Abstract
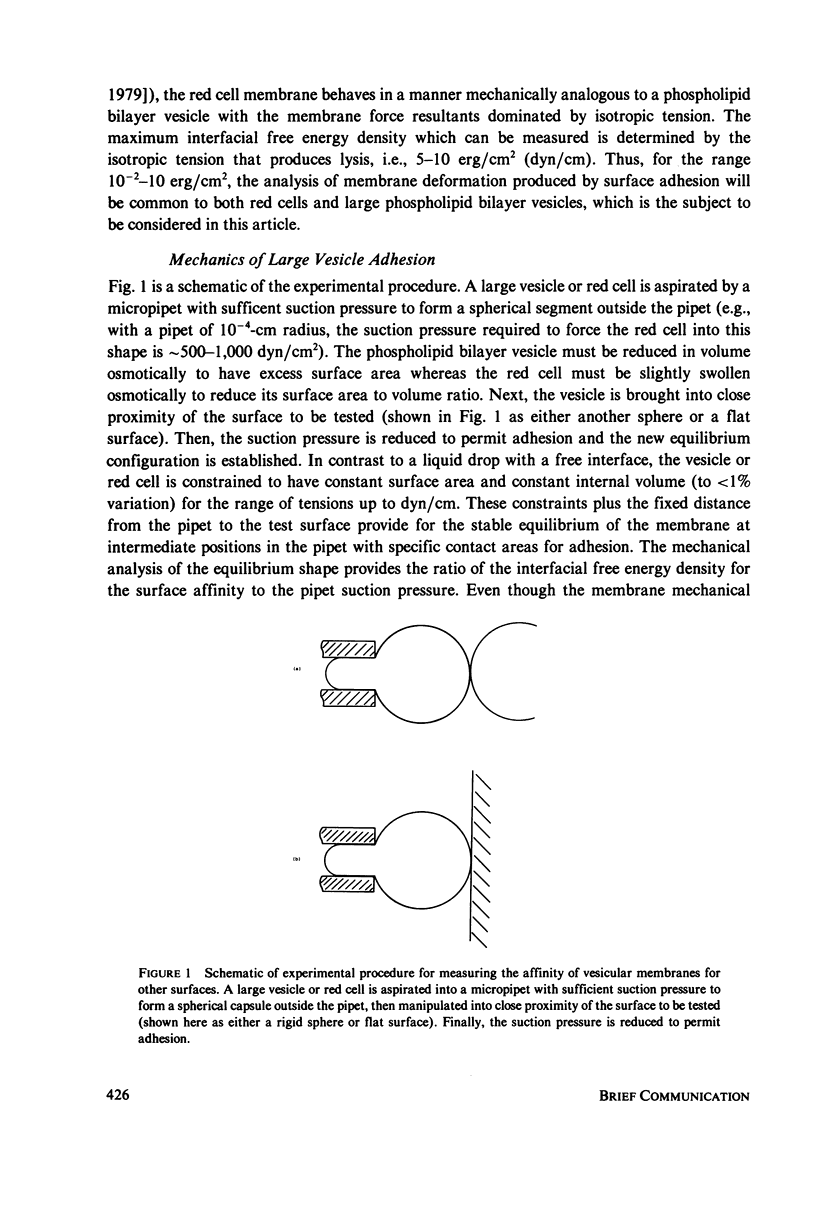
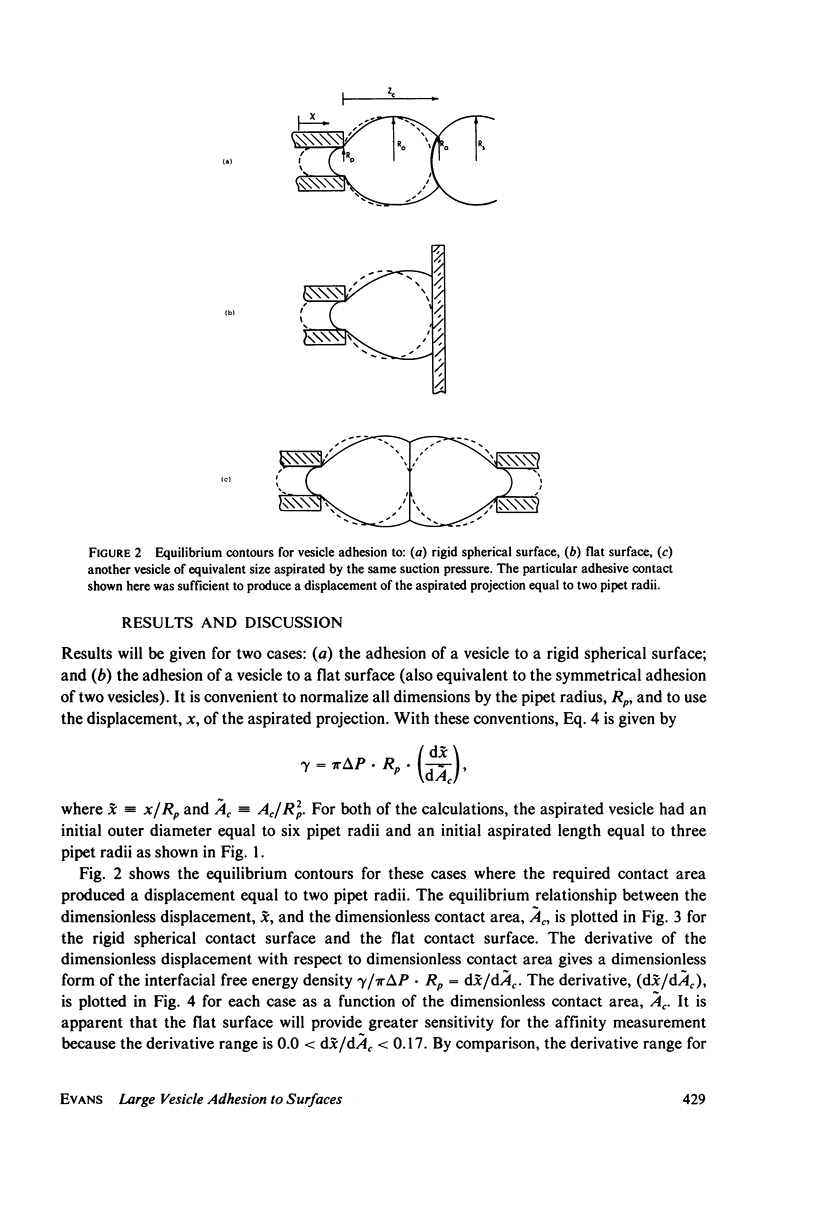
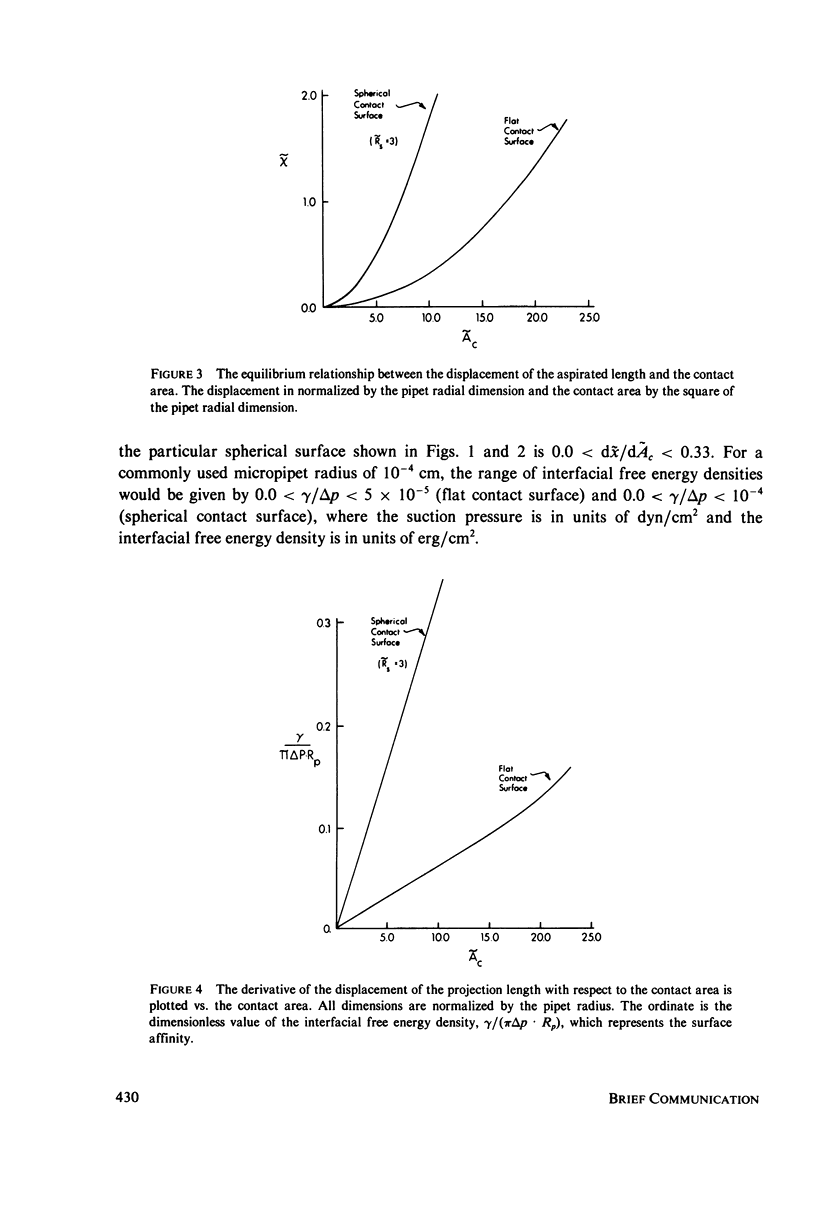
An experimental procedure that can be used to measure the interfacial free energy density for the adhesion of membranes of large vesicles to other surfaces is outlined and analyzed. The approach can be used for both large phospholipid bilayer vesicles and red blood cells when the membrane force resultants are dominated by isotropic tension. The large vesicle or red cell is aspirated by a micropipet with sufficient suction pressure to form a spherical segment outside the pipet. The vesicle is then brought into close proximity of the surface to be tested and, the suction pressure reduced to permit adhesion, and the new equilibrium configuration is established. The mechanical analysis of the equilibrium shape provides the interfacial free energy density for the surface affinity. With this approach, the measurable range of membrane surface affinity is 10(-4)-3 erg/cm2 for large phospholipid bilayer vesicles and 10(-2)-10 erg/cm2 for red blood cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans E. A. Minimum energy analysis of membrane deformation applied to pipet aspiration and surface adhesion of red blood cells. Biophys J. 1980 May;30(2):265–284. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85093-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Waugh R. Osmotic correction to elastic area compressibility measurements on red cell membrane. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):307–313. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85551-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R., Evans E. A. Thermoelasticity of red blood cell membrane. Biophys J. 1979 Apr;26(1):115–131. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85239-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


