Abstract
Gramicidin A single-channel current-voltage characteristics were studied at low permeant ion concentrations and very high applied potentials. The purpose of these experiments was to elucidate the basis for the small, but definite, voltage dependence observed under these circumstances. It was found that this residual voltage dependence is a reflection of interfacial polarization effects, similar to those proposed by Walz et al. (Biophys. J. 9:1150-1159). It will be concluded that there exists an effectively voltage-independent step in the association reaction between a gramicidin A channel and the permeating ion. Some consequences of interfacial polarization effects for the analysis of conductance vs. activity relations will be discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
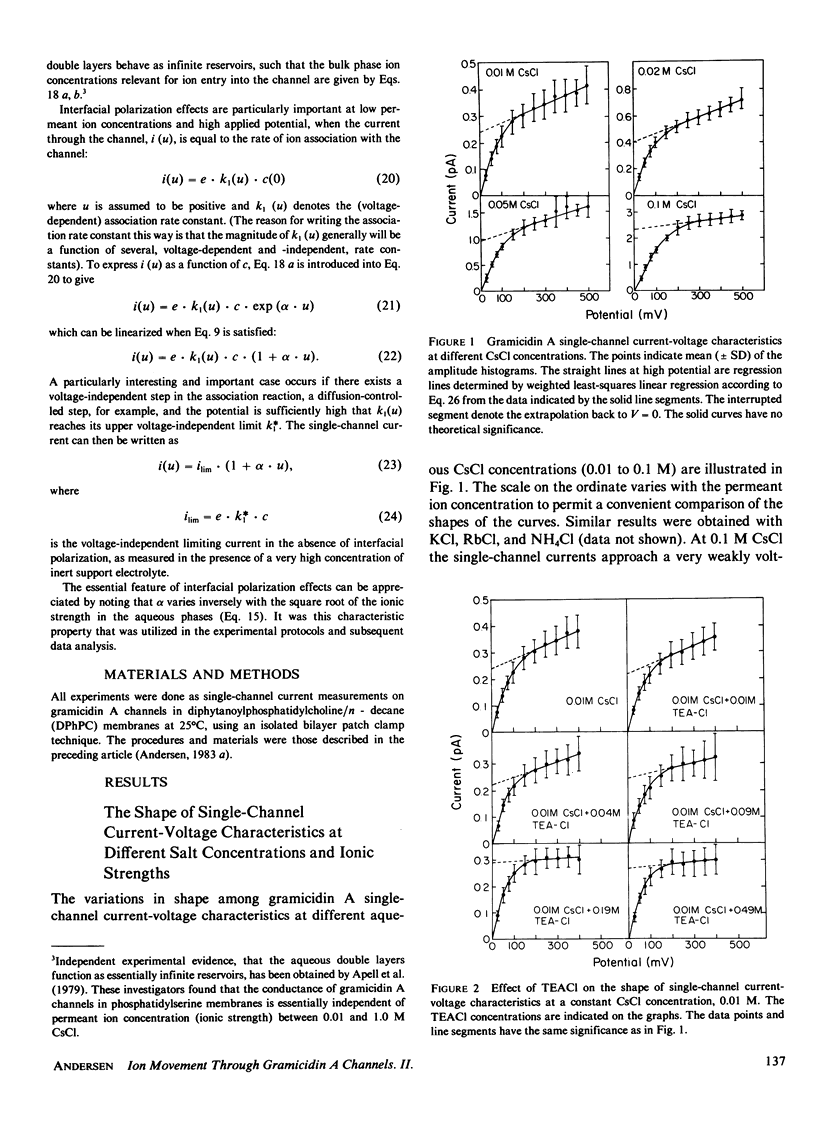
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Single-channel measurements at very high potentials. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):119–133. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84414-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O. S. Ion movement through gramicidin A channels. Studies on the diffusion-controlled association step. Biophys J. 1983 Feb;41(2):147–165. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84416-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apell H. J., Bamberg E., Läuger P. Effects of surface charge on the conductance of the gramicidin channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 19;552(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K. Voltage-induce capacitance relaxation of lipid bilayer membranes. Effects of membrane composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):721–738. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg M., Gresalfi T., Riccio T., McLaughlin S. Adsorption of monovalent cations to bilayer membranes containing negative phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5213–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Hägglund J., Sandblom J., Enos B. The current-voltage behavior of ion channels: important features of the energy profile of the gramicidin channel deduced from the conductance-voltage characteristic in the limit of low ion concentration. Ups J Med Sci. 1980;85(3):247–257. doi: 10.3109/03009738009179195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt C. T., Haydon D. A. Electrical capacitance of a lipid membrane separating two aqueous phases. J Theor Biol. 1968 Mar;18(3):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Andersen O. S. The gramicidin A channel: a review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 30;59(3):155–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01875422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A. Functions of the lipid in bilayer ion permeability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:2–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry B. M., Urban B. W., Haydon D. A. The blockage of the electrical conductance in a pore-containing membrane by the n-alkanes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):106–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D. G. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85485-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport through pores: a rate-theory analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):423–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Eibl H. The influence of phospholipid polar groups on gramicidin channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tredgold R. H., Hole P. N. Dielectric behaviour of dry synthetic polypeptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 4;443(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. Protein conformation in biomembranes: optical rotation and absorption of membrane suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):115–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz D., Bamberg E., Läuger P. Nonlinear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes. I. Ion injection. Biophys J. 1969 Sep;9(9):1150–1159. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86442-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



