Abstract
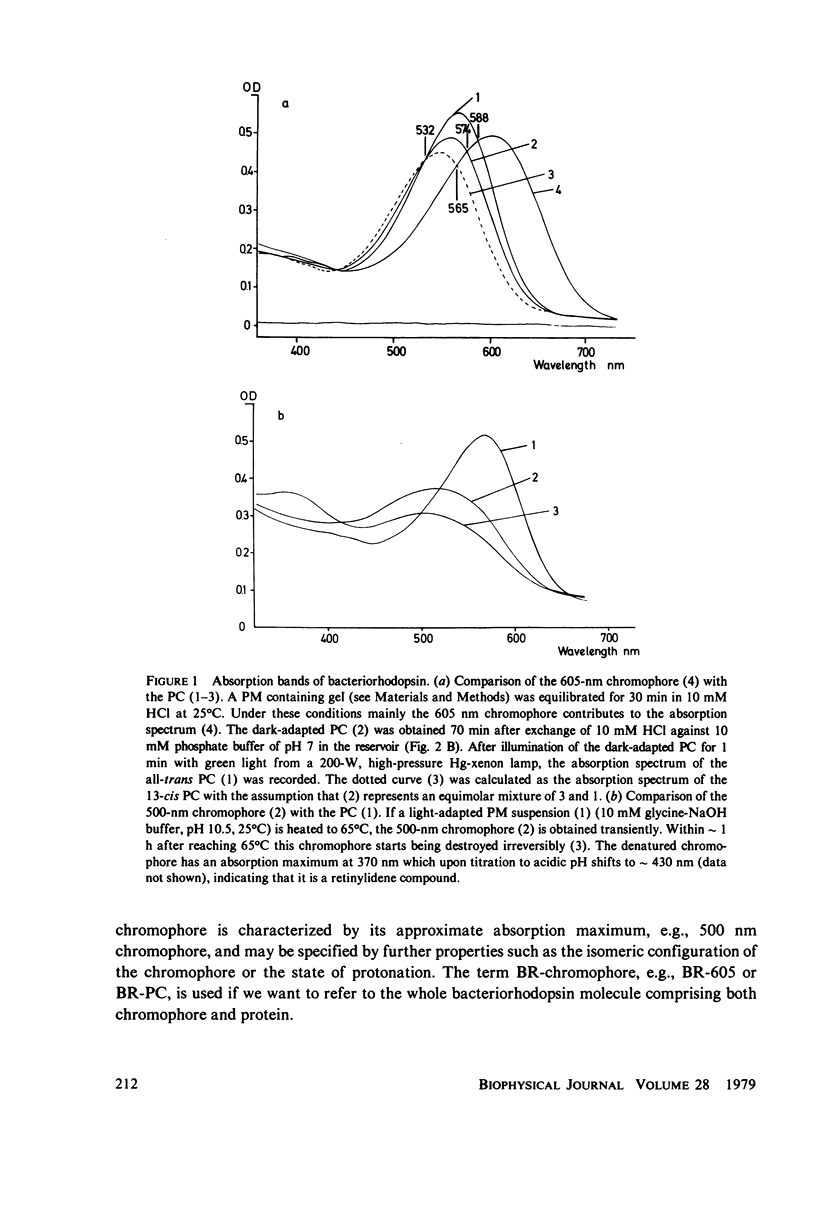
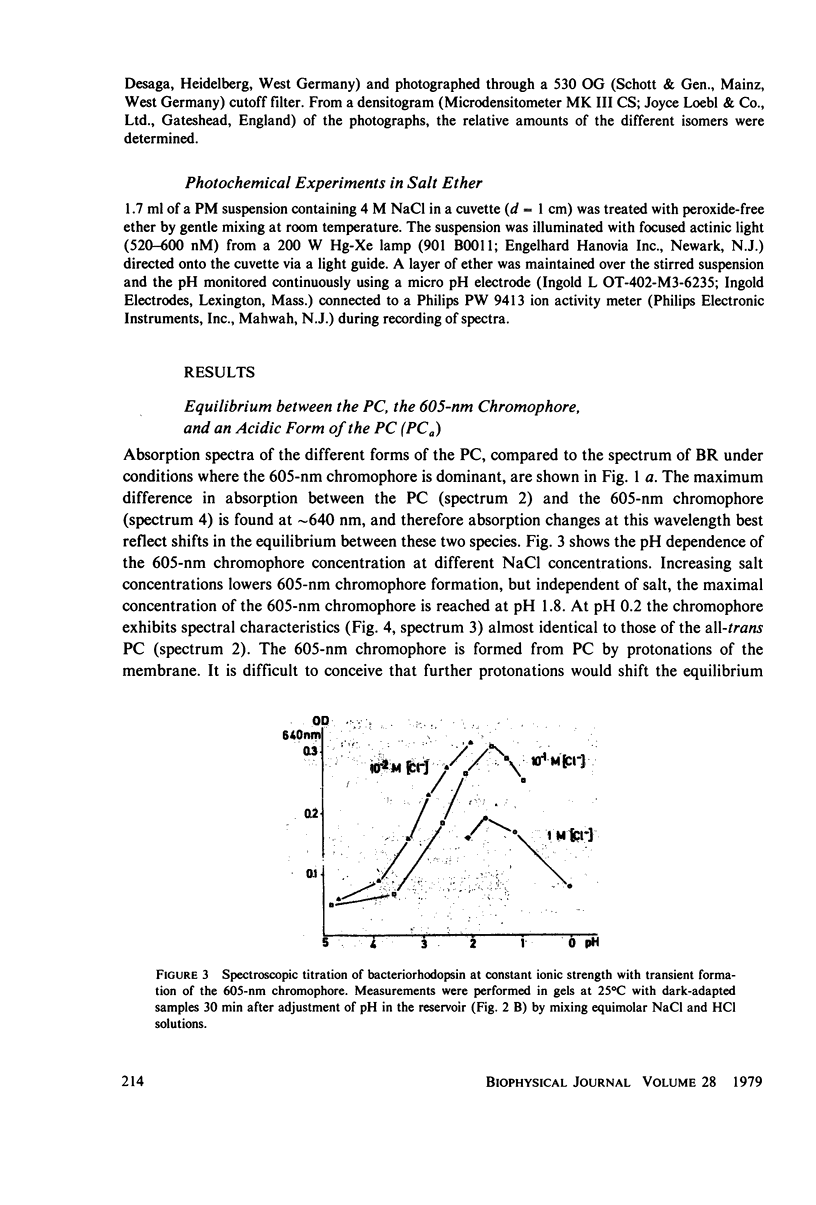
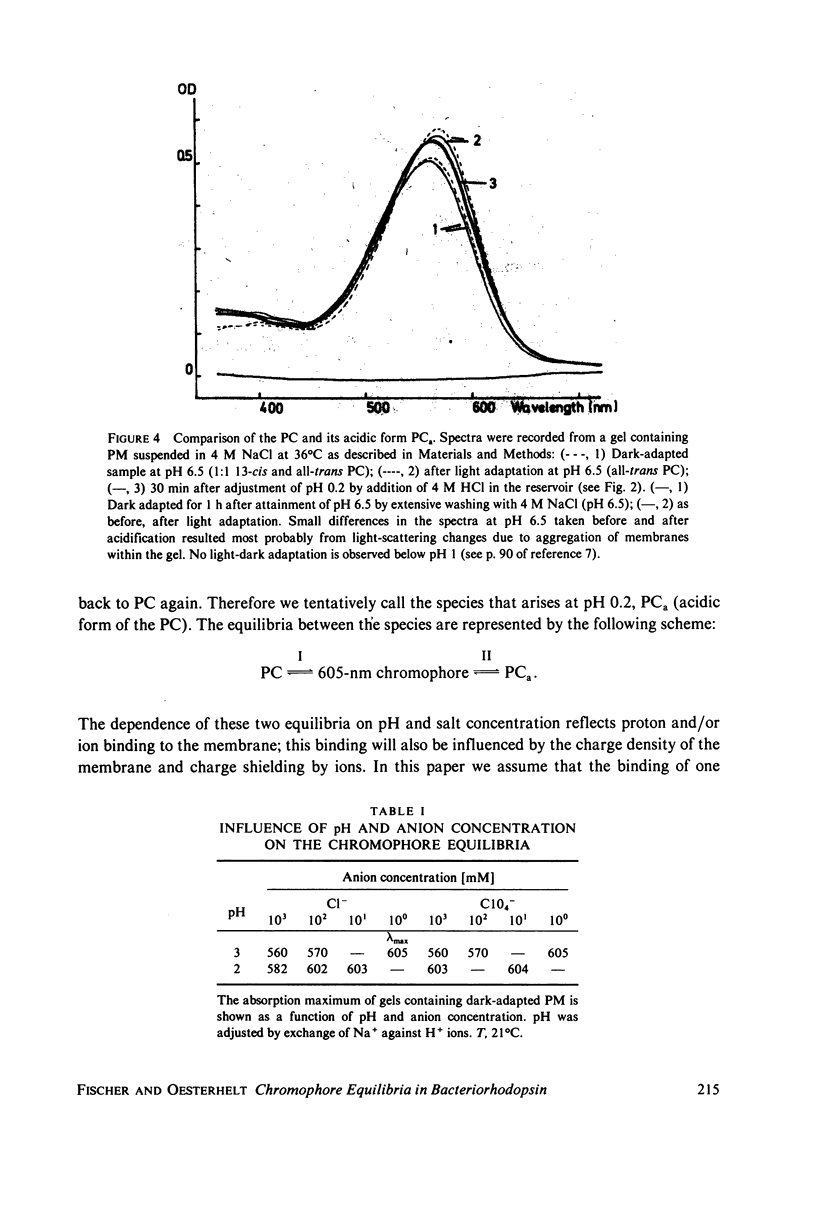
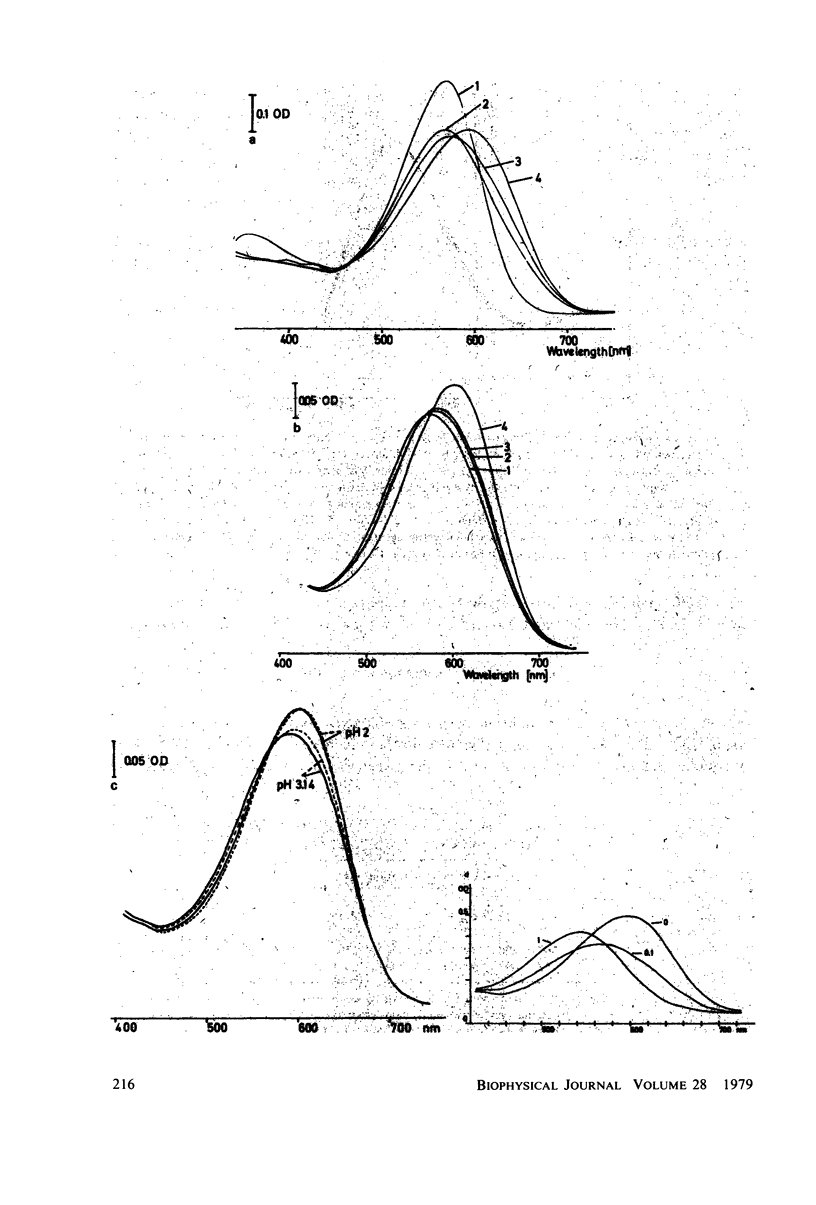
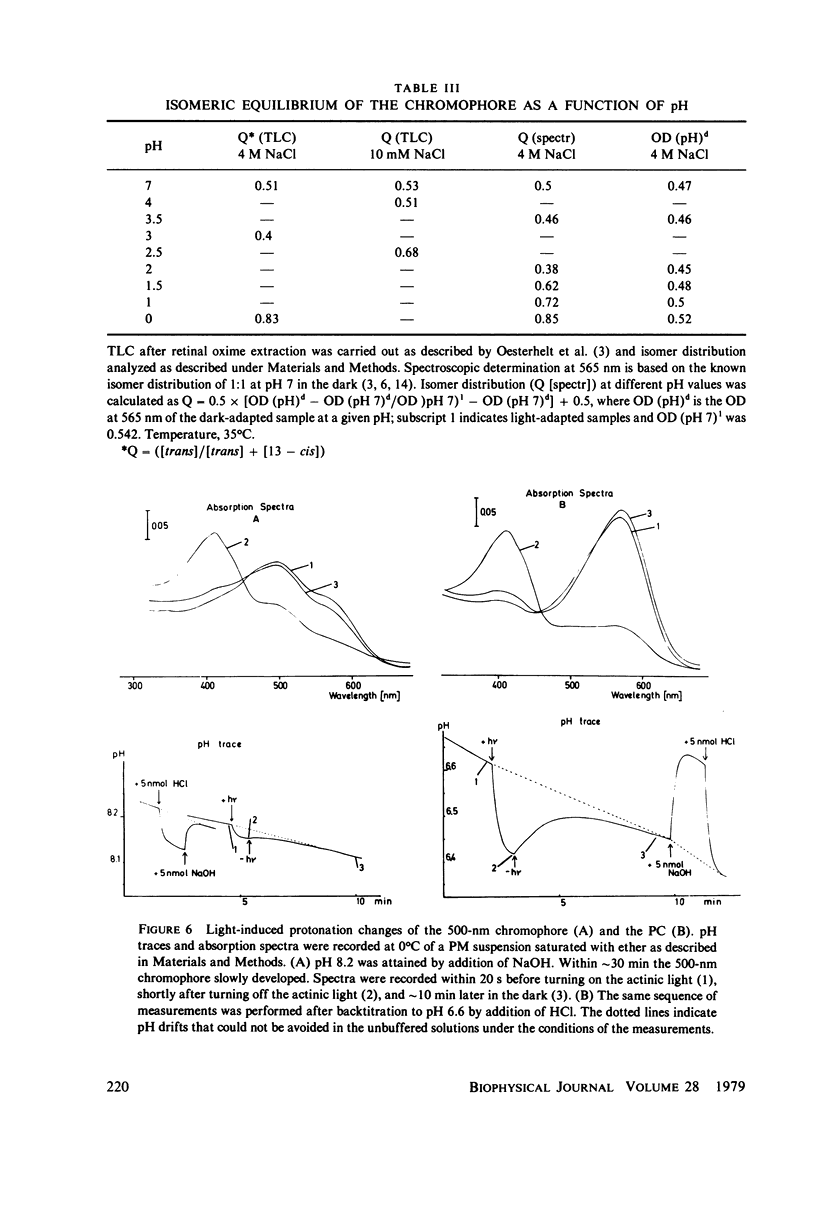
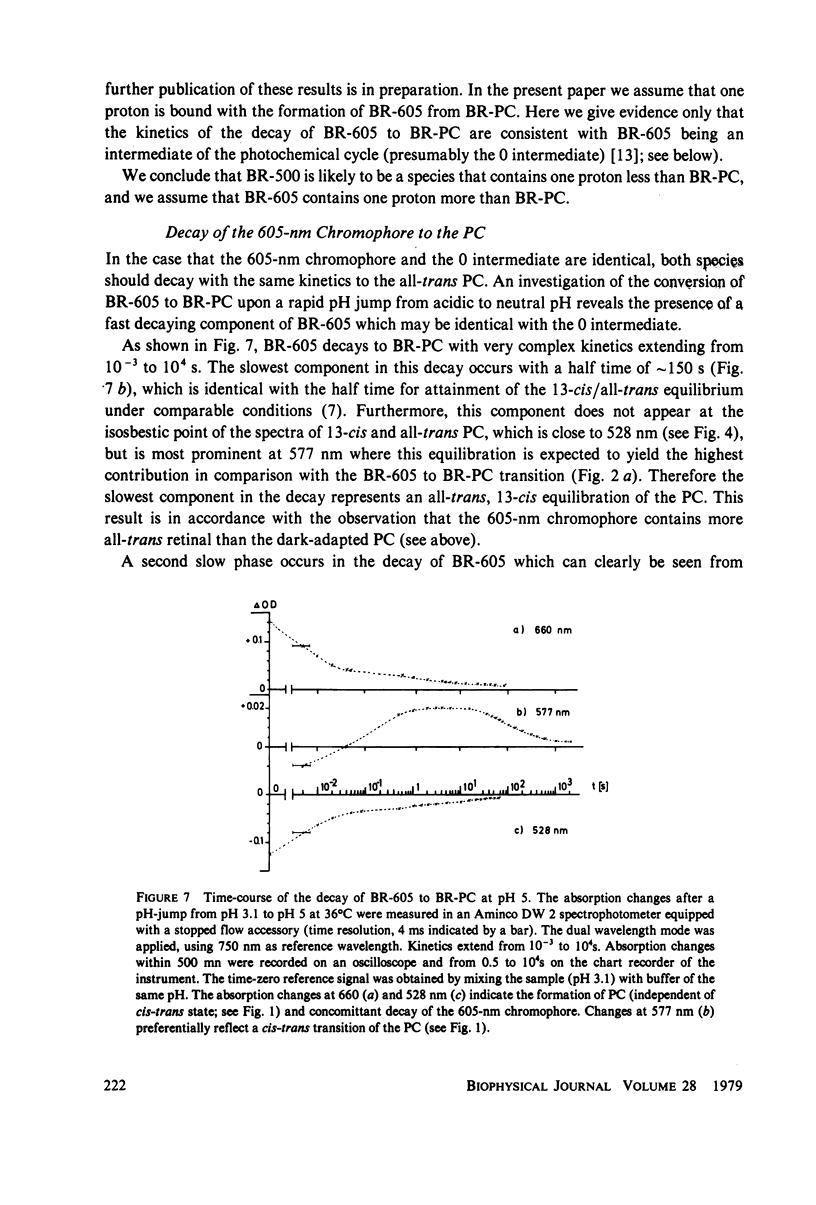
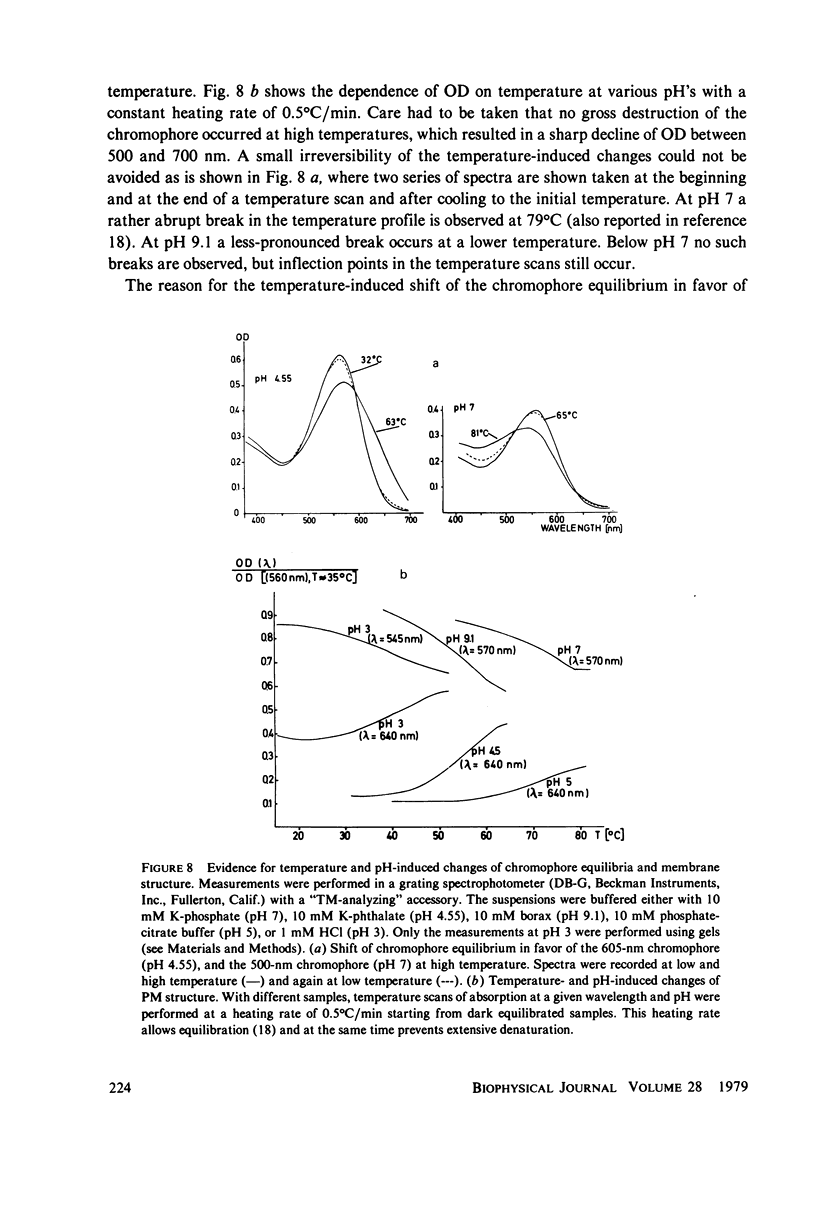
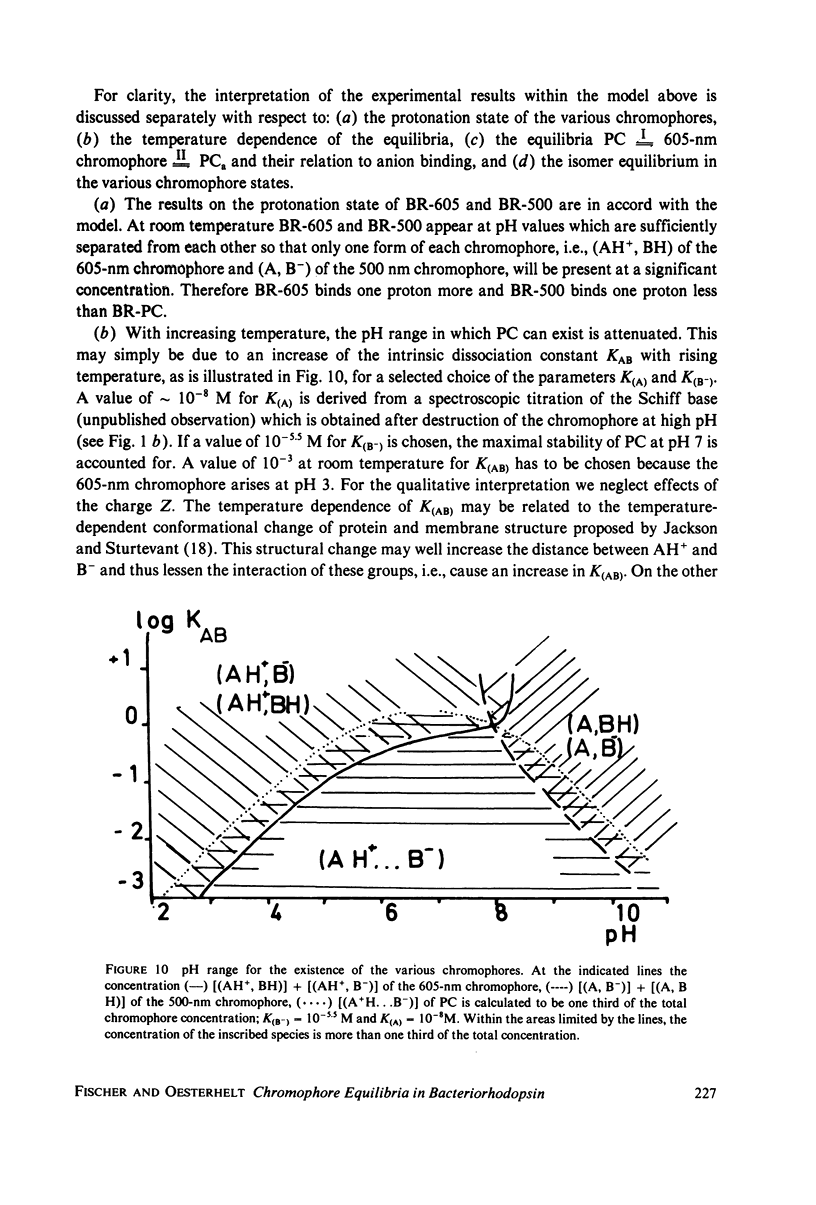
An investigation of the dark equilibria between different chromophores of bacteriorhodopsin (BR) and studies of the kinetics of their interconversion and photochemical activity have led to the following conclusions. (a) A component of the 605-nm chromophore of BR decays in the millisecond range and is likely to be identical to the intermediate O of the photochemical cycle of BR and is assumed to be formed from the purple complex (PC) by the binding of one proton to BR. (b) An acidic form the PC, PCaL-, arises from the 605-nm chromophore by selective binding of anions L- (F- greater than Cl- greater than Br- greater than I- greater than Cl04-) to BR. (c) The isomeric equilibrium between 13-cis and all-trans retinal is approximately 0.15/0.85 in PCaCl-, 0.3/0.7 in the 605-nm chromophore as compared to 0.5/0.5 in the PC. (d) The 500-nm chromophore is formed from the PC by release of nearly one proton from BR. (e) The pH range in which the PC exists is reduced in a high-temperature structure of the purple membrane as compared to its low temperature structure. A model for the chromophore structure is proposed as a hypothesis, which allows a comprehensive interpretation of the results. In this model the absorption spectrum of the retinylidene lysine Schiff base is modulated by its protonation state and the interaction with an anionic group.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatz P. E., Mohler J. H., Navangul H. V. Anion-induced wavelength regulation of absorption maxima of Schiff bases of retinal. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):848–855. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N., Wilms M. Flash photometric experiments on the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys Struct Mech. 1975 May 30;1(3):259–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00535760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T. G. The structure and spectra of the chromophore of the visual pigments. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):151–177. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Sturtevant J. M. Phase transitions of the purple membranes of Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):911–915. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W., Bogomolni R. A., Hwang S., Stoeckenius W. Kinetics and stoichiometry of light-induced proton release and uptake from purple membrane fragments, Halobacterium halobium cell envelopes, and phospholipid vesicles containing oriented purple membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Niederberger W. The photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Fed Proc. 1977 May;36(6):1805–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda A., Iwasa T., Yoshizawa T. Isomeric composition of retinal chromophore in dark-adapted bacteriorhodopsin. J Biochem. 1977 Dec;82(6):1599–1604. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. A., Edgerton M. E., Parr G., Greenwood C., Perham R. N. Studies of an acid-induced species of purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium. Biochem J. 1978 May 1;171(2):469–476. doi: 10.1042/bj1710469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Hess B. Reversible photolysis of the purple complex in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):316–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Meentzen M., Schuhmann L. Reversible dissociation of the purple complex in bacteriorhodopsin and identification of 13-cis and all-trans-retinal as its chromophores. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):453–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Takeuchi Y., Yoshida M. Effect of light-adaptation on the photoreaction of bacteriorhodopsin from Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 23;462(3):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreckenbach T., Walckhoff B., Oesterhelt D. Studies on the retinal-protein interaction in bacteriorhodopsin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):499–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H. Light energy conversion in Halobacterium halobium. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):769–774. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A. Charge stabilization mechanism in the visual and purple membrane pigments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2558–2562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


