Abstract
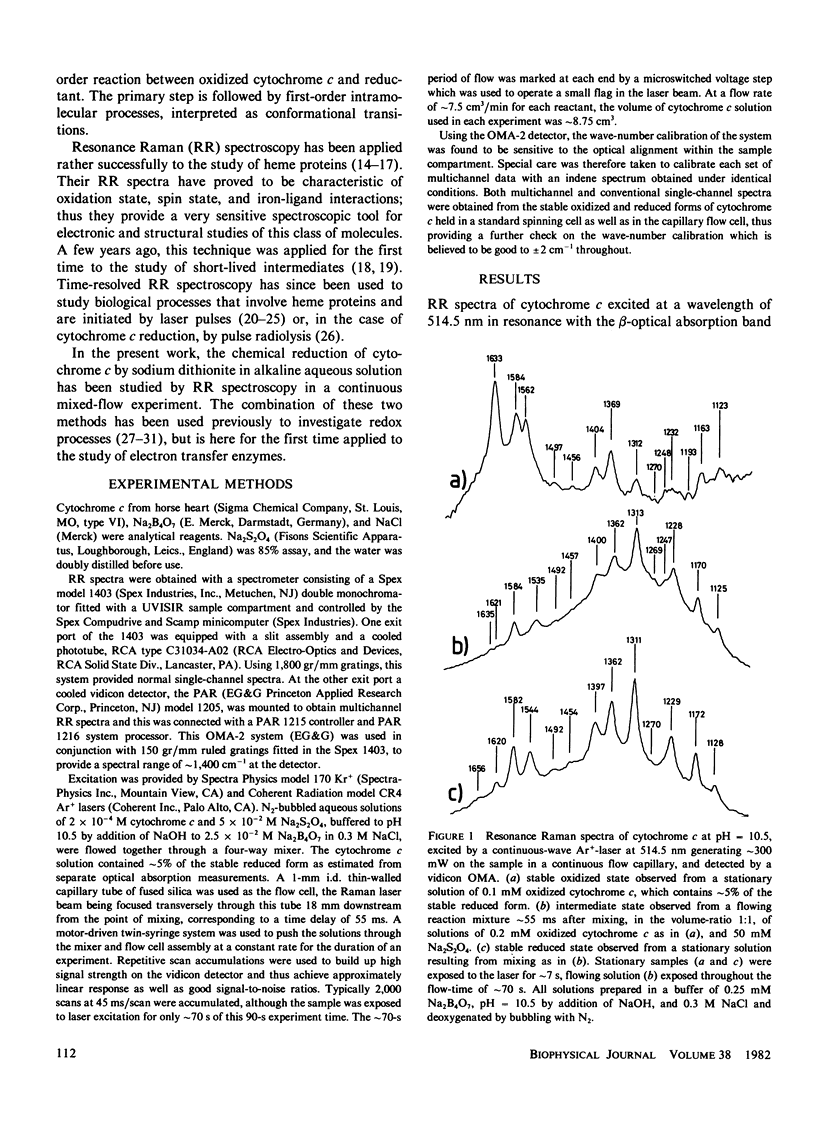
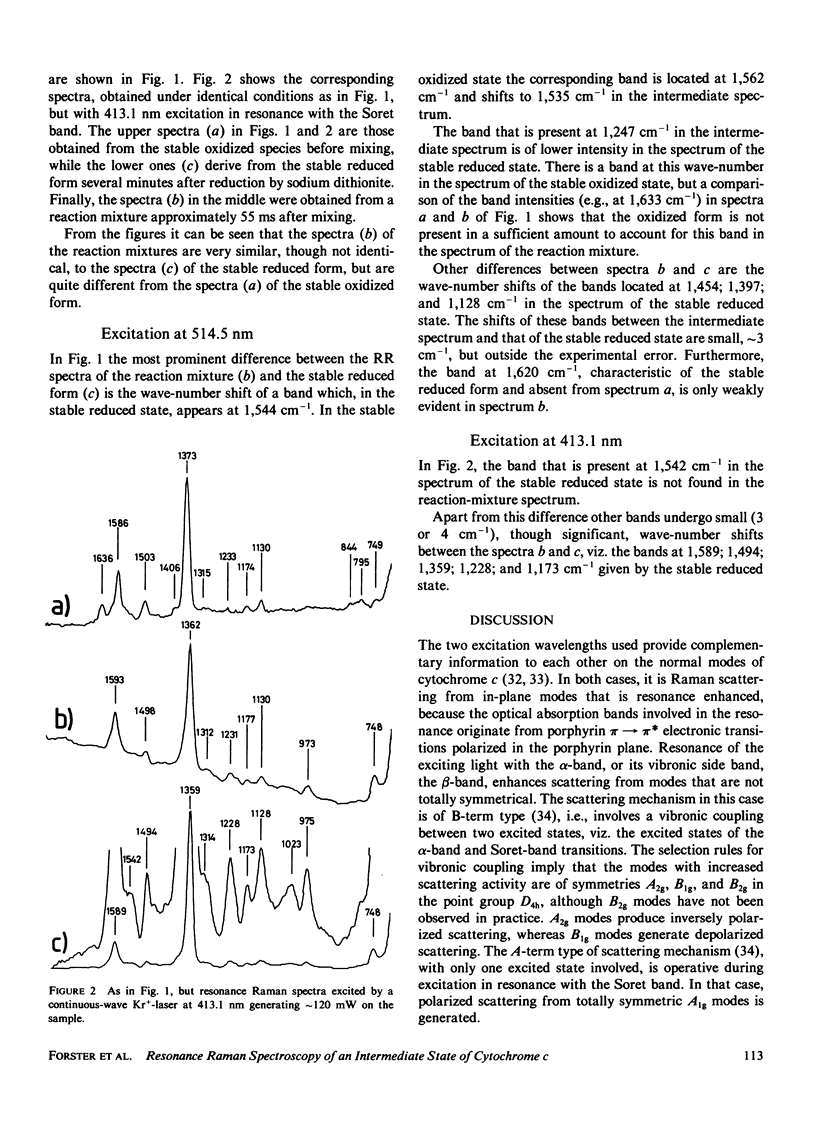
An intermediate redox state of cytochrome c at alkaline pH, generated upon rapid reduction by sodium dithionite, has been observed by resonance Raman (RR) spectroscopy in combination with the continuous flow technique. The RR spectrum of the intermediate state is reported for excitation both in the (alpha, beta) and the Soret optical absorption band. The spectra of the intermediate state are more like those of the stable reduced form than those of the stable oxidized form. For excitation of 514.5 nm, the most prominent indication of an intermediate state is the wave-number shift of one RR band from 1,562 cm-1 in the stable oxidized state through 1,535 cm-1 in the intermediate state to 1,544 cm-1 in the stable reduced state. For excitation at 413.1 nm, a band, present at 1,542 cm-1 in the stable reduced state but not present in the stable oxidized state, is absent in the intermediate state. We interpret the intermediate species as the state where the heme iron is reduced but the protein remains in the conformation of the oxidized state, with methionine-80 displaced as sixth ligand to the heme iron, before relaxing to the conformation of the stable reduced state, with methionine-80 returned as sixth ligand.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenfeld L. A. The physical aspects of energy transduction in biological systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 Aug;11(3):251–308. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey P. R. Resonance Raman spectroscopy in biochemistry and biology. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 Aug;11(3):309–370. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartling B., Ehrenberg A. A molecular mechanism of the energetic coupling of a sequence of electron transfer reactions to endergonic reactions. Biophys J. 1978 Sep;23(3):451–461. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85461-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartling B., Wilbrandt R. Time-resolved resonance Raman spectroscopy of cytochrome c reduced by pulse radiolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 12;637(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppey M., Tourbez H., Valat P., Alpert B. Study of haem structure of photo-deligated haemoglobin by picosecond resonance Raman spectra. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):568–570. doi: 10.1038/284568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. A., Schejter A., Hess G. P. Alkaline isomerization of oxidized cytochrome c. Equilibrium and kinetic measurements. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2624–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Lyons K. B. Transient Raman study of CO-haemoprotein photolysis: origin of the quantum yield. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):570–572. doi: 10.1038/284570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Palmer G. Evidence for the existence of two functionally distinct forms cytochrome c manomer at alkaline pH. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3660–3663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. M., Brown M. L., Trontell M. Effects on pregnant adolescents of attending a special school. J Am Diet Assoc. 1976 Jun;68(6):538–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda-Saito M., Kitagawa T., Iizuka T., Kyogoku Y. Resonance Raman scattering from hemoproteins: pH-dependence of Raman spectra of ferrous dicarboxymethyl-methionyl-cytochrome c. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):233–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Kyogoku Y., Iizuka T., Ikeda-Saito M., Yamanaka T. Resonance Raman scattering from hemoproteins. Effects of ligands upon the Raman spectra of various C-type cytochromes. J Biochem. 1975 Oct;78(4):719–728. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Ozaki Y., Teraoka J., Kyogoku Y., Yamanaka T. The pH dependence of the resonance raman spectra and structural alterations at heme moieties of various c-type cytochromes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 27;494(1):100–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambeth D. O., Campbell K. L., Zand R., Palmer G. The appearance of transient species of cytochrome c upon rapid oxidation or reduction at alkaline pH. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8130–8136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land E. J., Swallow A. J. One-electron reactions in biochemical systems as studied by pulse radiolysis. V. Cytochrome c. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land E. J., Swallow A. J. One-electron reactions in biochemical systems as studied by pulse radiolysis. VI. Stages in the reduction of ferricytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 18;368(1):86–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons K. B., Friedman J. M., Fleury P. A. Nanosecond transient Raman spectra of photolysed carboxyhaemoglobin. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):565–566. doi: 10.1038/275565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecht I., Faraggi M. Electron transfer to ferricytochrome c: reaction with hydrated electrons and conformational transitions involved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):902–906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter A., Aviram I. The effects of alkylation of methionyl residues on the properties of horse cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1552–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafferman A., Stein G. Study of biochemical redox processes by the technique of pulse radiolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 30;416(3-4):287–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(75)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro T. G., Burke J. M. Protein control of porphyrin conformation. Comparison of resonance Raman spectra of heme proteins with mesoporphyrin IX analogues. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Sep 1;98(18):5482–5489. doi: 10.1021/ja00434a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro T. G., Strekas T. C. Resonance Raman spectra of heme proteins. Effects of oxidation and spin state. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Jan 23;96(2):338–345. doi: 10.1021/ja00809a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro T. G., Strekas T. C. Resonance Raman spectra of hemoglobin and cytochrome c: inverse polarization and vibronic scattering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2622–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P., Burke J. M., Spiro T. G. Letter: Structural interpretation of heme protein resonance Raman frequencies. Preliminary normal coordinate analysis results. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Apr 16;97(8):2304–2305. doi: 10.1021/ja00841a070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strekas T. C., Spiro T. G. Cytochrome c: resonance Raman spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki A., Otsuka J., Kotani M. Magnetic susceptibility measurements on hemoproteins down to 4.2 degrees K. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 27;140(2):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wart H. E., Scheraga H. A. Raman and resonance raman spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:67–149. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. T., Greenwood C. Studies on ferricytochrome c. 2. A correlation between reducibility and the possession of the 695mm absorption band of ferricytochrome c. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 13;22(1):11–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff W. H., Farquharson S. Time-resolved resonance raman spectroscopy of hemoglobin derivatives: heme structure changes in 7 nanoseconds. Science. 1978 Sep 1;201(4358):831–833. doi: 10.1126/science.684409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


