Abstract
The electric response of a back photoreaction in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle was investigated. The proton pumping activity of green flash excited bacteriorhodopsin stops if the M412 form is illuminated by blue light (Karvaly and Dancsházy, 1977). In the present work a fast negative displacement current signal was measured in an oriented membrane suspension system, indicative of back movement of protons from M412 to BR570. Quantitative evaluation of the data shows that there are at least two steps in the back reaction, with different rate constants. The temperature dependence of the rate constants show simple linear Arrhenius behavior between 5 degree and 40 degree C. The rate constants were slower by a factor of 1.8 in D2O suspension. The relevance of the protein electric response signals (PERS) observed in this paper to the early receptor potential is discussed.
Full text
PDF

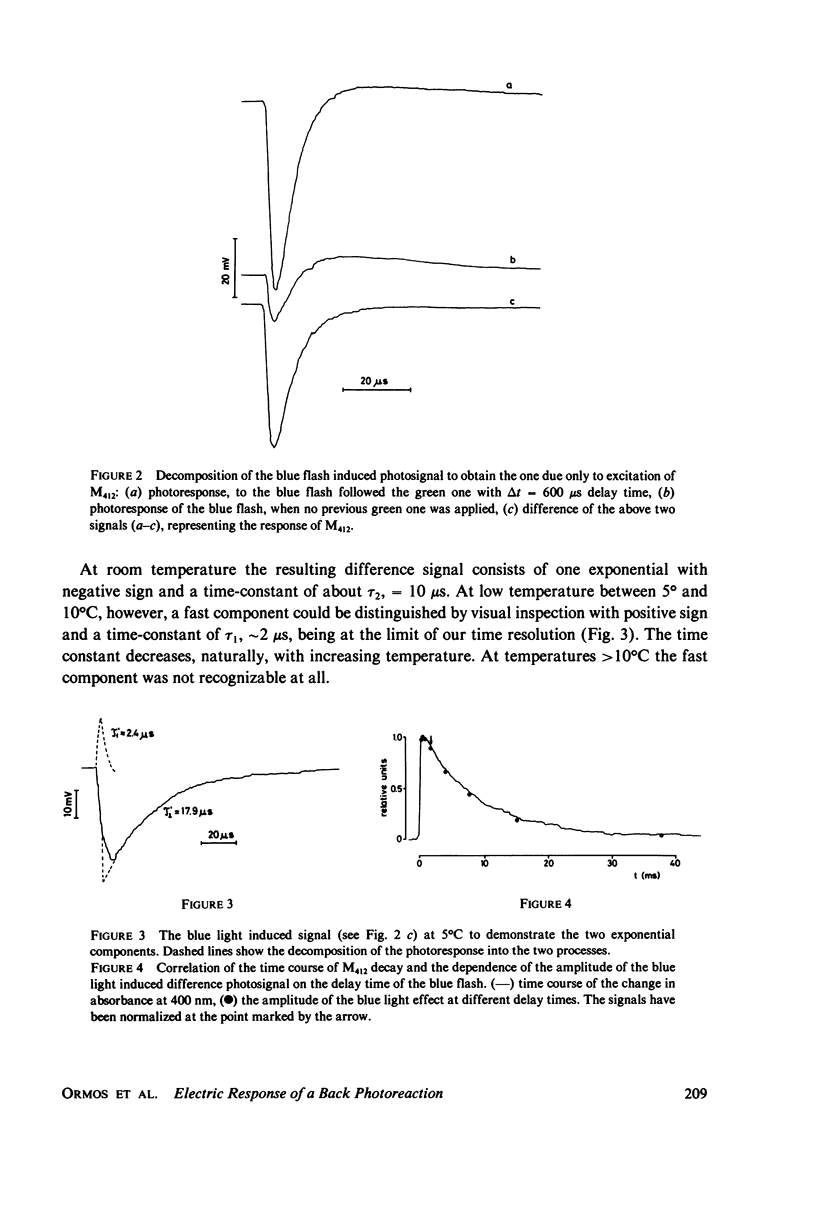




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bol'shakov V. I., Drachev A. L., Drachev L. A., Kalamkarov G. R., Kaulen A. D. Obshchnost' svoistv bakterial'nogo i zritel'nogo rodopsinov: prevrashchenie énergii sveta v raznost' élektricheskikh potentsialov. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1979;249(6):1462–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Early receptor potential: photoreversible charge displacement in rhodopsin. Science. 1967 Mar 3;155(3766):1128–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3766.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancsházy Z., Drachev L. A., Ormos P., Nagy K., Skulachev V. P. Kinetics of the blue light-induced inhibition of photoelectric activity of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 1;96(1):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachev L. A., Kaulen A. D., Skulachev V. P. Time resolution of the intermediate steps in the bacteriorhodopsin-linked electrogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess B., Kuschmitz D. Kinetic interaction between aromatic residues and the retinal chromophore of bacteriorhodopsin during the photocycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):334–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong F. T., Montal M. Bacteriorhodopsin in model membranes. A new component of the displacement photocurrent in the microsecond time scale. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):465–472. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85316-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Korenbrot J. I., Stoeckenius W. Transient photovoltages in purple membrane multilayers. Charge displacement in bacteriorhodopsin and its photointermediates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 18;509(2):300–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karvaly B., Dancsházy Z. Bacteriorhodopsin: a molecular photoelectric regulator. Quenching of photovoltaic effect of bimolecular lipid membranes containing bacteriorhodopsin by blue light. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J., Bogomolni R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Tunable laser resonance raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4462–4466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litvin F. F., Balashov S. P. Novye intermediaty v fotokhimicheskikh prevrashcheniiakh bakteriorodopsina. Biofizika. 1977 Nov-Dec;22(6):1111–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos P., Dancsházy Z., Karvaly B. Mechanism of generation and regulation of photopotential by bacteriorhodopsin in bimolecular lipid membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 8;503(2):304–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90190-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Abdulaev N. G., Feigina M. Y., Kiselev A. V., Lobanov N. A. The structural basis of the functioning of bacteriorhodopsin: an overview. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl H. W. Light-induced conformational changes in cattle rhodopsin as probed by measurements of the interface potential. Photochem Photobiol. 1979 Mar;29(3):579–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1979.tb07093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt H. T., Zickler A. Electrical evidence for the field indicating absorption change in bioenergetic membranes. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80484-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


