Abstract
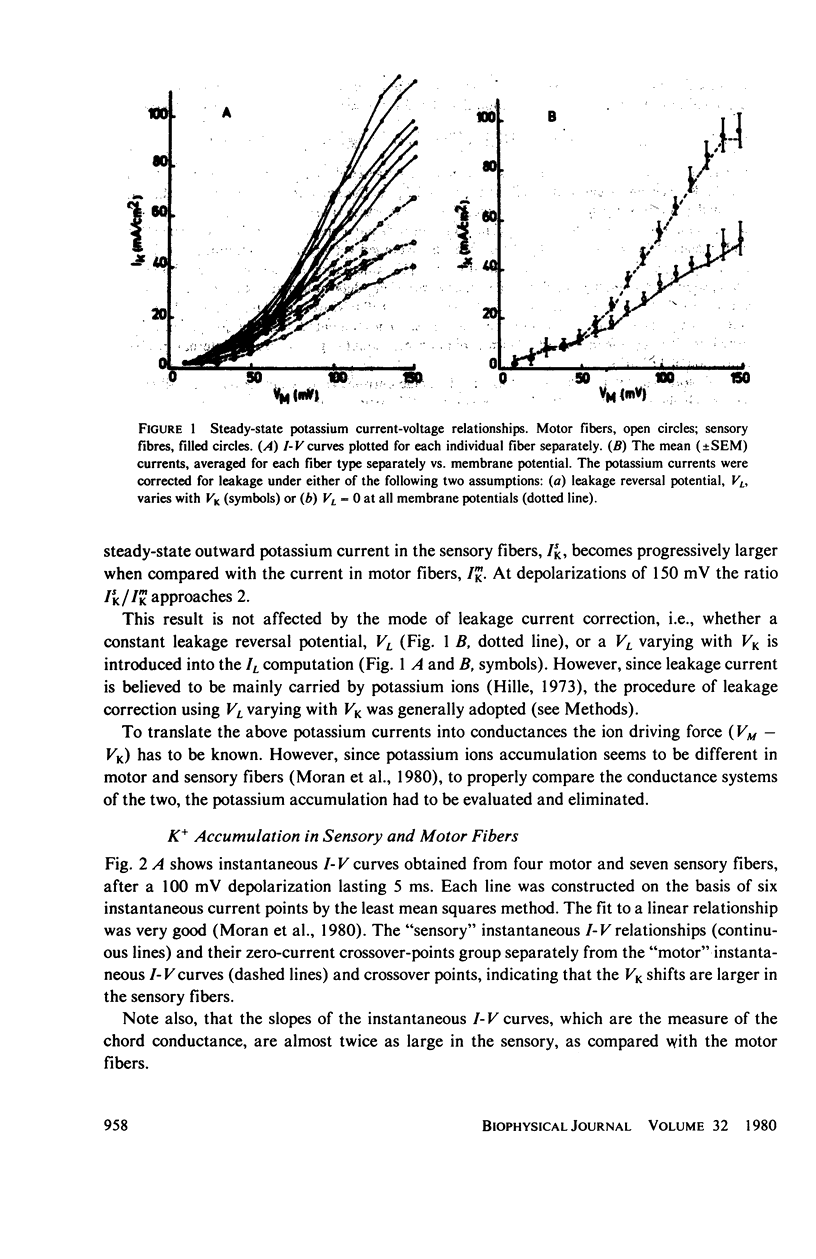
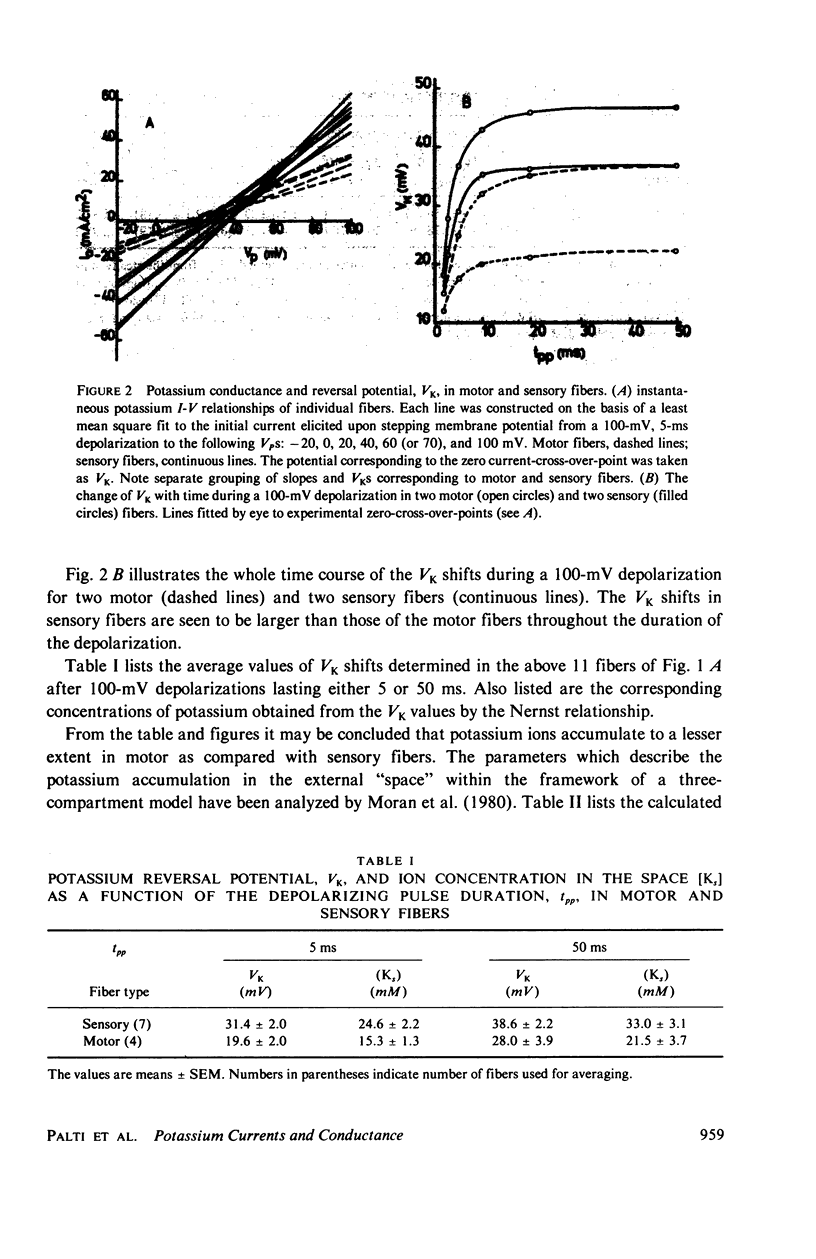
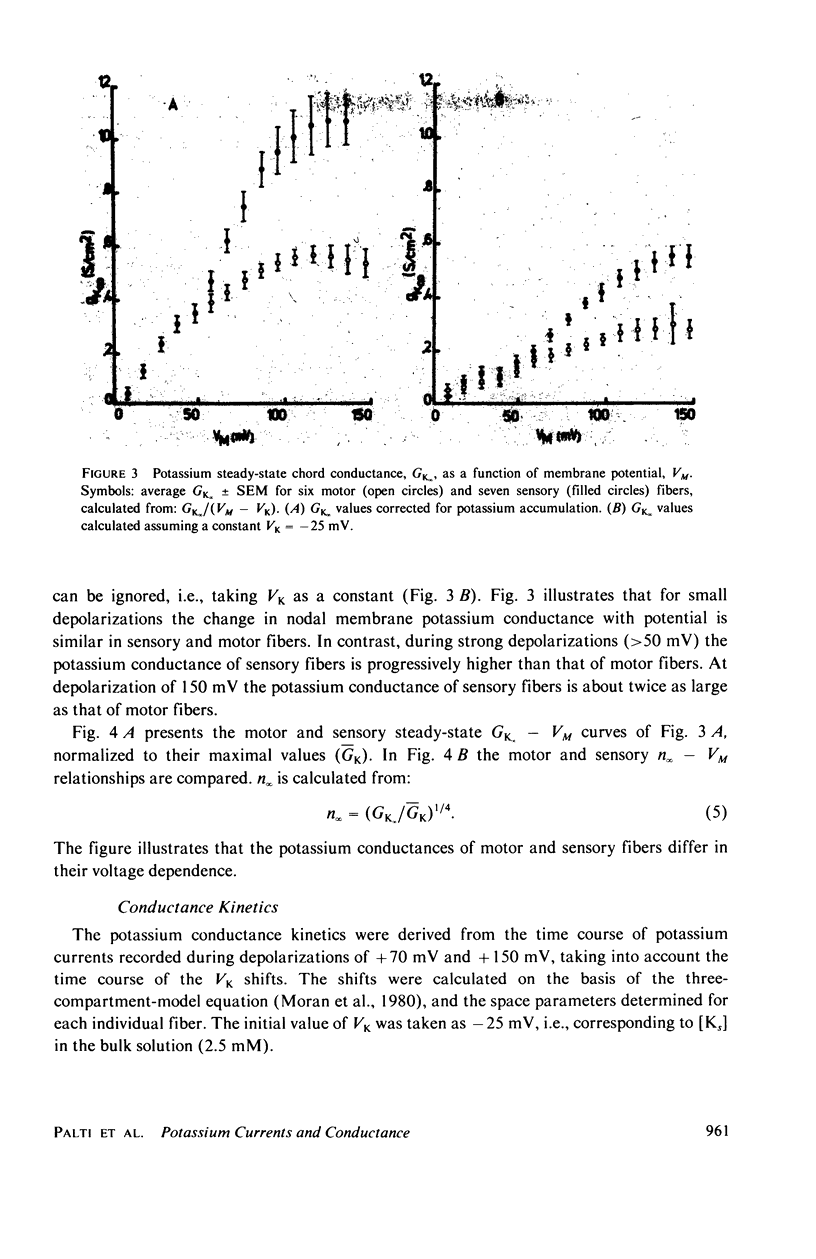
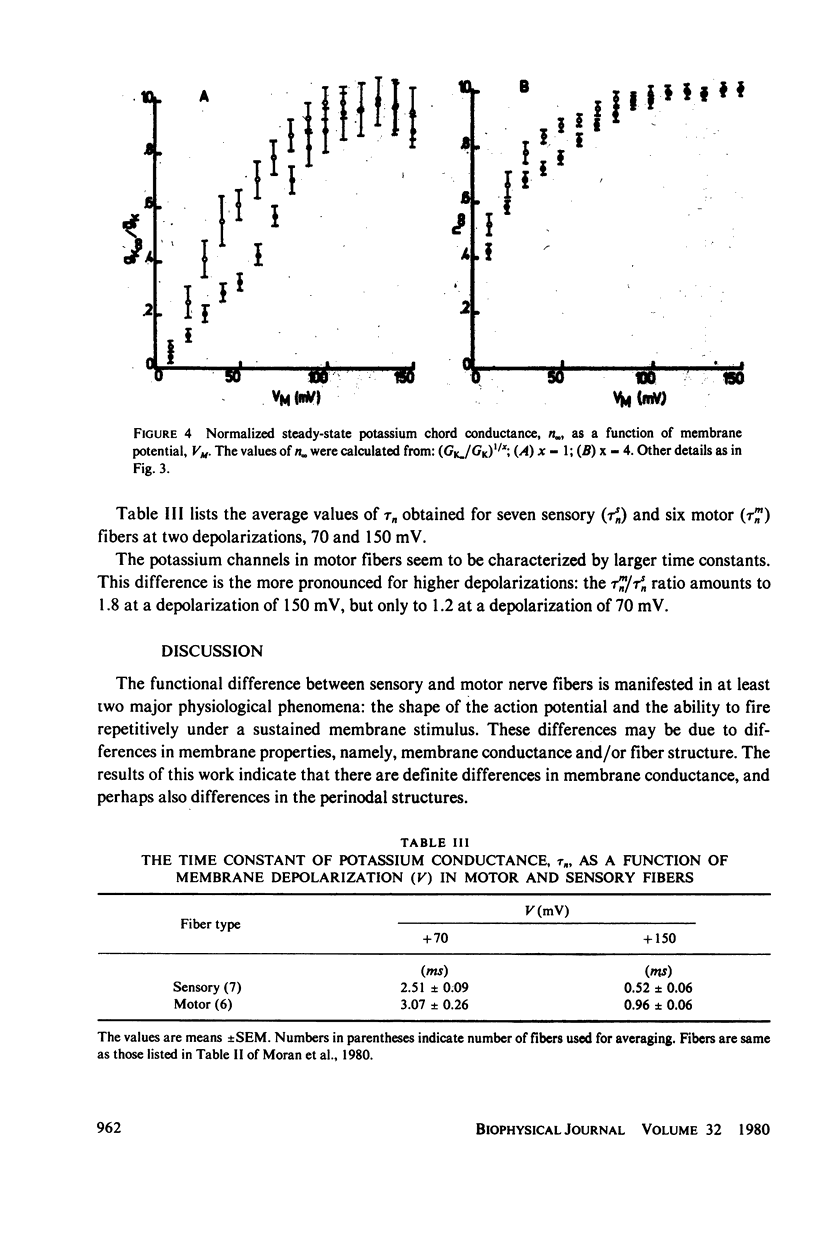
The potassium conductance system of sensory and motor fibers from the frog Rana esculenta were studied and compared by means of the voltage clamp. The potassium ion accumulation was first estimated from the currents and reversal potentials within the framework of both a three-compartment model and diffusion-in-an-unstirred-layer model. The potassium conductance parameters were then computed using the measured currents and corrected ionic driving forces. It was found that the potassium accumulation is faster and more pronounced in sensory fibers, the voltage dependency of the potassium conductance is steeper in sensory fibers, the maximal potassium conductance, corrected for accumulation, is approximately 1.1 S/cm2 in sensory and 0.55 S/cm2 in motor fibers, and that the conductance time constants, tau n, are smaller in sensory than in motor fibers. These differences, which increase progressively with depolarization, are not detectable for depolarization of 50 mV or smaller. The interpretation of these findings in terms of different types of potassium channels as well as their implications with regard to the differences between the excitability phenomena in motor and sensory fibers are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begenisich T. Conditioning hyperpolarization-induced delays in the potassium channels of myelinated nerve. Biophys J. 1979 Aug;27(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85215-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretag A. H., Stämpfli R. Differences in action potentials and accommodation of sensory and motor myelinated nerve fibres as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(3):257–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00584649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):669–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I., Peganov E. M., Revenko S. V., Shishkova L. D. Sodium currents in voltage clamped nerve fiber of frog under the combined action of batrachotoxin and procaine. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 14;84(3):541–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90771-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenhöfer E., Schmidt H. Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. I. Die Permeabilitäten PNa und PK. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(2):133–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00592631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenhöfer E., Schmidt H. Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. II. Unvollständiage Natrium-Inaktivierung. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(2):150–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00592632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran N., Palti Y., Levitan E., Stämpfli R. Potassium ion accumulation at the external surface of the nodal membrane in frog myelinated fibers. Biophys J. 1980 Dec;32(3):939–954. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85028-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W. A new voltage clamp method for Ranvier nodes. Pflugers Arch. 1969;309(2):176–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00586967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W., Rojas E., Stämpfli H. Displacement currents in the node of Ranvier. Voltage and time dependence. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palti Y., Ganot G., Stämpfli R. Effect of conditioning potential on potassium current kinetics in the frog node. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):261–273. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85686-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT H., STAEMPFLI R. NACHWEIS UNTERSCHIEDLICHER ELEKTROPHYSIOLOGISCHER EIGENSCHAFTEN MOTORISCHER UND SENSIBLER NERVENFASERN DES FROSCHES. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1964 Oct;64:C143–C145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Stämpfli R. Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf den einzelnen Ranvierschen Schnürring. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;287(4):311–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLBO A. B. ACCOMMODATION OF SINGLE MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS RELATED TO TYPE OF END ORGAN. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:413–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLBO A. B. ACCOMMODATION RELATED TO INACTIVATION OF THE SODIUM PERMEABILITY IN SINGLE MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES FROM XENOPUS LAEVIS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:429–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


