Abstract
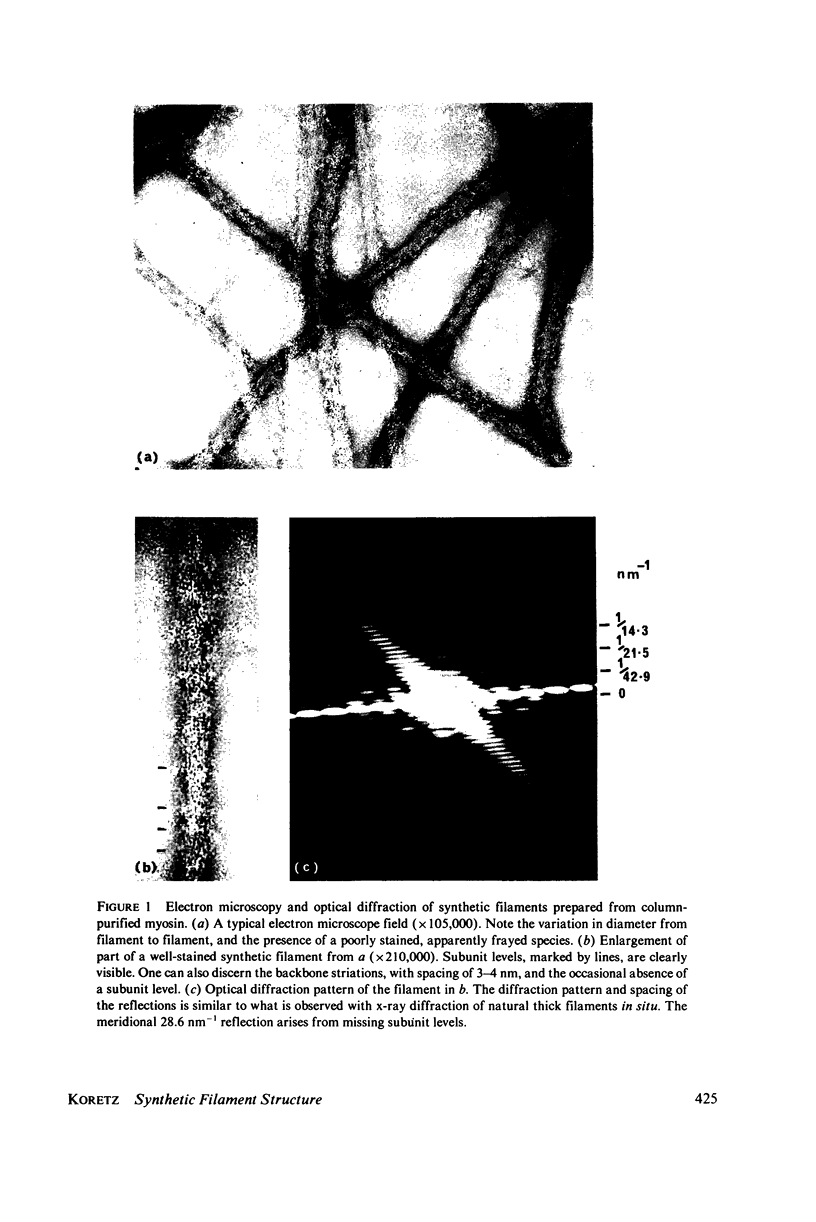
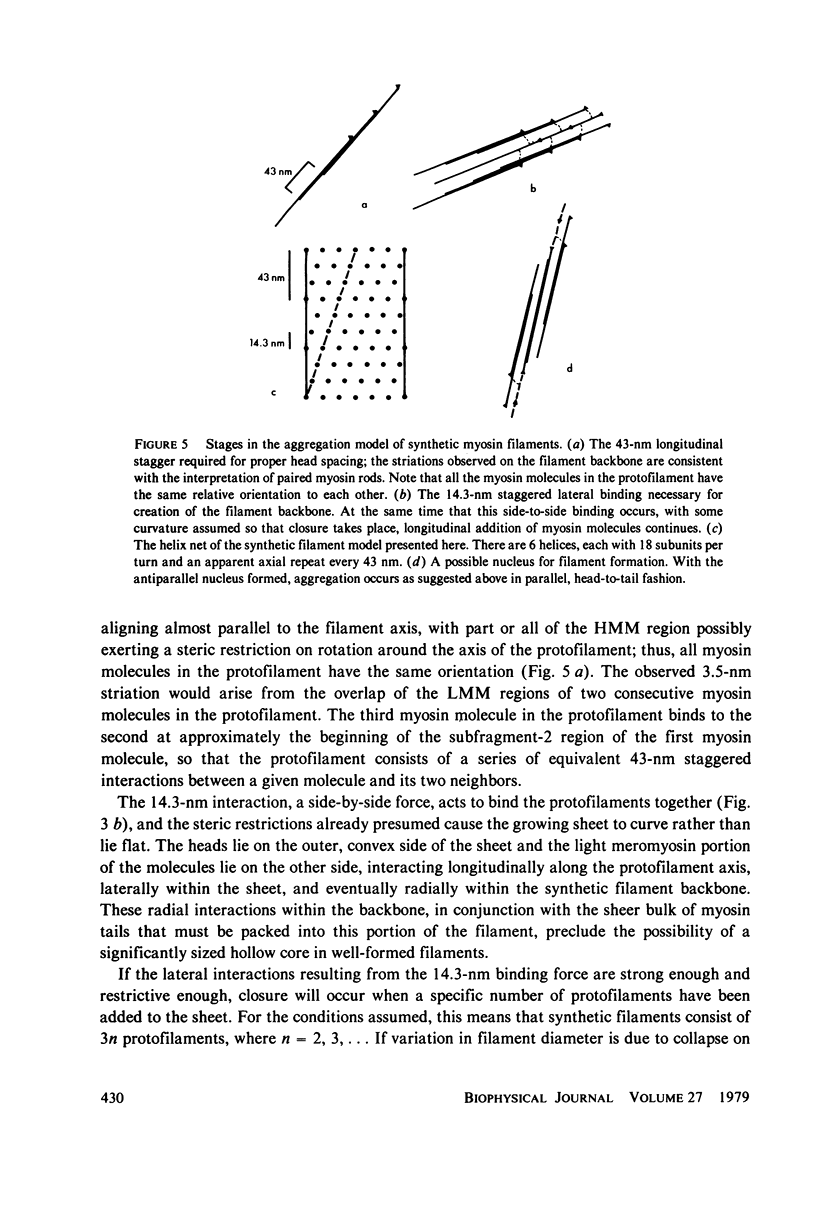
Synthetic filaments prepared from column-purified rabbit skeletal myosin by slow dialysis exhibit characteristic bipolar organization and 14-nm axial subunit spacing. Backbone substructure can be discerned in high resolution micrographs in the form of striations of 3--4-nm width and slight angular tilt from the direction of the filament axis. Filament backbone diameters vary over the population, although remaining relatively constant for a single filament. Approximately 25% of the filaments appear poorly stained and frayed, which may be due to collapse on the electron microscope grid. Optical diffraction studies reveal a 43-nm axial repeat as well as the 14.3-nm subunit repeat, indicating a structural homology with natural filaments. A model for synthetic filament aggregation is presented that is consistent with observations of backbone diameter variation, absence of bare zones, and the presence of fraying filaments.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eaton B. L., Pepe F. A. Letter: Myosin filaments showing a 430 A axial repeat periodicity. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):421–423. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90600-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M., O'Brien E. J. The effect of calcium ions on the structure of reconstituted muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):445–459. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Brown W. The low-angle x-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):383–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer B., Bell A. L. Myosin filamentogenesis: effects of pH and ionic concentration. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R. A., Cheung P. Muscle crossbridges: absence of direct effect of calcium on movement away from the thick filaments. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):190–192. doi: 10.1126/science.194.4261.190-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos C., Offer G., Starr R., Bennett P. Interaction of C-protein with myosin, myosin rod and light meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto K., Harrington W. F. Isolation and composition of thick filaments from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 15;77(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto K., Harrington W. F. Substructure of the thick filament of vertebrate striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 15;83(1):83–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. J., Bennett P. M., Hanson J. Optical diffraction studies of myofibrillar structure. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 May 27;261(837):201–208. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. J., Gillis J. M., Couch J. Symmetry and molecular arrangement in paracrystals of reconstituted muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILPOTT D. E., SZENT-GYORGYI A. G. The structure of light-meromyosin: an electron microscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Oct;15(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepe F. A., Dowben P. The myosin filament. V. Intermediate voltage electron microscopy and optical diffraction studies of the substructure. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):199–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Electron microscopy of synthetic myosin filaments. Evidence for cross-bridge. Flexibility and copolymer formation. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):93–104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZENT-GYORGYI A. G. Meromyosins, the subunits of myosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Huxley H. E., Finch J. T. Regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. II. Structural studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):619–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K., Chiao Y. C., Harrington W. F. Effect of pH on the cross-bridge arrangement in synthetic myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1234–1239. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K., Harrington W. F. Cross-linking of myosin thick filaments under activating and rigor conditions. A study of the radial disposition of cross-bridges. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2441–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




