Abstract
Blocking of potassium channels by internally and externally applied barium ions has been studied in squid giant axons. Internal Ba (3-5 mM) causes rapid decay or "inactivation" of potassium current (IK). The kinetics and degree of block are strongly voltage-dependent. Large positive voltages speed blocking and make it more profound. Raising the external potassium concentration (Ko) from 0 to 250 mM has the opposite effect: block is made slower and less severe. In contrast, for positive voltages block by the tetraethylammonium derivative 3-phenylpropyltriethylammonium ion is almost independent of Ko and voltage. Recovery from block by internal Ba has a rapid phase lasting a few milliseconds and a slow phase lasting approximately 5 min. Internal Ba causes a "hook" in the IK tails recorded on repolarizing the fiber in high potassium external medium. External Ba, on the other hand, blocks without much altering IK time-course. KD (the dissociation constant) for block by external Ba is a few millimolar, and depends on the internal potassium concentration, the holding potential, and other factors. A reaction scheme for Ba and K channels is presented, postulating that internal and external Ba reach the same point in the channel. Once there, Ba blocks and also stabilizes the closed conformation of the channel. The extreme stability of the Ba channel complex implies the existence of negative charge within the channel.
Full text
PDF

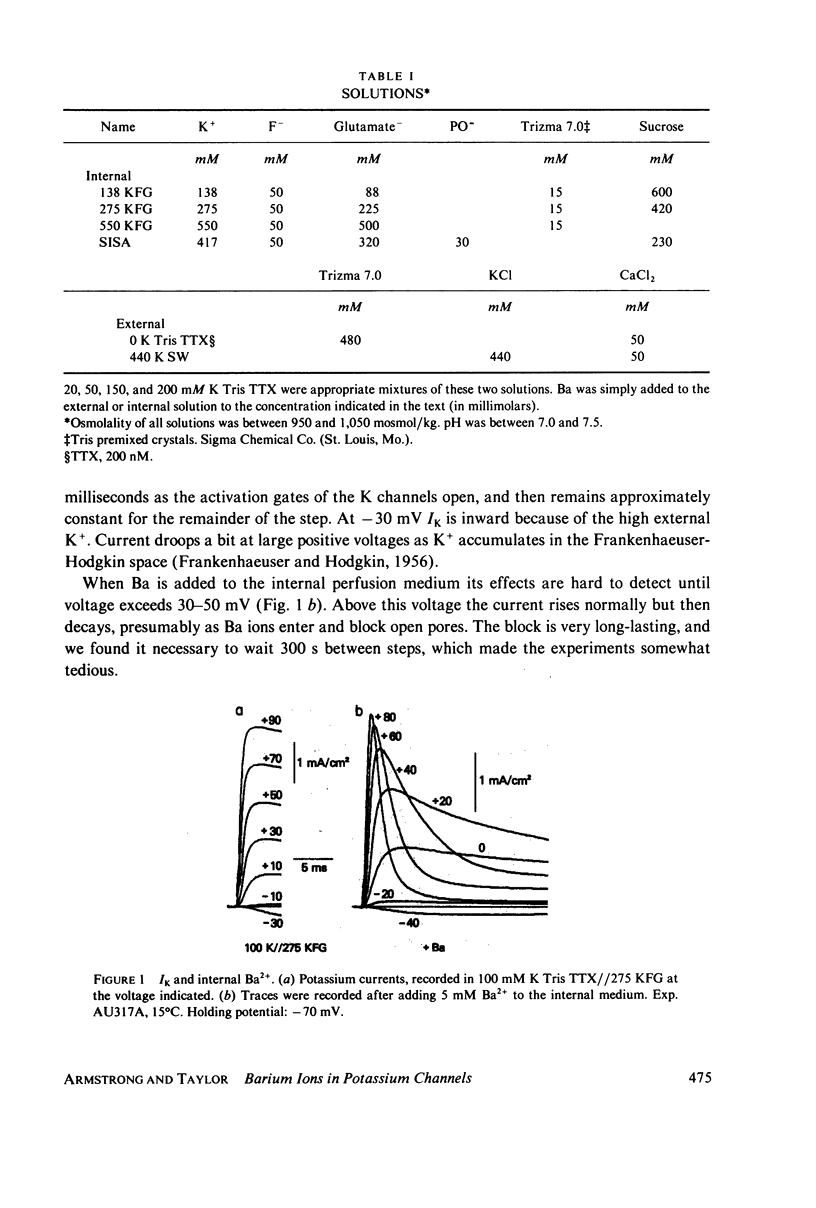

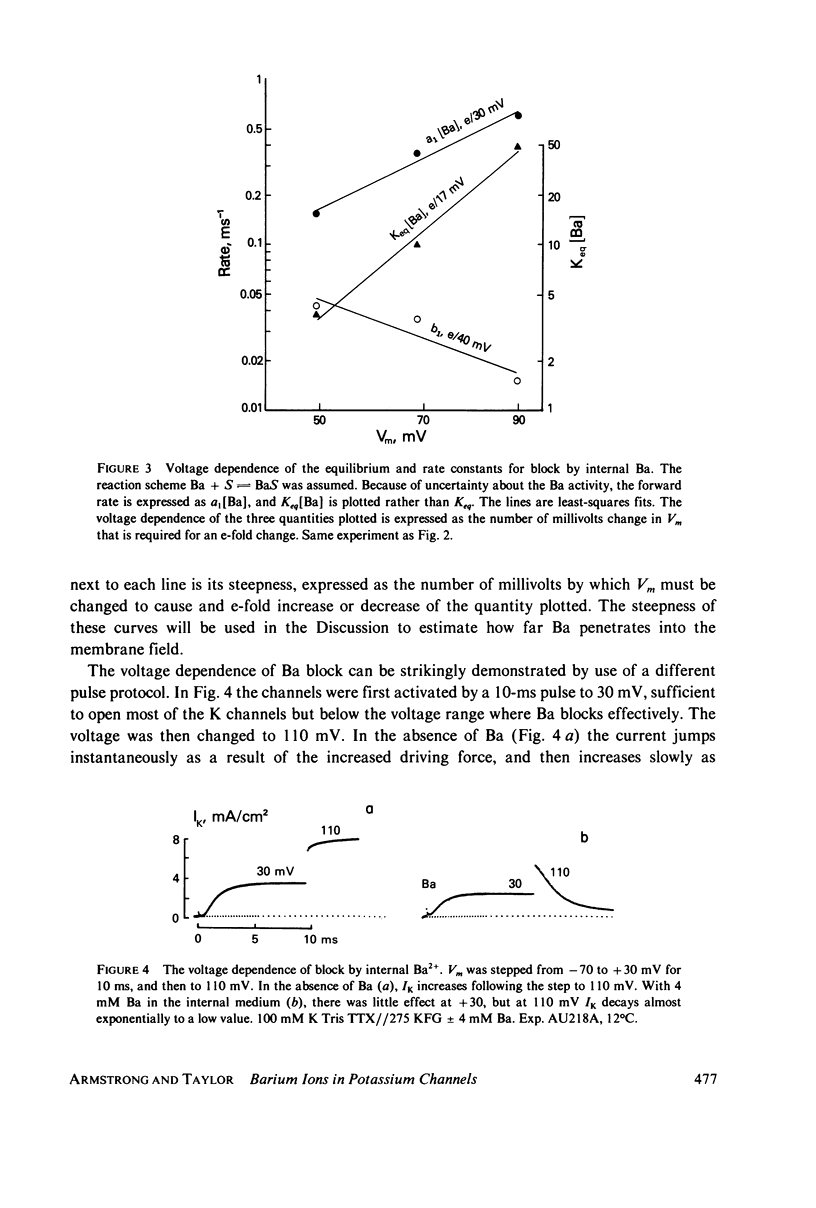
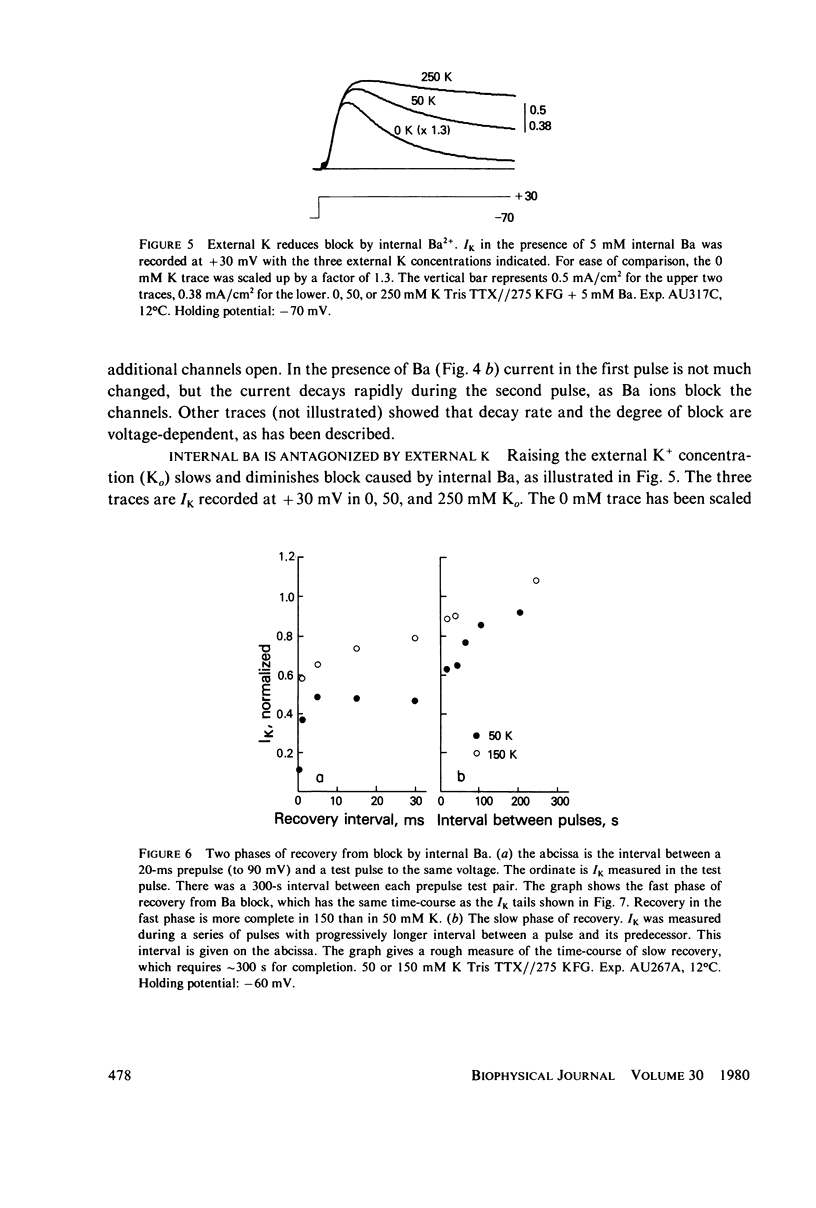
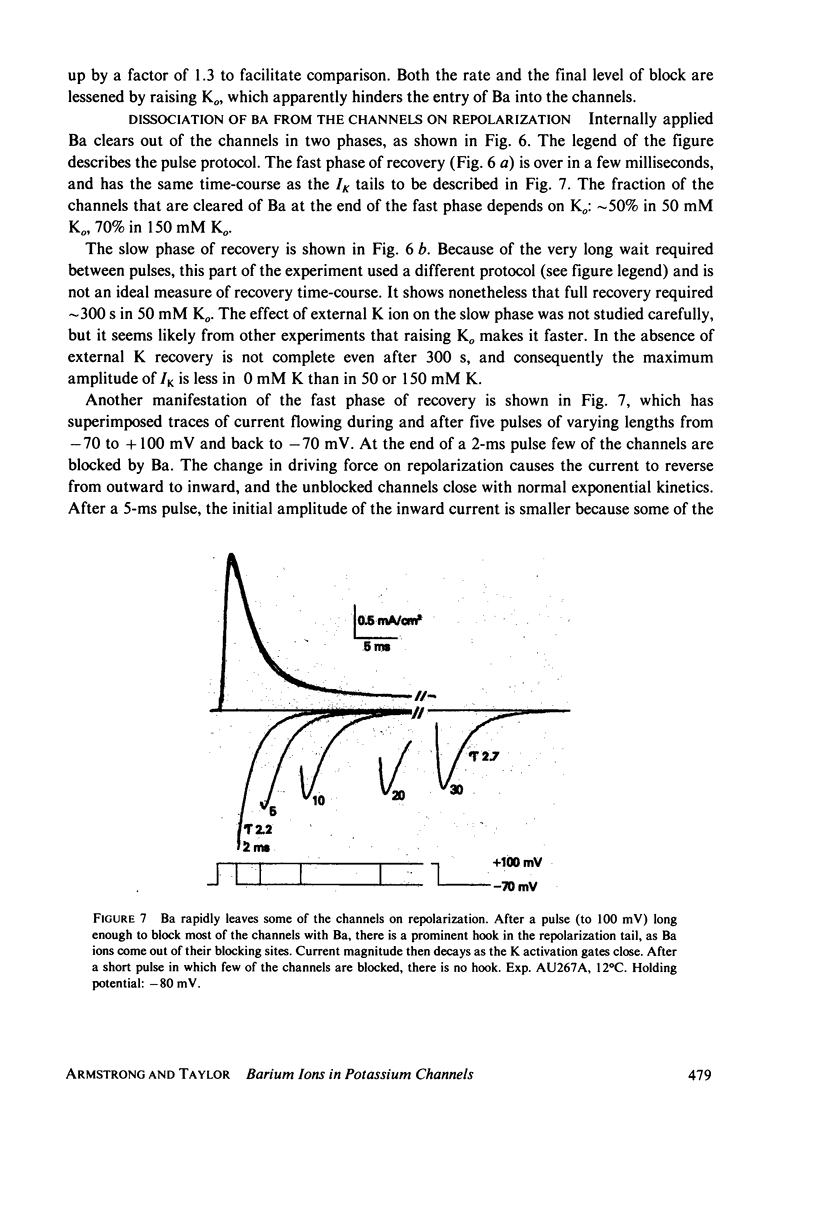
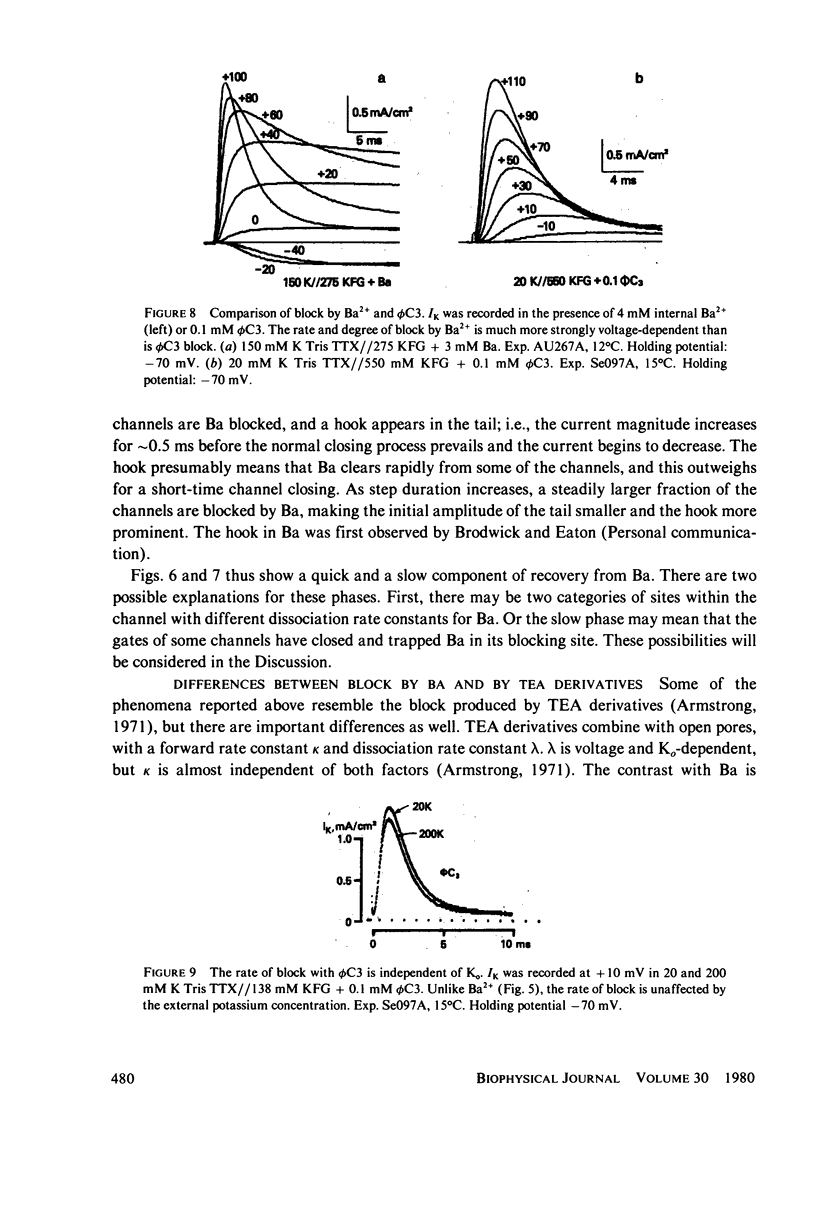
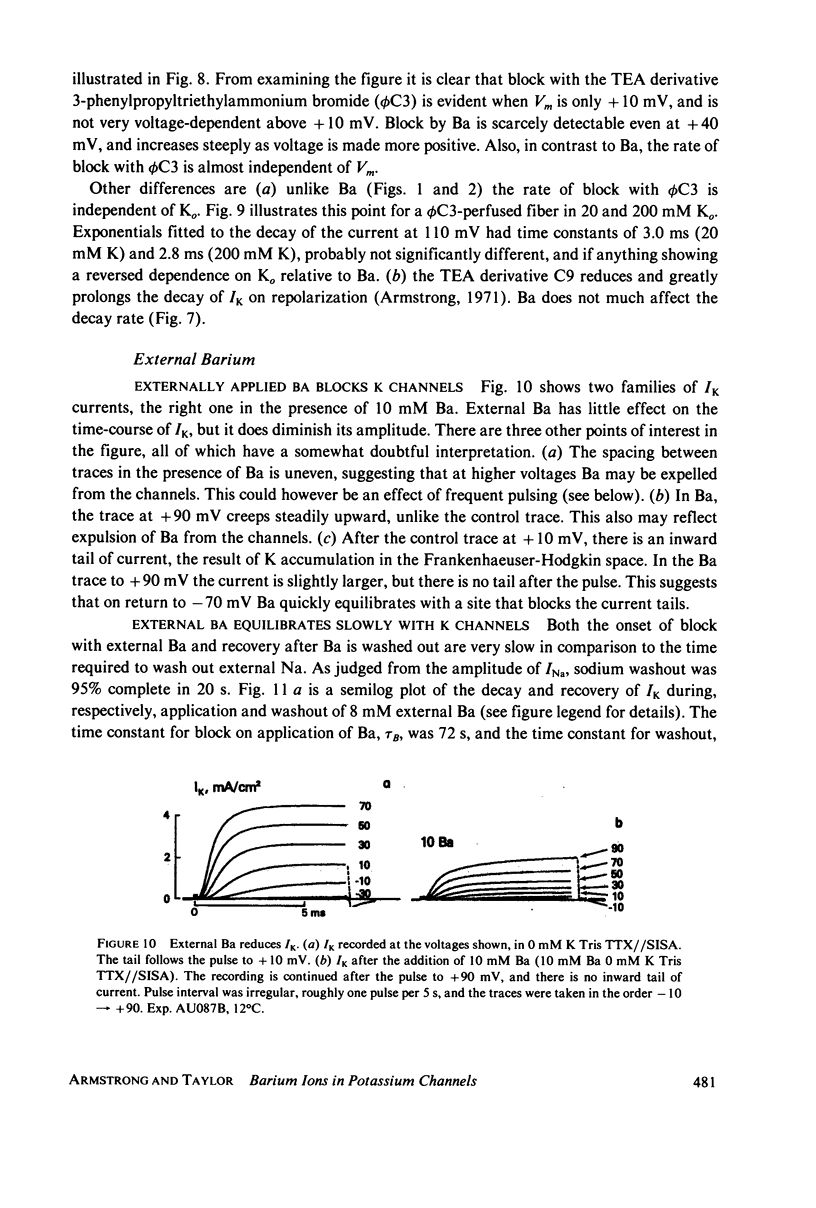







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, French R. J. Blocking of the squid axon potassium channel by external caesium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:13–25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Hille B. The inner quaternary ammonium ion receptor in potassium channels of the node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):388–400. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Time course of TEA(+)-induced anomalous rectification in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Nov;50(2):491–503. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., Stevens C. F. How many conductance states do potassium channels have? Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):843–846. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85858-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Negative conductance caused by entry of sodium and cesium ions into the potassium channels of squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):588–608. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., De Felice L. J., Wanke E. Potassium and sodium ion current noise in the membrane of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):45–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Kidokoro Y. Na and Ca components of action potential in amphioxus muscle cells. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):217–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):669–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Gage P. W., Eisenberg R. S. The role of the electrochemical gradient in determining potassium fluxes in frog striated muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1968 May 1;51(5):193–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J. An analysis of conductance changes in squid axon. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):1013–1035. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian A. Energy of an ion crossing a low dielectric membrane: solutions to four relevant electrostatic problems. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):844–846. doi: 10.1038/221844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N., Schneider M. F., Harris E. J. Decreased K+ conductance produced by Ba++ in frog sartorius fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6):1565–1583. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:169–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERMAN R., GRUNDFEST H. Graded and all-or-none electrogenesis in arthropod muscle. II. The effects of alkali-earth and onium ions on lobster muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:997–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



