Abstract
Two kinetic models are introduced which predict amplitudes and time-courses of endplate currents and miniature endplate currents at neuromuscular junctions, at both normal and acetylcholinesterase-inhibited endplates. Appropriate differential rate equations reflecting interactions of acetylcholine with acetylcholine receptor and with esterase, diffusion of acetylcholine both within and from the synaptic cleft, and cooperativity between receptor site occupancy and ion channel opening are solved. Acetylcholine release into the cleft is assumed to be instantaneous. The simpler homogeneous reaction space model accurately predicts decay phase time constants are inaccurate. The two-reaction space model predicts amplitudes and time constants within a factor of two of those observed experimentally. The simulations indicate that the amplitudes and time-courses are primarily determined by the chemical reaction rates that characterize acetylcholine interactions with receptor and esterase and that these interactions occur under nonequilibrium conditions. Approximately 50% of the total ion channels in the initial reaction space are predicted to be opened at the peak endplate current. The cooperative opening of ion channels by acetylcholine requires that acetylcholine be introduced into the cleft in discrete, concentrated elements. Virtually all the open channels are confined to the initial reaction space, although acetylcholine-bound receptor sites can be much more widely distributed.
Full text
PDF

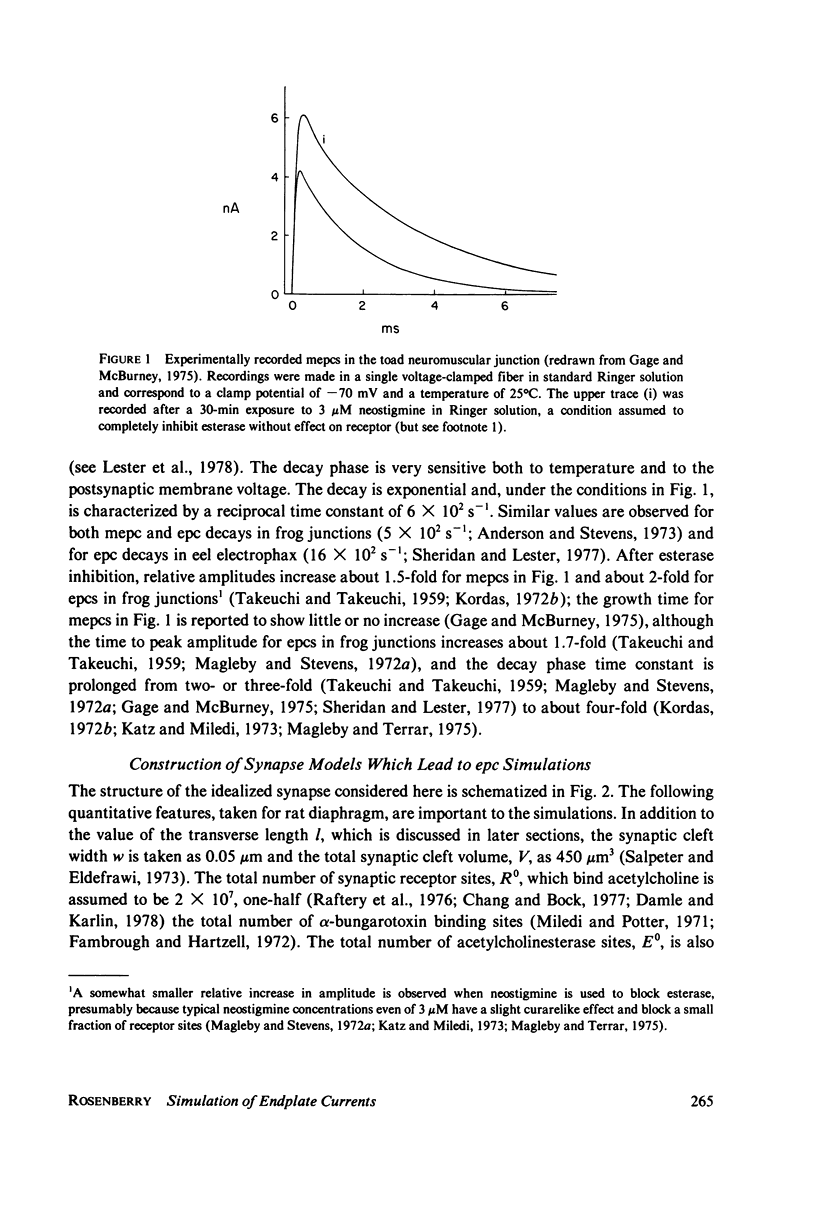







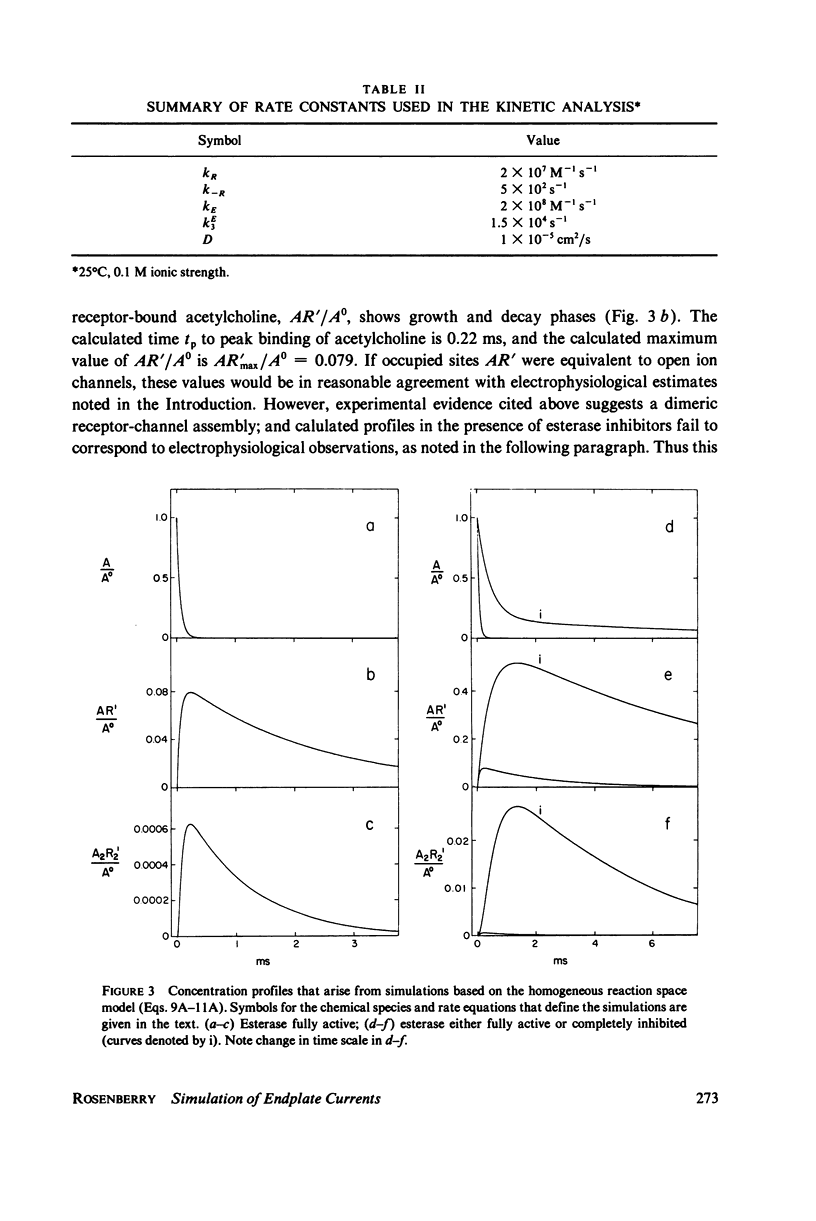



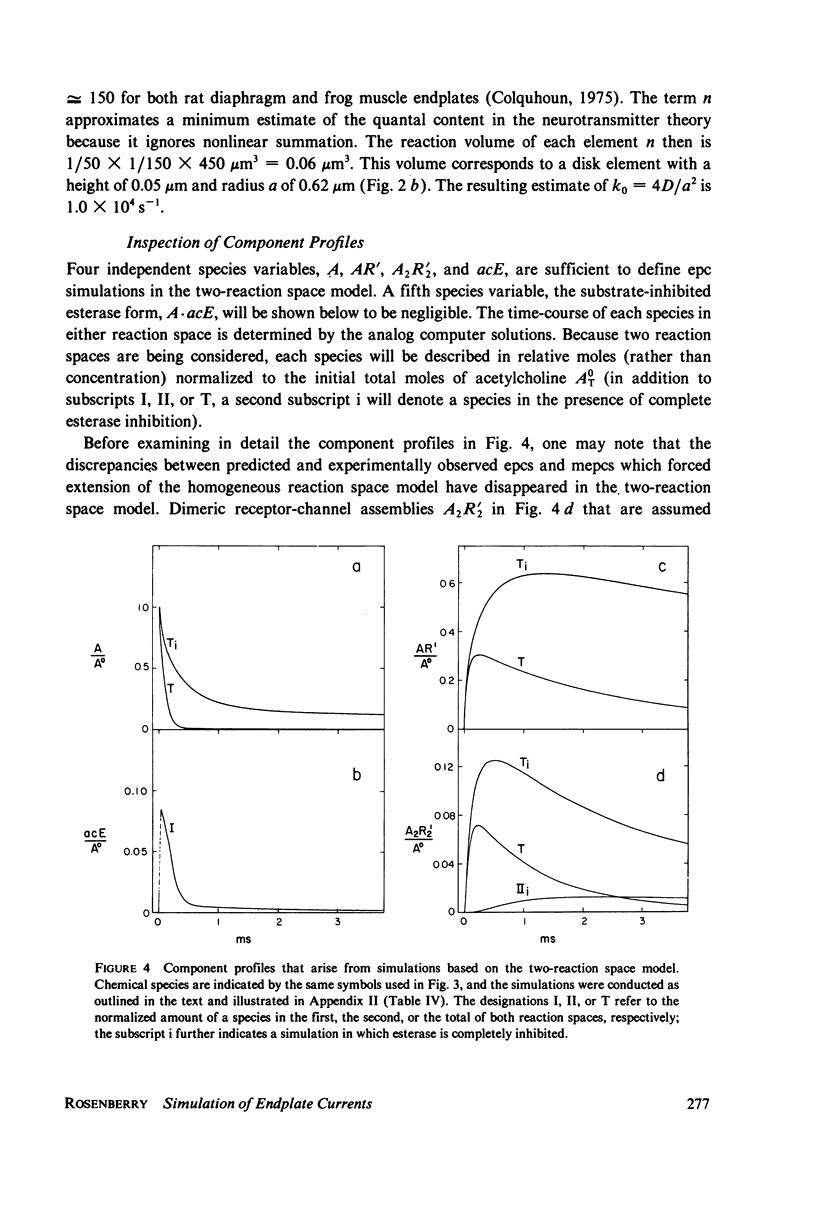


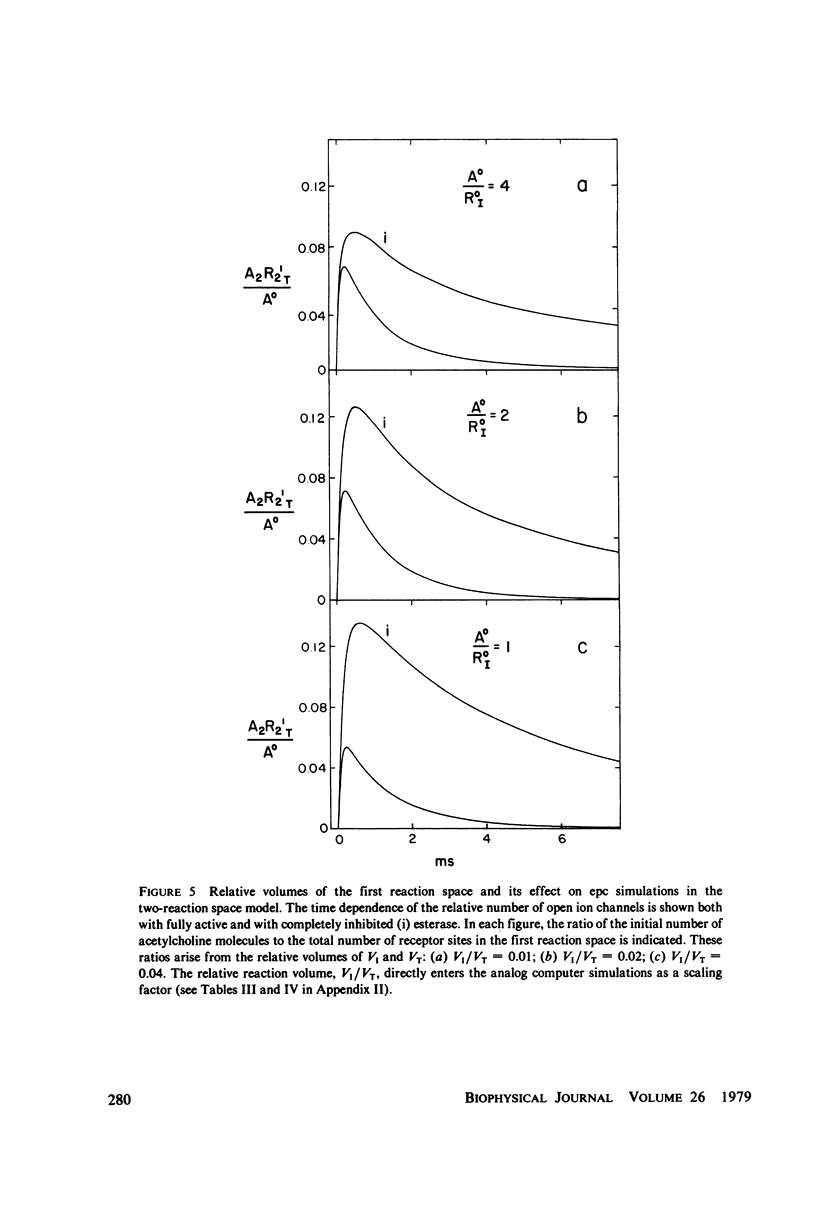







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. An analysis of the dose-response curve at voltage-clamped frog-endplates. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00580537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Reiner E. Acetylcholinesterase. Two types of inhibition by an organophosphorus compound: one the formation of phosphorylated enzyme and the other analogous to inhibition by substrate. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):147–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1150147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois J. -P., Ryter A., Menez A., Fromageot P., Boquet P., Changeux J. -P. Localization of the cholinergic receptor protein in Electrophorus electroplax by high resolution autoradiography. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 1;25(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80469-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J., Tung Y., Kittel C. On the cooperativity of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):335–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D. Mechanisms of drug action at the voluntary muscle endplate. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:307–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Interaction at end-plate receptors between different choline derivatives. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):369–381. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of one of two alpha-neurotoxin binding sites in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2039–2045. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdall M. J., Fox G., Wächtler K., Whittaker V. P., Zimmermann H. Recent studies on the comparative biochemistry of the cholinergic neuron. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:65–81. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., JAEGER J. C. The relationship between the mode of operation and the dimensions of the junctional regions at synapses and motor end-organs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):38–56. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Hartzell H. C. Acetylcholine receptors: number and distribution at neuromuscular junctions in rat diaphragm. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Quantitation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):144–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., McBurney R. N. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and neostigmine on the conductance change caused by a quantum or acetylcholine at the toad neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):385–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünhagen H. H., Iwatsubo M., Changeux J. P. Fast kinetic studies on the interaction of cholinergic agonists with the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata as revealed by quinacrine fluorescence. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):225–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MITCHELL J. F. The release of acetylcholine in the isolated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:246–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A. On the application of "a plausible model" of allosteric proteins to the receptor for acetylcholine. J Theor Biol. 1967 Aug;16(2):306–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. An attempt at an analysis of the factors determining the time course of the end-plate current. I. The effects of prostigmine and of the ratio of Mg 2+ to Ca 2+ . J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):317–332. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordas M. An attempt at an analysis of the factors determining the time course of the end-plate current. II. Temperature. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):333–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. The number of transmitter molecules in a quantum: an estimate from iontophoretic application of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):465–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Changeux J. P., Sheridan R. E. Conductance increases produced by bath application of cholinergic agonists to Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Koblin D. D., Sheridan R. E. Role of voltage-sensitive receptors in nicotinic transmission. Biophys J. 1978 Mar;21(3):181–194. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85518-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Terrar D. A. Factors affecting the time course of decay of end-plate currents: a possible cooperative action of acetylcholine on receptors at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):467–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Bellinger J., Salpeter M. M. Distribution of acetylcholine receptors at frog neuromuscular junctions with a discussion of some physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACHMANSOHN D., WILSON I. B. The enzymic hydrolysis and synthesis of acetylcholine. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1951;12:259–339. doi: 10.1002/9780470122570.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrete J., Del Castillo J., Escobar I., Yankelevich G. Correlation between amplitudes and rise times of the miniature endplate potentials in frog muscle. Int J Neurosci. 1972 Jul;4(1):1–10. doi: 10.3109/00207457209147158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Chang H. W. Dynamic properties of isolated acetylcholine receptor protein: kinetics of the binding of acetylcholine and Ca ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3994–3998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Nachmansohn D., Katchalsky A. An attempt at an integral interpretation of nerve excitability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peper K., Dreyer F., Müller K. D. Analysis of cooperativity of drug-receptor interaction by quantitative iontophoresis at frog motor end plates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:187–192. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Chiu T. H., Wieckowski J., Barnard E. A. Types and locations of cholinergic receptor-like molecules in muscle fibres. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):3–7. doi: 10.1038/newbio241003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T. Synthesis, storage and release of [14C]acetylcholine in isolated rat diaphragm muscles. J Physiol. 1970 Jan;206(1):145–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Vandlen R. L., Reed K. L., Lee T. Characterization of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor: its subunit composition and ligand-binding properties. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:193–202. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Acetylcholine receptors. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):283–399. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:103–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Bernhard S. A. Studies of catalysis by acetylcholinesterase. Synergistic effects of inhibitors during the hydrolysis of acetic acid esters. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4308–4321. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., Elderfrawi M. E. Sizes of end plate compartments, densities of acetylcholine receptor and other quantitative aspects of neuromuscular transmission. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Sep;21(9):769–778. doi: 10.1177/21.9.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan R. E., Lester H. A. Rates and equilibria at the acetylcholine receptor of Electrophorus electroplaques: a study of neurally evoked postsynaptic currents and of voltage-jump relaxations. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):187–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


