Abstract
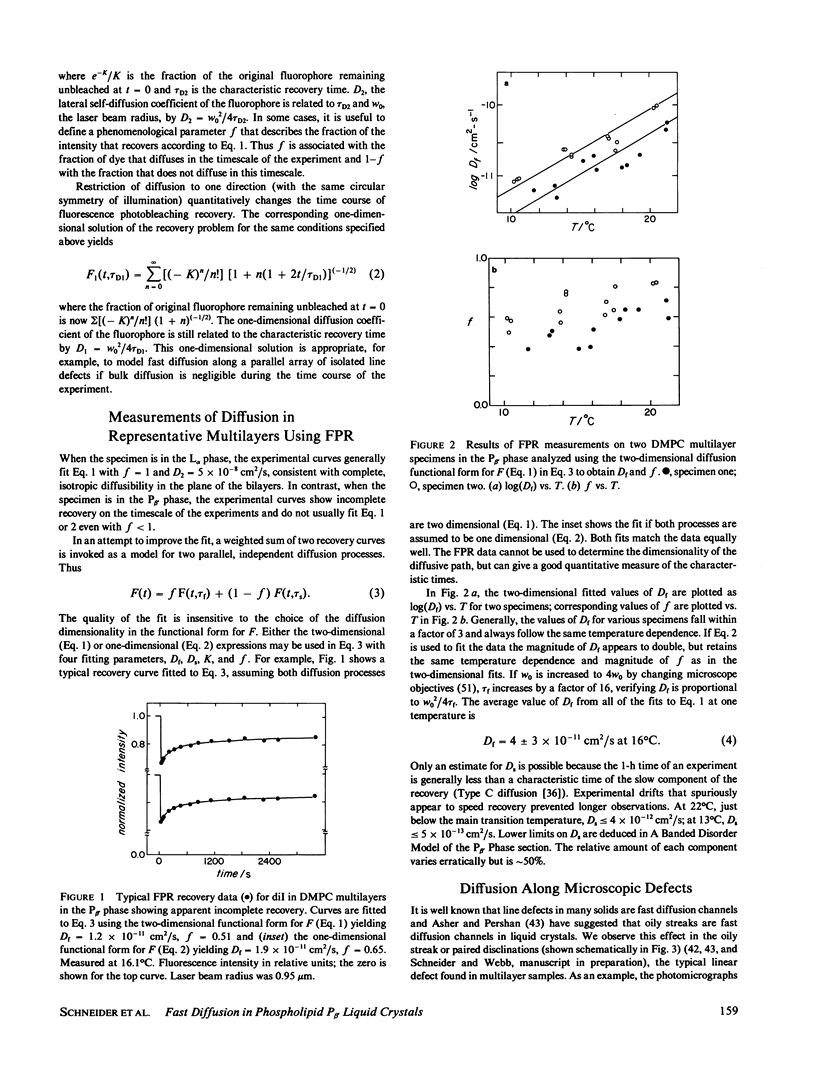
The diffusion of a fluorescent lipid analogue in liquid crystals of the anisotropic P beta, phase of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) had been found to be highly variable, suggesting structural defect pathways. Fluorescence photobleaching recovery (FPR) experiments imply two effective diffusion pathways with coefficients differing by at least 100. This is consistent with fast diffusion along submicroscopic bands of disordered material ("defects") in the bilayer corrugations characteristic of this phase. Due to strains during transformation from the L alpha phase, the axis of the corrugations is ordinarily disrupted by mosaic patches rotationally disoriented within the mean plane of the molecular bilayers, although larger oriented domains are sometimes adventitiously aligned into microscopically visible striped textures. The corrugations are also systematically aligned along positive disclinations pairs or "oily streaks." Thus, fast diffusion occurs parallel to the disclination lines and along the textured stripes. FPR results yield an upper limit on the effective diffusion in the ordered material of D less than or equal to 2 X 10(-16) cm2/s at 22 degrees C, D less than or equal to 3 X 10(-17) cm2/s at 13 degrees C. In contrast the diffusion coefficient along defect pathways where disordered ribbons are aligned is D approximately 4 X 10(-11) cm2/s at 16 degrees C.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asher S. A., Pershan P. S. Alignment and defect structures in oriented phosphatidylcholine multilayers. Biophys J. 1979 Sep;27(3):393–421. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85225-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. G., Casal H. L., Mantsch H. H., Boulanger Y., Smith I. C. The thermotropic behavior of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A Fourier transform infrared study of specifically labeled lipids. Biophys J. 1981 Jul;35(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84769-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies of biological membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:179–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland B. R., McConnel H. M. The rippled structure in bilayer membranes of phosphatidylcholine and binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 20;599(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derzko Z., Jacobson K. Comparative lateral diffusion of fluorescent lipid analogues in phospholipid multibilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6050–6057. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in spin-labeled phosphatidylcholine multilayers. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 28;94(13):4475–4481. doi: 10.1021/ja00768a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey P. F., Webb W. W. Lateral diffusion in phospholipid bilayer membranes and multilamellar liquid crystals. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):3046–3053. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkovitz M. S., Seul M., Frisch H. L., McConnell H. M. Theory of periodic structures in lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füldner H. H. Characterization of a third phase transition in multilamellar dipalmitoyllecithin liposomes. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5707–5710. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt C., Gruler H., Sackmann E. On domain structure and local curvature in lipid bilayers and biological membranes. Z Naturforsch C. 1977 Jul-Aug;32(7-8):581–596. doi: 10.1515/znc-1977-7-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Nature of the Thermal pretransition of synthetic phospholipids: dimyristolyl- and dipalmitoyllecithin. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4575–4580. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Temperature and compositional dependence of the structure of hydrated dimyristoyl lecithin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6068–6078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Wolf D. E. Selectivity of fluorescent lipid analogues for lipid domains. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6199–6203. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E., Axelrod D., Schlessinger J., Elson E. L., Webb W. W. Dynamics of fluorescence marker concentration as a probe of mobility. Biophys J. 1976 Nov;16(11):1315–1329. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85776-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krbecek R., Gebhardt C., Gruler H., Sackmann E. Three dimensional microscopic surface profiles of membranes reconstructed from freeze etching electrol micrographs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 13;554(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G., Birdsall N. J., Metcalfe J. C. Measurement of fast lateral diffusion of lipids in vesicles and in biological membranes by 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1650–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., McConnell H. M. The intermediate monoclinic phase of phosphatidylcholines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90331-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P., Blume A., Ohmes E., Neugebauer F. A., Kothe G. Structure and dynamics of phospholipid membranes: an electron spin resonance study employing biradical probes. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):526–534. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Dilatometric studies of the subtransition in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3817–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owicki J. C., McConnell H. M. Lateral diffusion in inhomogeneous membranes. Model membranes containing cholesterol. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85103-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M., Cone R. A. Lateral diffusion of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):438–441. doi: 10.1038/247438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H., Hoffman J. F. Studies on the mechanism by which cyanine dyes measure membrane potential in red blood cells and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3315–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. A., McConnell H. M. Determination of molecular motion in membranes using periodic pattern photobleaching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2759–2763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoff J., Feuer B., Guggenheim H. J., Tellez G., Yamane T. Amplitude of rippling in the P beta phase of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys J. 1982 Jun;38(3):217–226. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84551-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Träuble H., Sackmann E. Studies of the crystalline-liquid crystalline phase transition of lipid model membranes. 3. Structure of a steroid-lecithin system below and above the lipid-phase transition. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 28;94(13):4499–4510. doi: 10.1021/ja00768a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ververgaert P. H., Verkleij A. J., Elbers P. F., van Deenen L. L. Analysis of the crystallization process in lecithin liposomes: a freeze-etch study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):320–329. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb W. W. Applications of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Feb;9(1):49–68. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittebort R. J., Schmidt C. F., Griffin R. G. Solid-state carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance of the lecithin gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4223–4228. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]