Abstract
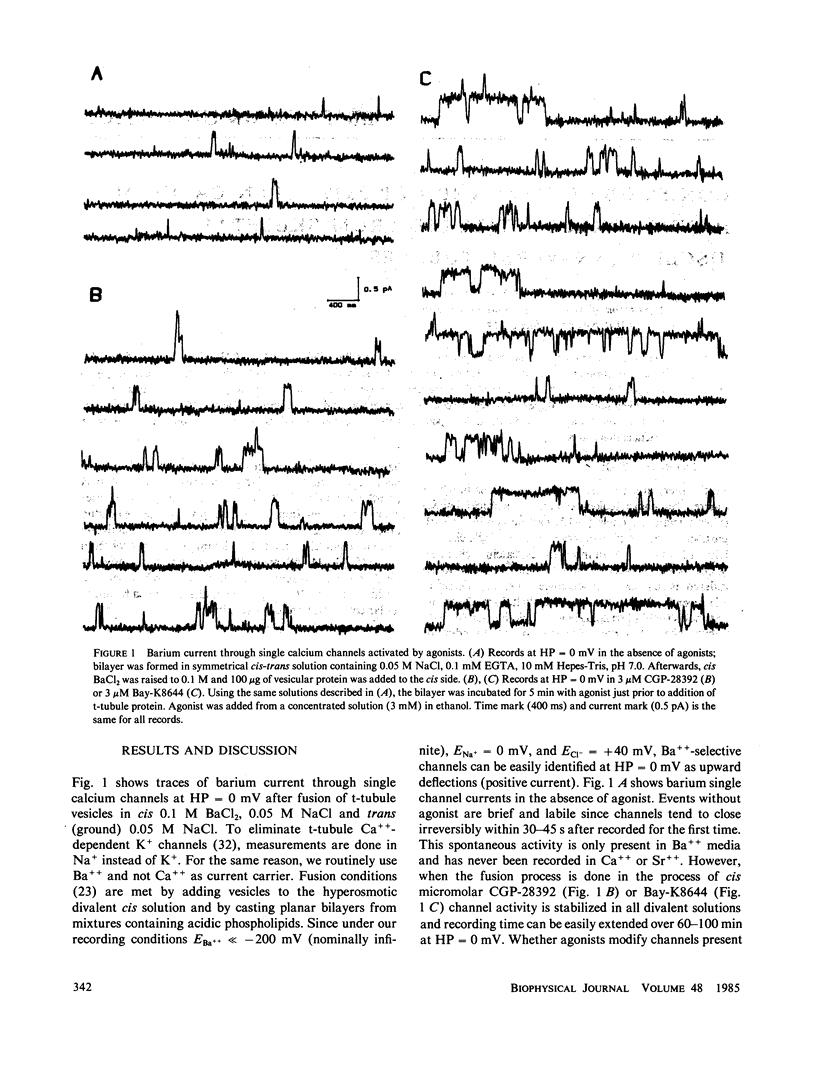
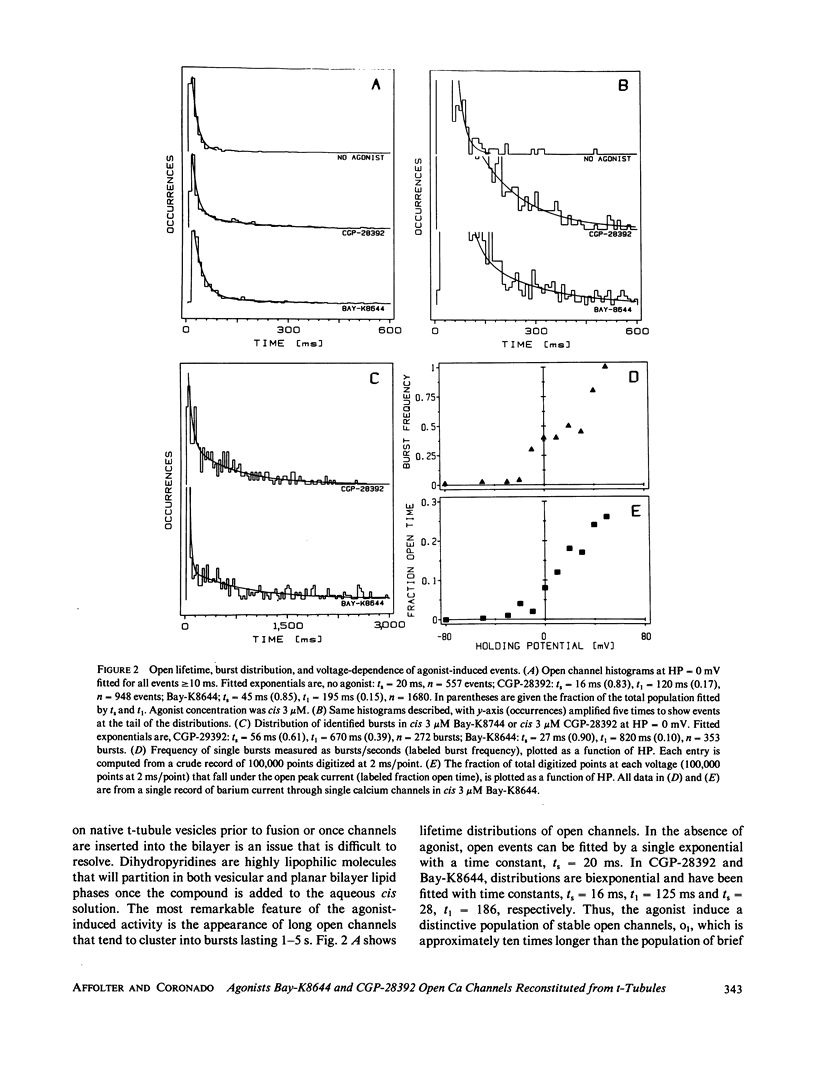
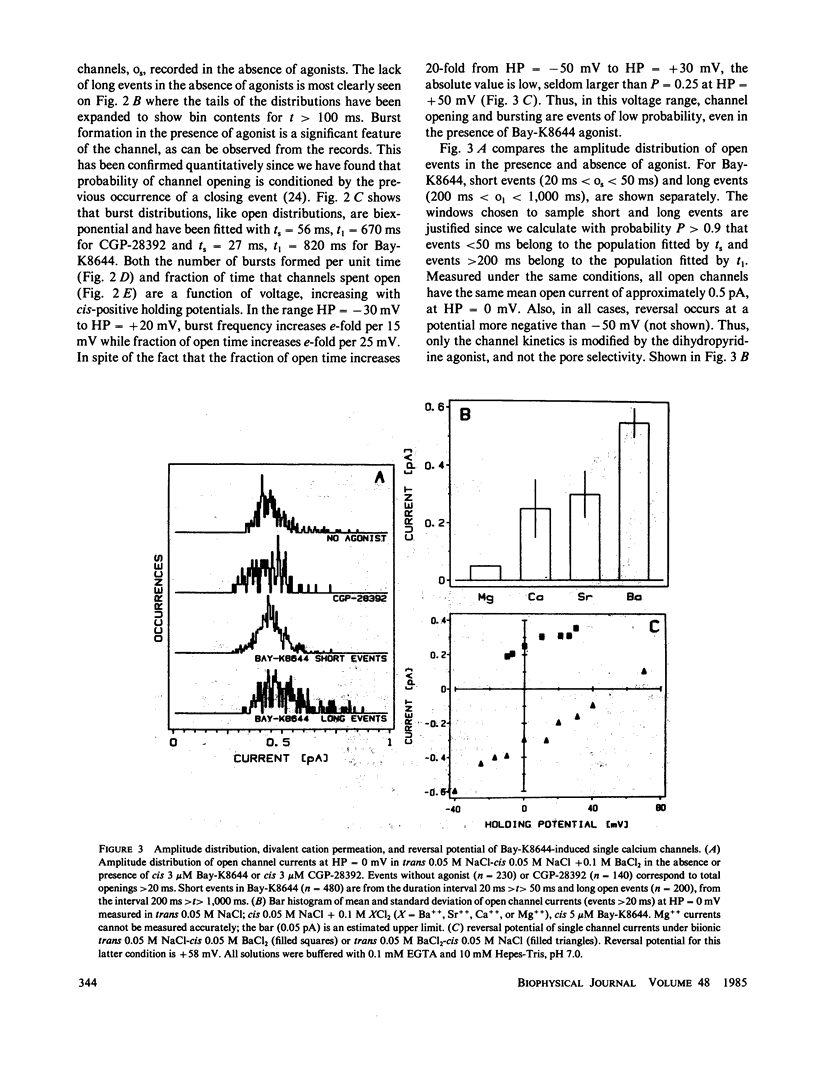
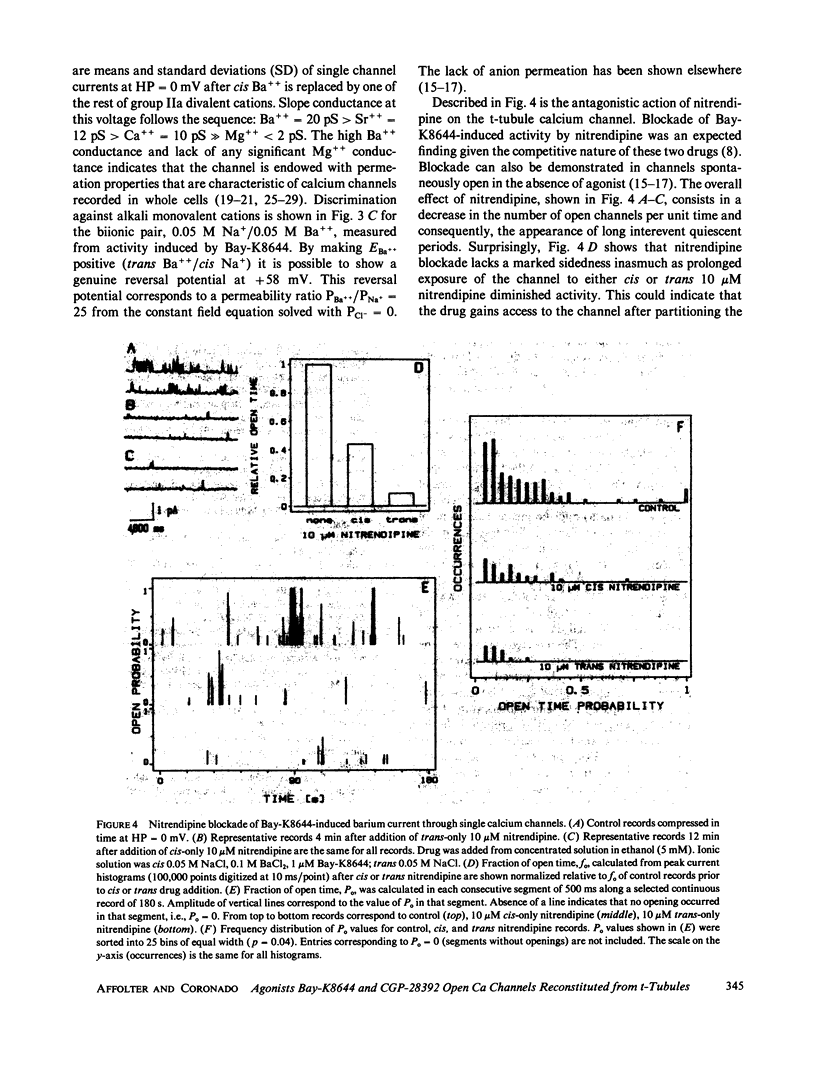
The recently described calcium channel agonists Bay-K8644 and CGP-28392 have been used to induce long-term opening of calcium channels from purified rat muscle transverse tubules (t-tubules) incorporated into planar phospholipid bilayers. Agonist-open channels are selective for divalent cations (except Mg++), display voltage-dependent kinetics, and are blocked by the calcium channel antagonist, nitrendipine. The sensitivity to dihydropyridine agonists and antagonists indicate that a pool of t-tubule calcium channels remain functional after membrane fractionation and purification.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Norman R. I., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Solubilization of the nitrendipine receptor from skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. Interactions with specific inhibitors of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Wilson D. L., Lux H. D. Activation of calcium channels. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):125–127. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84134-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Lipshutz G. M., Denney G. H. Direct photoaffinity labeling of the high affinity nitrendipine-binding site in subcellular membrane fractions isolated from canine myocardium. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5384–5387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Solubilization of the calcium antagonist receptor from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7280–7283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Finkelstein A., Forte M., Kung C. Voltage-dependent calcium channels from Paramecium cilia incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):427–428. doi: 10.1126/science.6330895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. B., Miller R. J. Calcium channel activation: a different type of drug action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5580–5583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel in mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2240–2242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Pelzer D., Trube G., Trautwein W. Does the organic calcium channel blocker D600 act from inside or outside on the cardiac cell membrane? Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00581411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S. Nisoldipine: a new, more selective calcium current blocker in cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):446–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokubun S., Reuter H. Dihydropyridine derivatives prolong the open state of Ca channels in cultured cardiac cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4824–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Voltage-gated cation conductance channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum: steady-state electrical properties. J Membr Biol. 1978 Apr 20;40(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01909736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E. G., Latorre R. Saxitoxin and ouabain binding activity of isolated skeletal muscle membrane as indicators of surface origin and purity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 27;732(2):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Gould R. J., Largent B. L., Snyder S. H. A unitary mechanism of calcium antagonist drug action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., French R. J., Krueger B. K. Voltage-dependent calcium channels from brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):77–80. doi: 10.1038/308077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemblatt M., Hidalgo C., Vergara C., Ikemoto N. Immunological and biochemical properties of transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8140–8148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. A., Stefani E. Inward calcium current in twitch muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:197–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento J. G., Janis R. A., Katz A. M., Triggle D. J. Comparison of high affinity binding of calcium channel blocking drugs to vascular smooth muscle and cardiac sarcolemmal membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;33(20):3119–3123. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):535–537. doi: 10.1038/303535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



