Abstract
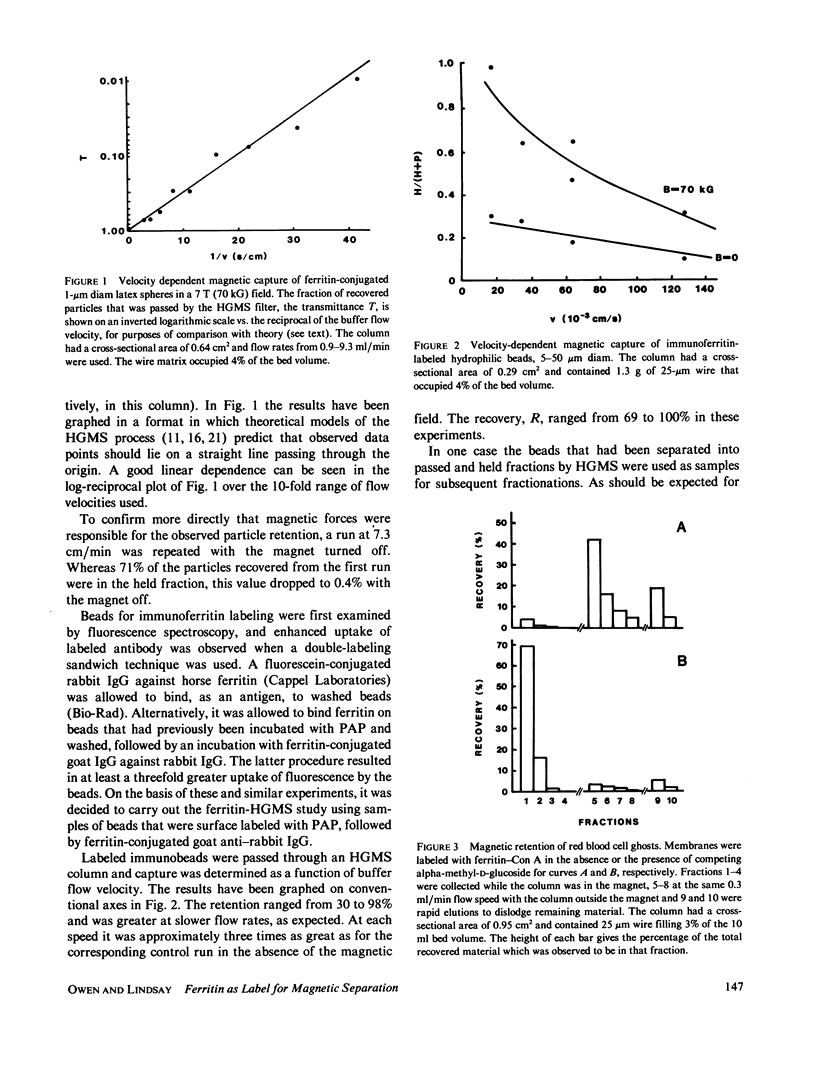
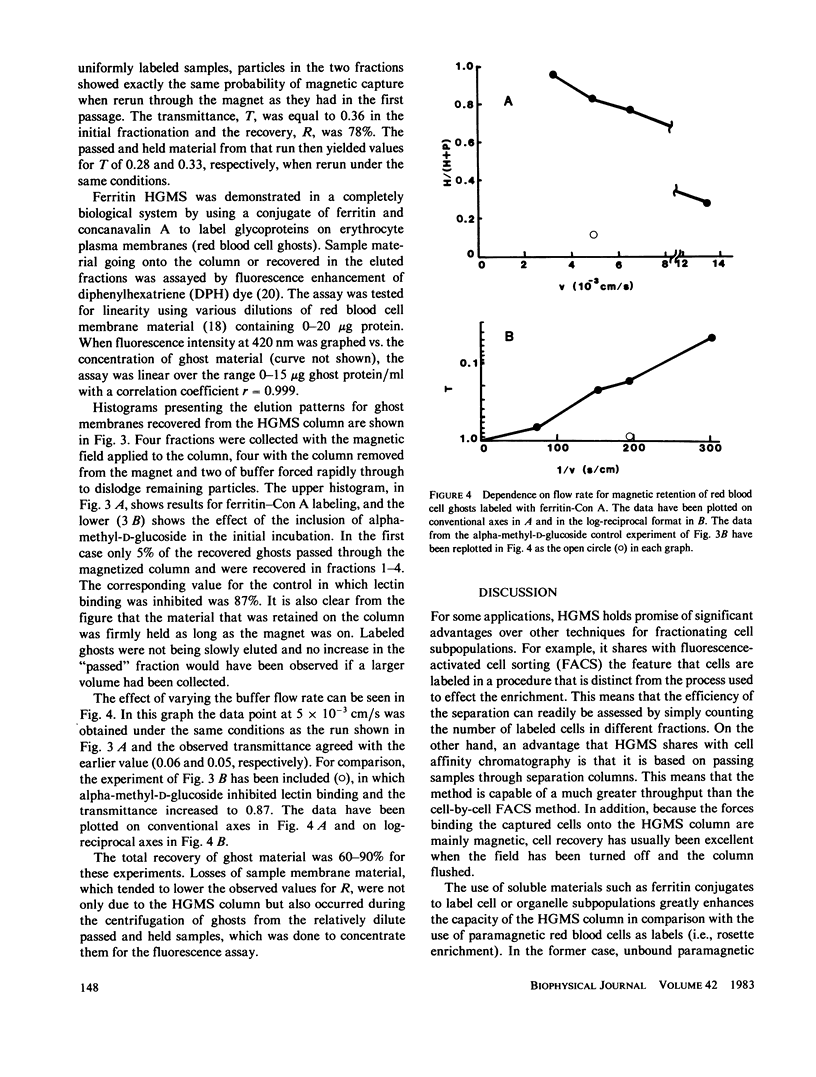
In three model systems, particles the size of cells or smaller have been surface labeled with ferritin to make them slightly paramagnetic, by virtue of the iron in the ferritin. In each case it was possible to show that labeled particles could be magnetically removed from a flowing suspension by the high-gradient magnetic separation (HGMS) technique. The first system of particles consisted of small (1 micron) carboxylate-modified latex spheres to which ferritin was covalently bound to create stable paramagnetic particles analogous to a ferritin-labeled subcellular membrane preparation. In the second system polyacrylamide beads that more closely approximated whole cells in size (5-50 microns) were labeled with immunoferritin. The third system was a biomembrane preparation: erythrocyte ghosts labeled with a ferritin-lectin conjugate. A field of 7 T (tesla) (70 kG) was used in each case, along with buffer flow rates through the HGMS column in the range 0.1-1.0 ml/min.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoine J. C., Ternynck T., Rodrigot M., Avrameas S. Lymphoid cell fractionation on magnetic polyacrylamide--agarose beads. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronick P. L., Campbell G. L., Joseph K. Magnetic microspheres prepared by redox polymerization used in a cell separation based on gangliosides. Science. 1978 Jun 2;200(4345):1074–1076. doi: 10.1126/science.653356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melville D. Direct magnetic separation of red cells from whole blood. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):706–706. doi: 10.1038/255706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., Yen S. P., Rembaum A. Application of magnetic microspheres in labelling and separation of cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):437–438. doi: 10.1038/268437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C. S., Babu U. M., Cohen S. W., Maurer P. H. Magnetic enrichment of antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jun 11;51(2):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C. S. High gradient magnetic separation of erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85482-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C. S., Moore E. High gradient magnetic separation of rosette-forming cells. Cell Biophys. 1981 Jun;3(2):141–153. doi: 10.1007/BF02788130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C. S., Winger L. A., Symington F. W., Nowell P. C. Rapid magnetic purification of rosette-forming lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1778–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul F., Roath S., Melville D. Differential blood cell separation using a high gradient magnetic field. Br J Haematol. 1978 Feb;38(2):273–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul F., Roath S., Melville D., Warhurst D. C., Osisanya J. O. Separation of malaria-infected erythrocytes from whole blood: use of a selective high-gradient magnetic separation technique. Lancet. 1981 Jul 11;2(8237):70–71. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Difference in microviscosity induced by different cholesterol levels in the surface membrane lipid layer of normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widder K. J., Senyei A. E., Ovadia H., Paterson P. Y. Specific cell binding using staphylococcal protein A magnetic microspheres. J Pharm Sci. 1981 Apr;70(4):387–389. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600700411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


