31-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell J. J., Wixted J. T. The linear system theory's account of behavior maintained by variable-ratio schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jan;49(1):143–169. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerson J., Hale S. Choice in transition: A comparison of melioration and the kinetic model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Mar;49(2):291–302. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Baum W. M. Feedback functions for variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):207–217. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palya W. L. Dynamics in the fine structure of schedule-controlled behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1992 May;57(3):267–287. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1992.57-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. A molar theory of reinforcement schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Nov;30(3):345–360. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Effects of alternative reinforcement: does the source matter? J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):231–241. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. A. A two-state analysis of fixed-interval responding in the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):677–687. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Quasi-dynamic choice models: Melioration and ratio invariance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Mar;49(2):303–320. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


