Abstract
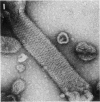
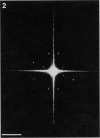
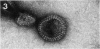
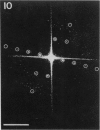
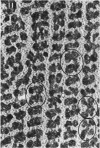
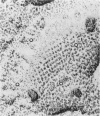
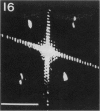
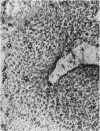
Isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) vesicles with polymerized calcium pump protein were freeze-dried and rotary shadowed following uranyl acetate stabilization. This technique allows direct observation of a single side of the vesicle without requiring optical filtering. The heads of individual ATPase molecules, projecting above the cytoplasmic surface, are clearly resolved in the replicas. Ca ATPase molecules form extensive arrays in vanadate-treated, rabbit SR vesicles and in gently isolated, native SR vesicles from scallop. Gentle isolation results in limited areas of orderly structure in native SR isolated from vertebrate muscles. Special attention is given to the effect of various shadow thicknesses on the appearance of the heads. This information is essential to the interpretation of images in the accompanying paper (Franzini-Armstrong, C., and D.J. Ferguson, 1985, Biophys. J., 48:607-615).
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN A. D., SHOREY C. D. THE CELL ENVELOPES OF TWO EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA. J Cell Biol. 1963 Sep;18:681–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasie J. K., Herbette L., Pierce D., Pascolini D., Scarpa A., Fleischer S. Static and time-resolved structural studies of the Ca2+-ATPase of isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:478–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady G. W., Fein D. B., Meissner G., Harder M. E. Liquid diffraction analysis of sarcoplasmic reticulum. II. Solvent electron contrast variation. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):637–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhle E. L., Jr, Knox B. E., Serpersu E., Aebi U. The structure of the Ca2+ ATPase as revealed by electron microscopy and image processing of ordered arrays. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Nov;85(2):186–203. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Franzini-Armstrong C., Shamoo A. E. Further characterization of light and heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Identification of the 'sarcoplasmic reticulum feet' associated with heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 16;602(1):97–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Purification and characterization of the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4626–4632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani L., Hardwicke P. M. Crystalline structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum from scallop. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. L., Tanford C. Reactivation of lipid-depleted Ca2+-ATPase by a nonionic detergent. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3551–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Membrane crystals of Ca2+-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast and slow skeletal and cardiac muscles. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. The regulation of ATPase-ATPase interactions in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. I. The effects of Ca2+, ATP, and inorganic phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11896–11902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Two-dimensional arrays of proteins in sarcoplasmic reticulum and purified Ca2+-ATPase vesicles treated with vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2599–2603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Iino M. Specific perforation of muscle cell membranes with preserved SR functions by saponin treatment. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Mar;1(1):89–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00711927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley R. A. Identification of hydrophobic regions of the calcium-transport ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum after photochemical labeling with adamantane diazirine. Int J Biochem. 1983;15(12):1423–1427. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(83)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson D. G., Schwartz H. W., Franzini-Armstrong C. Subunit structure of junctional feet in triads of skeletal muscle: a freeze-drying, rotary-shadowing study. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1735–1742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Aebi U. Preparation of single molecules and supramolecular complexes for high-resolution metal shadowing. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Jun;83(3):319–334. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C., Ferguson D. G. Density and disposition of Ca2+-ATPase in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane as determined by shadowing techniques. Biophys J. 1985 Oct;48(4):607–615. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83816-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwicke P. M., Green N. M. The effect of delipidation on the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Electron microscopy and physical properties. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):183–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach W., Elfvin L. G. Structural and chemical asymmetry of the calcium-transporting membranes of the sarcotubular system as revealed by electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Mar;17(5):598–622. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert H., Jørgensen P. L., Skriver E., Maunsbach A. B. Crystallization patterns of membrane-bound (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 12;689(3):571–574. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbette L., Marquardt J., Scarpa A., Blasie J. K. A direct analysis of lamellar x-ray diffraction from hydrated oriented multilayers of fully functional sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):245–272. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85547-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Ikemoto N. Disposition of proteins and aminophospholipids in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8446–8454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto N. Structure and function of the calcium pump protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:297–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Kurzmack M., Nakamoto R., de Meis L., Bernhard S. A. Uncoupling of calcium control and phosphohydrolase activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6040–6043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Scales D. Tryptic cleavage of sarcoplasmic reticulum protein. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3298–3306. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilka R. L., Martonosi A. N., Tillack T. W. Effect of the purified (Mg2+ + Ca2+)-activated ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum upon the passive Ca2+ permeability and ultrastructure of phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7511–7524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Maire M., Moller J. V., Tanford C. Retention of enzyme activity by detergent-solubilized sarcoplasmic Ca2+ -ATPase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2336–2342. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4508–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Seeman P., Iles G. H., Yip C. C. Membrane formation by the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2702–2710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medda P., Hasselbach W. The vanadate complex of the calcium-transport ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, its formation and dissociation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):7–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Fleischer S. Characterization of sarcoplasmic reticulum from skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):356–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak M., Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Localization of the high affinity calcium binding protein and an intrinsic glycoprotein in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1317–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohraz M., Smith P. R. Structure of (Na+,K+)-ATPase as revealed by electron microscopy and image processing. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1836–1841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller J. V., Andersen J. P., le Maire M. The sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Feb 5;42(2):83–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00222696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller J. V., Lind K. E., Andersen J. P. Enzyme kinetics and substrate stabilization of detergent-solubilized and membraneous (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-activated ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effect of protein-protein interactions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1912–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peracchia C., Dux L., Martonosi A. N. Crystallization of intramembrane particles in rabbit sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles by vanadate. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Aug;5(4):431–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00818261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Wang C. T., Fleischer S. Membrane asymmetry and enhanced ultrastructural detail of sarcoplasmic reticulum revealed with use of tannic acid. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):601–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon E. D., DeRosier D. A surveying optical diffractometer. J Microsc. 1981 Sep;123(Pt 3):239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb02468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales D., Giuseppeinesi Assembly of ATPase protein in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):735–751. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85725-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. Structure of Limulus telson muscle thick filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):781–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90418-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. S., MacLennan D. H. Surface particles of sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Structural features of the adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):985–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K., Dux L., Martonosi A. Structure of the vanadate-induced crystals of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. T., Saito A., Fleischer S. Correlation of ultrastructure of reconstituted sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane vesicles with variation in phospholipid to protein ratio. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9209–9219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampighi G., Kyte J., Freytag W. Structural organization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in purified membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1851–1864. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]