Abstract
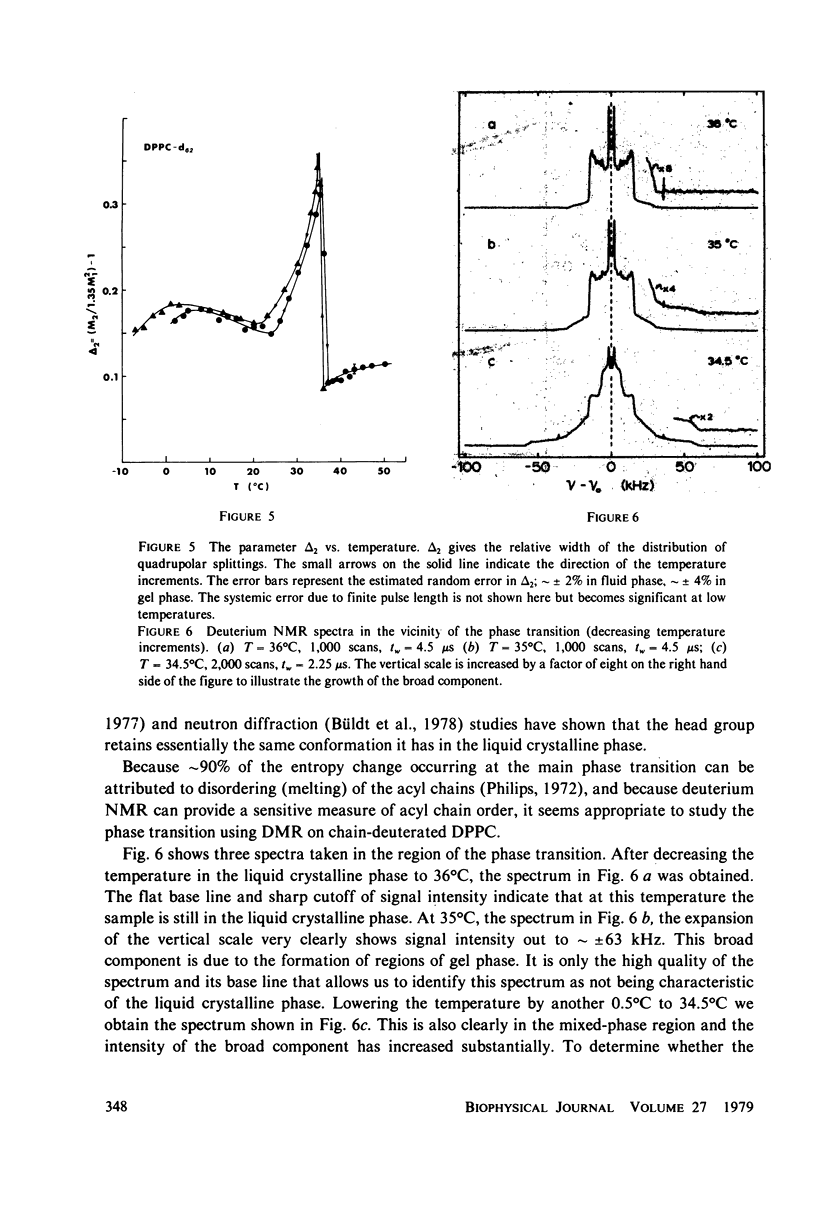
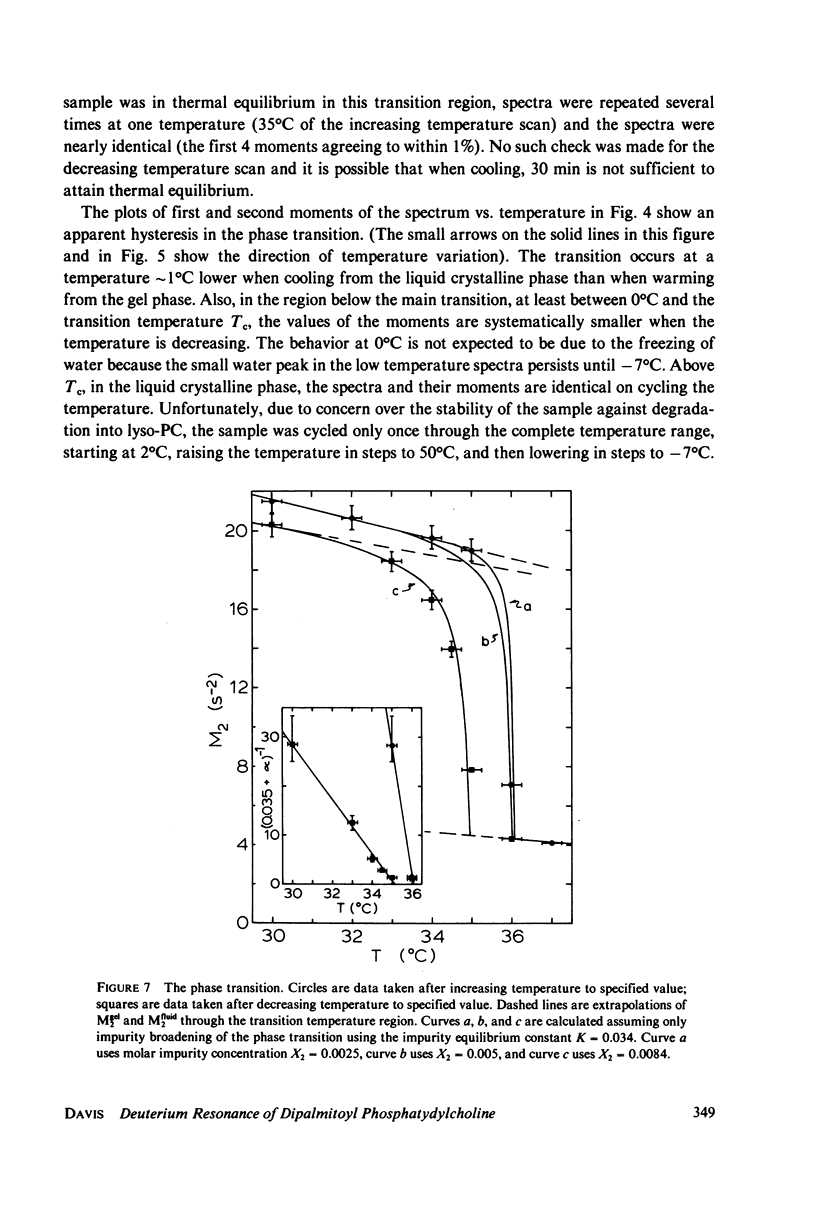
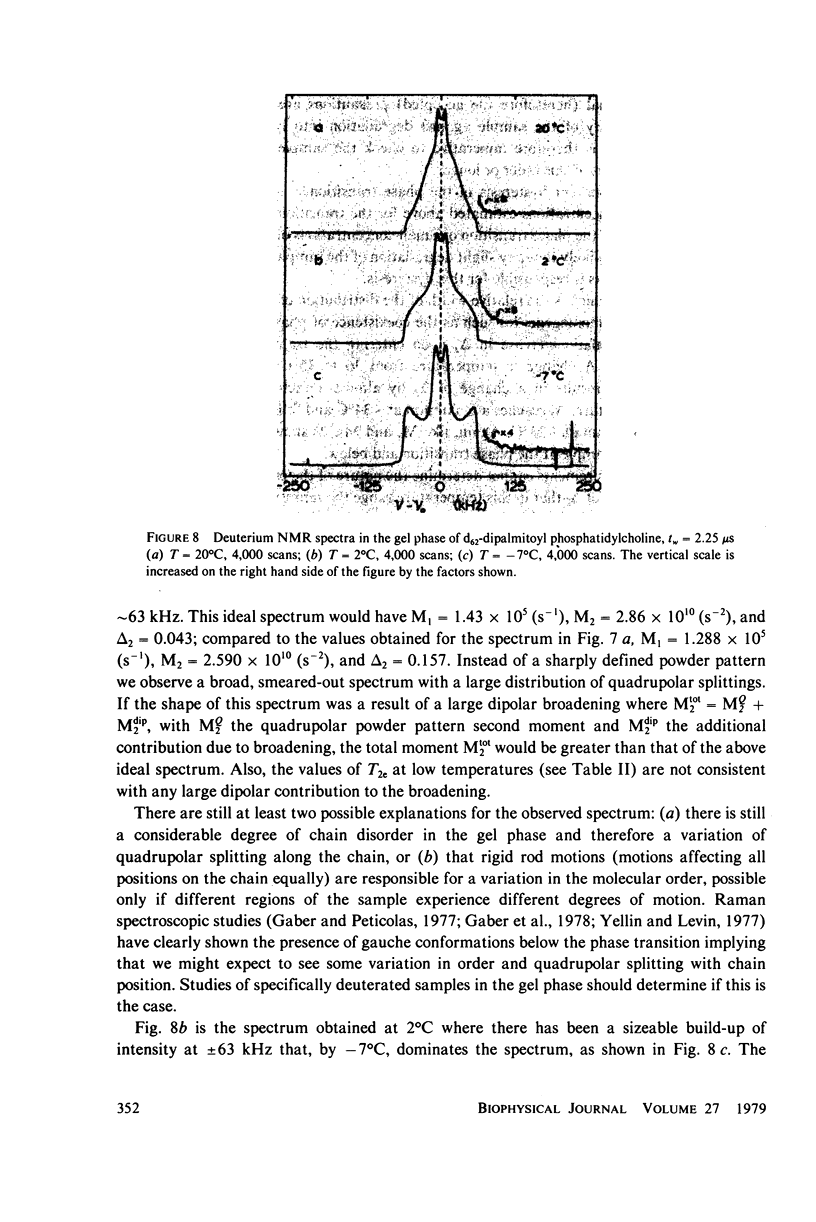
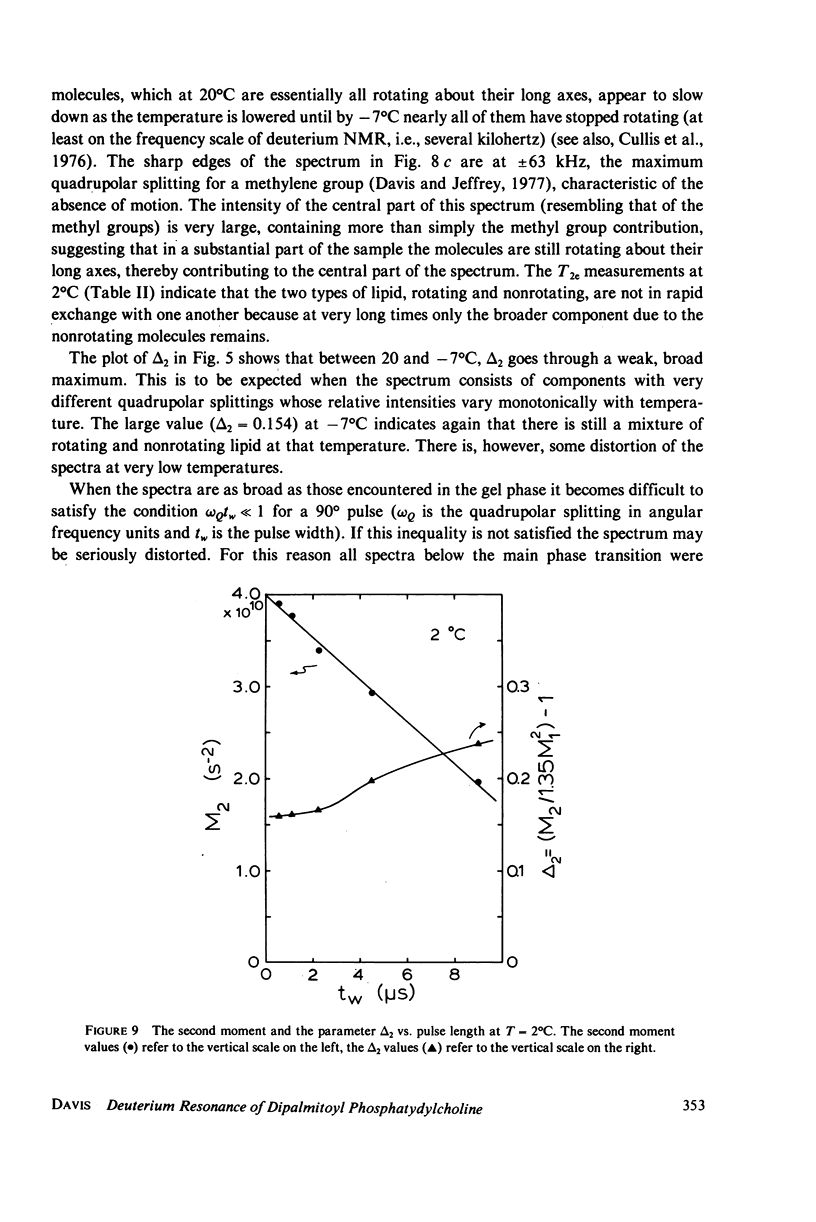
Deuterium magnetic resonance is applied to the study of the liquid crystalline and gel phases, and of the phase transition, of a multilamellar dispersion of chain perdeuterated (d62)-dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine/H2O. Analysis of the deuterium spectra in terms of the moments of the spectra allows one to make quantitative statements concerning the distribution of quadrupolar splittings even in complicated situations, e.g., when using perdeuterated sampled or when there are mixed phases. This analysis indicates that d62-dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine in excess H2O undergoes a sharp phase transition (with a width of less than 1 degree C) at approximately 37 degrees C and that there appears to be hysteresis in the phase transition of approximately 1 degree C. In the lamellar liquid crystalline phase above 37 degrees C the spectra show a number of well-resolved features whose quadrupolar splittings can be followed as the temperature is varied. The gel phase near 20 degrees C possesses a very broad, almost featureless spectrum that does not seem to support a model of the gel phase wherein the hydrocarbon chains are fully extended in the all-trans conformation. At temperatures near 0 degrees C the spectra clearly indicate that a large fraction of the lipid molecules cease the rotation about their long axes, giving a spectrum more characteristic of a rigid or solid sample. These results give a picture of the gel phase as a phase characterized by considerable hydrocarbon chain disorder near 20 degrees C and becoming a more solid-like phase near 0 degrees C. The spin-lattice relaxation time, T1, has been measured at 20 degrees C in the gel phase, and at 37 and 45 degrees C in the liquid crystalline phase. The values of T1 obtained for each of the resolvable peaks in the spectrum at 37 degrees C are compared to the values (for each peak) of T2e, the decay time of the quadrupolar echo, obtained at the same temperature. These results are discussed in terms of a simple two-motion model.
Full text
PDF


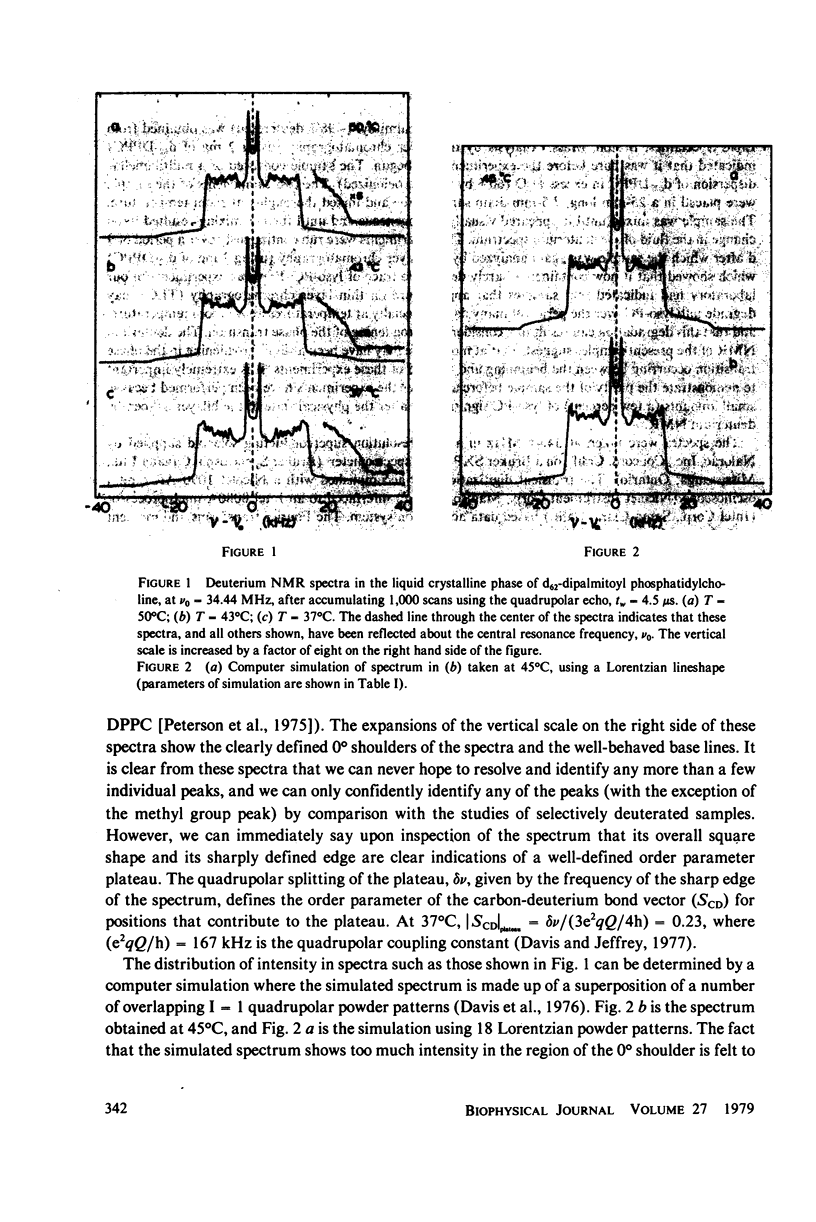
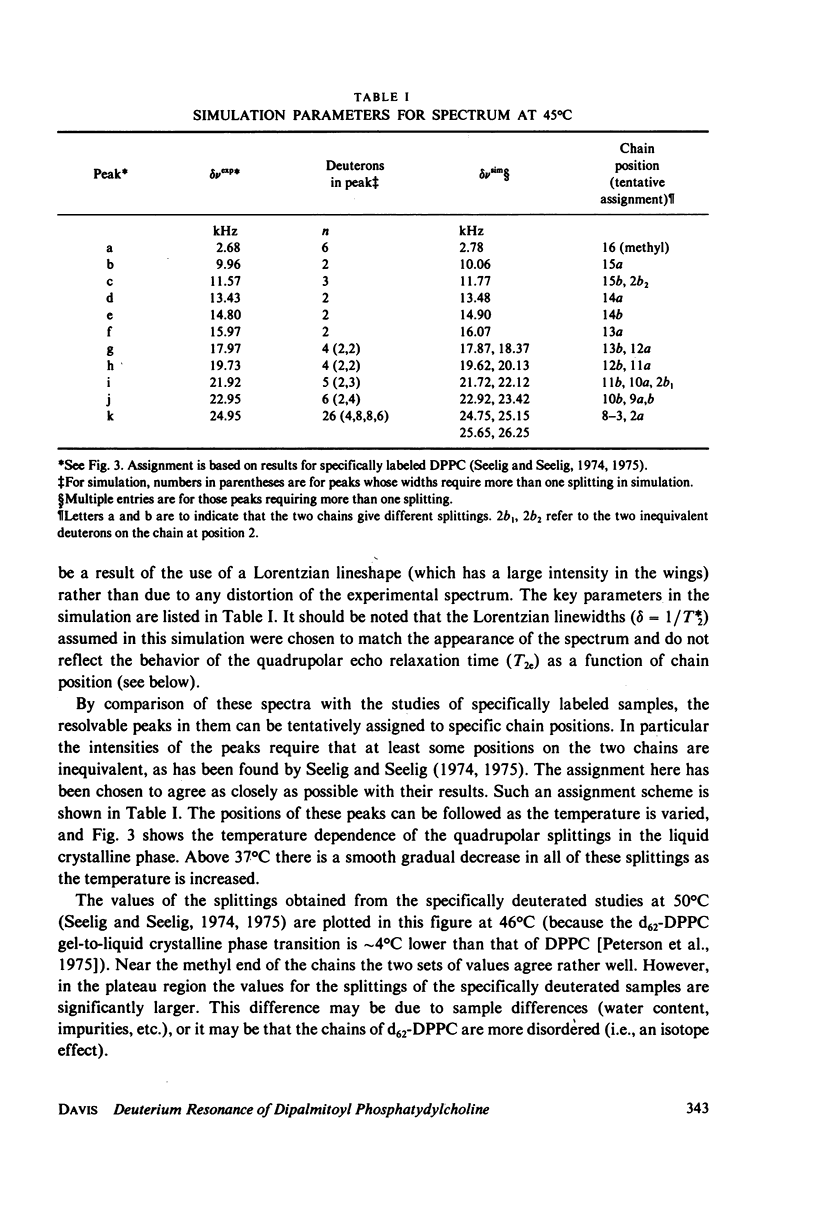
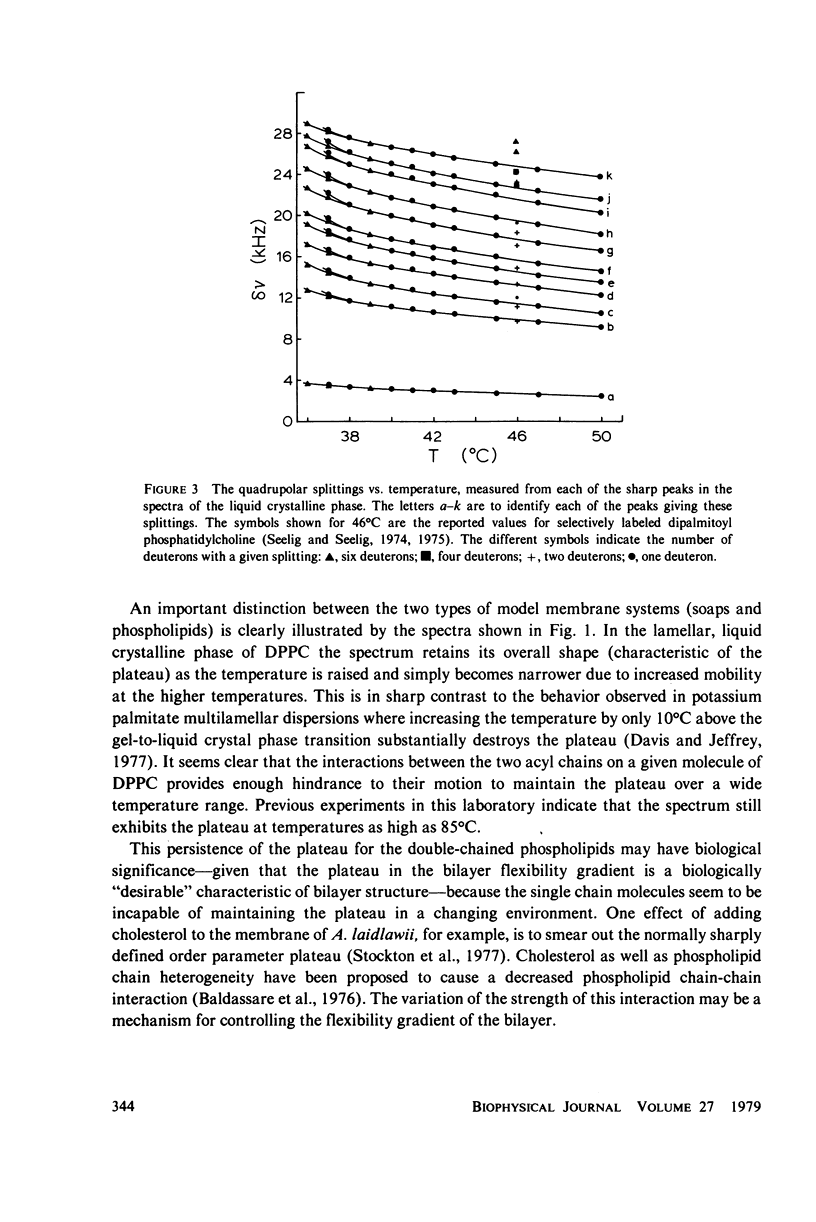


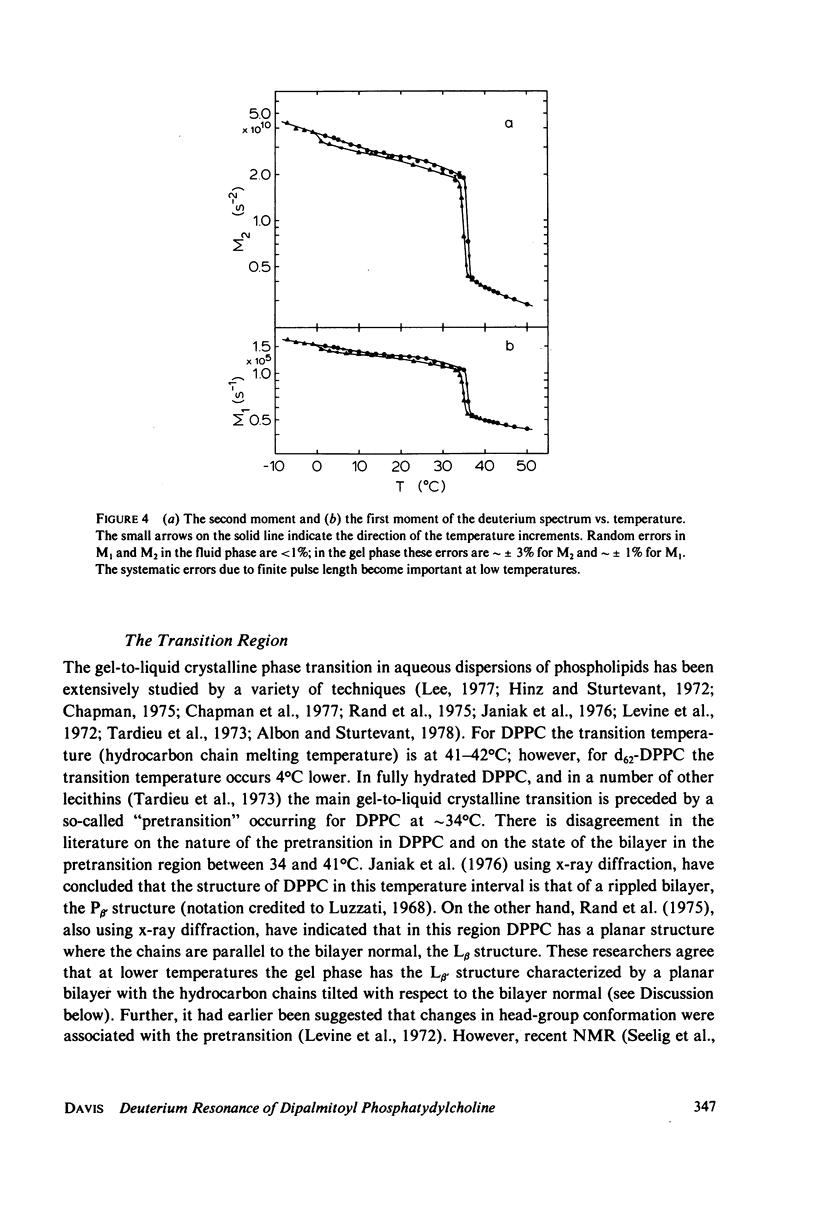






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albon N., Sturtevant J. M. Nature of the gel to liquid crystal transition of synthetic phosphatidylcholines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2258–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Rhinehart K. B., Silbert D. F. Modification of membrane lipid: physical properties in relation to fatty acid structure. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):2986–2994. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M., Burnell E. E., MacKay A. L., Nichol C. P., Valic M. I., Weeks G. Fatty acyl chain order in lecithin model membranes determined from proton magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5750–5762. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig A., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on selectively deuterated phospholipid bilayers. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):182–184. doi: 10.1038/271182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Peel W. E., Kingston B., Lilley T. H. Lipid phase transitions in model biomembranes. The effect of ions on phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 21;464(2):260–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 May;8(2):185–235. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., De Kruyff B., Richards R. E. Factors affecting the motion of the polar headgroup in phospholipid bilayers. A 31P NMR study of unsonicated phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 19;426(3):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R. Lateral diffusion rates of phosphatidylcholine in vesicle membranes: effects of cholesterol and hydrocarbon phase transitions. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80762-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H., Maraviglia B., Weeks G., Godin D. V. Bilayer rigidity of the erythrocyte membrane2H-NMR of a perdeuterated palmitic acid probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 19;550(2):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. H., Nichol C. P., Weeks G., Bloom M. Study of the cytoplasmic and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):2103–2112. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber B. P., Peticolas W. L. On the quantitative interpretation of biomembrane structure by Raman spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):260–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber B. P., Yager P., Peticolas W. L. Interpretation of biomembrane structure by Raman difference spectroscopy. Nature of the endothermic transitions in phosphatidylcholines. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):161–176. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85516-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. B., Mason R., Thomas K. M., Shipley G. G. Structural chemistry of 1,2 dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine: molecular conformation and intermolecular packing of phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3036–3040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Lipid phase transitions and phase diagrams. I. Lipid phase transitions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 9;472(2):237–281. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine Y. K., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation measurements of synthetic lecithins and the effect of spin-labeled lipids. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1416–1421. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Chapman D., Derbyshire W. Deuteron resonance: A novel approach to the study of hydrocarbon chain mobility in membrane systems. FEBS Lett. 1971 Aug 1;16(2):102–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O., Kroon P. A., Kainoshio M., Chan S. I. Thermal phase transitions in deuterated lecithin bilayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1975 Aug;14(4):343–349. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(75)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O., Kroon P. A., Kainoshio M., Chan S. I. Thermal phase transitions in deuterated lecithin bilayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1975 Aug;14(4):343–349. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(75)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Chapman D., Larsson K. Tilted hydrocarbon chains of dipalmitoyl lecithin become perpendicular to the bilayer before melting. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1117–1124. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85888-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Bilayers of dipalmitoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine. Conformational differences between the fatty acyl chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 16;406(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Effect of a single cis double bond on the structures of a phospholipid bilayer. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 11;16(1):45–50. doi: 10.1021/bi00620a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Gally G. U., Wohlgemuth R. Orientation and flexibility of the choline head group in phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 2;467(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockton G. W., Polnaszek C. F., Tulloch A. P., Hasan F., Smith I. C. Molecular motion and order in single-bilayer vesicles and multilamellar dispersions of egg lecithin and lecithin-cholesterol mixtures. A deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance study of specifically labeled lipids. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):954–966. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veksli Z., Salsbury N. J., Chapman D. Physical studies of phospholipids. XII. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of molecular motion in some pure lecithin-water systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):434–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin N., Levin I. W. Hydrocarbon trans-gauche isomerization in phospholipid bilayer gel assemblies. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):642–647. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



