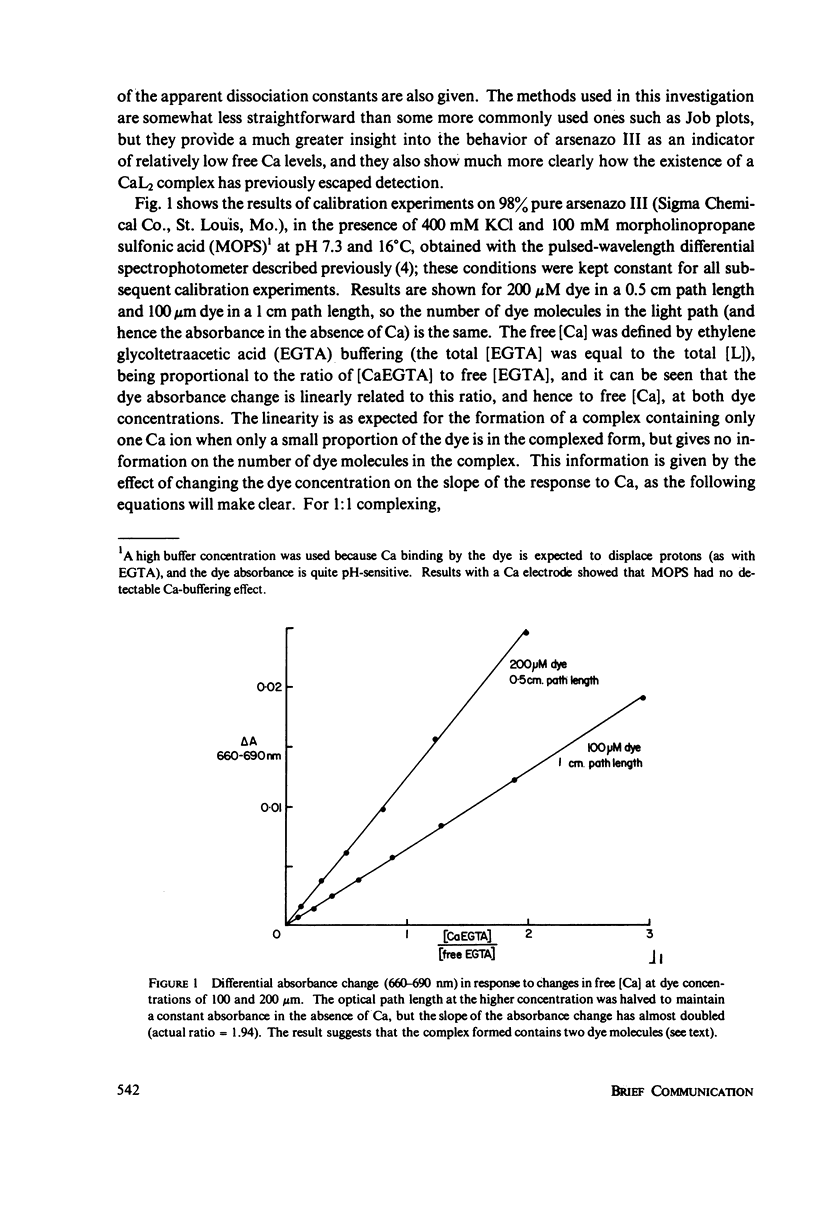
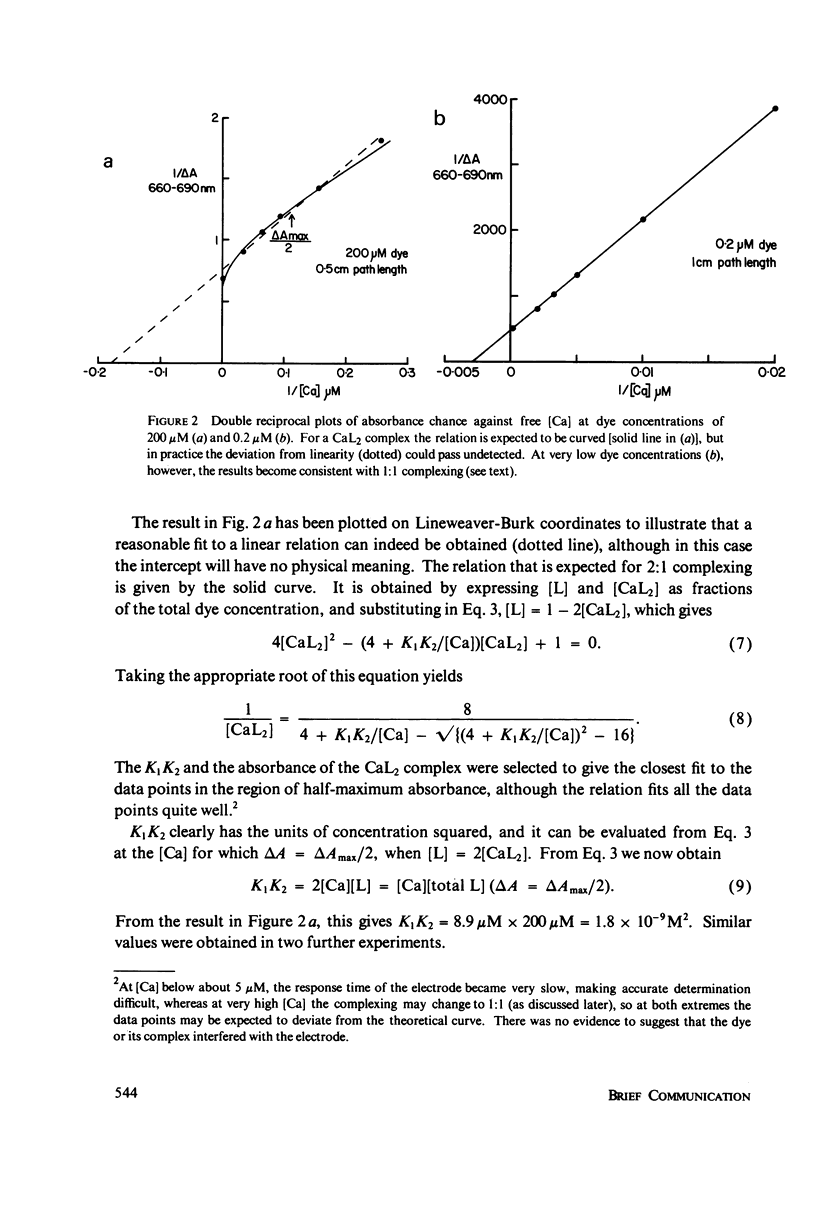
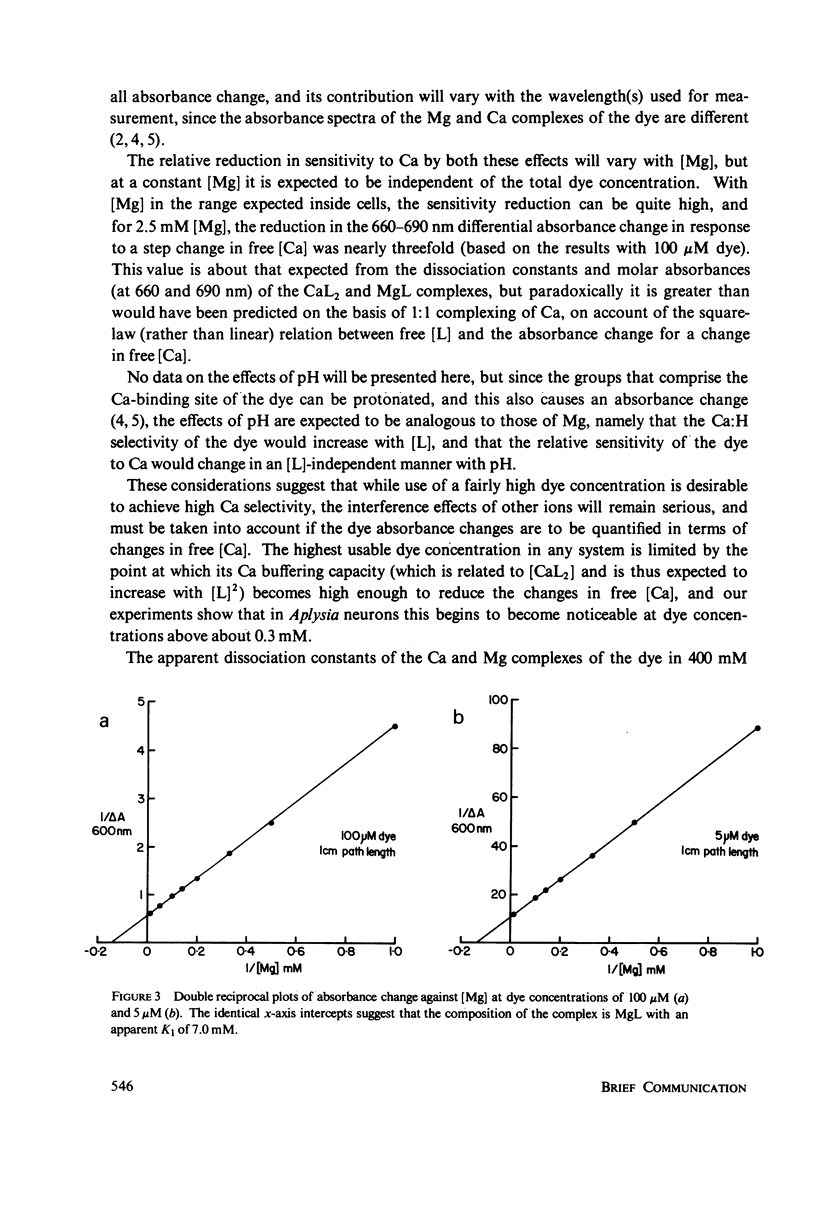
Abstract
Experiments to determine the apparent dissociation constants of the Ca and Mg complexes of arsenazo III clearly indicated that the predominant Ca complex contains one Ca ion and two dye molecules, although previous reports have either claimed or assumed 1:1 complexing. The evidence is based on the effects of varying [dye] as well as [Ca] and [Mg], and clear evidence for the formation of 1:1 complexes with Ca was obtained only at submicromolar [dye], whereas Mg formed 1:1 complexes exclusively. The implications of these findings with regard to the use of arsenazo III as an indicator of intracellular free [Ca] are discussed, with particular reference to its selectivity for Ca and the interference effects of other ions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Brown P. K., Pinto L. H. Detection of light-induced changes of intracellular ionized calcium concentration in Limulus ventral photoreceptors using arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):299–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Cohen L. B., De Weer P., Pinto L. H., Ross W. N., Salzberg B. M. Rapid changes in intracellular free calcium concentration. Detection by metallochromic indicator dyes in squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1155–1160. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85891-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pace-maker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick N. C. Purification of arsenazo III, a Ca2+-sensitive dye. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick N. C., Ratzlaff R. W., Blaustein M. P. Arsenazo III as an indicator for ionized calcium in physiological salt solutions: its use for determination of the CaATP dissociation constant. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):433–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D. The determination of the stability constant for calcium-EGTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. V., Gorman A. L. Internal calcium changes in a bursting pacemaker neuron measured with arsenazo III. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.850795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



