Abstract
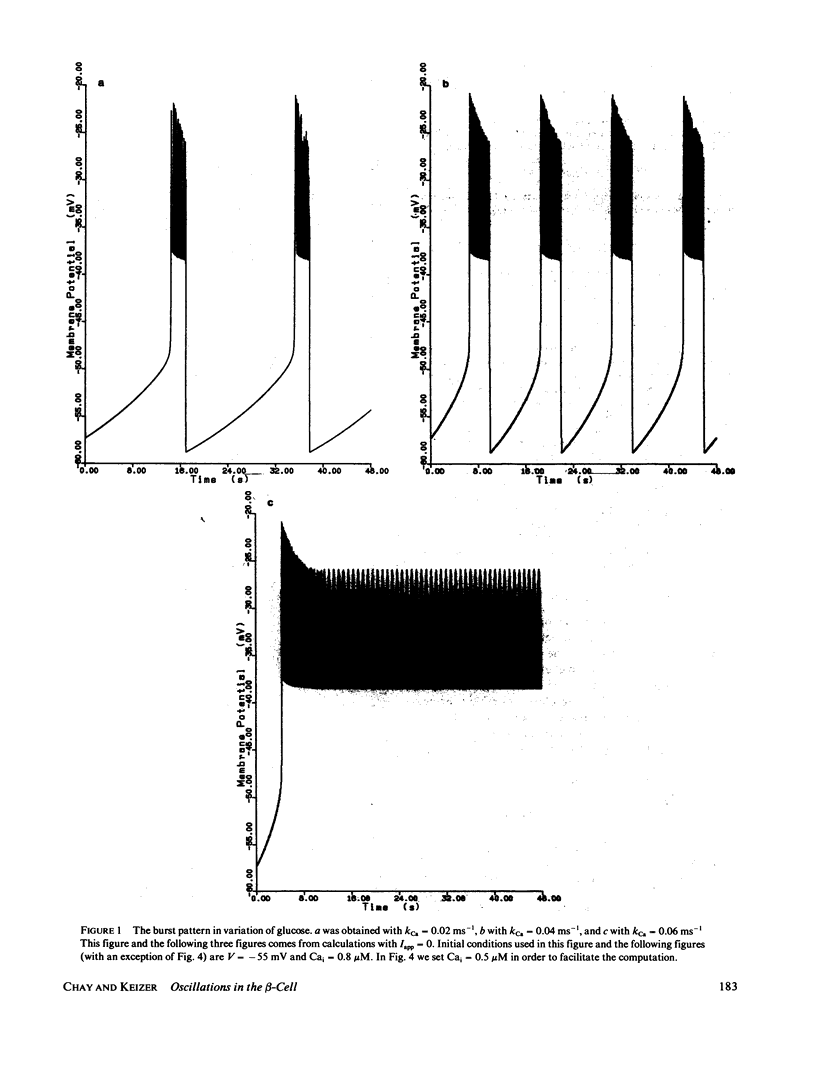
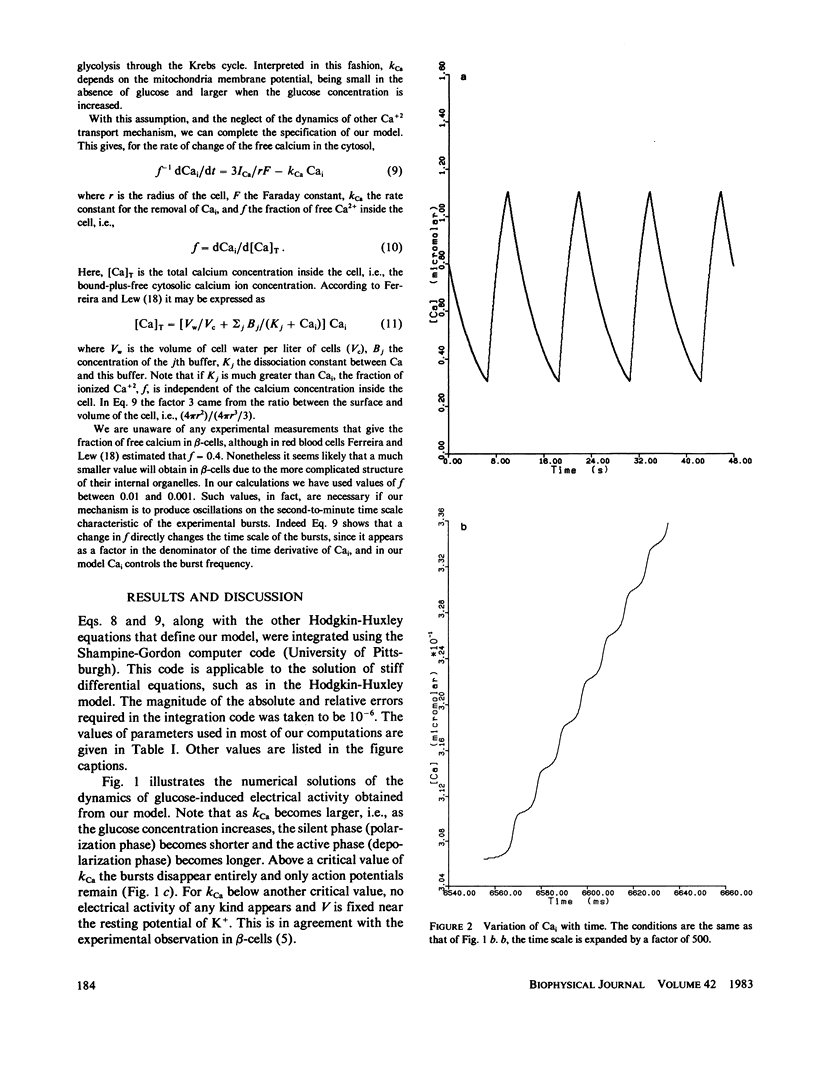
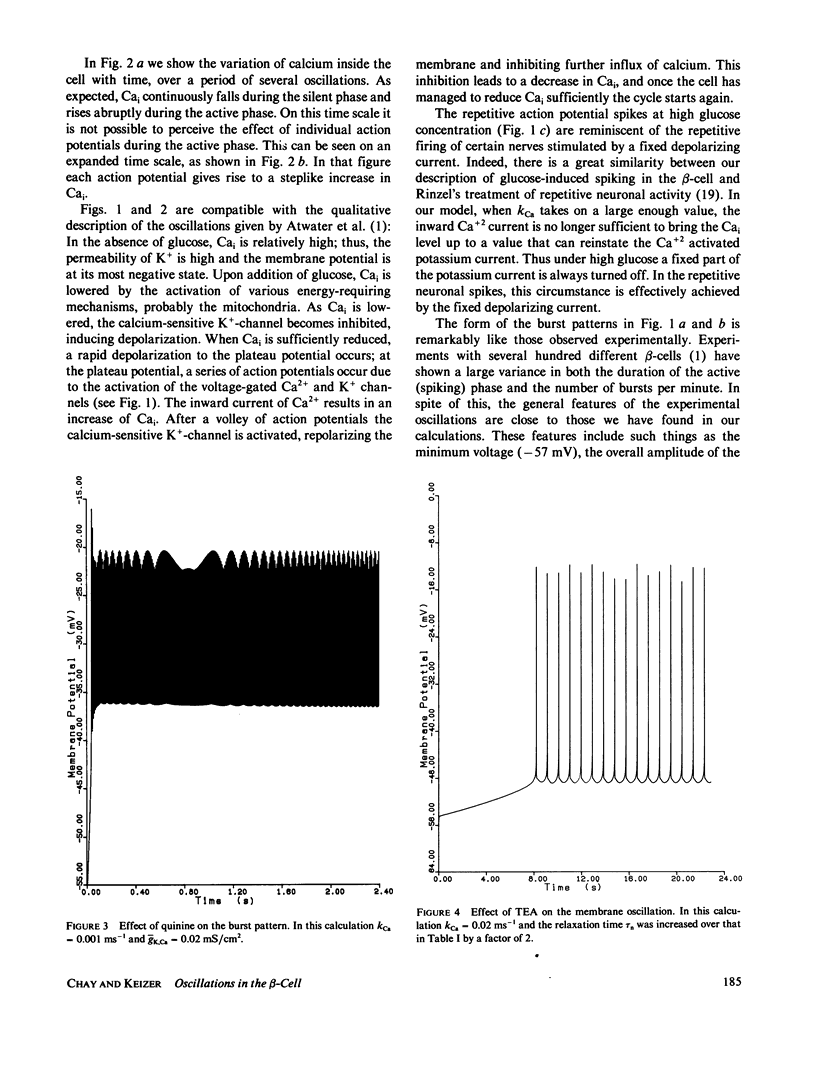
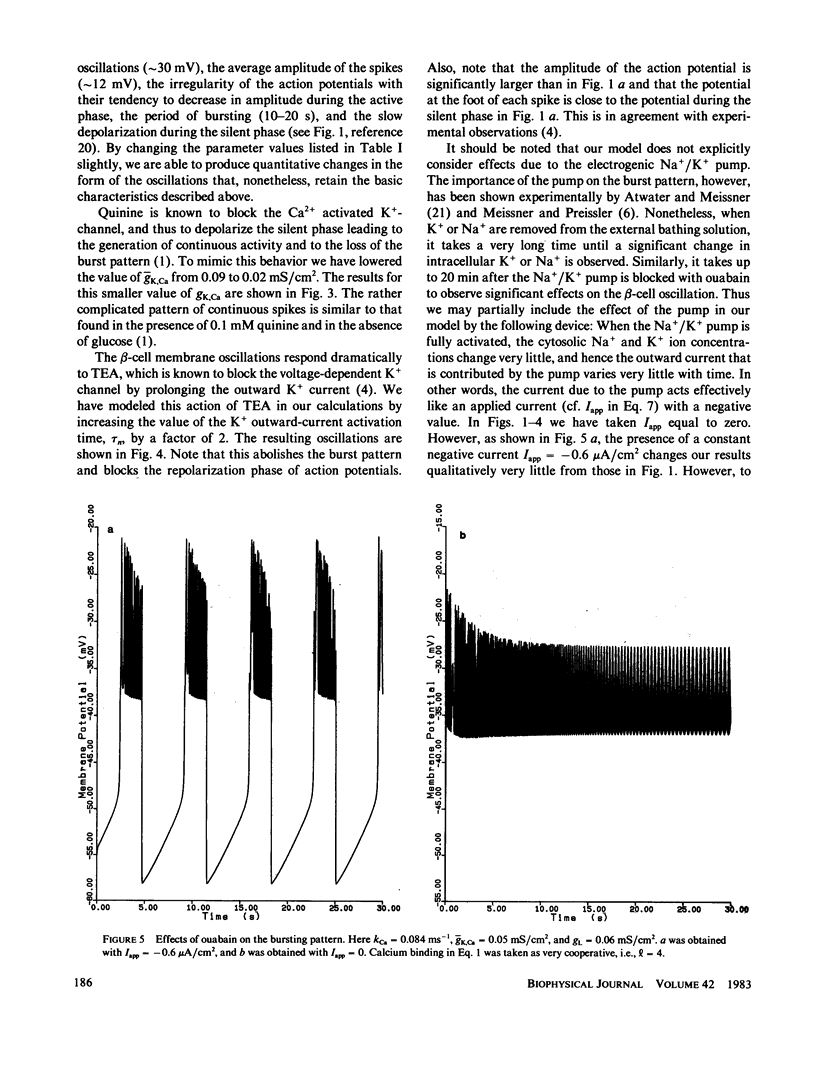
Following the experimental findings of Atwater et al. (In Biochemistry Biophysics of the Pancreatic-beta-Cell, George Thieme Verlag, New York, 100-107), we have formulated a mathematical model for ionic and electrical events that take place in pancreatic-beta-cells. Our formulation incorporates a Hodgkin-Huxley type gating mechanism for Ca2+ and K+ channels, in addition to Ca2+ gated K+-channels. Consistent with the experimental observations, our model generates spikes and bursts in beta-cell membrane potentials and gives the correct responses to additions of glucose, quinine, and tetraethylammonium ions. The response of the oscillations to ouabain and changing concentrations of external K+ can be incorporated into the present model, although a more complete treatment would require inclusion of the Na+/K+ pump.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Potassium permeability activated by intracellular calcium ion concentration in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:575–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Scott A., Eddlestone G., Rojas E. The nature of the oscillatory behaviour in electrical activity from pancreatic beta-cell. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the beta-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:117–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Mouse pancreatic beta-cells: tetraethylammonium blockage of the potassium permeability increase induced by depolarization. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:561–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The ins and outs of calcium transport in squid axons: internal and external ion activation of calcium efflux. Fed Proc. 1976 Dec;35(14):2574–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L. Mitochondria and the control of intracellular calcium. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1978 Feb;53(1):43–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1978.tb00992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Pancreatic islet cells: effects of monosaccharides, glycolytic intermediates and metabolic inhibitors on membrane potential and electrical activity. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):459–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira H. G., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure cytoplasmic Ca buffering and activation of the Ca pump by internal Ca. Nature. 1976 Jan 1;259(5538):47–49. doi: 10.1038/259047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge D., Stephens C. L. Cyclic variation of potassium conductance in a burst-generating neurone in Aplysia. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):155–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B., Harmar A. J., Adams W. B. Synaptic and hormonal modulation of a neuronal oscillator: a search for molecular mechanisms. J Exp Biol. 1979 Aug;81:131–151. doi: 10.1242/jeb.81.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., O'Connor M. D. Dynamic oscillations in the membrane potential of pancreatic islet cells. J Exp Biol. 1979 Aug;81:75–91. doi: 10.1242/jeb.81.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant R. E. Bifurcation and resonance in a model for bursting nerve cells. J Math Biol. 1981 Jan;11(1):15–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00275821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant R. E., Kim M. Mathematical description of a bursting pacemaker neuron by a modification of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Biophys J. 1976 Mar;16(3):227–244. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85683-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant R. E. The effects of calcium++ on bursting neurons. A modeling study. Biophys J. 1978 Mar;21(3):217–237. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85521-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Calcium action potentials and potassium permeability activation in pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):C124–C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1980.239.3.C124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Cyclic variation of K+ conductance in pancreatic beta-cells: Ca2+ and voltage dependence. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):C137–C146. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.237.3.C137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinzel J. On repetitive activity in nerve. Fed Proc. 1978 Dec;37(14):2793–2802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


