Abstract
The pair distribution functions have been measured from freeze-fracture pictures of bacteriorhodopsin and rhodopsin recombinants with diacyl phosphatidylcholines (PC) of various hydrocarbon chain lengths. Pictures were used of samples that had been frozen from above the phase transition temperature of the lipid. Measured functions were compared with those calculated from two model interparticle potential energy functions, (a) a hard-disk repulsion only, and (b) a hard-disk repulsion plus electrostatic repulsion for a point charge buried in the membrane. The measured functions for bacteriorhodopsin di 12:0 PC, di 14:0 PC, and di 16:0 PC recombinants can be simulated using an interparticle hard-disk repulsion only. Bleached rhodopsin di 12:0 PC and di 18:1 trans-PC recombinants, and dark-adapted rhodopsin di 10:0 PC recombinants yield functions that are better simulated by assuming an additional repulsive interaction. The measured functions resemble those calculated using the hard-disk plus electrostatic repulsion model. The picture of dark-adapted rhodopsin in di 18:1 trans-PC frozen from 20 degrees C shows partial aggregation that is apparent in the measured pair distribution function. This attractive interaction persists even at 37 degrees C, where the measured function shows deviations from the hard-disk repulsive model, indicative of an attractive interparticle interaction. Implications of these results are discussed in terms of protein-lipid interactions.
Full text
PDF


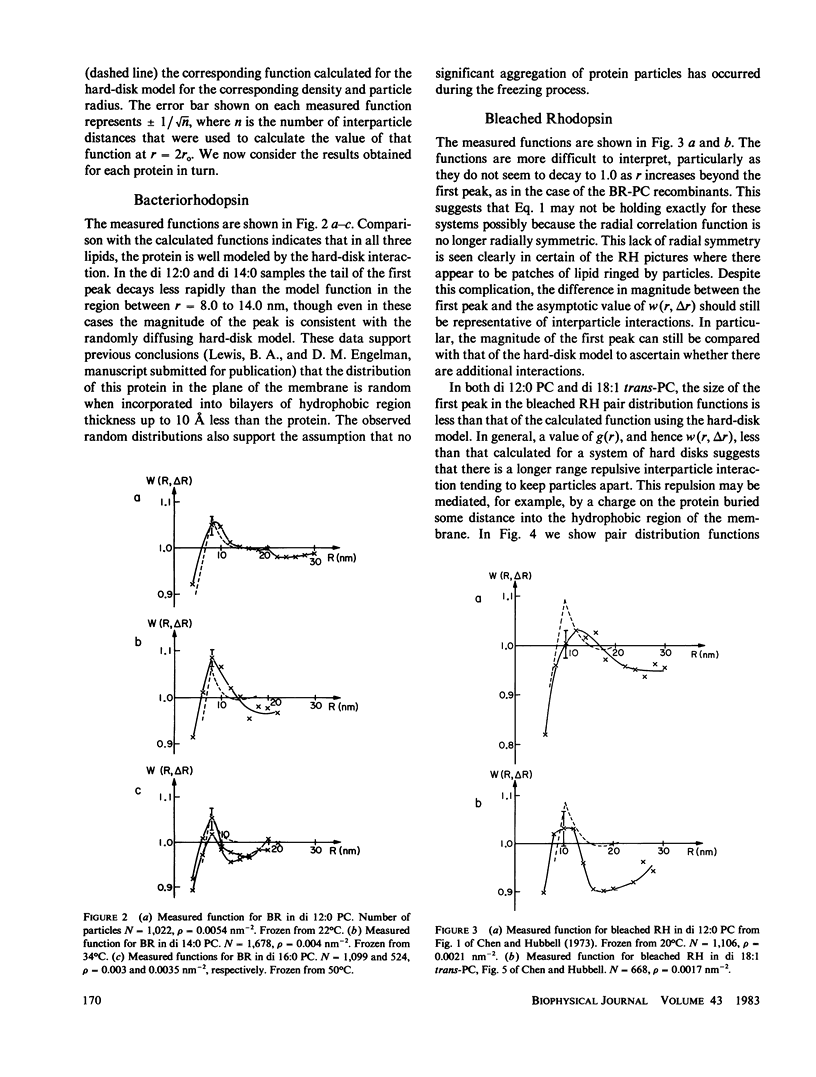



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann L., Schmitt W. W. Improved cryofixation applicable to freeze etching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2149–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. S., Hubbell W. L. Temperature- and light-dependent structural changes in rhodopsin-lipid membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Dec 24;17(6):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
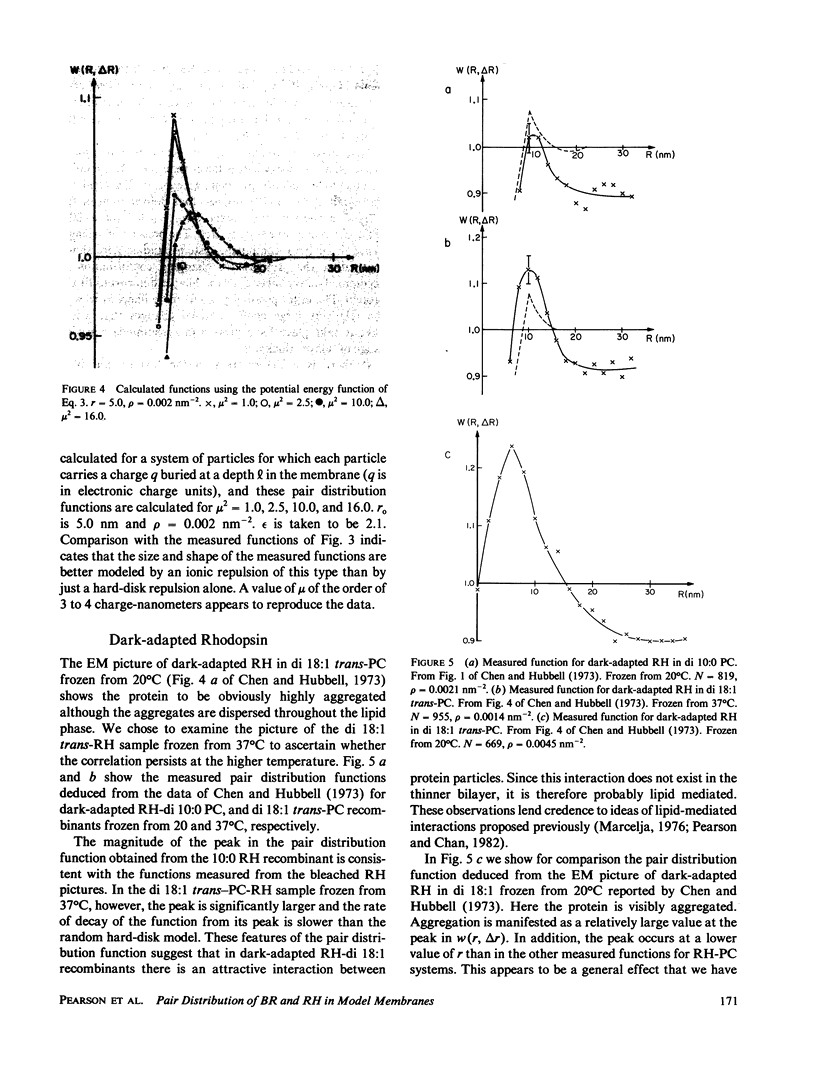
- Decker R. S., Friend D. S. Assembly of gap junctions during amphibian neurulation. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):32–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnell J. T., 2nd, Finegold L. X. Testing of aggregation measurement techniques for intramembranous particles. Biophys J. 1981 Sep;35(3):783–798. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84827-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Rudolf I. Acrosomal disruption in sperm. Freeze-fracture of altered membranes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):466–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon N. D., Demsey A., Stackpole C. W. Analysis of local order in the spatial distribution of cell surface molecular assemblies. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Aug;122(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Bayley H., Khorana H. G. Delipidation of bacteriorhodopsin and reconstitution with exogenous phospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelja S. Lipid-mediated protein interaction in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovics J., Glass L., Maul G. G. Pore patterns on nuclear membranes. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Apr;85(2):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Pates R. D., Uhl R., Knowles P. F., Esmann M. ESR spin-label studies of lipid-protein interactions in membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84675-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A., Fuller N., Rand R. P. Measured work of deformation and repulsion of lecithin bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2750–2754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. P., Hui S. W., Stewart T. P. Correlative statistical analysis and computer modelling of intramembraneous particle distributions in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):265–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T., Chan S. I. Effects of Lipid-mediated Interactions on Protein Pair Distribution Functions. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):141–142. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84641-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S. Spatial distribution of surface immunoglobulin on B lymphocytes. Local ordering. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 15;112(2):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Cherry R. J. Lateral and rotational diffusion of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid bilayers: experimental test of the Saffman-Delbrück equations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4317–4321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A. Reversible particle movements associated with unstacking and restacking of chloroplast membranes in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):136–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Hladky S. B. Ion repulsion within membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Jul;39(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84489-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. S. Changes in plasma membrane structure associated with malignant transformation in human urinary bladder epithelium. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 2):2518–2524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]