Abstract
Impedance studies were performed on small spherical clusters of embryonic chick heart cells grown in tissue culture. Each syncytial cluster was impaled with two microelectrodes; one injected low amplitude stochastic current and the other recorded the resulting perturbation of intracellular potential. The current and potential records were digitized, decomposed into their sinusoidal components, and the frequency domain impedance of the cluster was determined. The impedance data were compared with a theory for current flow in a spherical syncytium and values were derived for parameters describing the membranes and intercellular clefts of the tissue. The clusters were spontaneously active but usually became temporarily quiescent when impaled with two electrodes. The potential stabilized at a value close to -30 mV. At this depolarized potential, active slow currents, presumably present in the cardiac action potential, contributed noticeably to the linear impedance, producing a resonant peak in the magnitude of the impedance at a frequency of 1-3 Hz. The linearized impedance functions for these currents were characterized in the presence and absence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and D-600. TTX had no noticeable effect on the impedance but D-600 essentially abolished the active currents. Although the ionic basis of these currents is not known, frequency domain analysis appears to be a viable technique for studying slow currents in heart muscle.
Full text
PDF


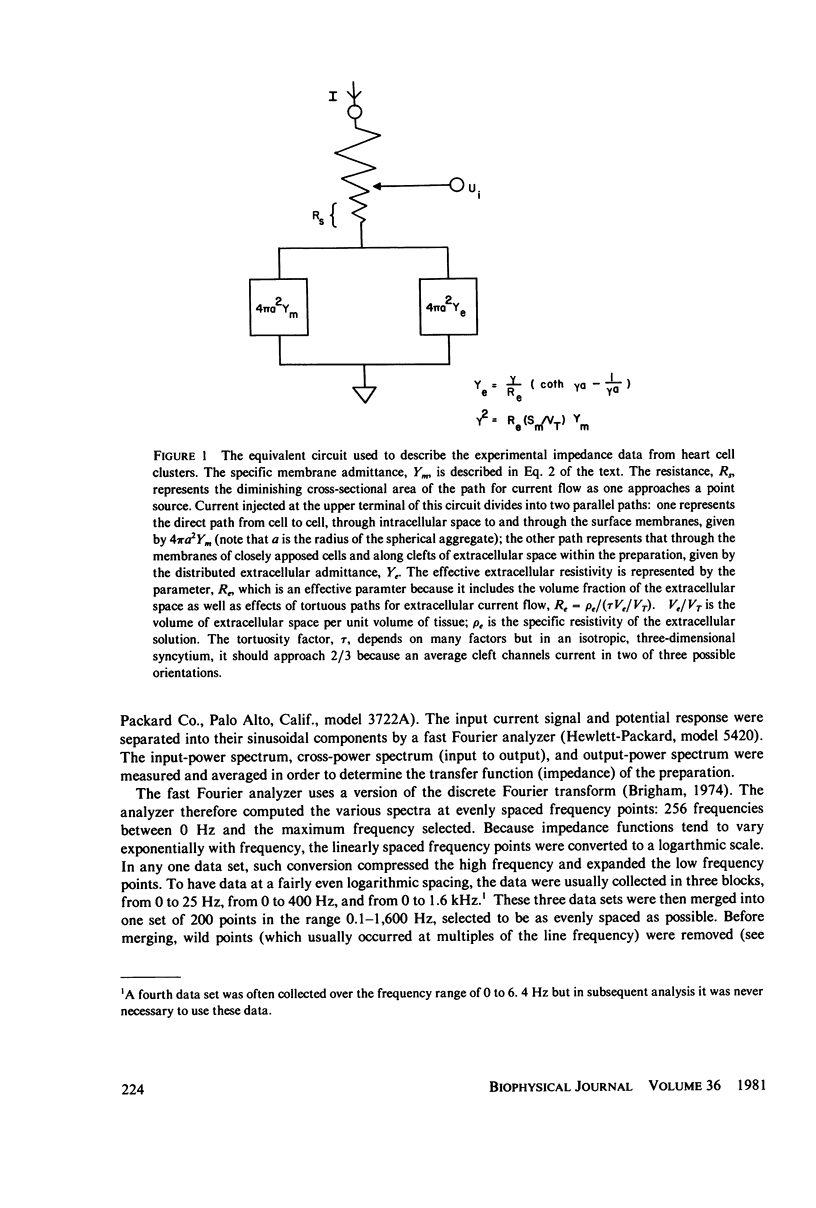
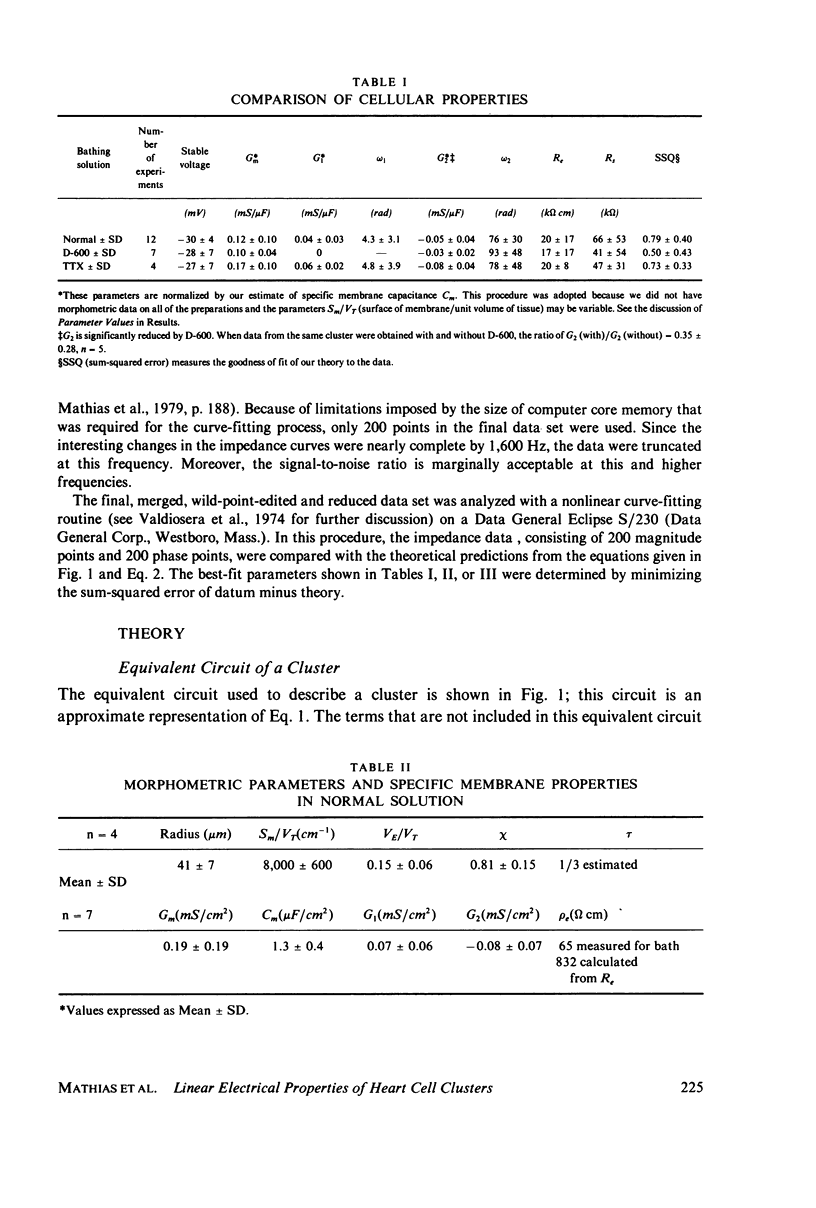




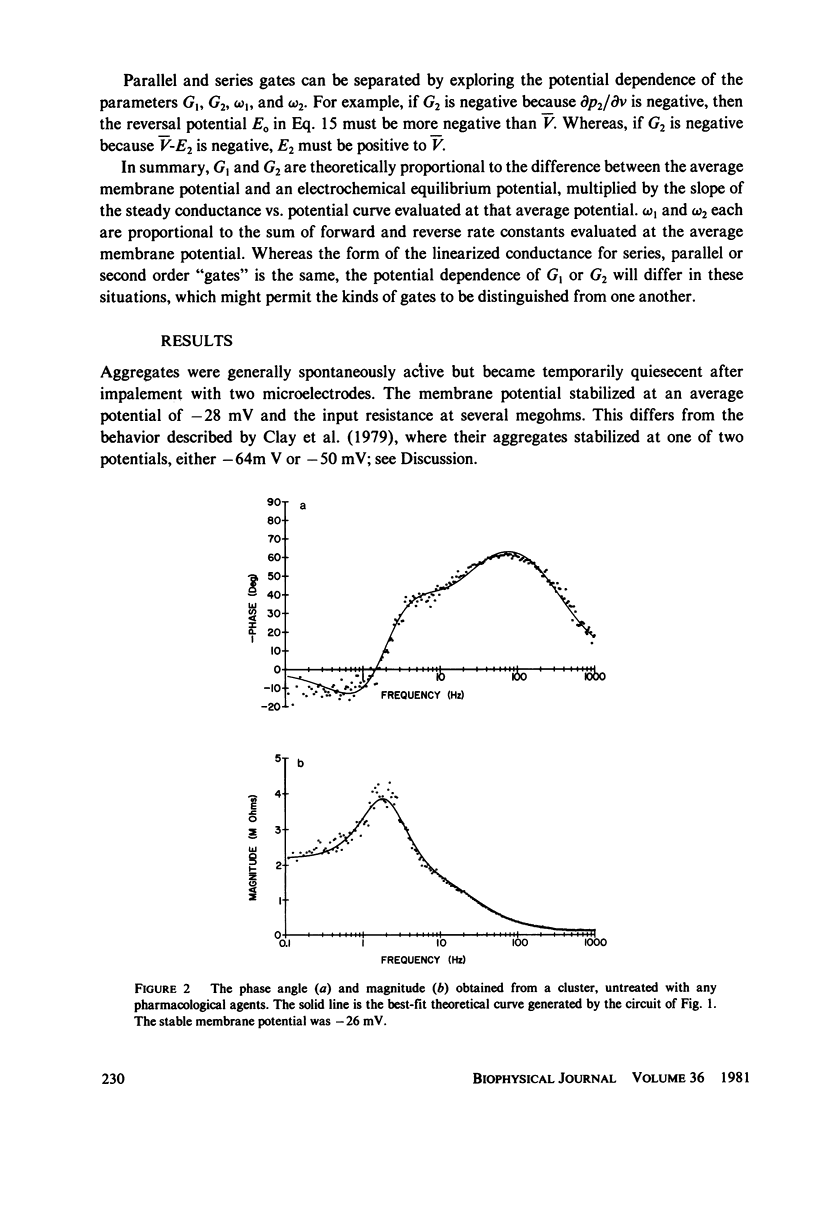
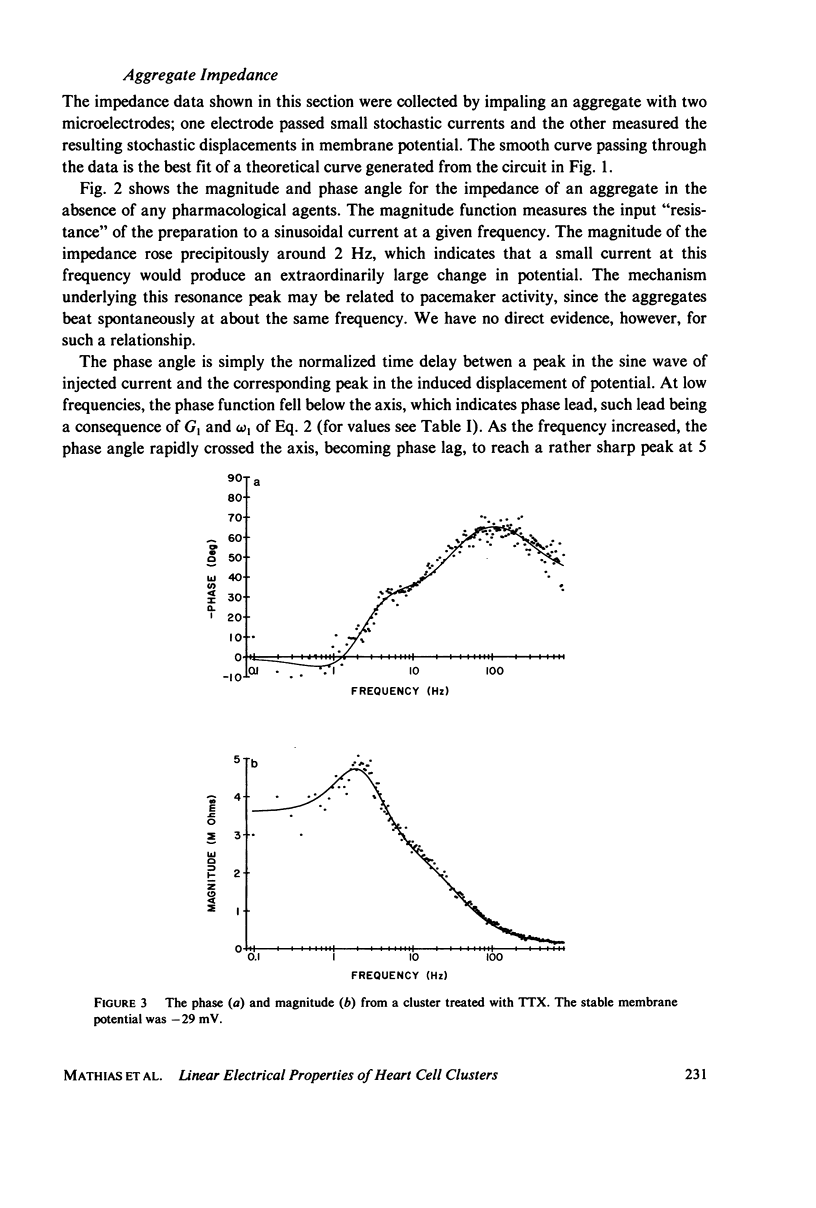
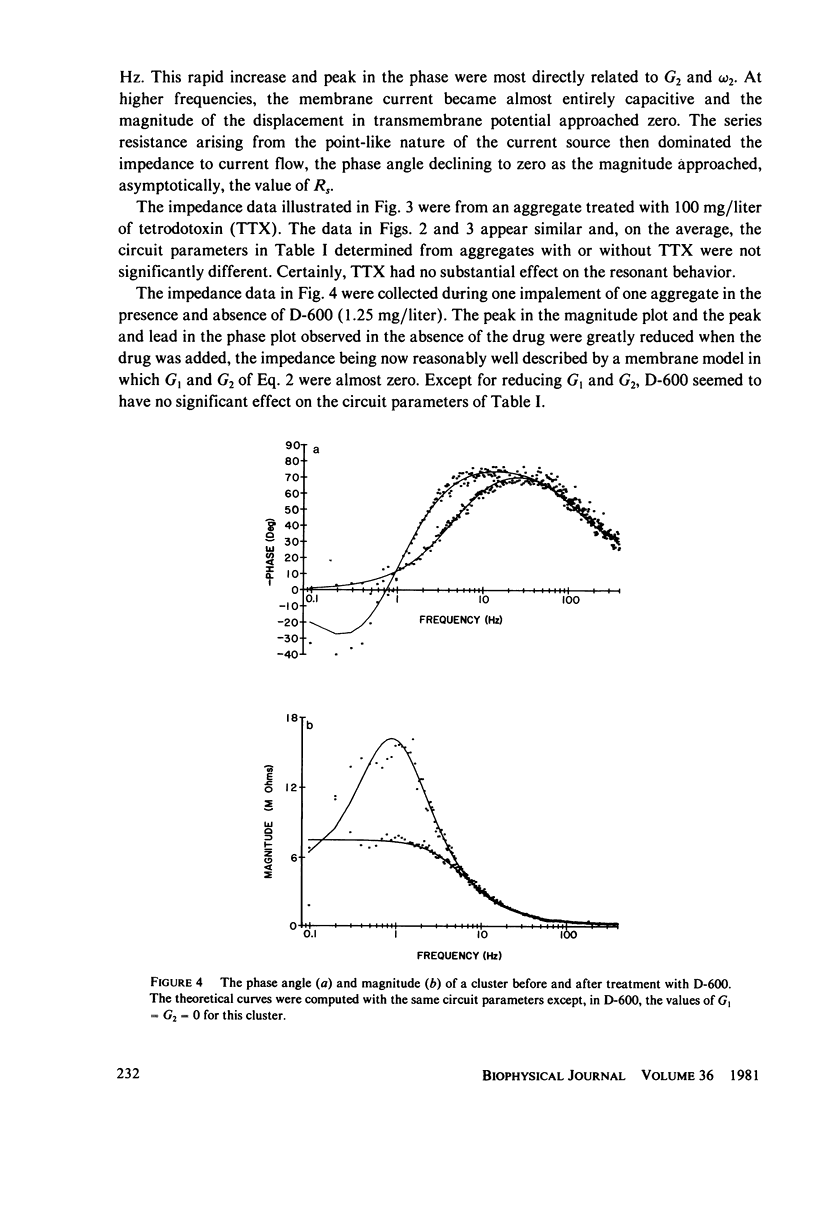

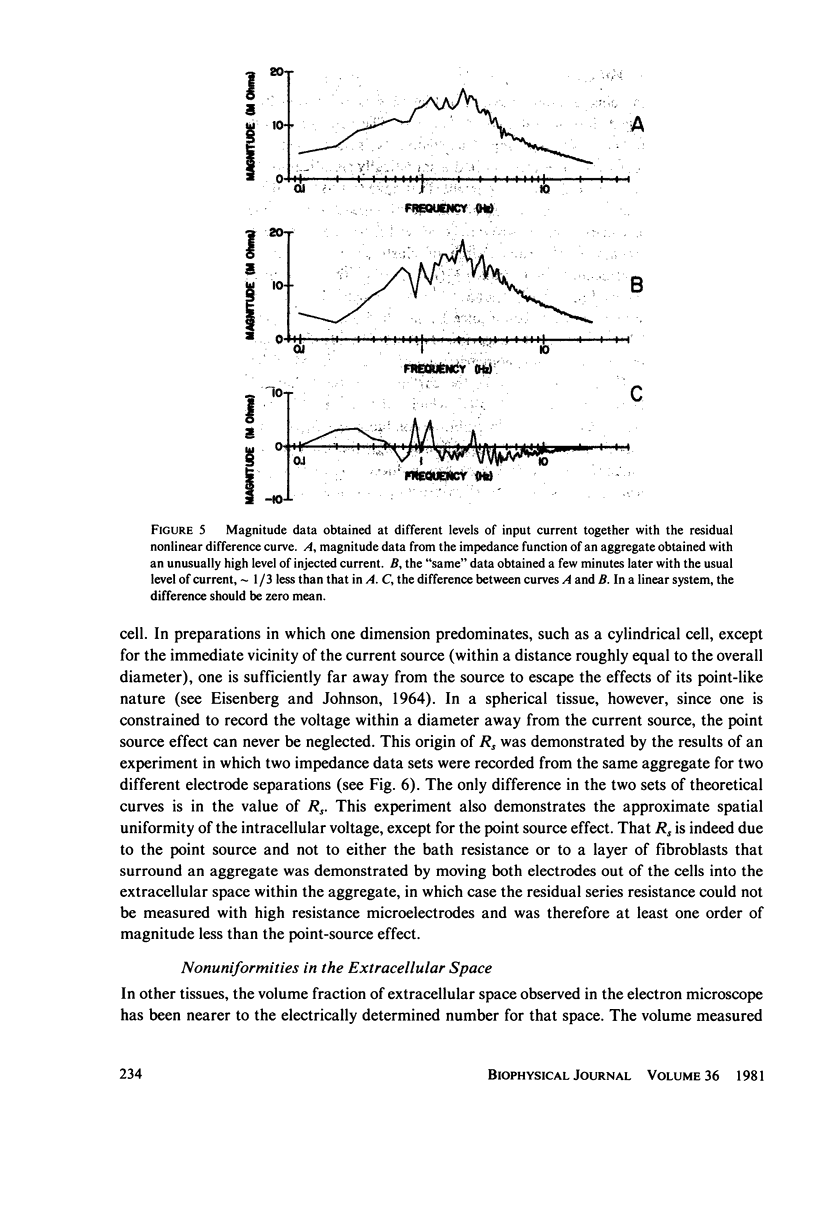
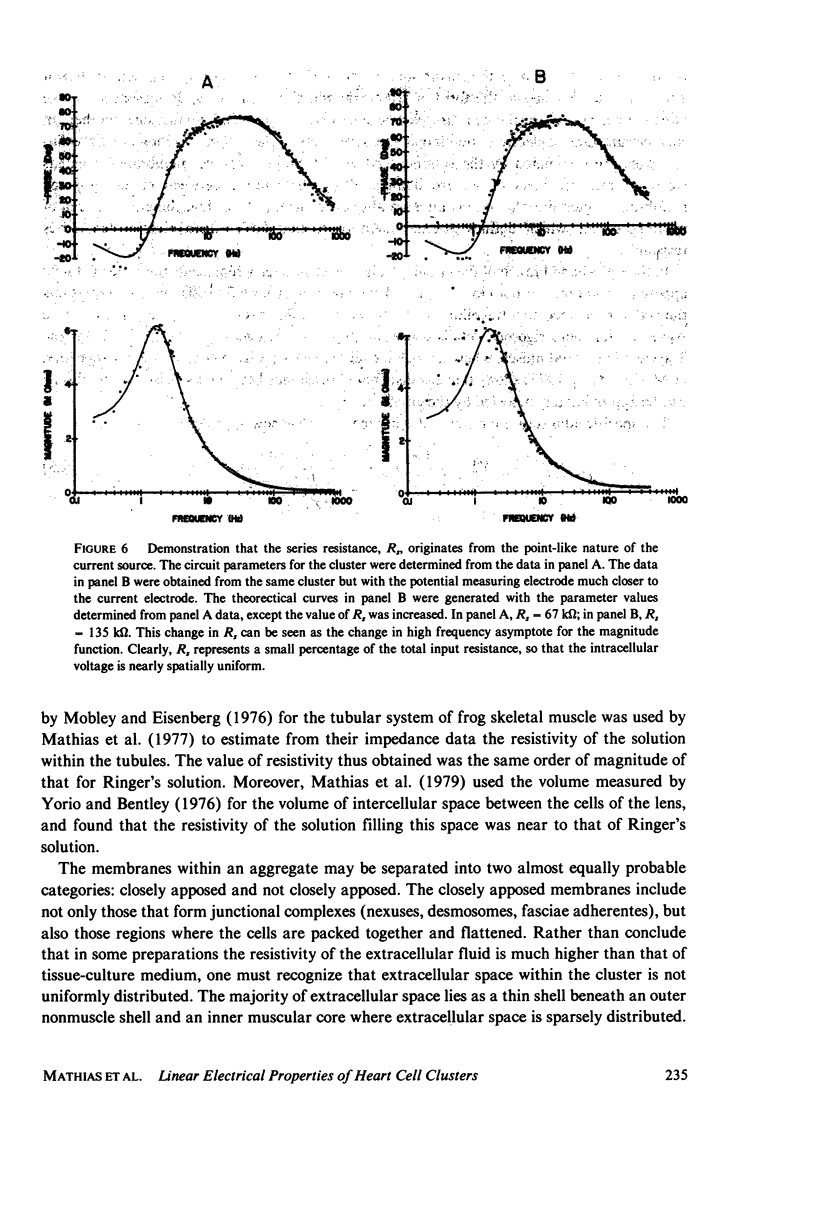
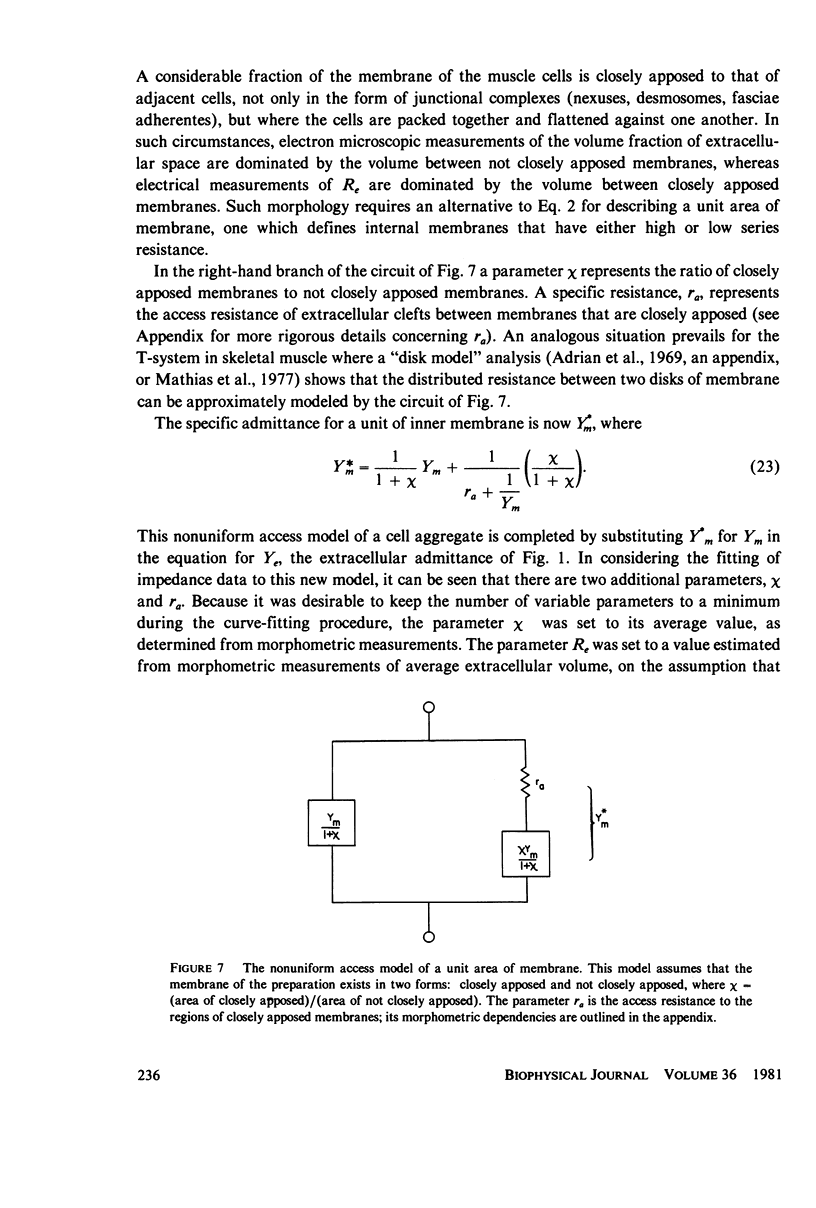






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Properties of the sodium channel gating current. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:297–304. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANDLER W. K., FITZHUGH R., COLE K. S. Theoretical stability properties of a space-clamped axon. Biophys J. 1962 Mar;2:105–127. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86844-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. On the admittance of membranes associated with channel conduction. Application to channels at non-equilibrium steady state. J Theor Biol. 1979 Dec 21;81(4):633–644. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay J. R., DeFelice L. J., DeHaan R. L. Current noise parameters derived from voltage noise and impedance in embryonic heart cell aggregates. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):169–184. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85169-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colatsky J. J., Tsien R. W. Sodium channels in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):265–268. doi: 10.1038/278265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehaan R. L., Fozzard H. A. Membrane response to current pulses in spheroidal aggregates of embryonic heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Feb;65(2):207–222. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Shigeto N., Lieberman M., Johnson E. A. The initial inward current in spherical clusters of chick embryonic heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Apr;75(4):437–456. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Barcilon V., Mathias R. T. Electrical properties of spherical syncytia. Biophys J. 1979 Jan;25(1):151–180. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85283-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Mathias R. T. Structural analysis of electrical properties of cells and tissues. Crit Rev Bioeng. 1980;4(3):203–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M., Poussart D., Moore L. E. Complex admittance of Na+ conduction in squid axon. J Membr Biol. 1979 Oct 5;50(1):43–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01868787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horres C. R., Lieberman M., Purdy J. E. Growth orientation of heart cells on nylon monofilament. Determination of the volume-to-surface area ratio and intracellular potassium concentration. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 15;34(4):313–329. doi: 10.1007/BF01870306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sommer J. R. A strand of cardiac muscle. Its ultrastructure and the electrophysiological implications of its geometry. J Cell Biol. 1967 Apr;33(1):103–129. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M., Sawanobori T., Kootsey J. M., Johnson E. A. A synthetic strand of cardiac muscle: its passive electrical properties. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Apr;65(4):527–550. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Eisenberg R. S., Valdiosera R. Electrical properties of frog skeletal muscle fibers interpreted with a mesh model of the tubular system. Biophys J. 1977 Jan;17(1):57–93. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85627-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Rae J. L., Eisenberg R. S. Electrical properties of structural components of the crystalline lens. Biophys J. 1979 Jan;25(1):181–201. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85284-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Rae J. L., Eisenberg R. S. The lens as a nonuniform spherical syncytium. Biophys J. 1981 Apr;34(1):61–83. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84837-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Eisenberg B. R. Sizes of components in frog skeletal muscle measured by methods of stereology. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jul;66(1):31–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A., Page E. The surface area of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):547–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Salama G. Optical probes of membrane potential in heart muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:267–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan R. D., DeHaan R. L. Voltage clamp analysis of embryonic heart cell aggregates. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Feb;73(2):175–198. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F. Linear electrical properties of the transverse tubules and surface membrane of skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Nov;56(5):640–671. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.5.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdiosera R., Clausen C., Eisenberg R. S. Impedance of frog skeletal muscle fibers in various solutions. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Apr;63(4):460–491. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.4.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


