Abstract
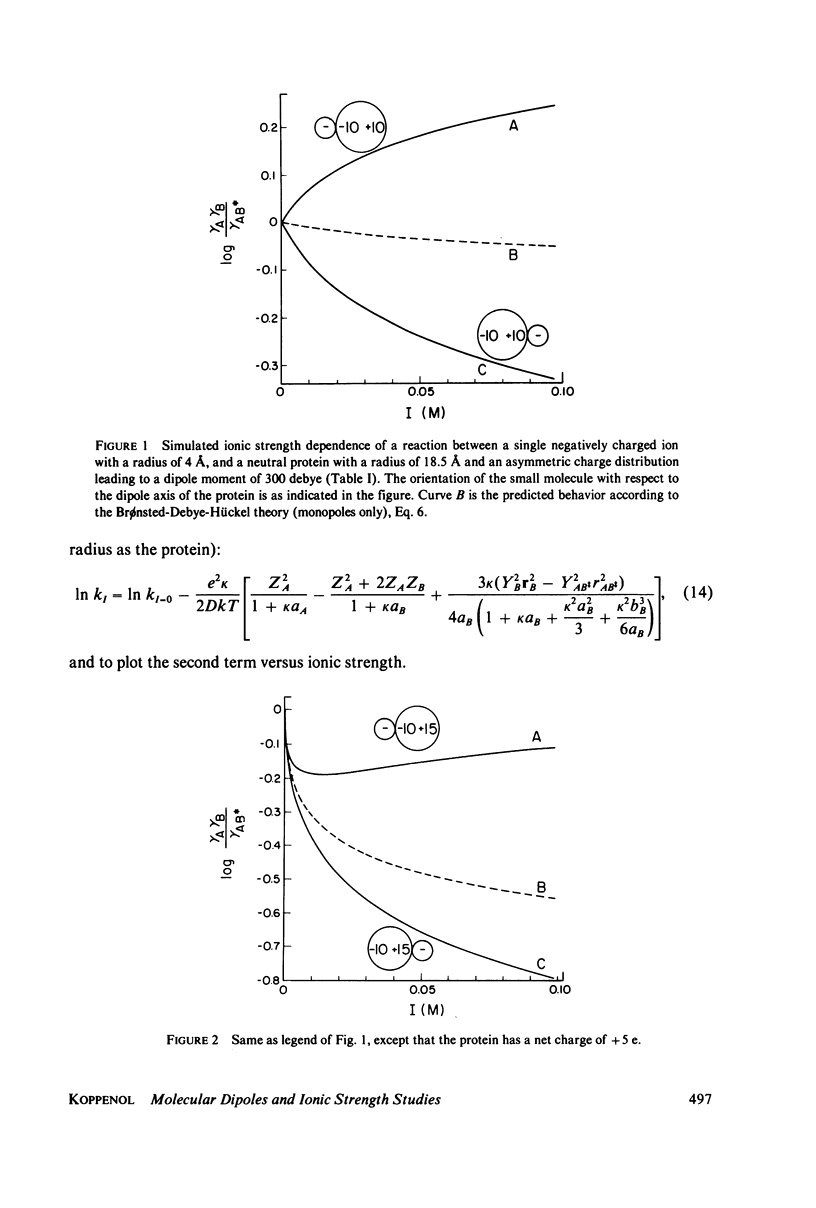
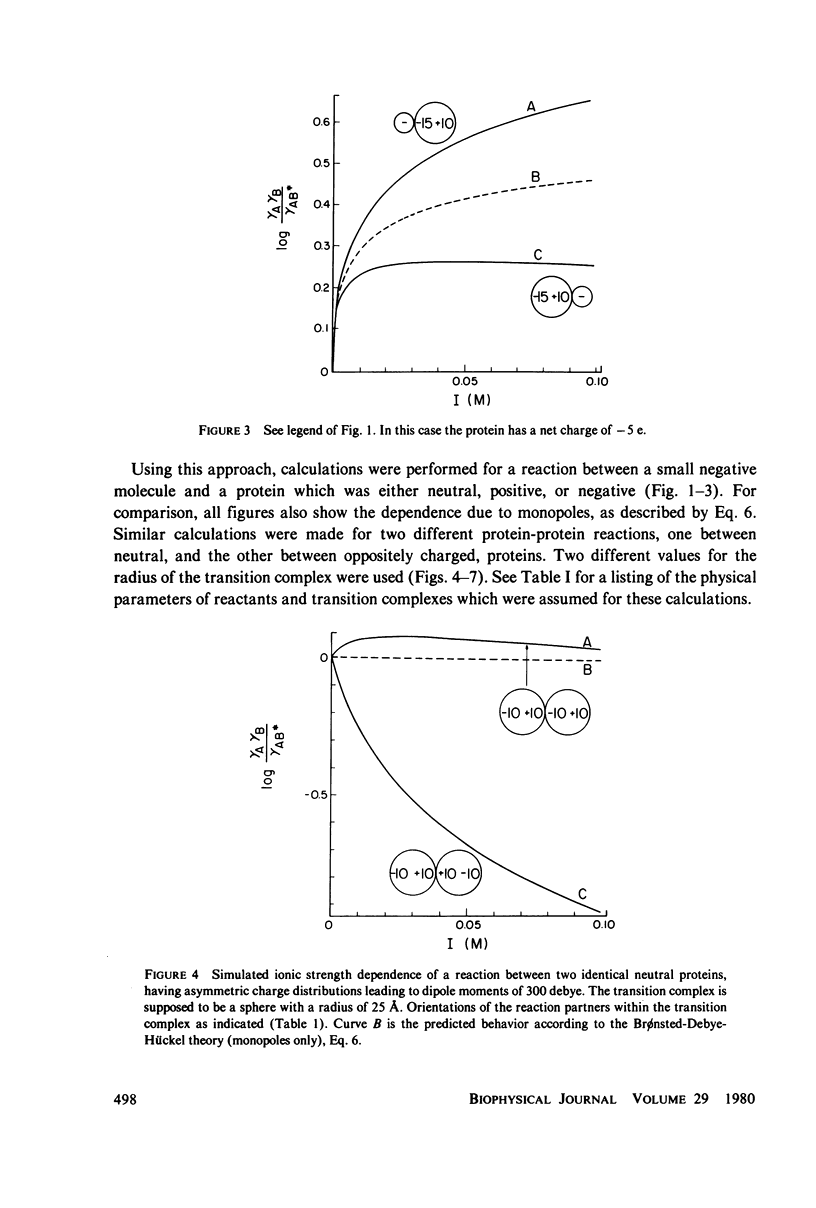
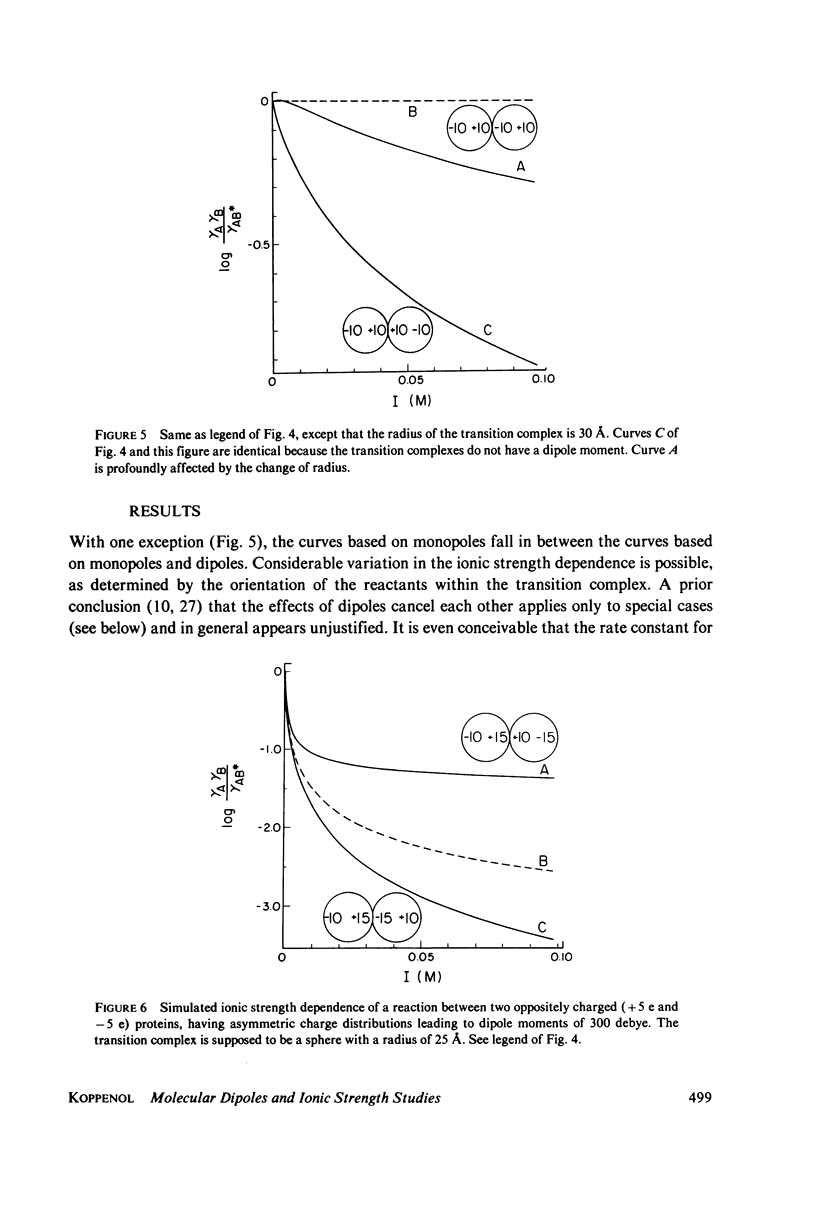
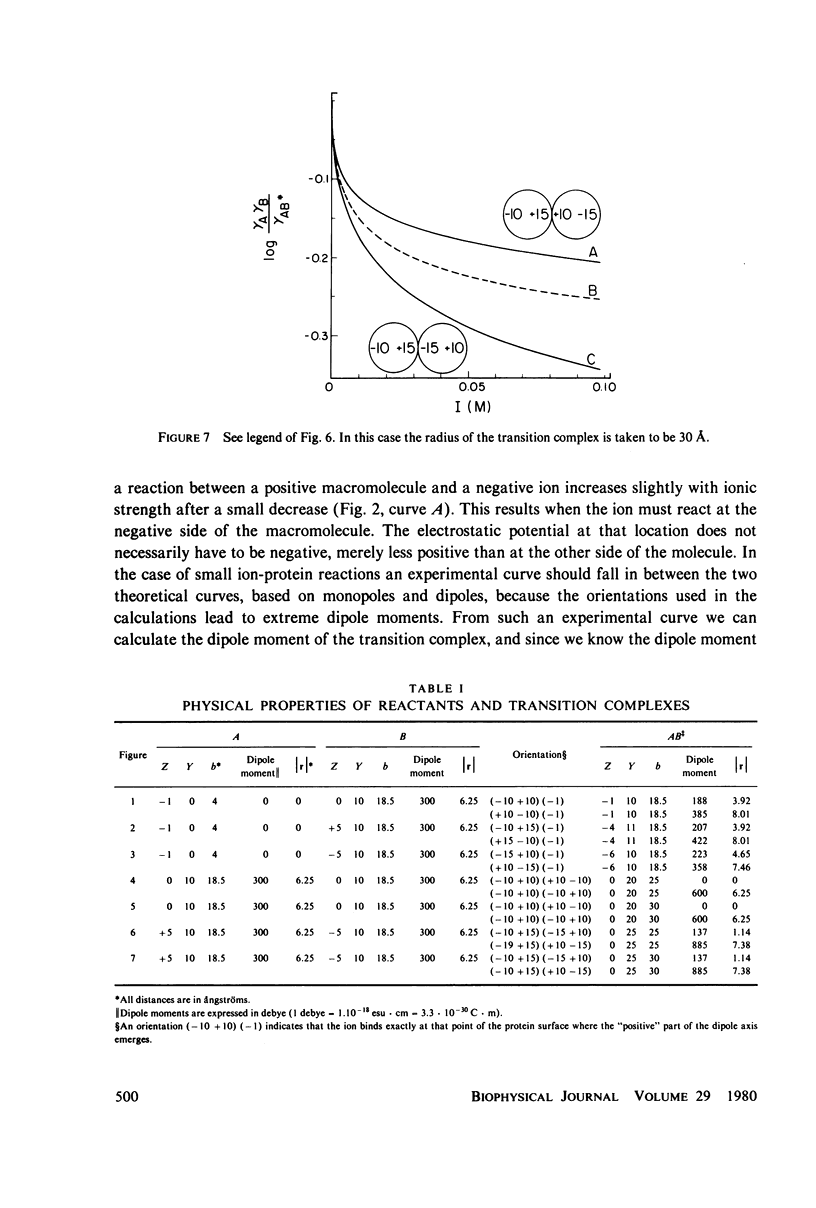
A theory is proposed for determining the location of a reaction site on a protein of known tertiary structure with an asymmetric charge distribution by an analysis of the effect of ionic strength on the rate of reaction of the protein with a small ion, using equations of Brønsted (J. N. Brønsted, 1922, Z. Phys, Chem. 102:169-207), Debye and Hückel (P. Debye and E. Hückel, 1923, Phys. Z. 24:185-206), and Kirkwood (J. G. Kirkwood, 1934, J. Chem. Phys. 2:351-361). The theory is based on the fact that the dipole moment of the transition complex differs from that of the protein, which will be reflected in the ionic strength dependence of the reaction. The location of the small ion with respect to the dipole axis of the protein can be calculated from this difference. For protein-protein reactions, an a priori assumption has to be made about the orientation of one of the reaction partners, since many different orientations of the reactants with respect to each other result in dipole moments of the same magnitude.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botelho L. H., Friend S. H., Matthew J. B., Lehman L. D., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of histidine ionizations in myoglobins of various species. Comparison of observed and computed pK values. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5197–5205. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S., Hayes M. B. Nuclear magnetic resonance titration curves of histidine ring protons. V. Comparative study of cytochrome c from three species and the assignment of individual proton resonances. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5472–5477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins D., Gray H. B. Electron-transfer protein reactivities. Kinetic studies of the oxidation of horse heart cytochrome c, Chromatium vinosum high potential iron-sulfur protein, Pseudomonas aeruginosa azurin, bean plastocyanin, and Rhus vernicifera stellacyanin by pentaamminepyridineruthenium(III). J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Jul 20;99(15):5158–5167. doi: 10.1021/ja00457a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Schejter A. Electrostatic effects on the kinetics of oxidation-reduction reactions of c-type cytochromes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12562–12566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Schejter A. The redox potential of cytochrome c-552 from Euglena gracillis: a thermodynamic study. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Nov;177(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hol W. G., van Duijnen P. T., Berendsen H. J. The alpha-helix dipole and the properties of proteins. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):443–446. doi: 10.1038/273443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood J. G., Shumaker J. B. Forces between Protein Molecules in Solution Arising from Fluctuations in Proton Charge and Configuration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Oct;38(10):863–871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.10.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood J. G., Shumaker J. B. The Influence of Dipole Moment Fluctuations on the Dielectric Increment of Proteins in Solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Oct;38(10):855–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.10.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenol W. H., Vroonland C. A., Braams R. The electric potential field around cytochrome c and the effect of ionic strength on reaction rates of horse cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 7;503(3):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenol W. H., van Buuren K. J., Butler J., Braams R. The kinetics of the reduction of cytochrome c by the superoxide anion radical. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 9;449(2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDERSTR|OM-LANG K. The activity coefficient of large multipolar ions. C R Trav Lab Carlsberg Chim. 1953;28(9):281–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit R., Schejter A. Cytochrome c: a thermodynamic study of the relationships among oxidation state, ion-binding and structural parameters. 1. The effects of temperature, pH and electrostatic media on the standard redox potential of cytochrome c. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 1;32(3):492–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Friend S. H., Botelho L. H., Lehman L. D., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Discrete charge calculations of potentiometric titrations for globular proteins: sperm whale myoglobin, hemoglobin alpha chain, cytochrome c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91549-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Solvent accessibility calculations for sperm whale ferrimyoglobin based on refined crystallographic data. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander W., Horváth C. Salt effect on hydrophobic interactions in precipitation and chromatography of proteins: an interpretation of the lyotropic series. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Sep;183(1):200–215. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orttung W. H. Proton binding and dipole moment of hemoglobin. Refined calculations. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 9;9(12):2394–2402. doi: 10.1021/bi00814a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterman B. F., Morton R. A. The oxidation of ferrocytochrome c in nonbinding buffer. Can J Biochem. 1977 Aug;55(8):796–803. doi: 10.1139/o77-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran G. N., Srinivasan R. Effective dielectric constant values to be used in biopolymer energy calculations. Indian J Biochem. 1970 Jun;7(2):95–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W., Dintzis H. M., Oncley J. L. Changes in the electric dipole vector of human serum albumin due to complexing with fatty acids. Biophys J. 1976 May;16(5):417–431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85698-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shire S. J., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Electrostatic effects in myoglobin. Hydrogen ion equilibria in sperm whale ferrimyoglobin. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2967–2974. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Shulman R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the rate of electron transfer between cytochrome c and iron hexacyanides. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):559–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stonehuerner J., Williams J. B., Millett F. Interaction between cytochrome c and cytochrome b5. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5422–5427. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A. The alpha-helix as an electric macro-dipole. Adv Biophys. 1976:1–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wherland S., Gray H. B. Metalloprotein electron transfer reactions: analysis of reactivity of horse heart cytochrome c with inorganic complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2950–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



