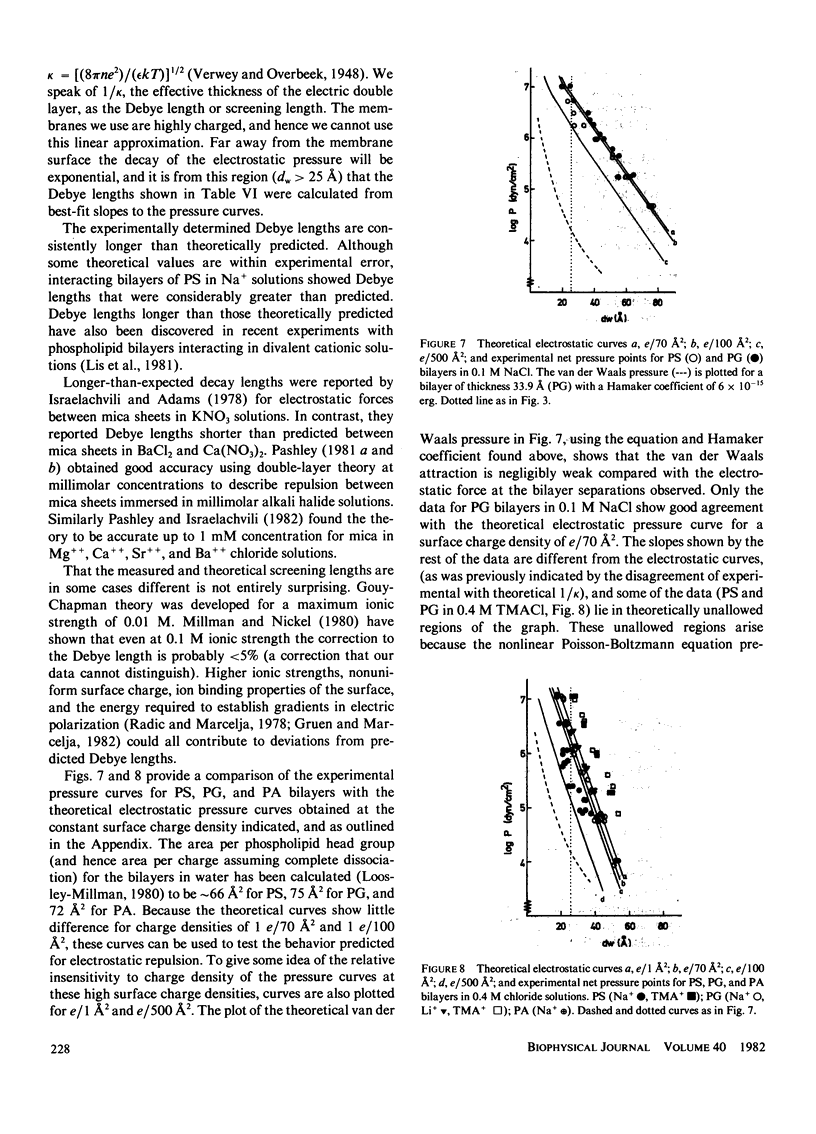
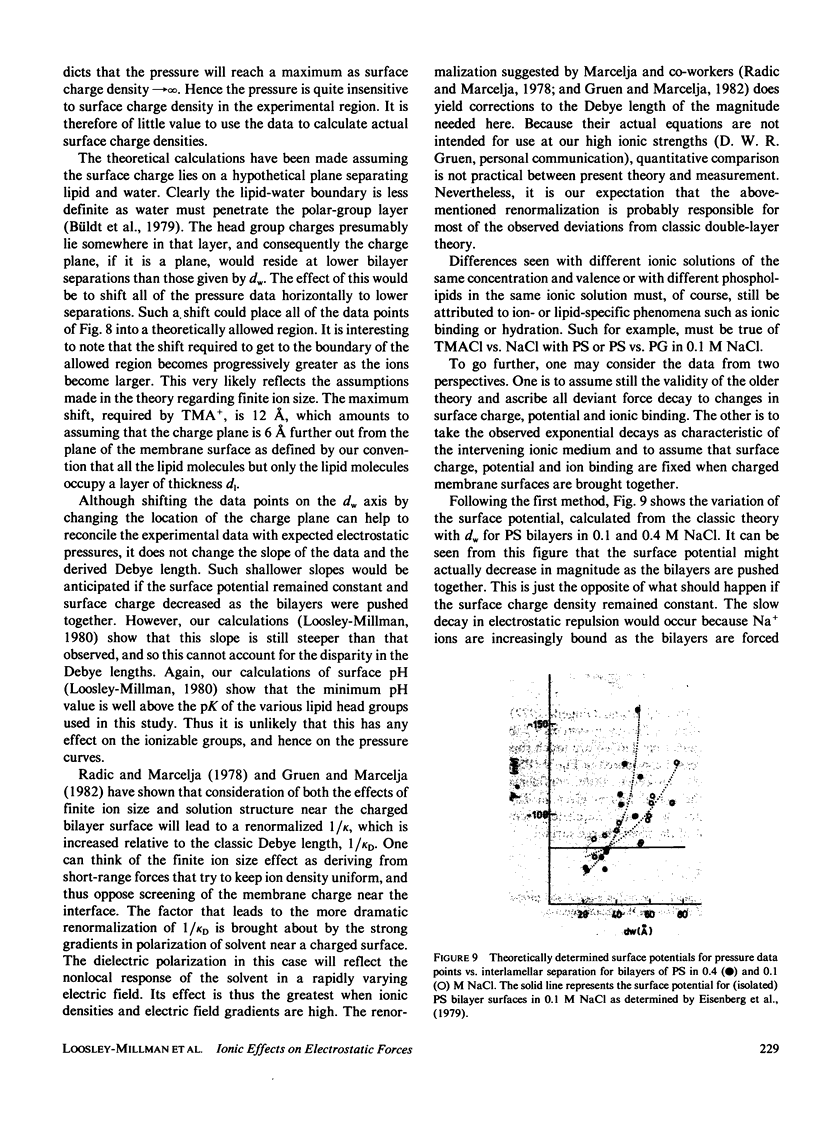
Abstract
In an effort to determine the role that monovalent ions play in the modification of intermembrane forces, we have measured these forces between charged phospholipid bilayers in monovalent ionic solutions. The osmotic stress technique allowed the net electrostatic pressure between the bilayers to be measured while their separation was concurrently determined by x-ray diffraction. Taken together, these measurements yielded electrostatic pressure as a function of bilayer separation. We have related measured pressures to the bilayer surface charge density and surface potential through an exact solution of the full nonlinear Poisson-Boltzmann equation for this system. Quantitative differences in bilayer separation amongst monovalent alkali metal cations indicated differential binding of these to phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylserine (PS), and phosphatidic acid (PA); binding affinity series were determined for Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, and TMA+ ions to these lipids. The anions Cl-, Br-, I-, and CH3COO- were found to have no differential effect on the repulsive forces between PS bilayers. Debye lengths for the electric double layer estimated from the slopes of the experimental pressure curves were consistently longer than predicted on the basis of classic Gouy-Chapman theory. Estimates of the van der Waals Hamaker coefficient between bilayers of PS and PG in salt solution were found to be weaker than between phosphatidylcholine bilayers in pure water, a difference possibly due to electromagnetic retardation and ionic screening.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON M. B., KATZMAN R., GREGOR H. P. AQUEOUS DISPERSIONS OF PHOSPHATIDYLSERINE. IONIC PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:70–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Gally H. U., Seelig J., Zaccai G. Neutron diffraction studies on phosphatidylcholine model membranes. I. Head group conformation. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley A. C., Fuller N. L., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Measurement of repulsive forces between charged phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):3163–3168. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day E. P., Kwok A. Y., Hark S. K., Ho J. T., Vail W. J., Bentz J., Nir S. Reversibility of sodium-induced aggregation of sonicated phosphatidylserine vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4026–4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg M., Gresalfi T., Riccio T., McLaughlin S. Adsorption of monovalent cations to bilayer membranes containing negative phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5213–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell D., Fornes J. A. Demonstration of intermolecular forces in cell adhesion using a new electrochemical technique. Nature. 1975 Jul 17;256(5514):210–211. doi: 10.1038/256210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell D., Fornes J. A. Interaction of red blood cells with a polarized electrode: evidence of long-range intermolecular forces. Biophys J. 1976 Oct;16(10):1131–1153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85763-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell D., Todd I. Adhesion of red blood cells to charged interfaces between immiscible liquids. A new method. J Cell Sci. 1975 Jul;18(2):227–239. doi: 10.1242/jcs.18.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasdalen H., Göran Eriksson L. E., Westman J., Ehrenberg A. Surface potential effects on metal ion binding to phosphatidylcholine membranes 31P NMR study of lanthanide and calcium ion binding to egg-yolk lecithin vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 5;469(2):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Shipley G. G. Crystallization of phosphatidylserine bilayers induced by lithium. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11377–11380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland R., Newton C., Nir S., Papahadjopoulos D. Specificity of Na+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles from a 23Na NMR relaxation rate study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 20;551(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeNeveu D. M., Rand R. P. Measurement and modification of forces between lecithin bilayers. Biophys J. 1977 May;18(2):209–230. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85608-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeNeveu D. M., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Measurement of forces between lecithin bilayers. Nature. 1976 Feb 19;259(5544):601–603. doi: 10.1038/259601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P. Binding of divalent cations of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers and its effect on bilayer interaction. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1761–1770. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S., Mulrine N., Gresalfi T., Vaio G., McLaughlin A. Adsorption of divalent cations to bilayer membranes containing phosphatidylserine. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Apr;77(4):445–473. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman B. M., Nickel B. G. Electrostatic forces in muscle and cylindrical gel systems. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):49–63. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84915-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninham B. W., Parsegian V. A. Electrostatic potential between surfaces bearing ionizable groups in ionic equilibrium with physiologic saline solution. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jun;31(3):405–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Fuller N., Rand R. P. Measured work of deformation and repulsion of lecithin bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2750–2754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Gingell D. On the electrostatic interaction across a salt solution between two bodies bearing unequal charges. Biophys J. 1972 Sep;12(9):1192–1204. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86155-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Stamatoff J. Perturbation of membrane structure by uranyl acetate labeling. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):475–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84908-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puskin J. S. Divalent cation binding to phospholipids: an EPR study. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 24;35(1):39–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01869939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Interacting phospholipid bilayers: measured forces and induced structural changes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:277–314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Husson F. Structure des phases liquide-cristallines de différents phospholipides, monoglycérides, sphingolipides, anhydres ou en présence d'eau. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):363–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Phase equilibria and structure of dry and hydrated egg lecithin. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


