Abstract
The relationship between calcium current and transmitter release was studied in squid giant synapse. It was found that the voltage-dependent calcium current triggers the release of synaptic transmitter in direct proportion to its magnitude and duration. Transmitter release occurs with a delay of approximately 200 mus after the influx of calcium. A model is presented which describes these relations formally.
Full text
PDF


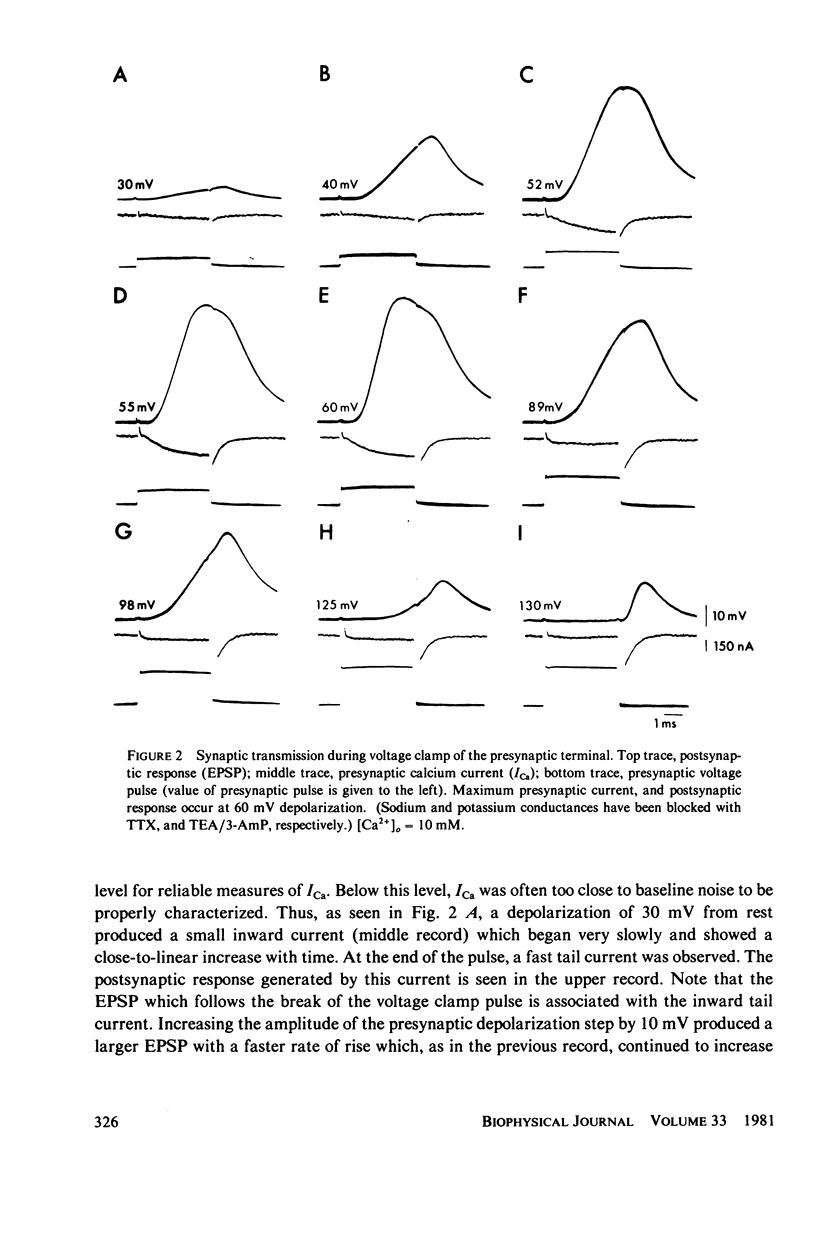

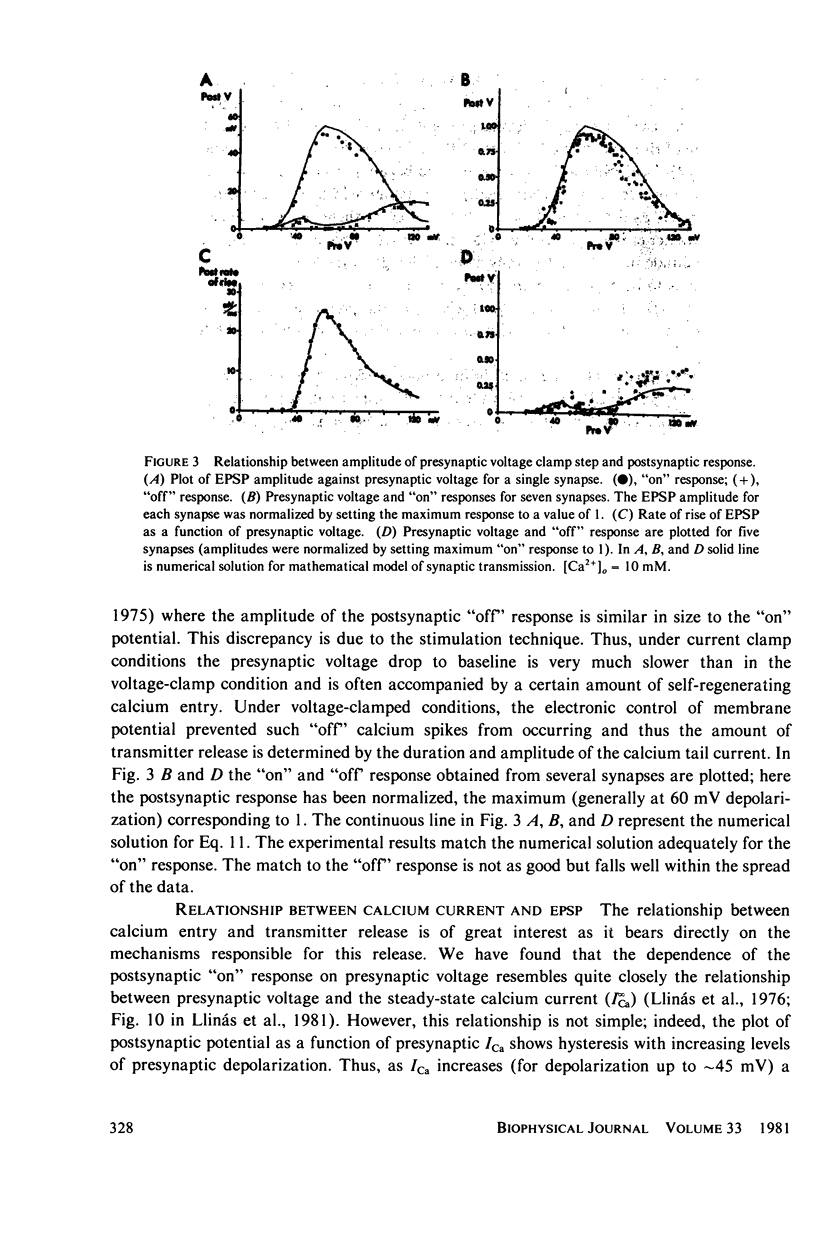
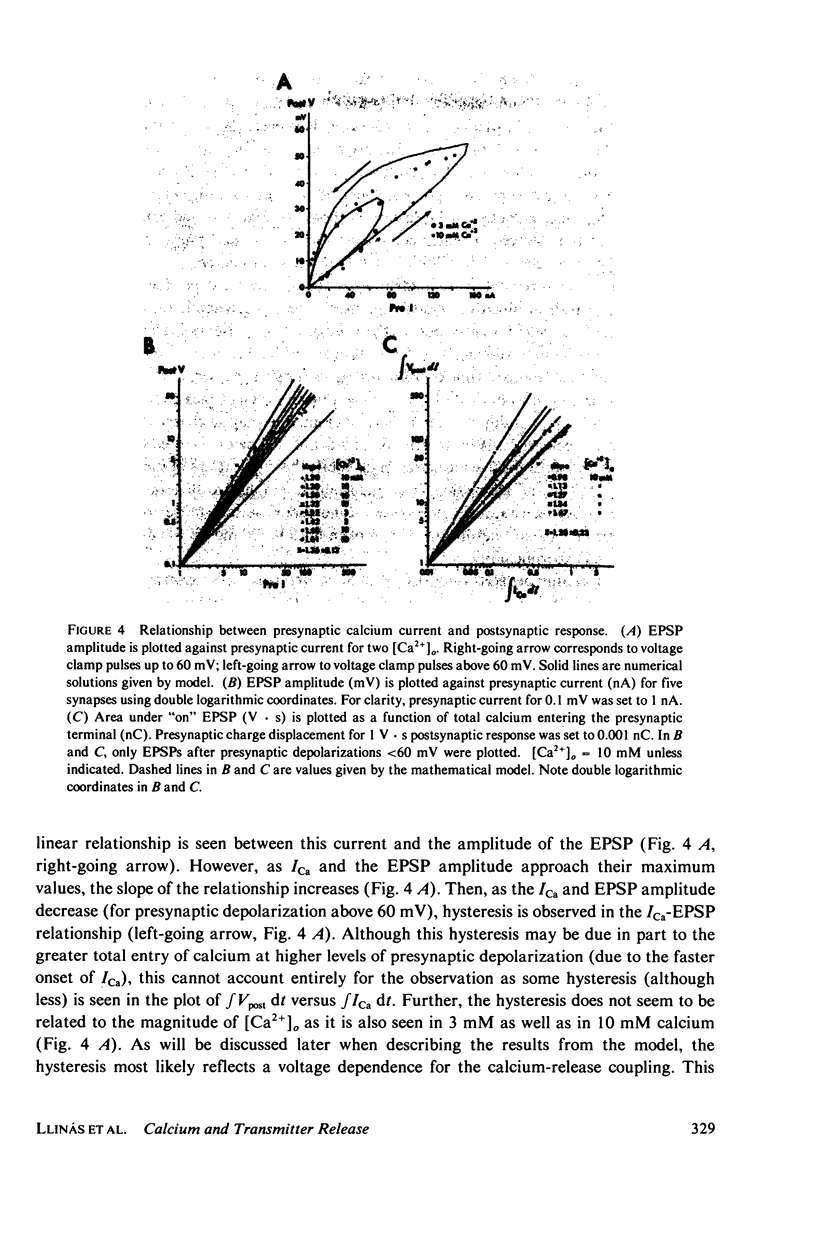
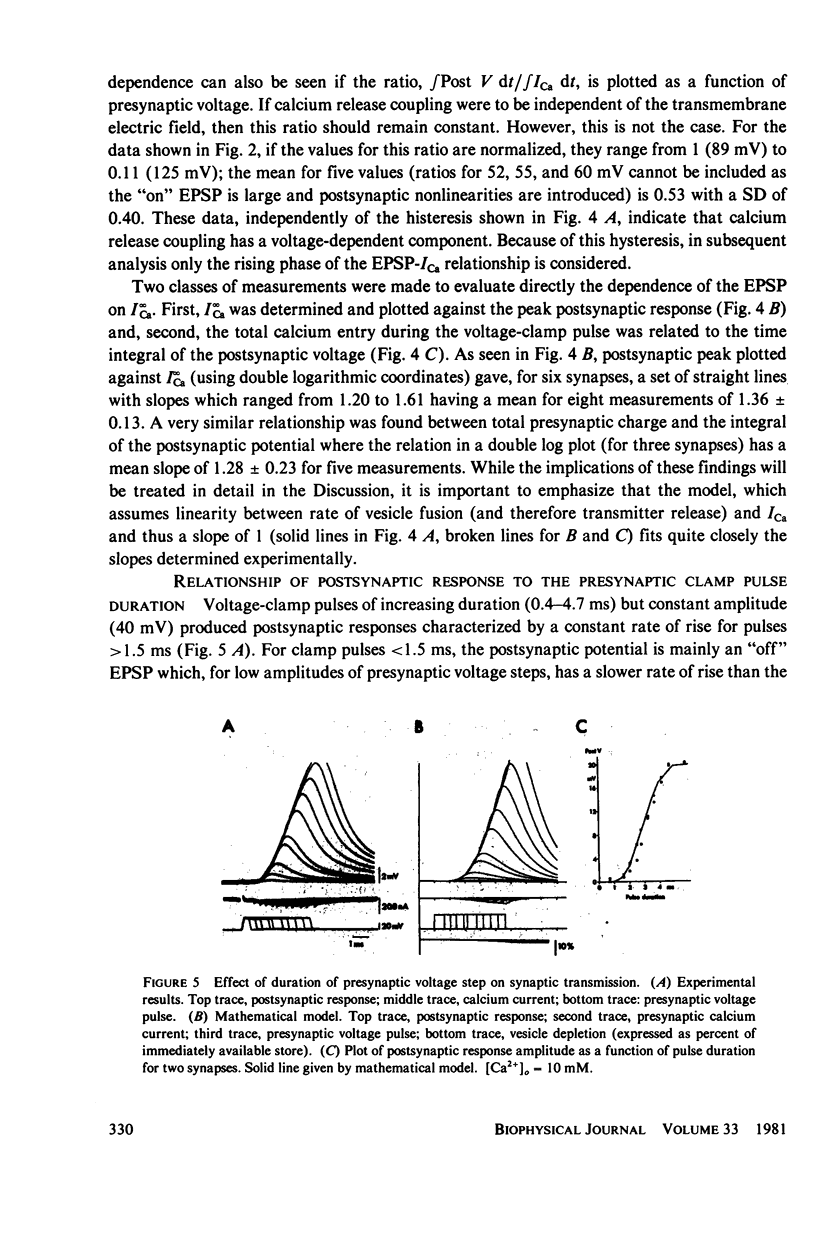

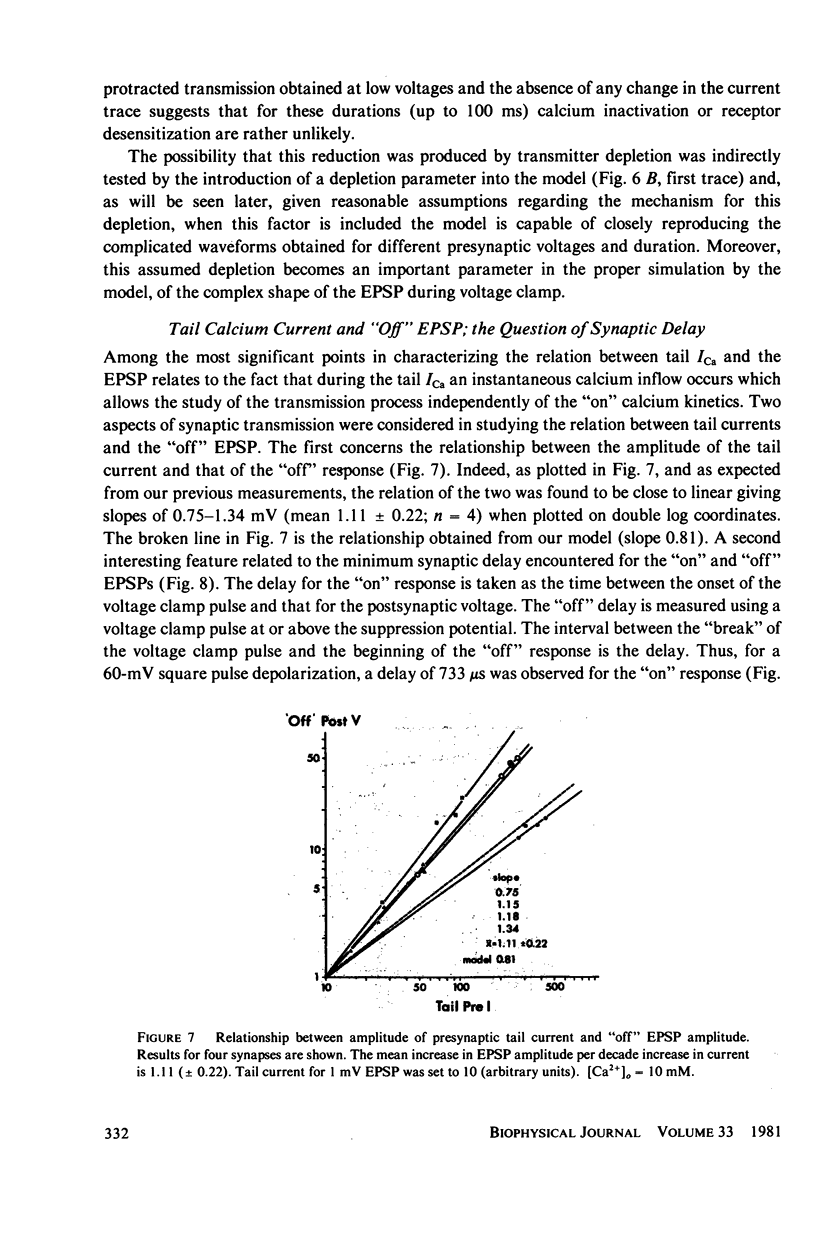

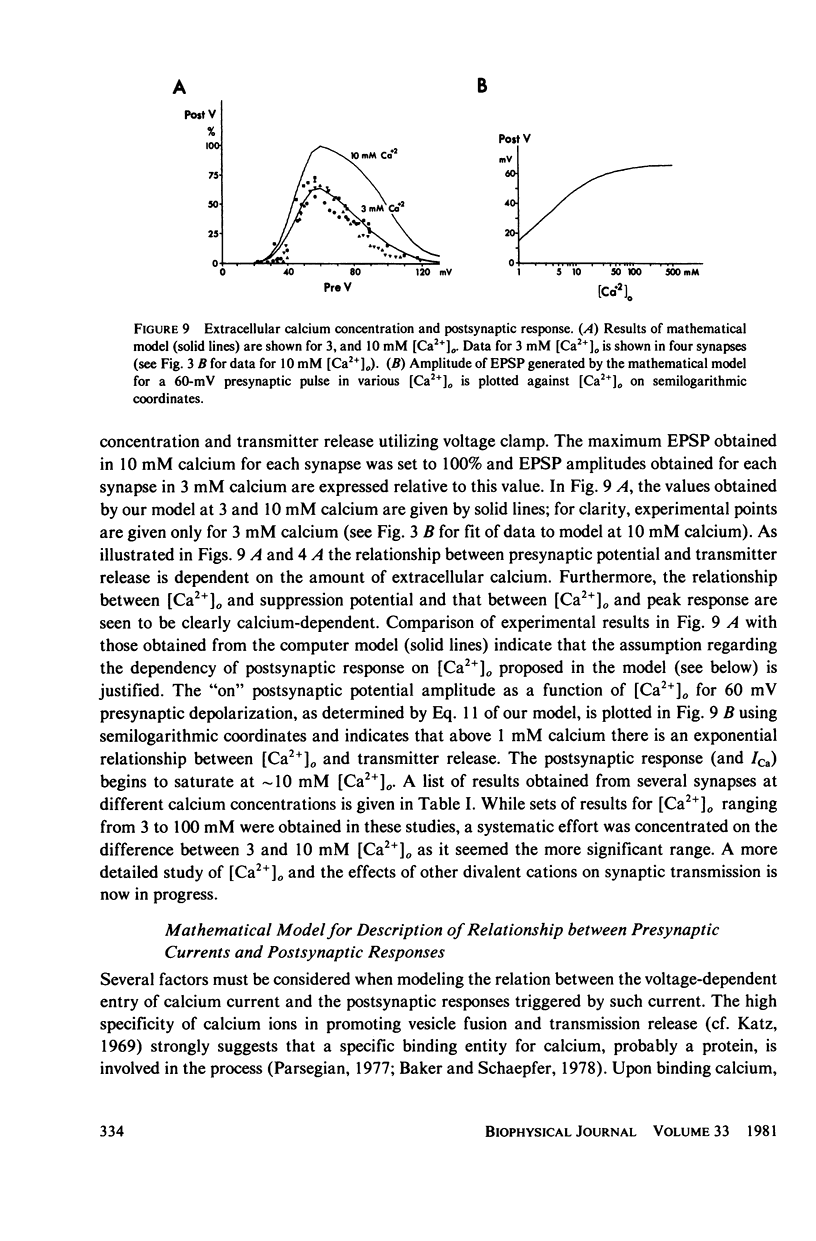
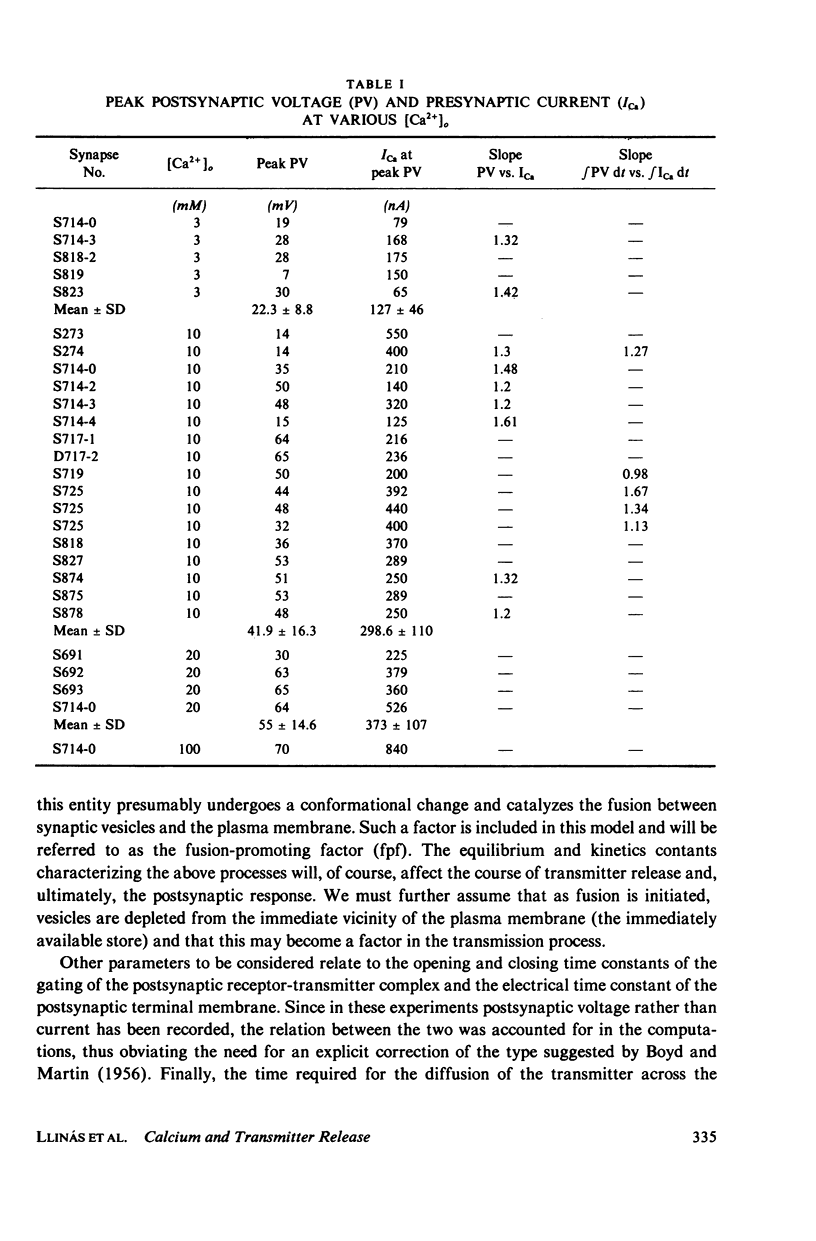

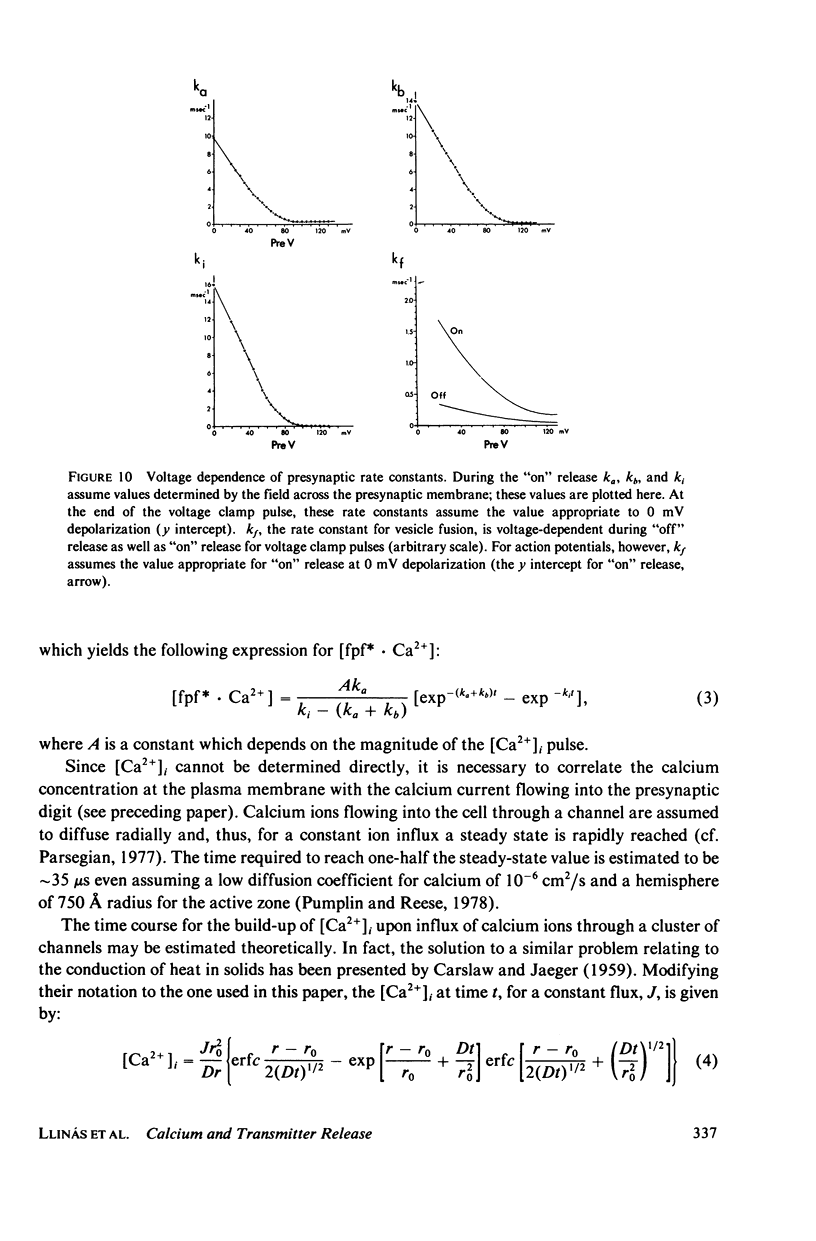











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemà S., Calissano P., Rusca G., Giuditta A. Identification of a calcium-binding, brain specific protein in the axoplasm of squid giant axons. J Neurochem. 1973 Mar;20(3):681–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT S. H. Transmission in squid giant synapses: the importance of oxygen supply and the effects of drugs. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Jan 20;41(3):473–484. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLOCK T. H., HAGIWARA S. Intracellular recording from the giant synapse of the squid. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Mar 20;40(4):565–577. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLOCK T. H. Properties of a single synapse in the stellate ganglion of squid. J Neurophysiol. 1948 Jul;11(4):343–364. doi: 10.1152/jn.1948.11.4.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Schlaepfer W. W. Uptake and binding of calcium by axoplasm isolated from giant axons of Loligo and Myxicola. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:103–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Kendrick N. C., Schweitzer E. S. Calcium buffering in presynaptic nerve terminals. I. Evidence for involvement of a nonmitochondrial ATP-dependent sequestration mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):15–41. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Kendrick N. K. The regulation of intracellular calcium in presynaptic nerve terminals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:195–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Schweitzer E. S. Calcium buffering in presynaptic nerve terminals. II. Kinetic properties of the nonmitochondrial Ca sequestration mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):43–66. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blight A. R., Llinás R. The non-impulsive stretch-receptor complex of the crab: a study of depolarization--release coupling at a tonic sensorimotor synapse. Proc Clin Dial Transplant Forum. 1980 Jul 31;290(1039):219–276. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloedel J., Gage P. W., Llinás R., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release at the squid giant synapse in the presence of tetrodotoxin. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):49–50. doi: 10.1038/212049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E. Organization of vertebrate retinas. Invest Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;9(9):655–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., TASAKI I. A study on the mechanism of impulse transmission across the giant synapse of the squid. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):114–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further study of the role of calcium in synaptic transmission. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):789–801. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of prolonged depolarization on synaptic transfer in the stellate ganglion of the squid. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):503–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Deutsch J. W., Carlson S. S., Wagner J. A. Biochemistry of neurotransmitter release. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:399–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K. Further study of the relationship between pre- and postsynaptic potentials in the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):326–345. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K. Influence of ionic environment on the relationship between pre- and postsynaptic potentials. J Neurobiol. 1970;1(4):435–437. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Landau E. M. Depression and recovery of transmission at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(1):13–32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Livengood D. R., Werman R. Correlation of transmitter release with membrane properties of the presynaptic fiber of the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Dec;50(11):2579–2601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.11.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. Transmitter release by presynaptic impulses in the squid stellate ganglion. Nature. 1970 Aug 1;227(5257):493–496. doi: 10.1038/227493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinas R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. A model for synaptic transmission. Brain Res Bull. 1979 Jan-Feb;4(1):170–173. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(79)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R. Depolarization-release coupling systems in neurons. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1977 Dec;15(4):555–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Joyner R. W., Nicholson C. Equilibrium potential for the postsynaptic response in the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Nicholson C. Calcium role in depolarization-secretion coupling: an aequorin study in squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):187–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):289–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84898-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Walton K., Bohr V. Synaptic transmission in squid giant synapse after potassium conductance blockage with external 3- and 4-aminopyridine. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85664-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Pichon Y. The effect of internal and external 4-aminopyridine on the potassium currents in intracellularly perfused squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. The action of calcium on neuronal synapses in the squid. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):473–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumplin D. W., Reese T. S. Membrane ultrastructure of the giant synapse of the squid Loligo pealei. Neuroscience. 1978;3(8):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff R., Erulkar S. D., Lev-Tov A., Meiri H. Intracellular and extracellular calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular synapse. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:583–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro E., Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic membrane potential affects transmitter release in an identified neuron in Aplysia by modulating the Ca2+ and K+ currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Electrical changes in pre- and postsynaptic axons of the giant synapse of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jul;45:1181–1193. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Dynamics of aminopyridine block of potassium channels in squid axon membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):519–535. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


