Abstract
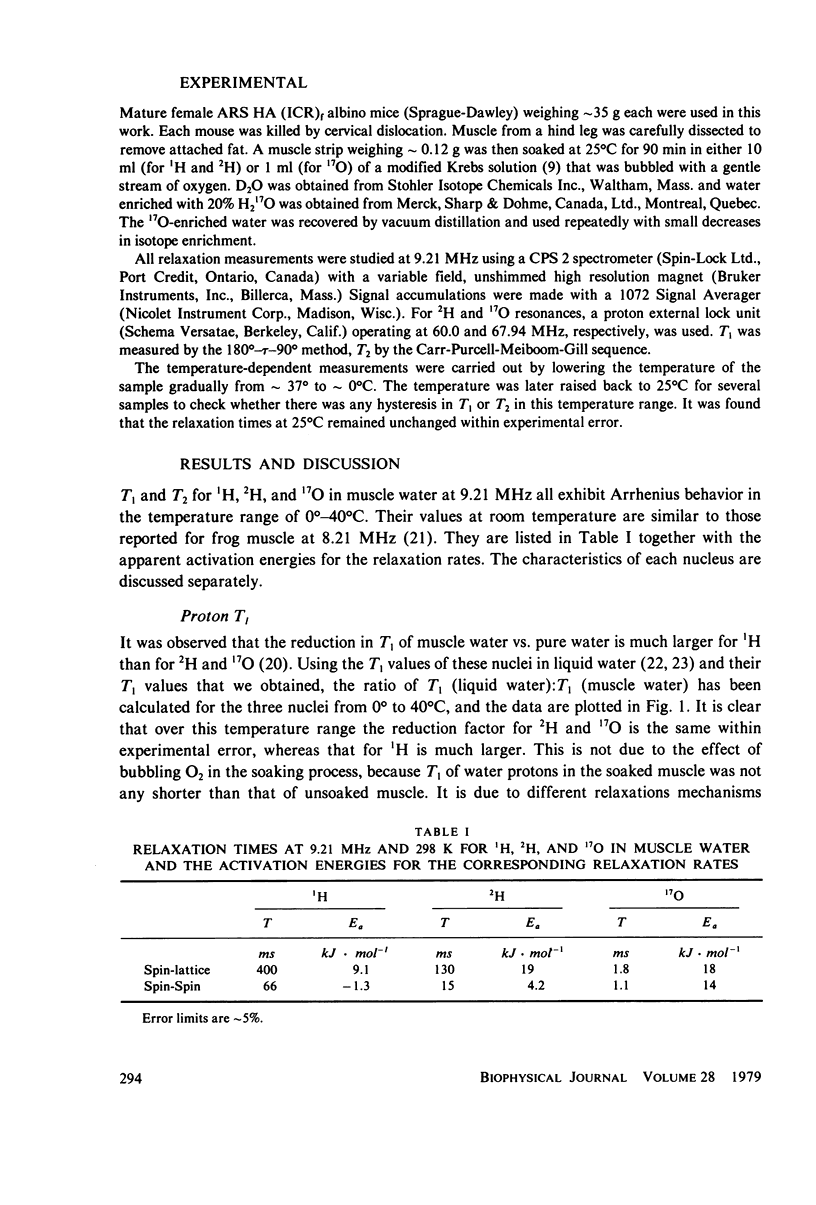
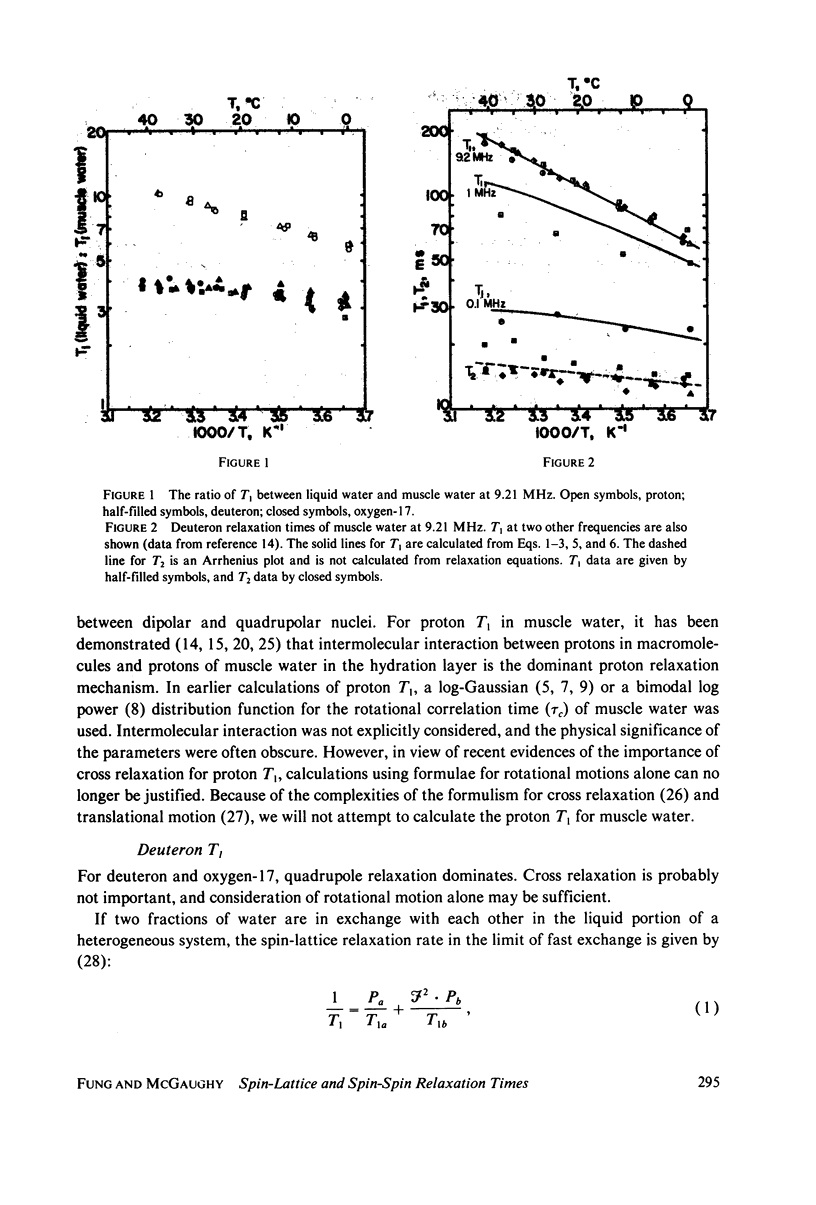
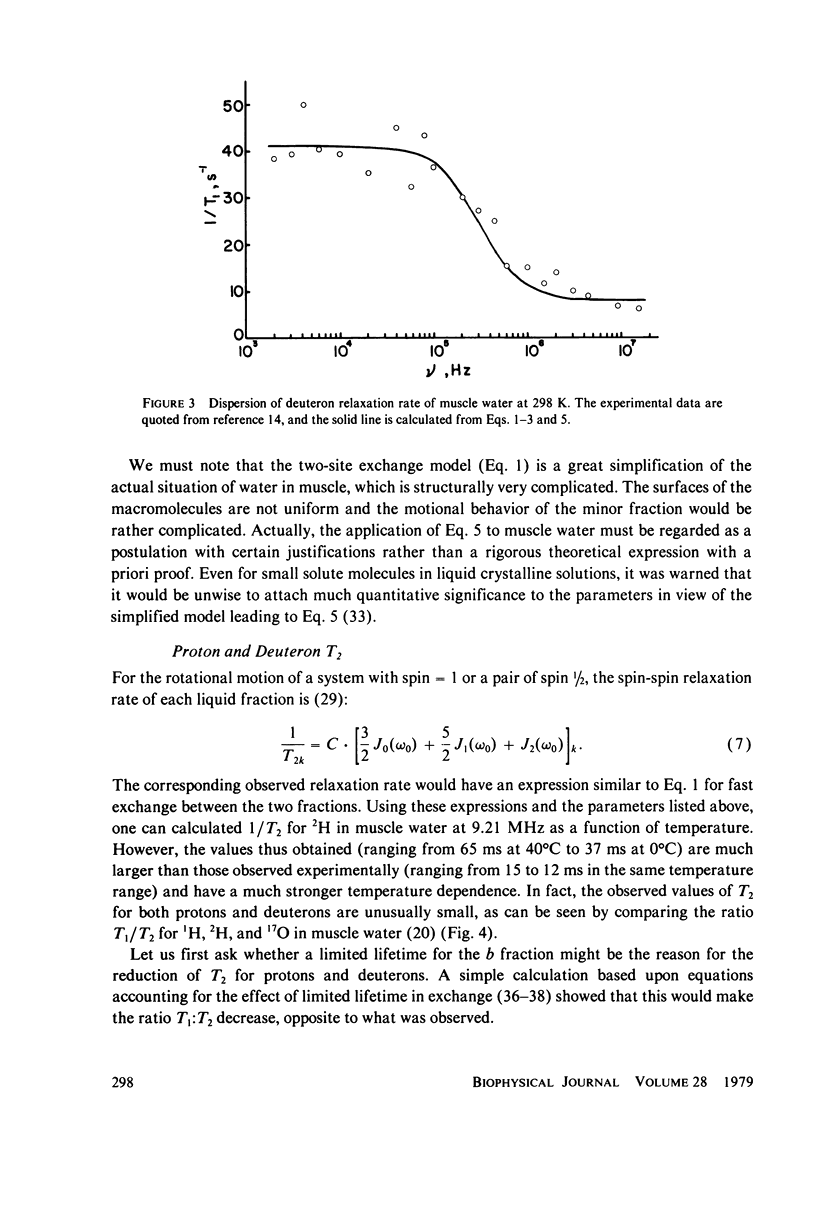
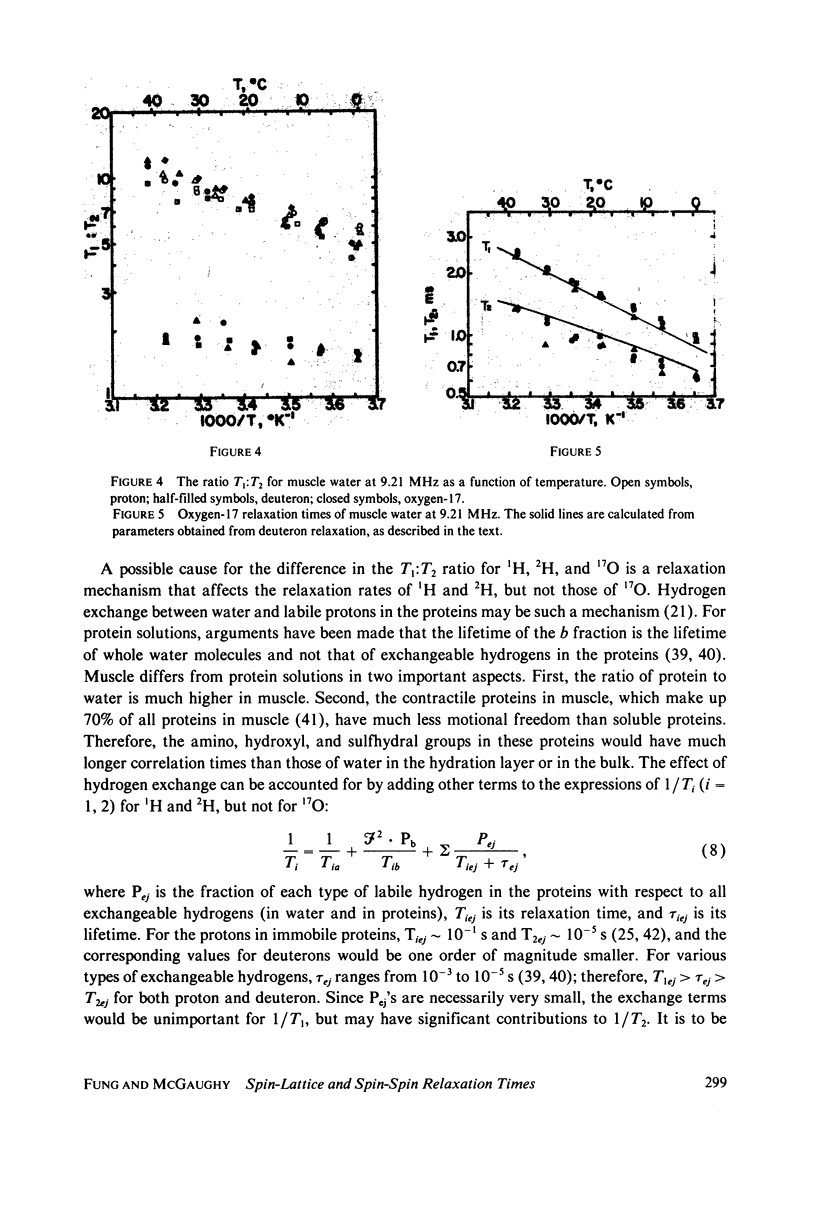
Spin-lattice (T1) and spin-spin (T2) relaxation times of proton, deuteron, and oxygen-17 in muscle water have been measured at 9.21 MHz in the temperature range of 0 degree--40 degrees C. The values of the apparent activation energy for the three nuclei are (in kJ . mol-1) 9.1, 19, and 18 for 1/T1, and -1.3, 4.2, and 14 for 1/T2, respectively. The relatively small values for T2 for 1H and 2H and their low apparent activation energies are attributed to hydrogen exchange between water and proteins; this exchange does not affect the 17O relaxation. Quantitative calculations on deuteron T1 and oxygen-17 T1 and T2 have been made. The effect of surface-induced anisotropy on a minor fraction of water molecules is considered in some detail, and a new expression for its spectral density similar to that of liquid crystalline systems is applied in the calculation. It is suggested that water on the surfaces of macromolecules has a rotational correlation time of tau c approximately 1 x 10(-9) S, with a time constant of tau x approximately 3 x 10(-7) S, which is characteristic of the relaxation of the local structure.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belton P. S., Jackson R. R., Packer K. J. Pulsed NMR studies of water in striated muscle. I. Transverse nuclear spin relaxation times and freezing effects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belton P. S., Packer K. J., Sellwood T. C. Pulsed NMR studies of water in striated muscle. II. Spin-lattice relaxation times and the dynamics of non-freezing fraction of water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 30;304(1):56–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Achlama A. M., Shporer M. The relationship between the transverse and longitudinal nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation rates of muscle water. Biophys J. 1978 Feb;21(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85513-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Shporer M. Pulsed NMR studies of 17O from H2 17O in frog striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 22;343(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Shporer M. Pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance study of 17-O, 2-D, and 1-H of water in frog striated muscle. Biophys J. 1975 Apr;15(4):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85820-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence using D2O for structured water in muscle and brain. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):303–319. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86388-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edzes H. T., Samulski E. T. Cross relaxation and spin diffusion in the proton NMR or hydrated collagen. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):521–523. doi: 10.1038/265521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. D., Homer L. D. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation measurements in frog muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Dec;14(12):907–921. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85958-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M., Durham D. L., Wassil D. A. The state of water in biological systems as studied by proton and deuterium relaxation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 14;399(1):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M., McGaughy T. W. The state of water in muscle as studied by pulsed NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 24;343(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. M. Proton and deuteron relaxation of muscle water over wide ranges of resonance frequencies. Biophys J. 1977 May;18(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85610-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenga K., Koenig S. H. Protein rotational relaxation as studied by solvent 1H and 2H magnetic relaxation. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4255–4264. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. R. Pulsed NMR study of water mobility in muscle and brain tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971;230(3):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Chang D. C., Nichols B. L., Woessner D. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation times of water protons in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):583–606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85937-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Hallenga K., Shporer M. Protein-water interaction studied by solvent 1H, 2H, and 17O magnetic relaxation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2667–2671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Schillinger W. E. Nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion in protein solutions. I. Apotransferrin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3283–3289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outhred R. K., George E. P. Water and ions in muscles and model systems. Biophys J. 1973 Feb;13(2):97–103. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85972-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi S. N., Peemoeller H., Thompson R. T., Kydon D. W., Pintar M. M. A study of molecular dynamics and freezing phase transition in tissues by proton spin relaxation. Biophys J. 1978 Jun;22(3):439–452. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85498-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


