Abstract
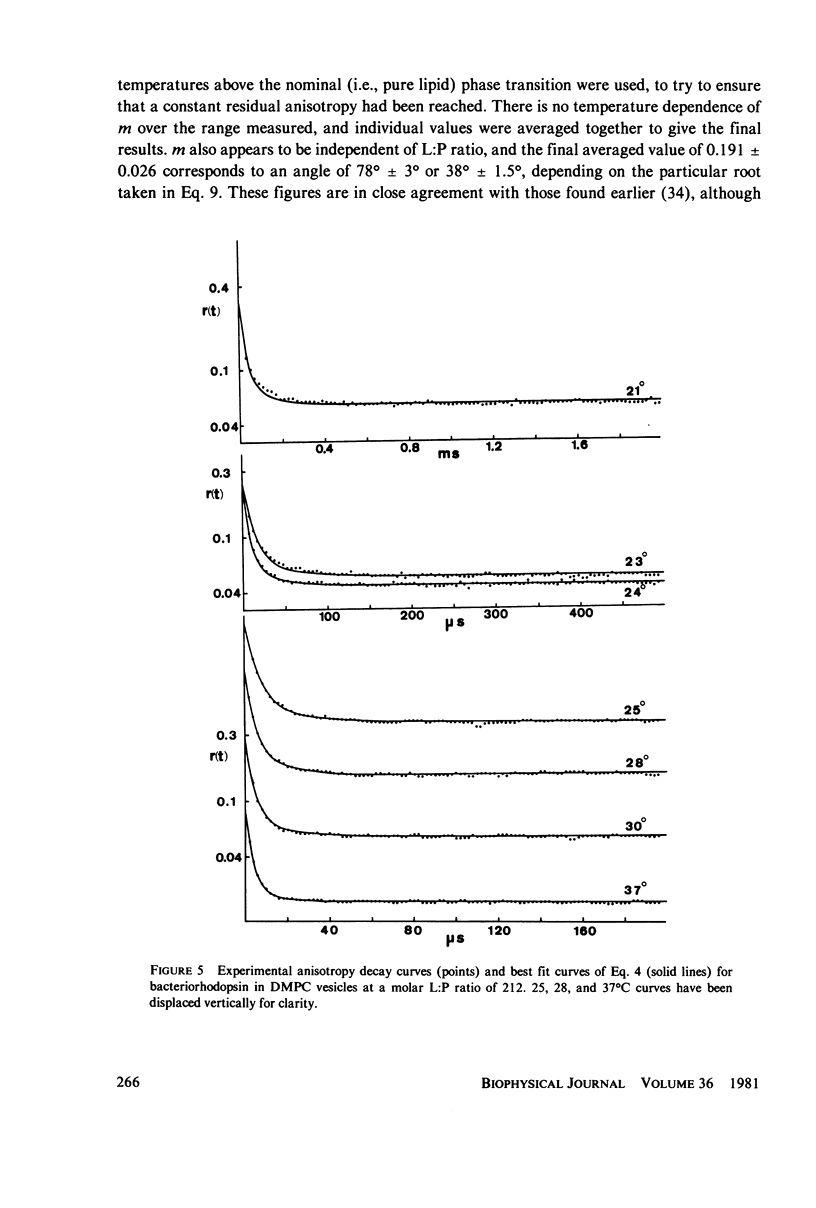
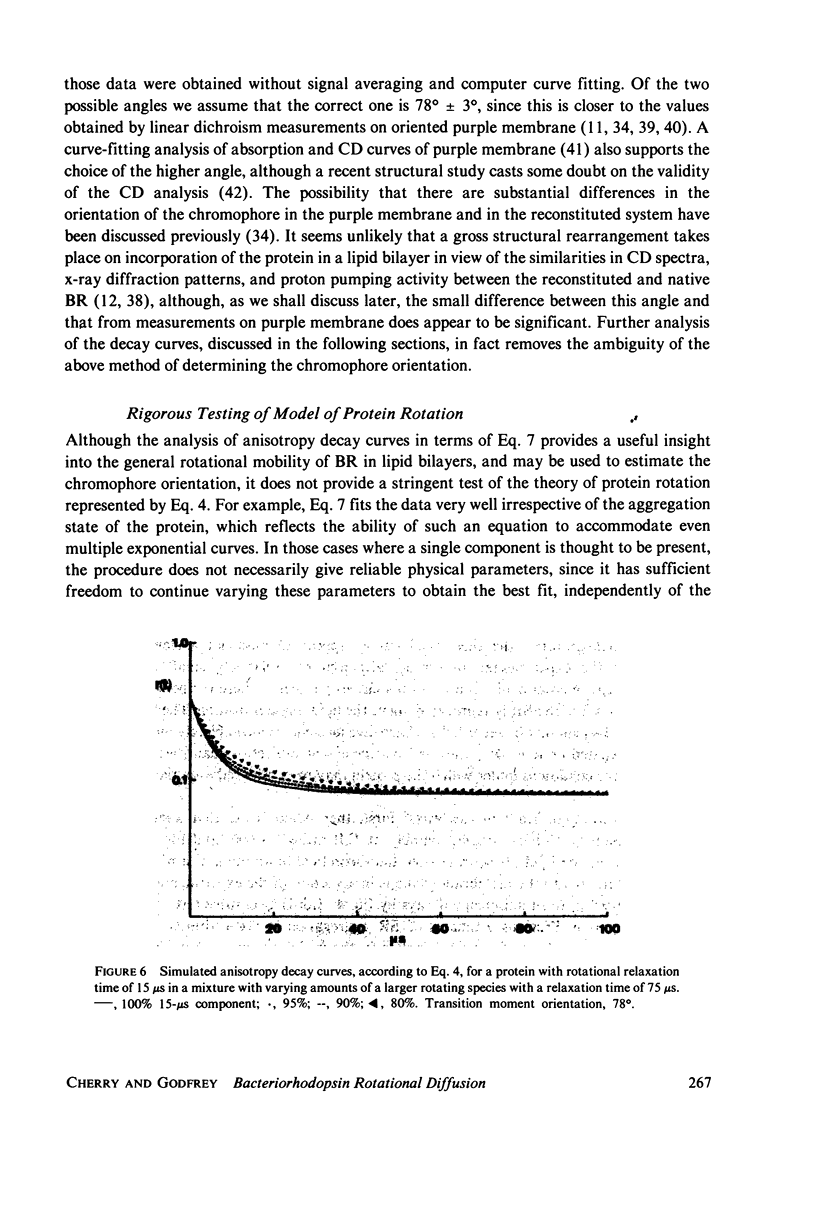
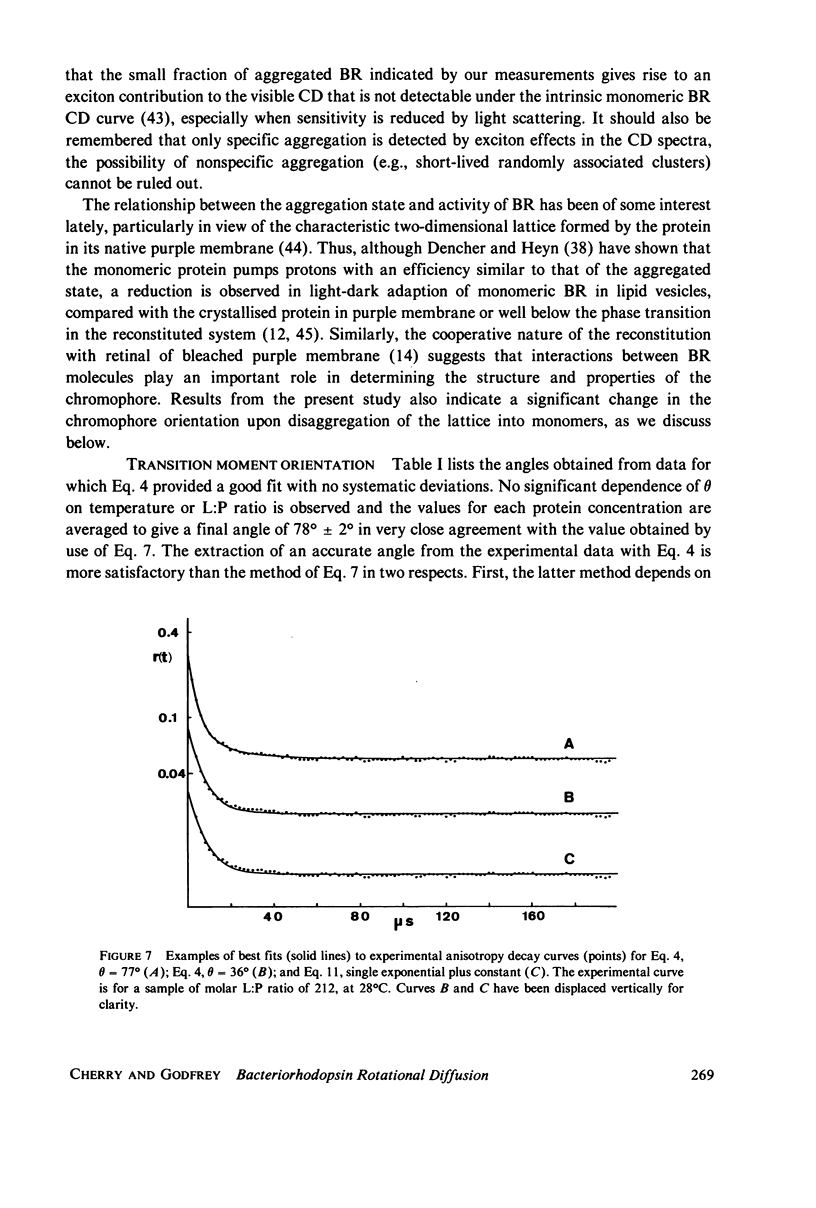
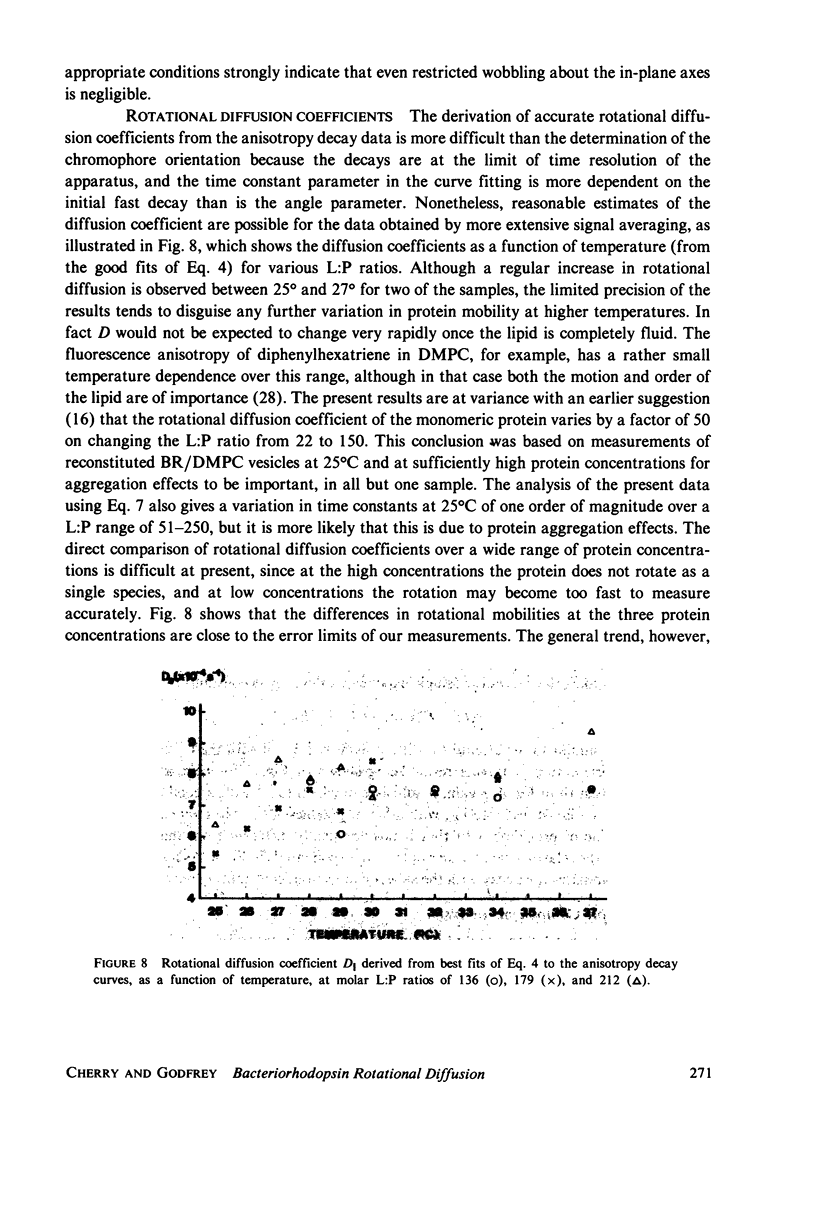
Rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine vesicles has been measured at different temperatures and lipid; protein ratios by the technique of flash-induced transient linear dichroism. The data are used to evaluate critically the theory of anisotropy decay due to protein rotation in the lipid bilayer. The theoretical model assumes that rotation of the protein occurs only around the membrane normal. Under conditions favoring completely monomeric bacteriorhodopsin, namely at molar lipid; protein ratios greater than or approximately 100 and for temperatures sufficiently above the lipid phase transition, it is found that the theoretical model provides an excellent description of the experimental data. Curve-fitting analyses of the experimental decay curves show that the retinal is oriented at an angle of 78 +/- 2 degrees with respect to the membrane normal. Between 25 and 37 degrees C, the protein rotates with a relaxation time of 15 +/- 5 micros in the lipid liquid crystalline phase, corresponding to the membrane viscosity of 3.7 +/- 1.3 P. The curve analysis also provides a sensitive test for the presence of protein aggregates in the lipid bilayer.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin R. H., Chan S. S., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of cell surface components by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. J., Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Evidence for chromophore-chromophore interactions in the purple membrane from reconstitution experiments of the chromophore-free membrane. Biophys Struct Mech. 1976 Apr 15;2(1):79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00535654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belford G. G., Belford R. L., Weber G. Dynamics of fluorescence polarization in macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1392–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Membrane structure: some general principles. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):622–629. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadio R., Stoeckenius W. Effect of protein-protein interaction on light adaptation of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3374–3381. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Gómez-Fernández J. C., Goñi F. M. Intrinsic protein--lipid interactions. Physical and biochemical evidence. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Heyn M. P., Oesterhelt D. Rotational diffusion and exciton coupling of bacteriorhodopsin in the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Measurement of protein rotational diffusion in membranes by flash photolysis. Methods Enzymol. 1978;54:47–61. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)54007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U., Schneider G. Rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid membranes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):465–469. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Müller U. Temperature-dependent aggregation of bacteriorhodopsin in dipalmitoyl- and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Rotational and lateral diffusion of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):289–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):39–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio236039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi H. L., Ferraro J. R. Active site structure of bacteriorhodopsin and mechanism of action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 28;91(2):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91561-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellweg H. G., Sumper M. Selective formation of bacterio-opsin trimers by chemical crosslinking of purple membrane. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Bacteriorhodopsin monomers pump protons. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrey T. G., Becher B., Mao B., Kilbride P., Honig B. Exciton interactions and chromophore orientation in the purple membrane. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):377–397. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Oesterhelt D. Chromophore equilibria in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1979 Nov;28(2):211–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85172-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Steinberg I. Z. On the analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics by the method of least-squares. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):583–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Cherry R. J., Dencher N. A. Lipid--protein interactions in bacteriorhodopsin--dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):840–849. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P., Cherry R. J., Müller U. Transient and linear dichroism studies on bacteriorhodopsin: determination of the orientation of the 568 nm all-trans retinal chromophore. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):607–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn M. P. Determination of lipid order parameters and rotational correlation times from fluorescence depolarization experiments. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):359–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Restall C. J., Hyla R., Chapman D. Protein rotation and chromophore orientation in reconstituted bacteriorhodopsin vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T., Callender R. H., Dinur U., Ottolenghi M. Photoisomerization, energy storage, and charge separation: a model for light energy transduction in visual pigments and bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2503–2507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S. Saturation-transfer spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:480–511. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Derzko Z., Wu E. S., Hou Y., Poste G. Measurement of the lateral mobility of cell surface components in single, living cells by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(4):565(417)–576(428). doi: 10.1002/jss.400050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr Time-dependent absorption anisotropy and rotational diffusion of proteins in membranes. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):277–296. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84728-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. I., Mowery P. C., Stoeckenius W., Crespi H. L., Schoenborn B. P. Location of the chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4726–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein R., Hess B. Immobilization of bacteriorhodopsin and orientation of its transition moment in purple membrane. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Marcus M. A., Ehrenberg B., Crespi H. Experimental evidence for secondary protein-chromophore interactions at the Schiff base linkage in bacteriorhodopsin: Molecular mechanism for proton pumping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4642–4646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipari G., Szabo A. Effect of librational motion on fluorescence depolarization and nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in macromolecules and membranes. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):489–506. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85109-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C., Boxer D., Garland P. Phosphorescence depolarization and the measurement of rotational motion of proteins in membranes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cherry R. J. Anchorage of a band 3 population at the erythrocyte cytoplasmic membrane surface: protein rotational diffusion measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4702–4706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Theory of protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions in bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehorek M., Heyn M. P. Binding of all-trans-retinal to the purple membrane. Evidence for cooperativity and determination of the extinction coefficient. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4977–4983. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Lipid-protein interaction in reconstituted cytochrome c oxidase/phospholipid membranes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Dec;359(12):1747–1756. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale F. W. Fluorescence depolarization by light-scattering in turbid solutions. Photochem Photobiol. 1969 Dec;10(6):363–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1969.tb05701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D. Large-scale rotational motions of proteins detected by electron paramagnetic resonance and fluorescence. Biophys J. 1978 Nov;24(2):439–462. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85394-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


