Abstract
Quaternary strychnine blocks sodium channels from the axoplasmic side, probably by insertion into the inner channel mouth. Block is strongly voltage dependent, being more pronounced in depolarized than in resting axons. Using potential steps as a means to modulate the level of block, we investigate strychnine effects on sodium and gating currents at +50 and -50 mV. We analyze our data in terms of the simplest possible model, wherein only an open channel may receive and retain a strychnine molecule. Our main findings are (a) block by strychnine and inactivation resemble each other and (b) block of sodium and gating currents by strychnine happen with closely similar time-courses. Our data support the hypothesis of Armstrong and Bezanilla (1977) wherein an endogenous blocking particle causes inactivation by inserting itself into the inner mouth of the sodium channel. Quaternary strychnine may act as an artificial substitute for the hypothetical endogenous blocking particle. Further, we suggest that at least 90% of the rapid asymmetrical displacement current in squid axons is sodium channel gating current, inasmuch as quaternary strychnine can block 90% of the displacement current simultaneously with sodium current.
Full text
PDF



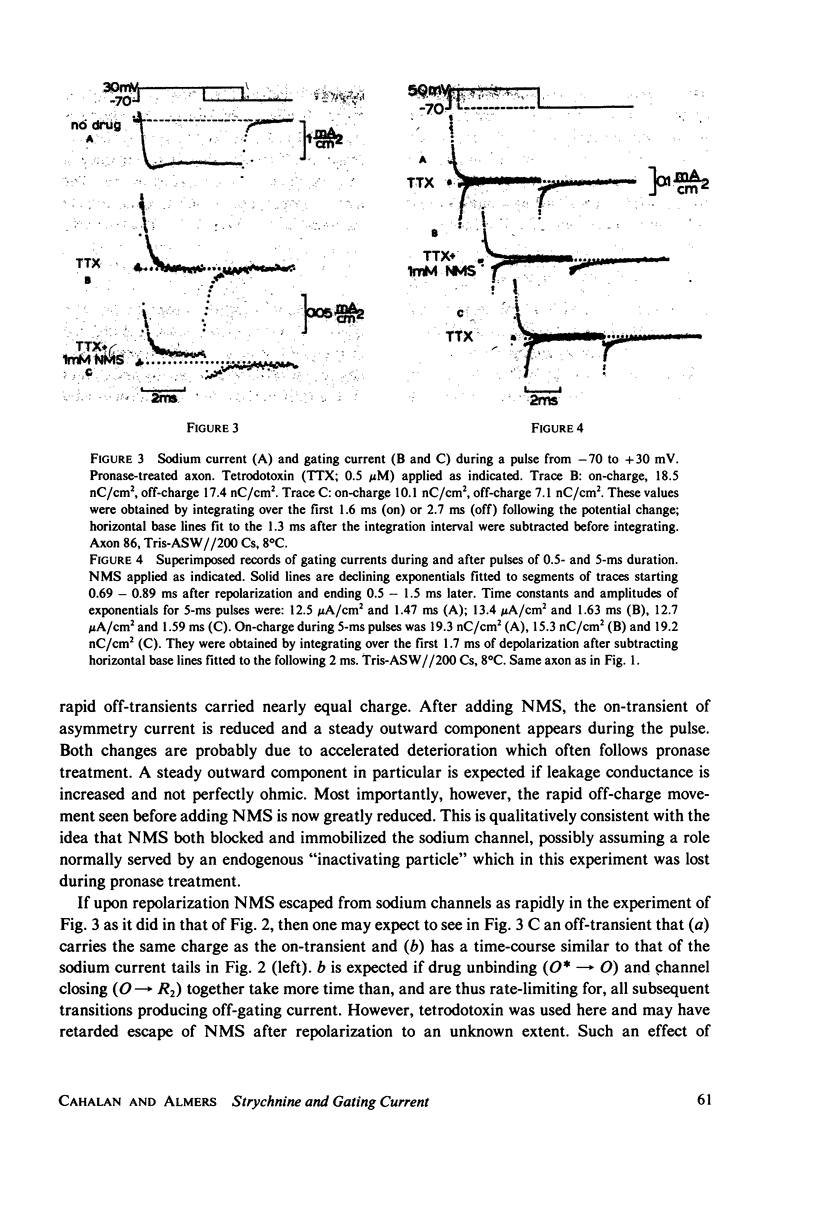



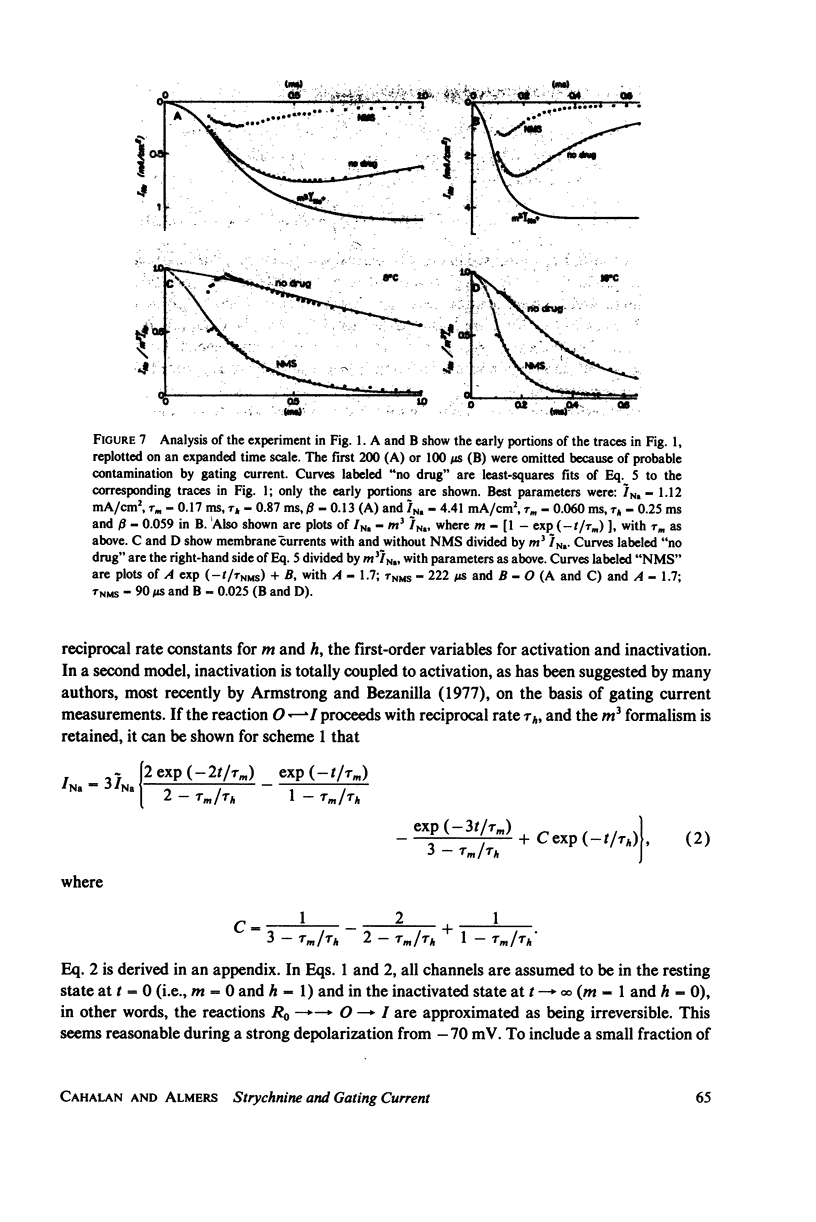


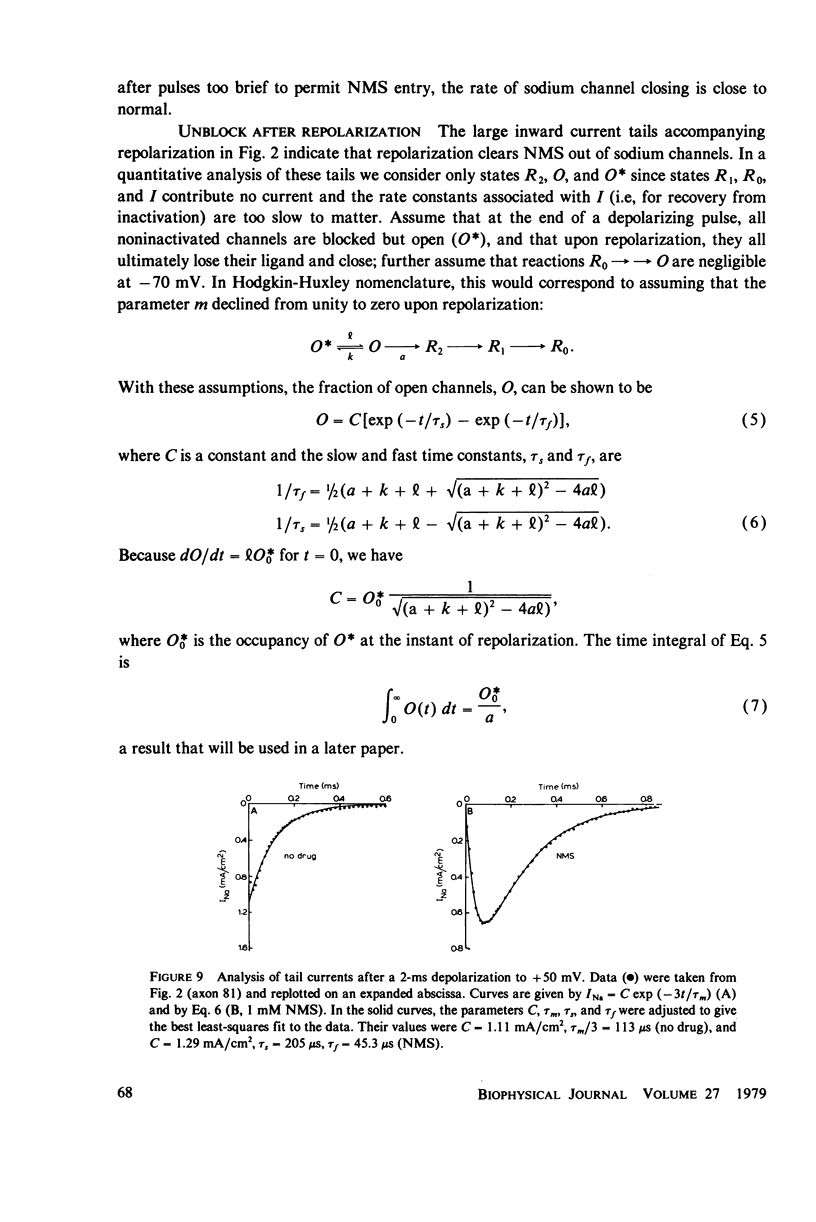
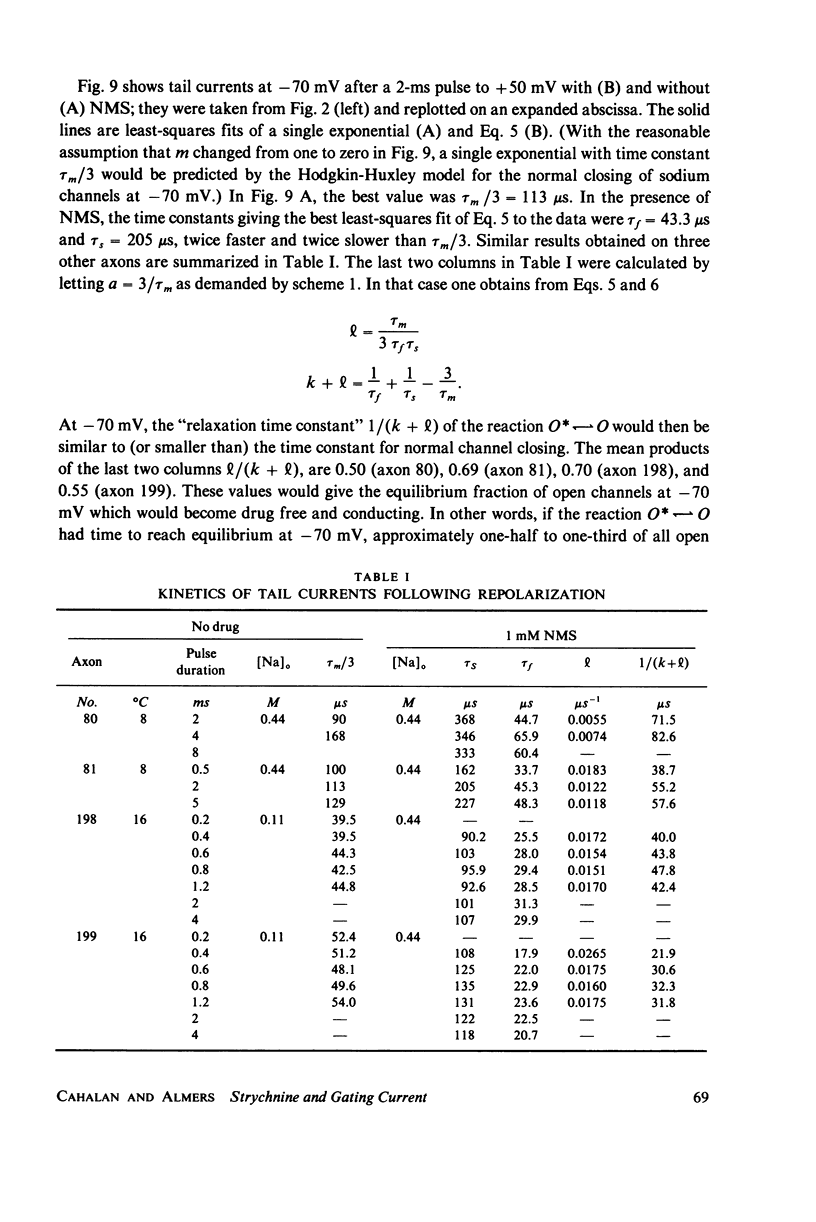




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W. Gating currents and charge movements in excitable membranes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;82:96–190. doi: 10.1007/BFb0030498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Levinson S. R. Tetrodotoxin binding to normal depolarized frog muscle and the conductance of a single sodium channel. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):483–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Inactivation of the sodium channel. II. Gating current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):567–590. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Oct;62(4):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):553–575. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Almers W. Interactions between quaternary lidocaine, the sodium channel gates, and tetrodotoxin. Biophys J. 1979 Jul;27(1):39–55. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85201-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D. Local anesthetic block of sodium channels in normal and pronase-treated squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):285–311. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85449-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Evidence for two types of sodium conductance in axons perfused with sodium fluoride solution. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):653–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The pH-dependent rate of action of local anesthetics on the node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):475–496. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E. Kinetics and steady-state properties of the charged system controlling sodium conductance in the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(2):393–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. I. Effects of strychnine on the potassium conductance of the frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jun;69(6):897–914. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. I. Effects of strychnine on the sodium conductance of the frog node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Jun;69(6):915–926. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Armstrong C. M. Immobilisation of gating charge by a substance that simulates inactivation. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):387–389. doi: 10.1038/273387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. Z., Narahashi T. Kinetic analysis of pancuronium interaction with sodium channels in squid axon membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Mar;69(3):293–323. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



