Abstract
The diffuse permeability and the diffusion coefficient of water (Dw) in the gramicidin channel is determined from the osmotic water permeability of the channel and "single file" pore theory. Dw is about 7% of the self-diffusion coefficient of bulk water. The diffusion coefficient of a single water molecule alone in the channel is also determined and is about equal to the value in bulk water. This provides an estimate of the mobility of water on the channel walls in the absence of water-water interaction. Since the gramicidin channel walls should be representative of uncharged polar protein surfaces, this result provides direct evidence that the presence of a cation in the channel reduces the hydraulic water permeability by a factor ranging from 60 for Tl+ to 5 for Na+. The diffusion coefficient of a cation (Dc) in the channel is estimated and compared with Dw. For Na+ it is found that Dc approximately equal to Dw, which implies that the movement of the row of water molecules through the channel determines the local mobility of Na+. Thus, it seems that short range ion-wall interactions are not important in determining the channel conductance for Na+. In contrast, for Li+, local ion-wall interactions probably do limit the conductance.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borisova M. P., Ermishkin L. N., Silberstein A. Y. Mechanism of blockage of amphotericin B channels in a lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 2;553(3):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant R. G., Shirley W. M. Dynamical deductions from nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation measurements at the water-protein interface. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84912-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
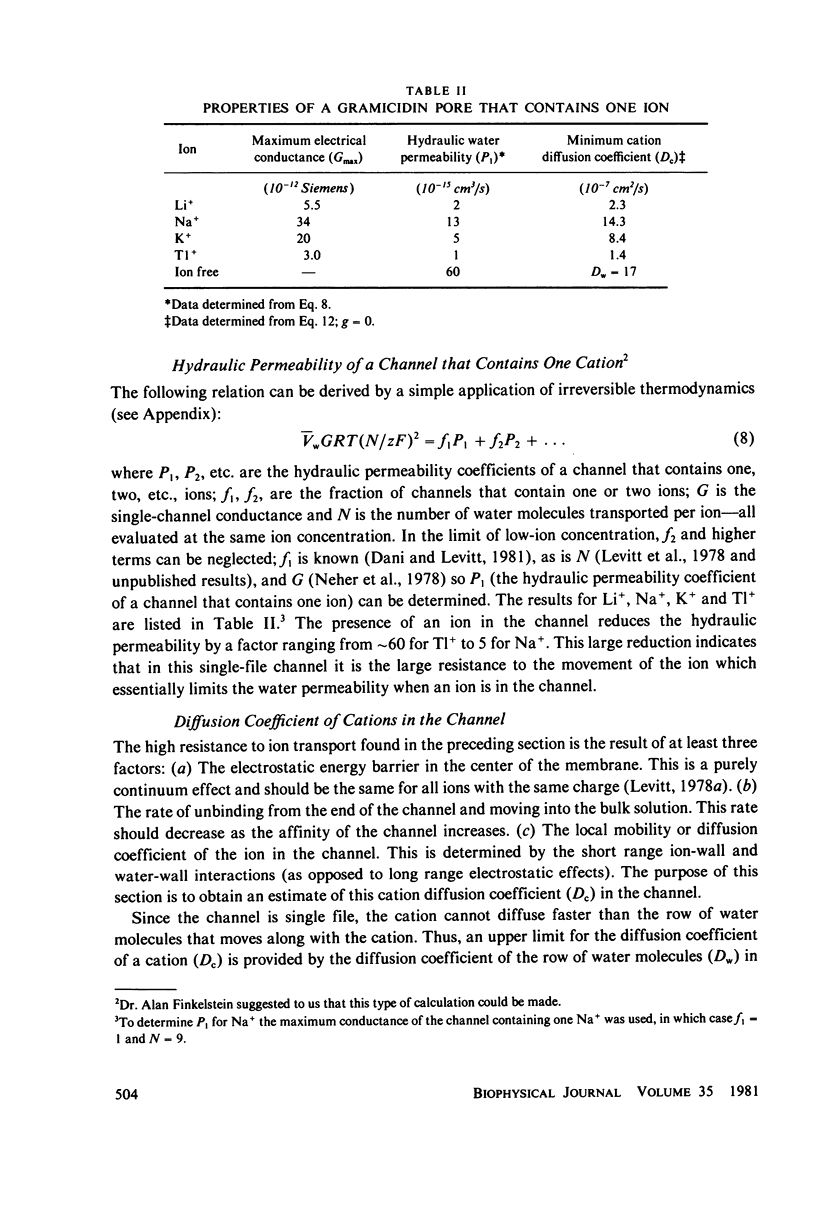
- Dani J. A., Levitt D. G. Binding constants of Li+, K+, and Tl+ in the gramicidin channel determined from water permeability measurements. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84804-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermishkin L. N., Kasumov K. M., Potseluyev V. M. Properties of amphotericin B channels in a lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 1;470(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic channels in excitable membranes. Current problems and biophysical approaches. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85489-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic selectivity of Na and K channels of nerve membranes. Membranes. 1975;3:255–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R., Finkelstein A. The water and nonelectrolyte permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):125–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe R. E., 2nd, Berg J. M., Hodgson K. O., Stryer L. Gramicidin A crystals contain two cation binding sites per channel. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):723–725. doi: 10.1038/279723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. A new theory of transport for cell membrane pores. I. General theory and application to red cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 27;373(1):115–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85485-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. II. Kinetic behavior of the gramicidin A channel. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):221–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85486-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Elias S. R., Hautman J. M. Number of water molecules coupled to the transport of sodium, potassium and hydrogen ions via gramicidin, nonactin or valinomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):436–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G., Subramanian G. A new theory of transport for cell membrane pores. II. Exact results and computer simulation (molecular dynamics). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 27;373(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sandblom J., Eisenman G. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in gramicidin A channels. II. Saturation behavior of single channel conductances and evidence for the existence of multiple binding sites in the channel. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 26;40(2):97–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01871143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Finkelstein A. Interaction of ions and water in gramicidin A channels: streaming potentials across lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):327–340. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P. A., Finkelstein A. Water permeability of gramicidin A-treated lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):341–350. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban B. W., Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion movements in gramicidin pores. An example of single-file transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 4;602(2):331–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Long M. M., Jacobs M., Harris R. D. Conformation and molecular mechanisms of carriers and channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:203–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: a proposed pi(L,D) helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):672–676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


