Abstract
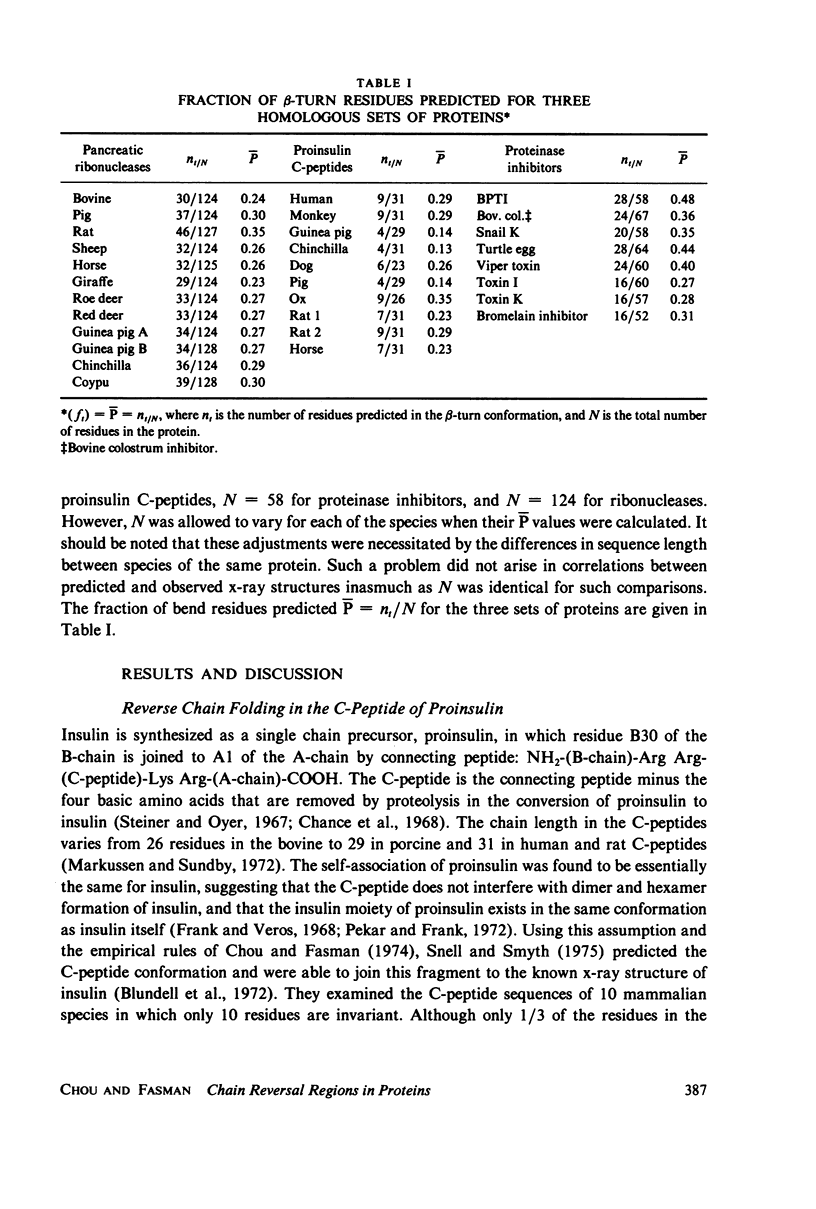
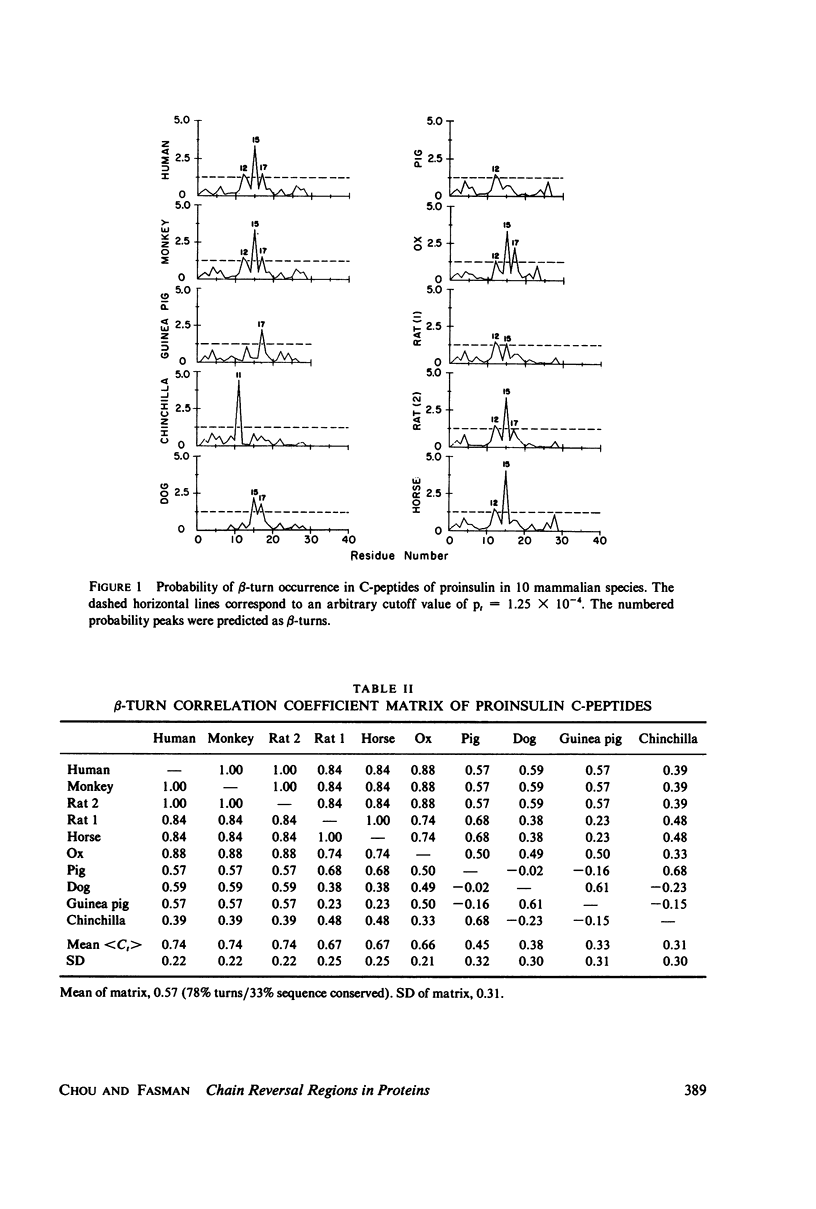
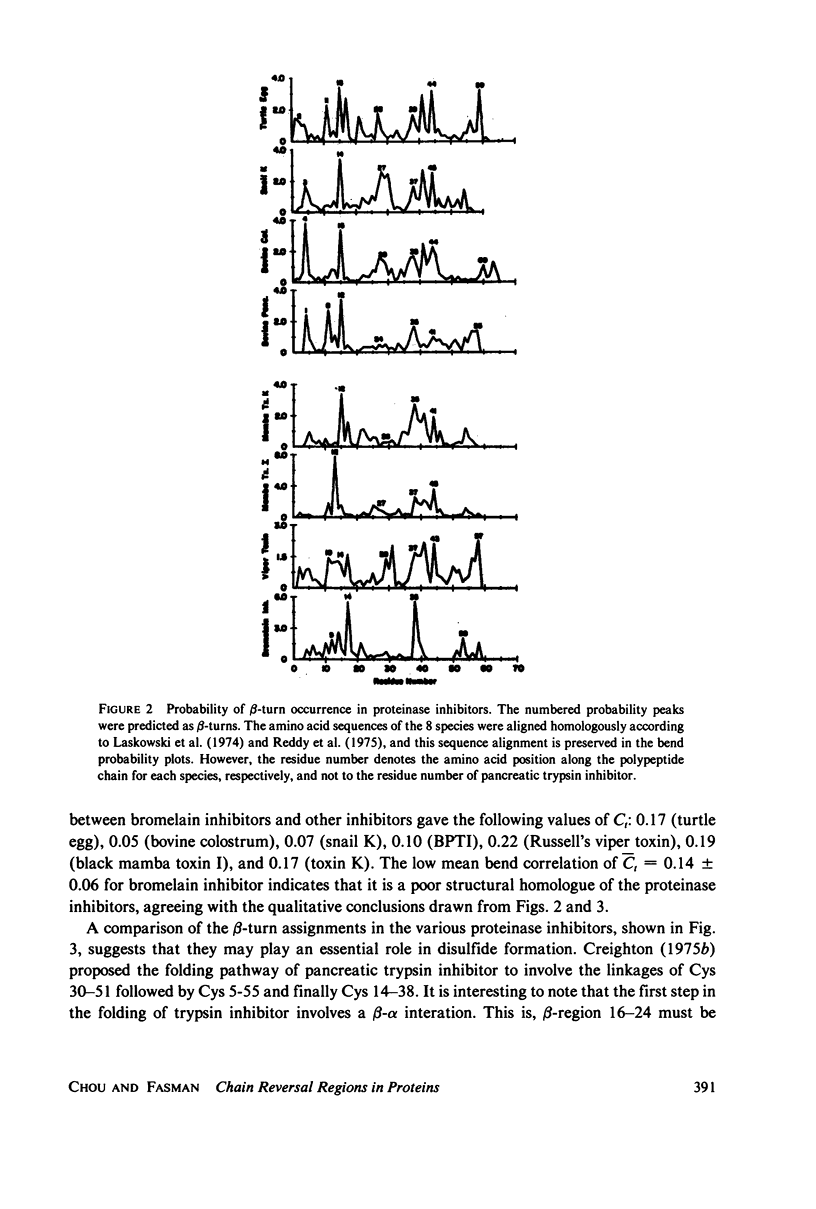
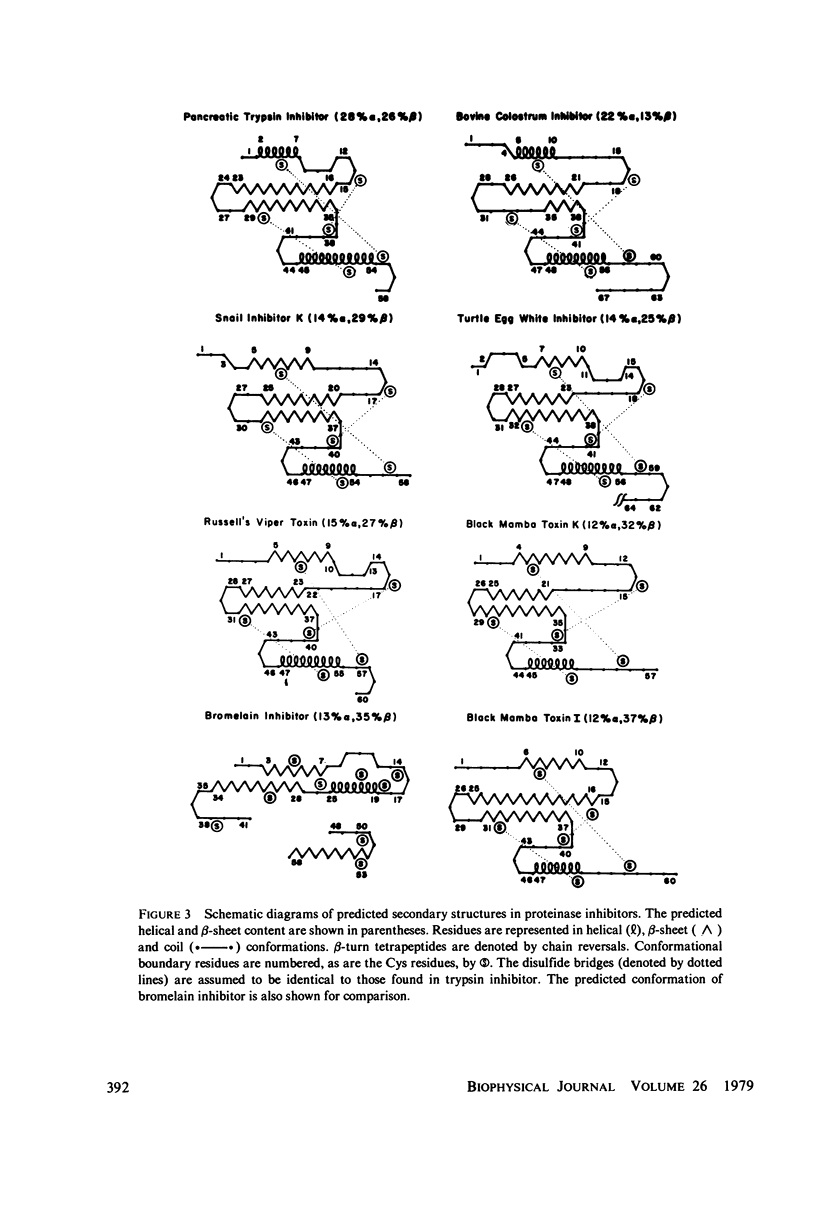
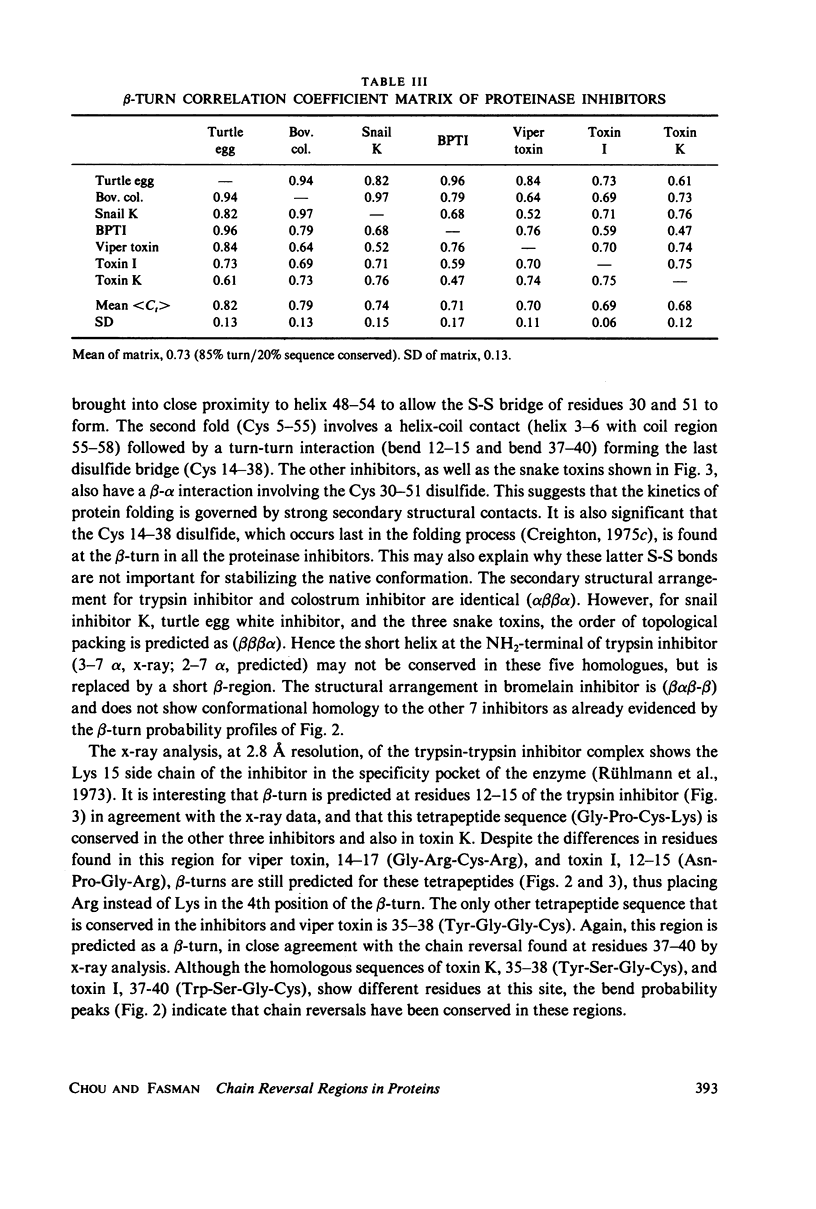
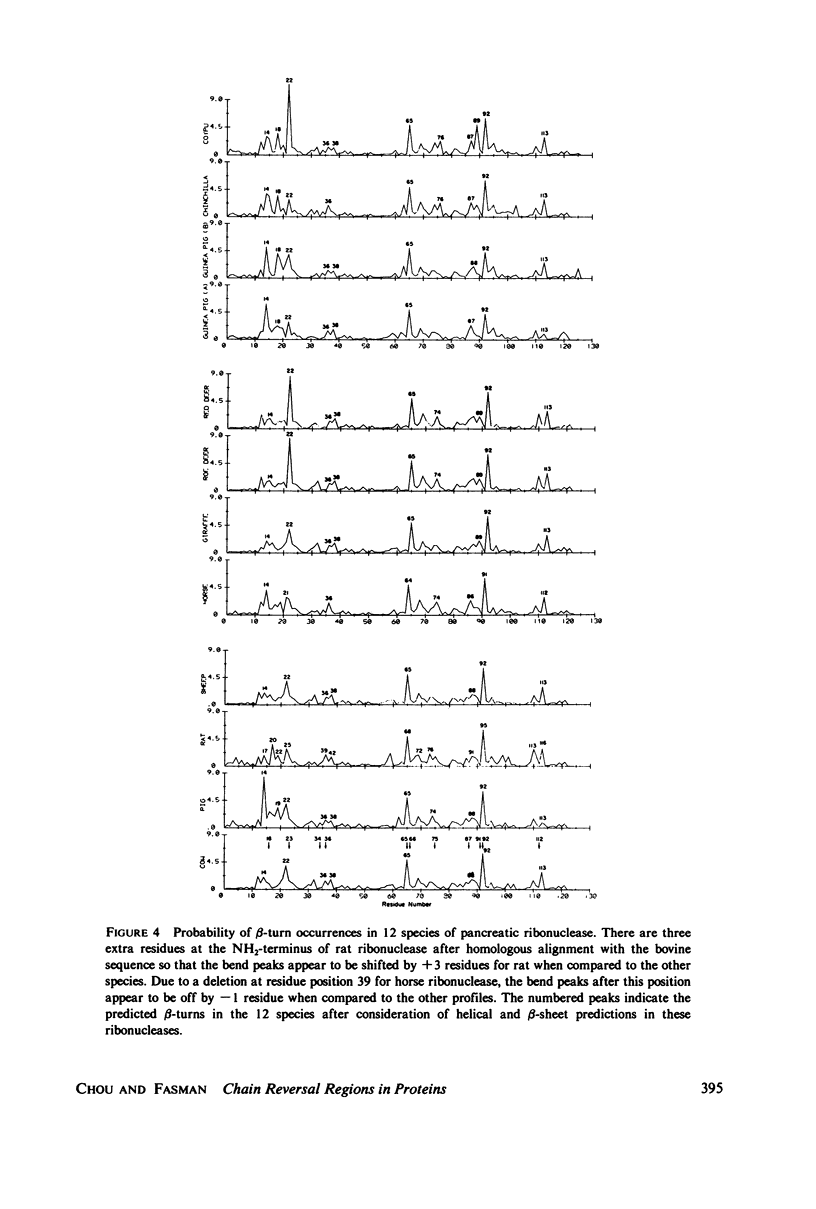
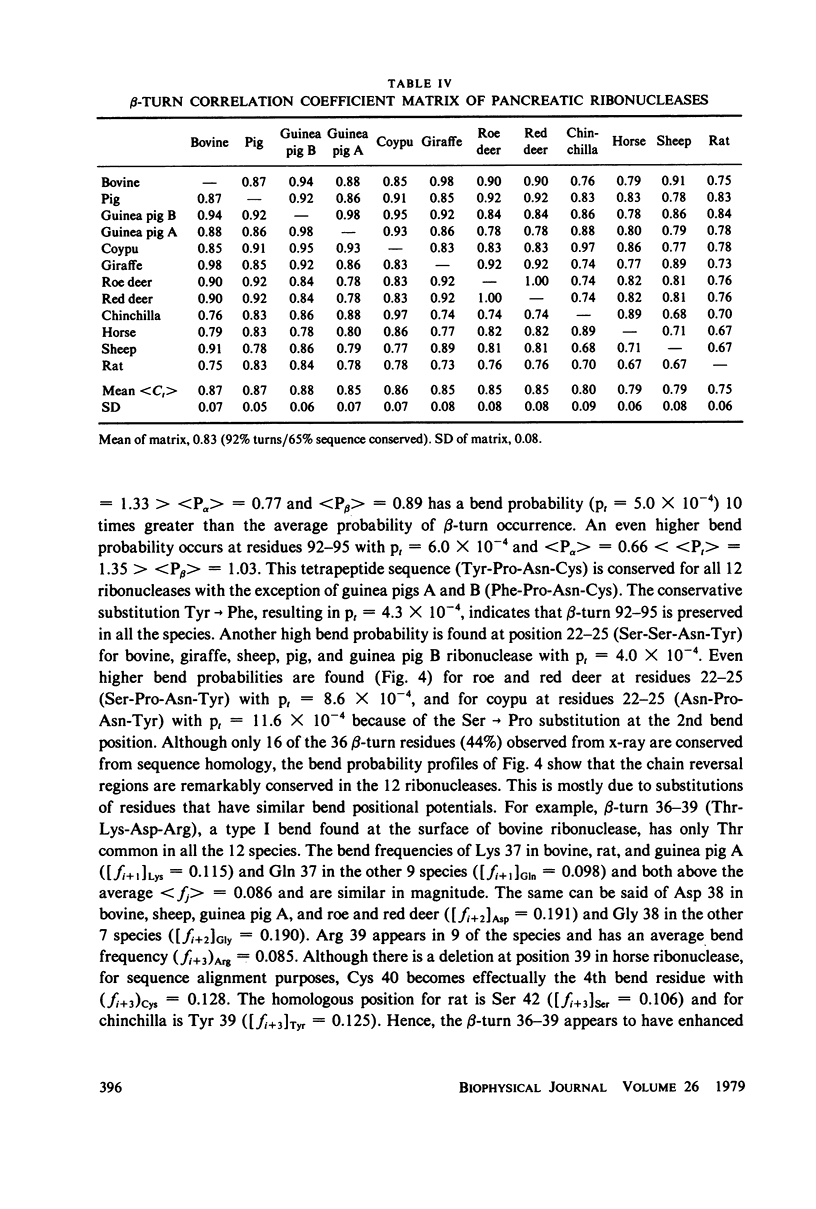
Using the bend frequencies based on 29 proteins in the previous paper (Chou and Fasman, 1979), beta-turn probability profiles were calculated for the C-peptides of 10 mammalian proinsulins, for 7 proteinase inhibitors, and for 12 species of pancreatic ribonucleases. Beta-turn correlation coefficient matrix tables were also computed to obtain the statistical mean between 45 pairs of proinsulin C-peptides, less than Ct greater than = 0.57 +/- 0.31; 21 pairs of proteinase inhibitors, less than Ct greater than = 0.73 +/- 0.13; and 66 pairs of ribonucleases, less than Ct greater than = 0.83 +/- 0.08. Despite relatively low sequence conservation in these three sets of proteins, beta-turns were predicted to be highly conserved: 33% sequence vs. 78% bend for the proinsulins, 20% sequence vs. 85% bend for the proteinase inhibitors, and 65% sequence vs. 92% bend for the ribonucleases. These results suggest that chain reversal regions play an essential role in keeping the active structural domains in hormones and enzymes intact for their specific biological function.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beintema J. J., Gaastra W., Lenstra J. A., Welling G. W., Fitch W. M. The molecular evolution of pancreatic ribonuclease. J Mol Evol. 1977 Sep 20;10(1):49–71. doi: 10.1007/BF01796134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance R. E., Ellis R. M., Bromer W. W. Porcine proinsulin: characterization and amino acid sequence. Science. 1968 Jul 12;161(3837):165–167. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Adler A. J., Fasman G. D. Conformational prediction and circular dichroism studies on the lac repressor. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):29–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Beta-turns in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 15;115(2):135–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of beta-turns. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85259-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Homology of protein structures: proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):743–745. doi: 10.1038/255743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Interactions between cysteine residues as probes of protein conformation: the disulphide bond between Cys-14 and Cys-38 of the pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. The two-disulphide intermediates and the folding pathway of reduced pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 25;95(2):167–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90389-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank B. H., Veros A. J. Physical studies on proinsulin-association behavior and conformation in solution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90362-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton W. W., Potter R., Low B. W. Proinsulin: Crystallization and preliminary x-ray diffraction studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1213–1219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., Groen G., Welling G. W., Beintema J. J. The primary structure of giraffe pancreatic ribonuclease. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra J. A., Hofsteenge J., Beintema J. J. Invariant features of the structure of pancreatic ribonuclease. A test of different predictive models. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Liu Y. S., Putnam F. W. Structure, function, and evolutionary relationships of Fc domains of human immunoglobulins A, G, M, and E. Science. 1976 Jan 30;191(4225):390–392. doi: 10.1126/science.1246619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markussen J., Sundby F. Rat-proinsulin C-peptides. Amino-acid sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):153–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markussen J., Volund A. Conformational analysis of circular dichroism spectra of insulin, proinsulin and c-peptides by non-linear regression. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1975;7(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1975.tb02413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):442–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menez A., Langlet G., Tamiya N., Fromageot P. Conformation of snake toxic polypeptides studied by a method of prediction and circular dichroism. Biochimie. 1978 Sep 4;60(5):505–516. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80866-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Ooi T. Comparison of homologous tertiary structures of proteins. J Theor Biol. 1974 Feb;43(2):351–374. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(74)80066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Love W. E. Three-dimensional structure of hemoglobin from the polychaete annelid, Glycera dibranchiata, at 2.5 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4067–4078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekar A. H., Frank B. H. Conformation of proinsulin. A comparison of insulin and proinsulin self-association at neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4013–4016. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittsyn O. B. Invariant features of globin primary structure and coding of their secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen R. A., Lindsay D. G., Wood S. P., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L., Wollmer A., Krail G., Brandenburg D., Zahn H., Gliemann J. Receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):369–373. doi: 10.1038/259369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. N., Keim P. S., Heinrikson R. L., Kezdy F. J. Primary structural analysis of sulfhydryl protease inhibitors from pineapple stem. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1741–1750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C., Thomas K. A., Silverton E. W., Davies D. R. Similarity of three-dimensional structure between the immunoglobulin domain and the copper, zinc superoxide dismutase subunit. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 5;102(2):221–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. A comparison of the heme binding pocket in globins and cytochrome b5. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7525–7532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rühlmann A., Kukla D., Schwager P., Bartels K., Huber R. Structure of the complex formed by bovine trypsin and bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Crystal structure determination and stereochemistry of the contact region. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 5;77(3):417–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTH D. G., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. The sequence of amino acid residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease: revisions and confirmations. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L., Shotton D. M., Campbell J. W., Wendell P. L., Muirhead H., Watson H. C. The atomic structure of crystalline porcine pancreatic elastase at 2.5 A resolution: comparisons with the structure of alpha-chymotrypsin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 15;118(2):137–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer A. J., Beintema J. J. Horse pancreatic ribonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 15;46(2):221–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Hartley B. S. Amino-acid sequence of porcine pancreatic elastase and its homologies with other serine proteinases. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):802–806. doi: 10.1038/225802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythies J. R., Benington F., Bradley R. J., Bridgers W. F., Morin R. D., Romine W. O., Jr The molecular structure of the receptor-ionophore complex at the neuromuscular junction. J Theor Biol. 1975 May;51(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(75)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell C. R., Smyth D. G. Proinsulin: a proposed three-dimensional structure. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6291–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Oyer P. E. The biosynthesis of insulin and a probable precursor of insulin by a human islet cell adenoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):473–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg A., Beintema J. J. Non-constant evolution rates in amino acid sequences of guinea pig, chinchilla and coypu pancreatic ribonucleases. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):207–210. doi: 10.1038/253207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt H. P., Wollmer A., Naithani V. K., Zahn H. The conformational protential of porcine proinsulin C-peptide. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jan;357(1):107–116. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu N. T., Liu C. S., O'Shea D. C. Laser Raman spectroscopy and the conformation of insulin and proinsulin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):117–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


