Abstract
In this paper we reconsider the theoretical and practical aspects of using KCl-filled microelectrodes in extended polyelectrolyte gels such as muscle to measure Donnan potentials, and then calculate protein fixed-charge concentrations. An analytical calculation of the electrical potential function between muscle filaments shows that whether the microelectrode averages the ionic concentration or the local potentials the results are indistinguishable in the practical regime. After consideration of this and other possible sources of error, we conclude that the charge-concentrations measurements that have appeared in the literature are legitimate.
Full text
PDF

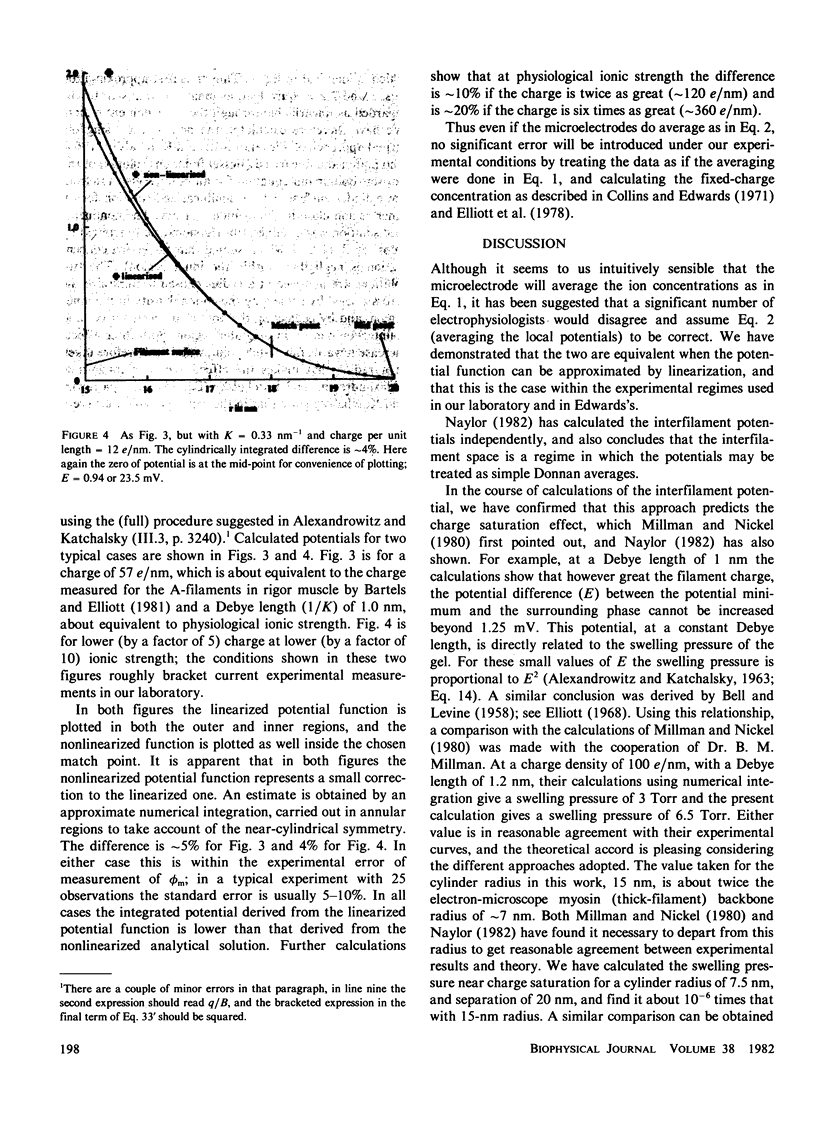

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caillé J. P. The myoplasmic fixed charges of the barnacle muscle fiber and the free Ca2+ concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 3;673(4):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins E. W., Jr, Edwards C. Role of Donnan equilibrium in the resting potentials in glycerol-extracted muscle. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1130–1133. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott G. F. Force-balances and stability in hexagonally-packed polyelectrolyte systems. J Theor Biol. 1968 Oct;21(1):71–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott G. F. Measurements of the electric charge and ion-binding of the protein filaments in intact muscle and cornea, with implications for filament assembly. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84927-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuoss R. M., Katchalsky A., Lifson S. The Potential of an Infinite Rod-Like Molecule and the Distribution of the Counter Ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Sep;37(9):579–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.9.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinke J. A., Gayton D. C. Transmembrane K + and Cl - activity gradients for the muscle fiber of the giant barnacle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;49(4):312–322. doi: 10.1139/y71-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinke J. A. Water and electrolyte content of the myofilament phase in the chemically skinned barnacle fiber. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):531–551. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Podolsky R. J. Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman B. M., Nickel B. G. Electrostatic forces in muscle and cylindrical gel systems. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):49–63. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84915-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor G. R. A simple circuit for automatic continuous recording of microelectrode resitance. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Dec 28;378(2):107–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00584442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor G. R. Average electrostatic potential between the filaments in striated muscle and its relation to a simple Donnan potential. Biophys J. 1982 May;38(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84547-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemrick S. M., Edwards C. Differences in the charge distribution of glycerol-extracted muscle fibers in rigor, relaxation, and contraction. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):551–567. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Wendt I. R., Forrest Q. G. Non-uniform ion distributions and electrical potentials in sarcoplasmic regions of skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):690–692. doi: 10.1038/289690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


