Abstract
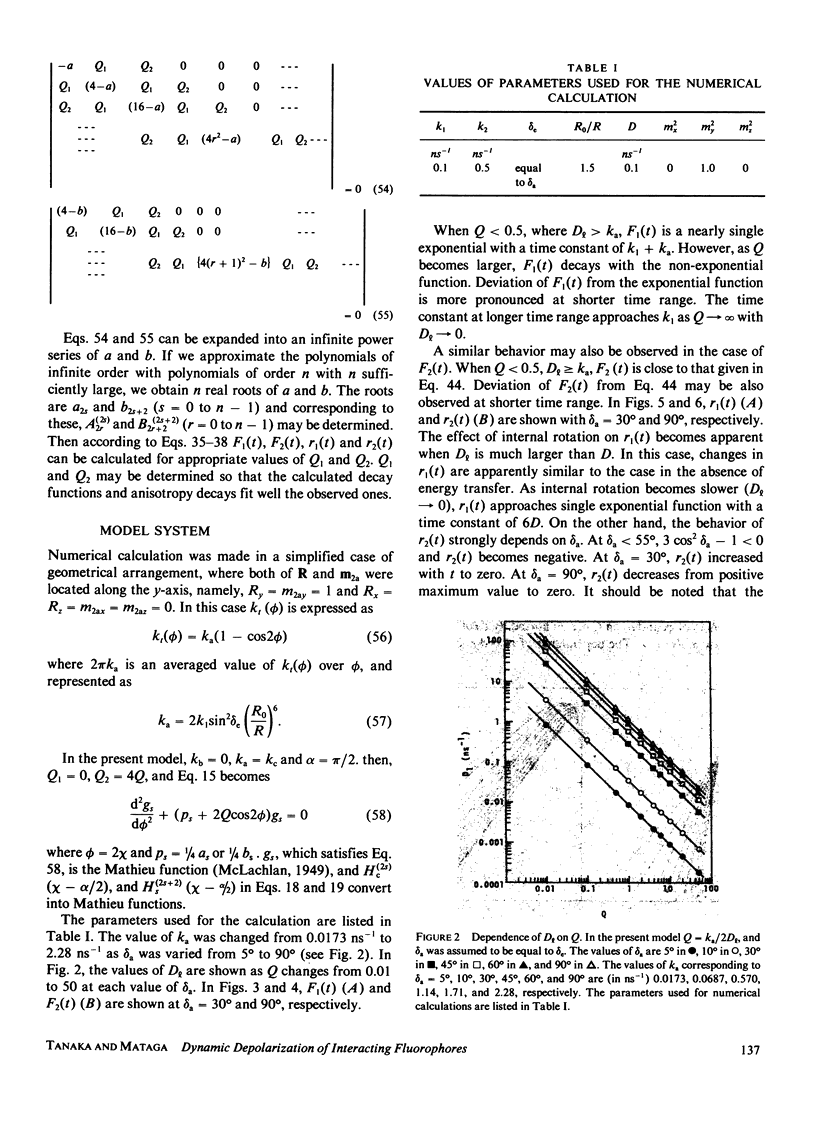
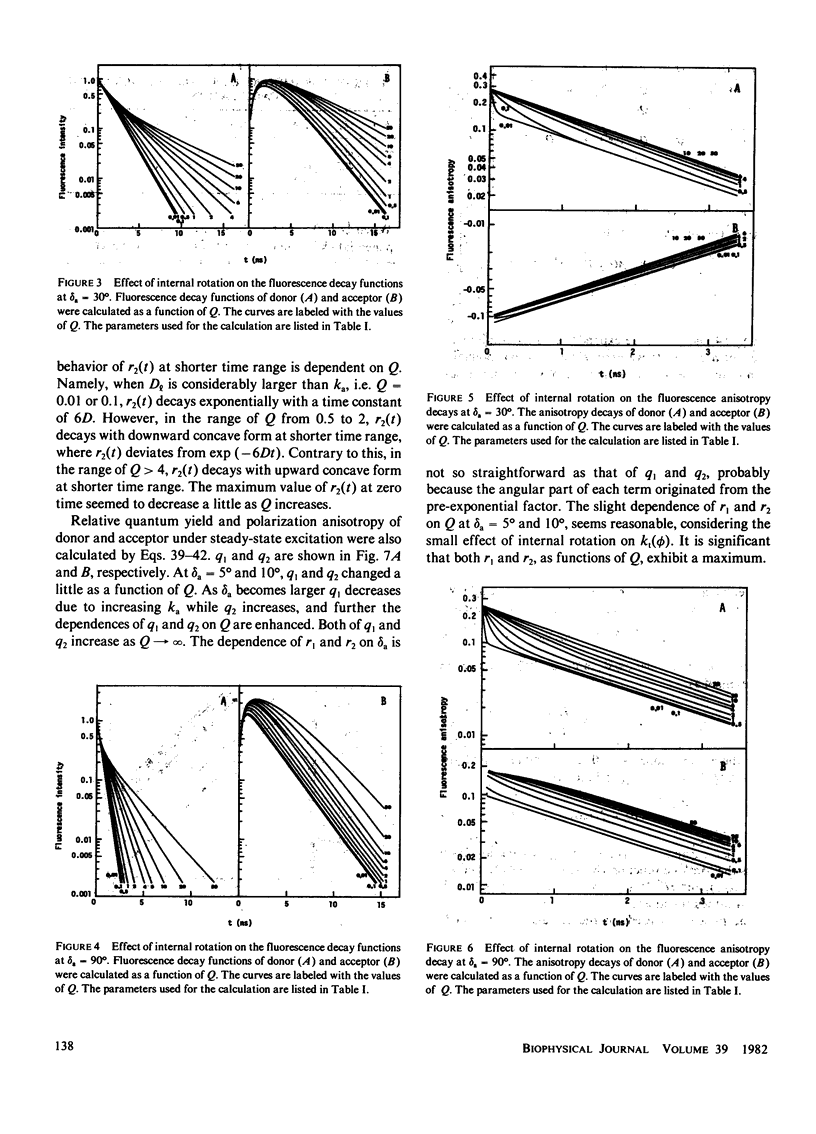
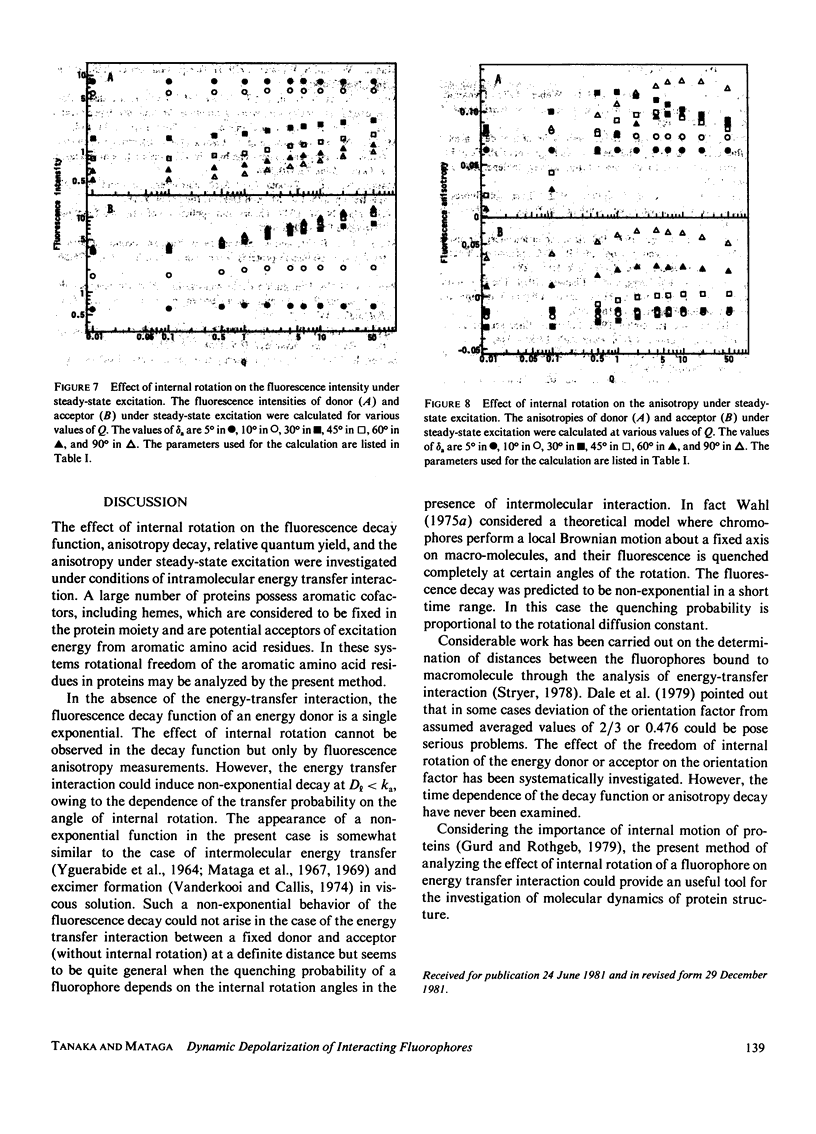
Effects of internal rotation on the fluorescence decay functions and time-dependent anisotropies of fluorophores bound to a spherical macromolecule are theoretically investigated in the presence of the intramolecular energy transfer interaction by solving relevant rotational diffusion equations. The model system examined is one in which the energy donor is internally rotating around an axis fixed at the macromolecule and the acceptor is fixed at a definite position in the macromolecule. The effect of internal rotation in the system is described by Hill's functions with two cosine terms. The fluorescence decay function and anisotropy decay are functions of the ratio of energy-transfer probability averaged over the internal rotation angle to the rotary diffusion co-efficient. When the internal rotation is much faster than energy transfer, the decay function of the donor is predicted to be a single exponential, and the anisotropy decay is essentially described by the expression derived by Gotlieb and Wahl (1963. J. Chim. Phys. 60:849-856). However, deviation from it becomes pronounced as the rotation becomes slower. Methods of numerical analysis are presented for decay function and anisotropy decay, as well as relative quantum yield and polarization anisotropy under steady-state excitation, and examined for a simplified system under the variation of the diffusion coefficient.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belford G. G., Belford R. L., Weber G. Dynamics of fluorescence polarization in macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1392–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brochon J. C., Wahl P. Measures des déclins de l'anisotropie de fluorescence de la gamma-globuline et de ses fragments Fab, Fc et F(ab) 2 marqués avec le 1-sulfonyl-5-diméthyl-aminonaphtalène. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):20–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. E., Eisinger J., Blumberg W. E. The orientational freedom of molecular probes. The orientation factor in intramolecular energy transfer. Biophys J. 1979 May;26(2):161–193. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85243-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd F. R., Rothgeb T. M. Motions in proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:73–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60459-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland R. P., Yguerabide J., Stryer L. Dependence of the kinetics of singlet-singlet energy transfer on spectral overlap. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):23–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopp J. A., Weber G. Fluorescence polarization of pyrenebutyric-bovine serum albumin and pyrenebutyric-human macroglobulin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6309–6315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATT S. A., CHEUNG H. T., BLOUT E. R. ENERGY TRANSFER. A SYSTEM WITH RELATIVELY FIXED DONOR-ACCEPTOR SEPARATION. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Mar 5;87:995–1003. doi: 10.1021/ja01083a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Cherek H. Dipolar relaxation in proteins on the nanosecond timescale observed by wavelength-resolved phase fluorometry of tryptophan fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Freshwater G., Weber G. Nanosecond segmental mobilities of tryptophan residues in proteins observed by lifetime-resolved fluorescence anisotropies. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):591–601. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84992-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro I., Pecht I., Stryer L. Subnanosecond motions of tryptophan residues in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a spectroscopic ruler. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:819–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Haugland R. P. Energy transfer: a spectroscopic ruler. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):719–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Callis J. B. Pyrene. A probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4000–4006. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Polarization of the fluorescence of macromolecules. II. Fluorescent conjugates of ovalbumin and bovine serum albumin. Biochem J. 1952 May;51(2):155–167. doi: 10.1042/bj0510155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl P., Weber G. Fluorescence depolarization of rabbit gamma globulin conjugates. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):371–382. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


